Electromagnetic Forces and Bonding in Cell Biology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the four fundamental forces that cause particles to interact?
Weak nuclear force, strong nuclear force, gravitational force, and electric force.
What is the significance of electric charge in cell biology?
Electric charge is fundamental to the interactions between particles, forming atoms, molecules, and biological structures.
What type of bond is formed between two hydrogen atoms in an H2 molecule?
A non-polar covalent bond.
Why is the bond between oxygen and hydrogen in water considered polar?
Oxygen has more protons and pulls electrons closer, creating a slight negative charge on oxygen and a slight positive charge on hydrogen.
What happens to electrons in an ionic bond between sodium and chlorine?
The electron from sodium is completely transferred to chlorine, resulting in sodium becoming positively charged and chlorine negatively charged.
What is electronegativity?
The attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond, which varies by element.
How does electronegativity change across a period and down a group?
Electronegativity increases across a period and decreases down a group.
What is the difference between dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonds?
Dipole-dipole interactions occur between opposite charges, while hydrogen bonds are a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction involving hydrogen and highly electronegative atoms like O, N, or F.
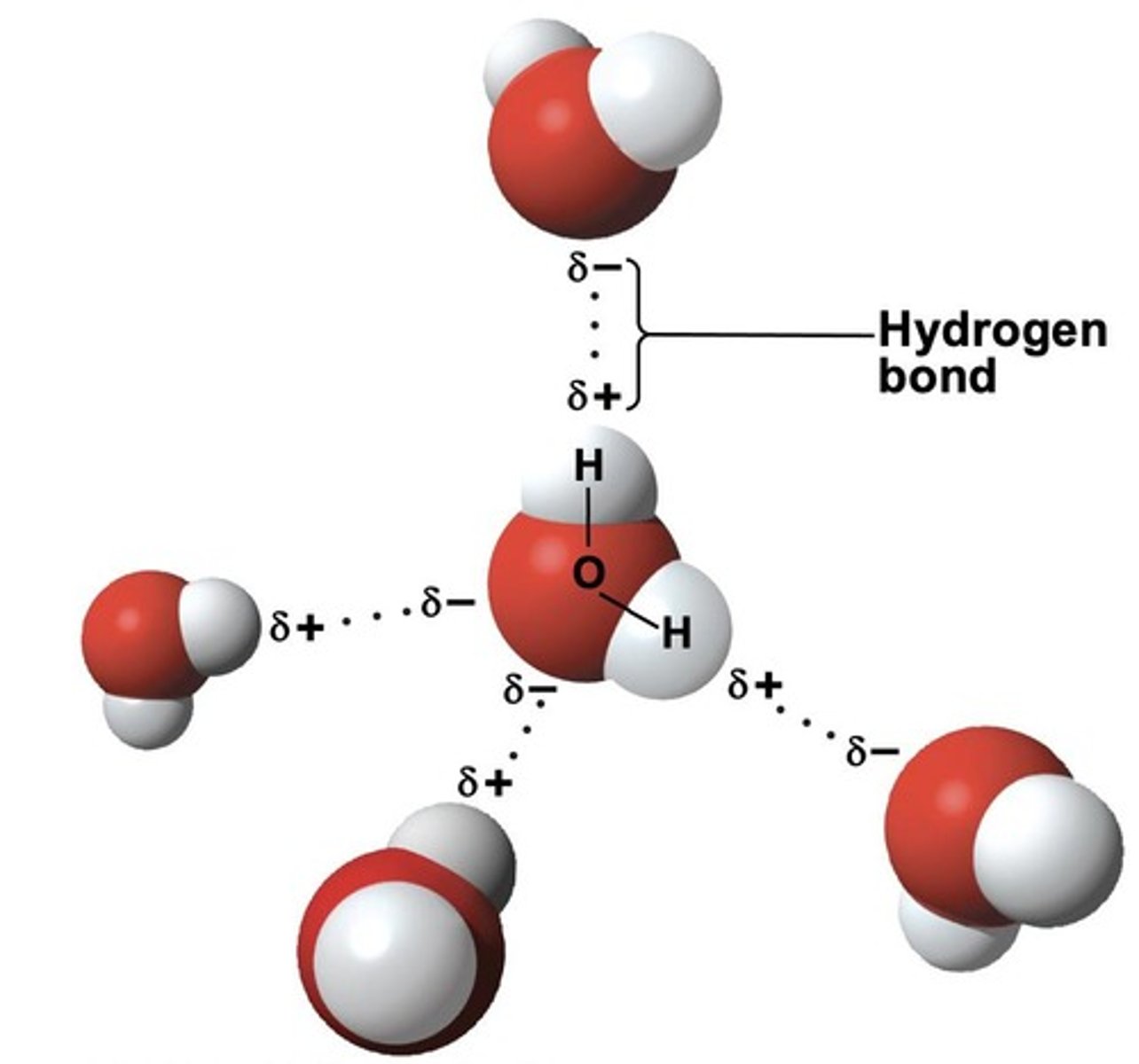
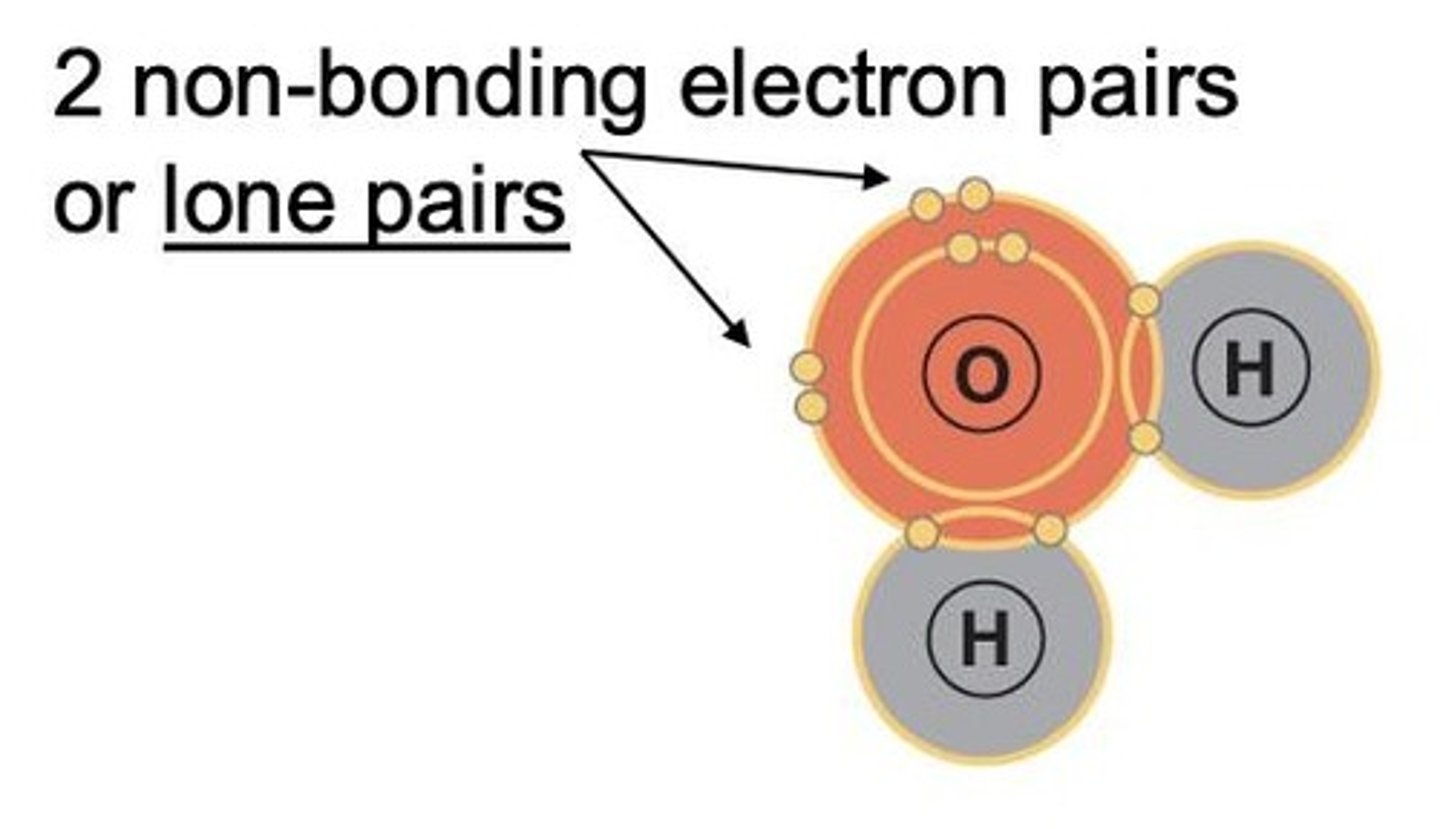
What is the structure of a water molecule?
Water is a polar molecule with two d+ charges (on H atoms) and two d- charges (on O atom's lone pairs), resulting in a unique symmetry.
What is an aqueous solution?
A solution in which water is the solvent.
What defines a hydrophilic substance?
A hydrophilic substance has a high affinity for water and can mix with it, typically due to ionic or polar covalent bonds.
What characterizes hydrophobic substances?
Hydrophobic substances do not mix with water and typically have non-polar covalent bonds.
What are London dispersion forces?
Weak intermolecular bonds that occur between non-polar molecules due to temporary fluctuating dipoles.
What are hydrophobic interactions?
Interactions that occur when non-polar molecules separate in solution due to stronger interactions between water molecules.
What role do polar covalent bonds play in biological structures?
They enable interactions between molecules through electrical attractions, facilitating higher levels of biological structure.
What is ionization in the context of polar covalent bonds?
Ionization occurs when the electrons are so unevenly distributed that some molecules dissociate to form ions.
What is the significance of the hydration shell formed by water?
The hydration shell forms around solutes, allowing them to interact with water and dissolve.
How do non-polar molecules interact in solution?
Non-polar molecules interact through weak London dispersion forces and tend to separate out in aqueous solutions.
What is the emergent property of water resulting from its hydrogen bonding?
Water remains liquid at temperatures suitable for life due to its unique hydrogen bonding properties.
What is a polar solvent?
A solvent that can dissolve ionic or polar covalent compounds, such as water.
What happens to oil when mixed with water?
Oil, being non-polar, does not mix with water due to the stronger interactions between water molecules.
What is the effect of functional groups on biological molecules?
Functional groups introduce polarity, increasing the solubility of biological molecules in water.
What is a dipole?
A dipole refers to a molecule that has opposite ends with different electric charges.
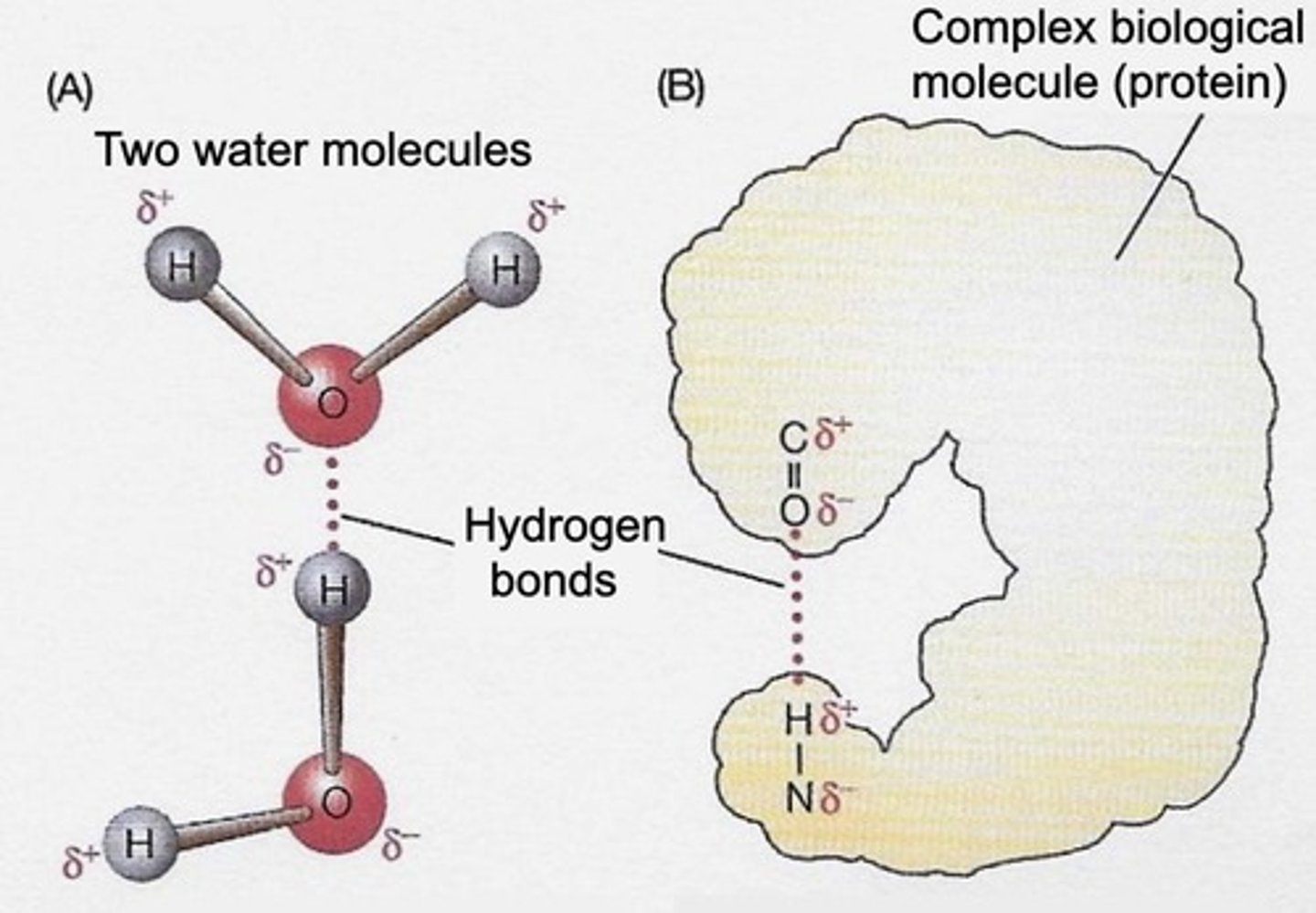
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure?
Hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of DNA together, contributing to its stability.
What is the relationship between electronegativity and bond polarity?
The difference in electronegativity between two atoms determines the polarity of the bond formed between them.
What is a non-polar covalent bond?
A bond where electrons are shared equally between two identical atoms, resulting in no charge separation.
What is the primary reason for the unique properties of water?
The unique properties of water arise from its ability to form extensive hydrogen bonds.