AP Psych - Intelligence and Testing
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
2
New cards
general intelligence (g)
* general intelligence factor that underlies mental skills (many who score highly in one area often score highly in others (so underlying level of intelligence))
* intelligence is one general mental ability
* intelligence is one general mental ability
3
New cards
Charles Spearman
* People have **g factor** (general intelligence) (so if they score highly on one factor, they will often score highly on others)
* **factor analysis**
* **factor analysis**
4
New cards
factor analysis
identifying clusters items (factors) on a test that have a common ability
5
New cards
L. L. Thurstone
* Disagreed w/ **Spearman**
* Identified 7 clusters of mental abilities (so said intelligence = *multiple* distinct abilities)
* Identified 7 clusters of mental abilities (so said intelligence = *multiple* distinct abilities)
6
New cards
Howard Gardner
* Believes conventional concept of intelligence was too narrow and that measuring only IQ ignores other “intelligences” an individual has
* Argues that we have multiple (8) intelligences
* Argues that we have multiple (8) intelligences
7
New cards
savant syndrome
condition where a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill
8
New cards
Robert Sternberg
Agrees w/ Gardner’s idea of *multiple* intelligences, but says there are 3 (*triarchic* theory)
9
New cards
creativity
ability to produce novel and valuable ideas
10
New cards
emotional intelligence
ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
11
New cards
John Mayer, Peter Salovey, David Caruso
developed a test that assesses emotional intelligence, the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
12
New cards
Alfred Binet
* Hired by France’s minister of public education to identify the abilities of children who had never attended school
* Along with **Theodore Simon**, assumed all children follow same course of intellectual development, just at different speeds. Thus, they wanted to measure **mental age**
* Believed intelligence tests didn’t measure anything fixed or innate, that it should just be used to identify the needs of French school children. Feared it would be used to label and limit opportunities
* Along with **Theodore Simon**, assumed all children follow same course of intellectual development, just at different speeds. Thus, they wanted to measure **mental age**
* Believed intelligence tests didn’t measure anything fixed or innate, that it should just be used to identify the needs of French school children. Feared it would be used to label and limit opportunities
13
New cards
mental age
* devised by **Alfred Binet**
* chronological age that frequently corresponds w/ a given level of performance
* chronological age that frequently corresponds w/ a given level of performance
14
New cards
Stanford-Binet
widely used revision (by **Lewis Terman** at Stanford University) of **Binet’s** intelligence test
15
New cards
Lewis Terman
Revised **Binet’s** intelligence test
16
New cards
intelligence quotient (IQ)
originally, IQ = (mental age/chronological age) x 100
17
New cards
achievement tests
designed to assess what a person has learned
18
New cards
aptitude tests
designed to predict future performance
19
New cards
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
* Created by **David Wechsler**
* Gives both overall intelligence score and separate scores for subcategories
* Gives both overall intelligence score and separate scores for subcategories
20
New cards
standardization
defining scores by comparison w/ the performance of a pretested group
21
New cards
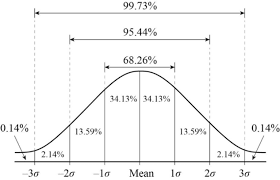
normal curve
symmetrical, bell shaped curve
22
New cards
reliability
extent to which a test yields consistent results
23
New cards
validity
extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
24
New cards
content validity
extent to which a test tests relevant material
25
New cards
predictive validity
extent to which a test predicts the behavior it is supposed to predict
26
New cards
intellectual disability
condition of limited mental ability
27
New cards
Down syndrome
A condition of intellectual disability and associated physical disorders caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21
28
New cards
Steven Pinker
* Evolutionary psychologist
* Argues that biological and social factors affect gender differences in life priorities, risk-taking, and math reasoning/spatial abilities
* Argues that biological and social factors affect gender differences in life priorities, risk-taking, and math reasoning/spatial abilities
29
New cards
heritability
proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes
30
New cards
stereotype threat
self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype