Self-assessment
1/306
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lab 1-5 (add Lab 6-11)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
307 Terms
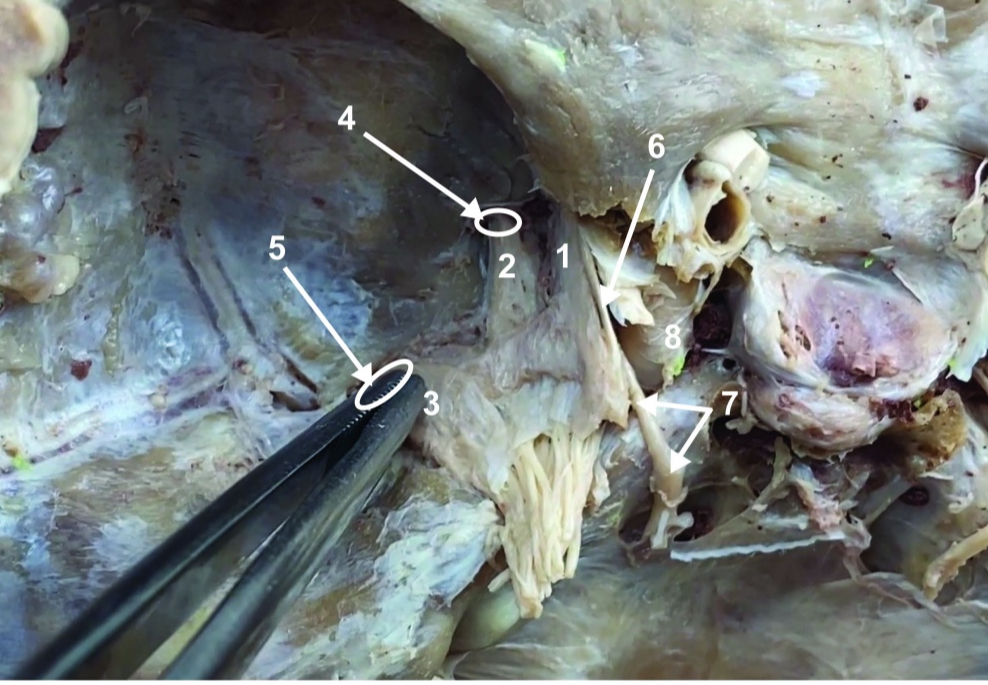
Body
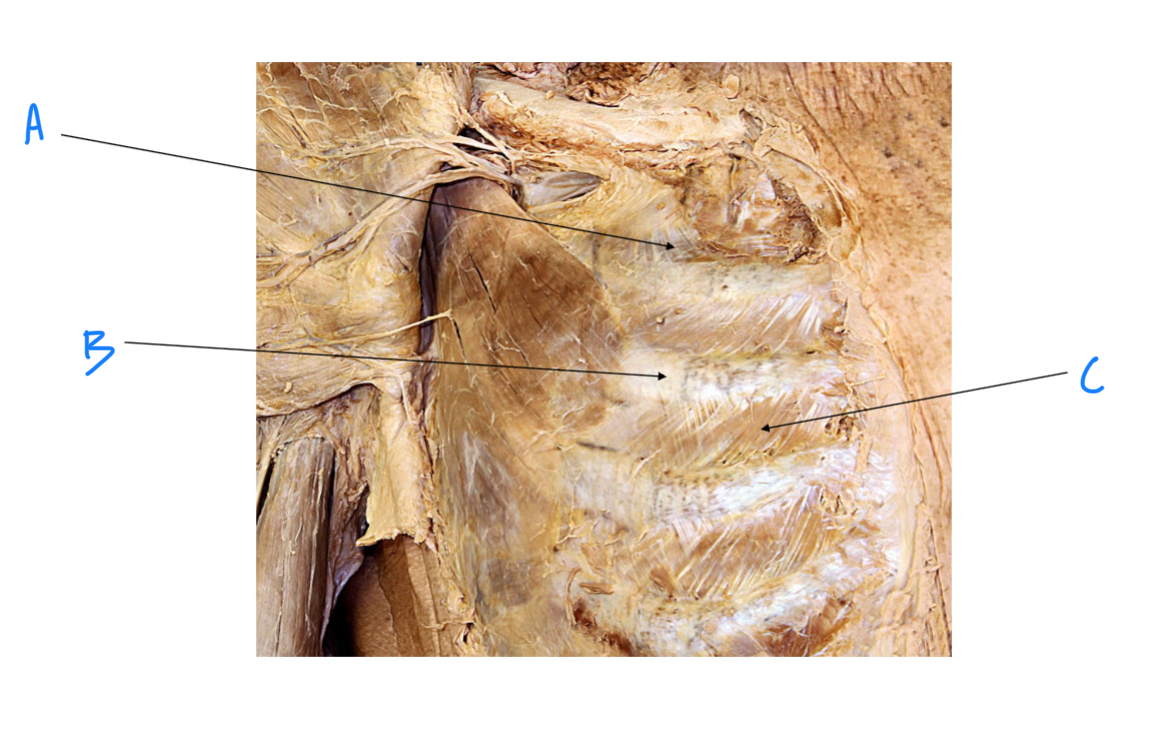
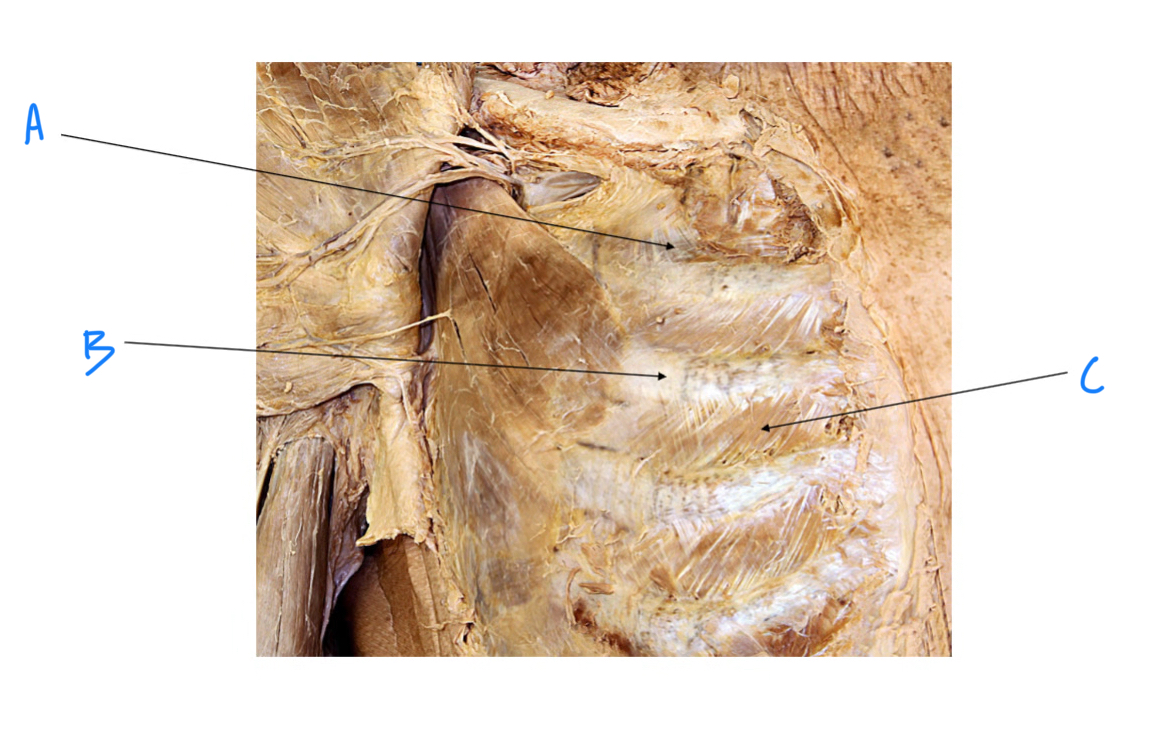
A. Identify structure
Transverse foramen; Vertebral a.
B. Identify structure; What goes through this feature?
Transverse process
C. Identify structure
Scapula
A. Identify the bone
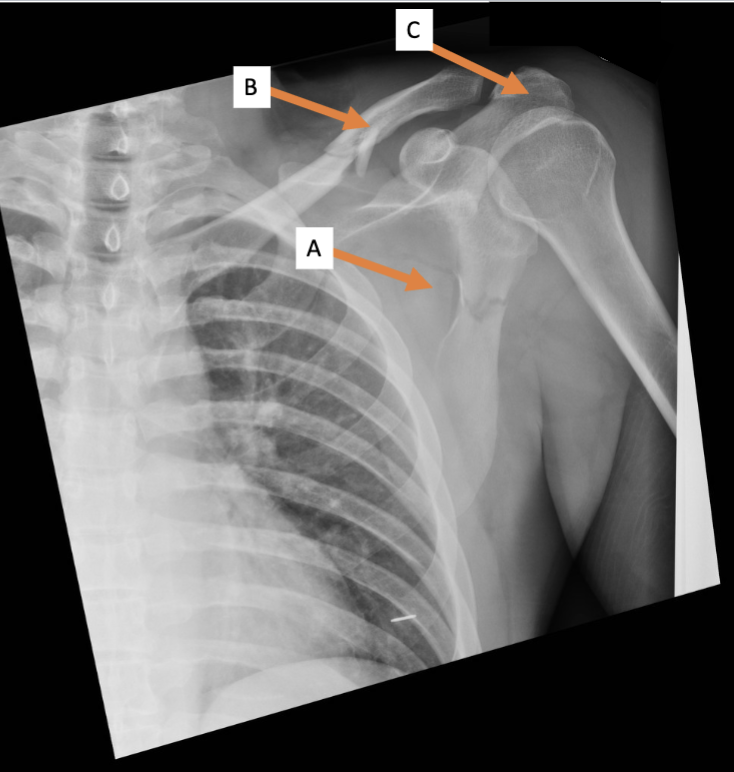
Clavicle
B. Identify the bone
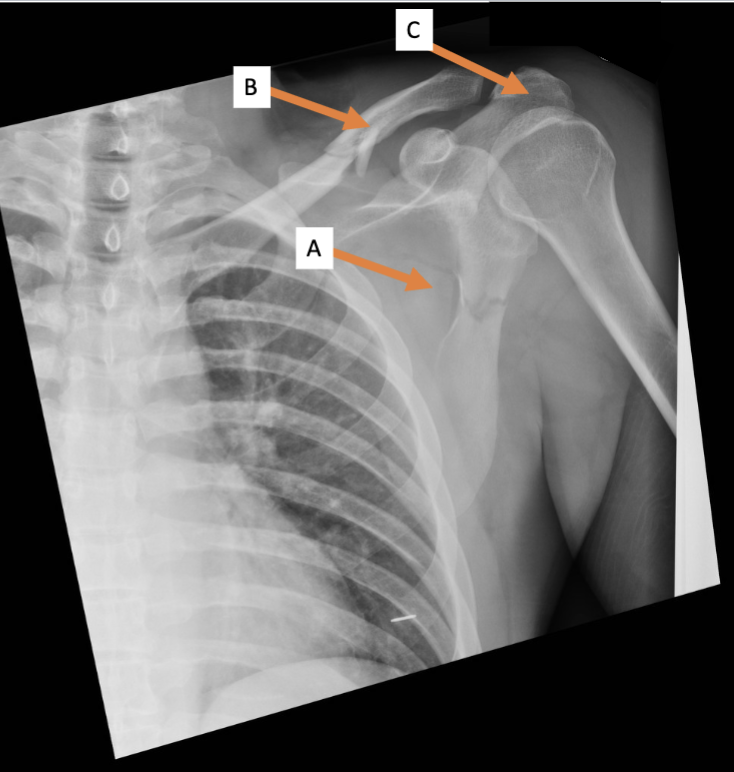
Acromion process
C. Identify the structure
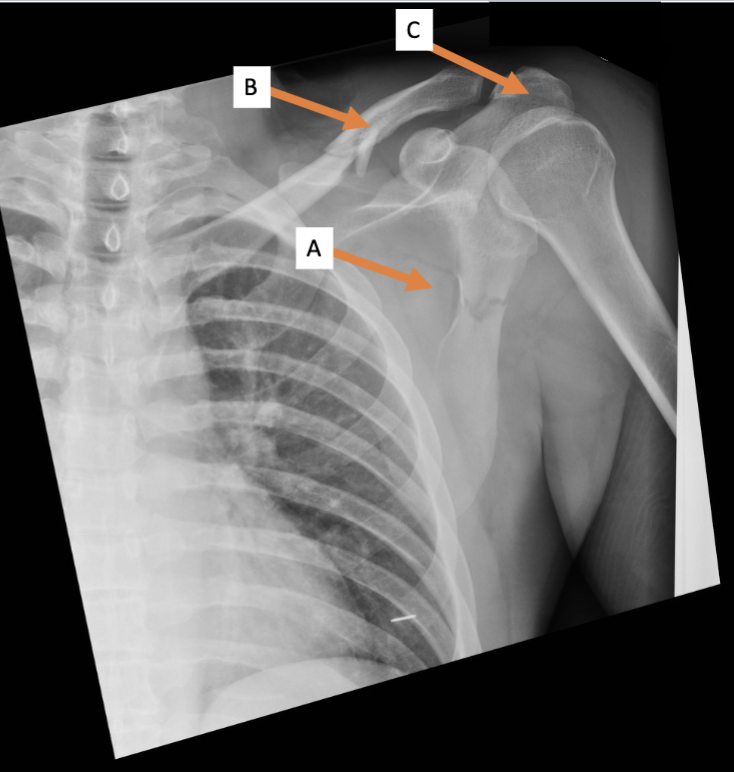
Trapezius (reflected)
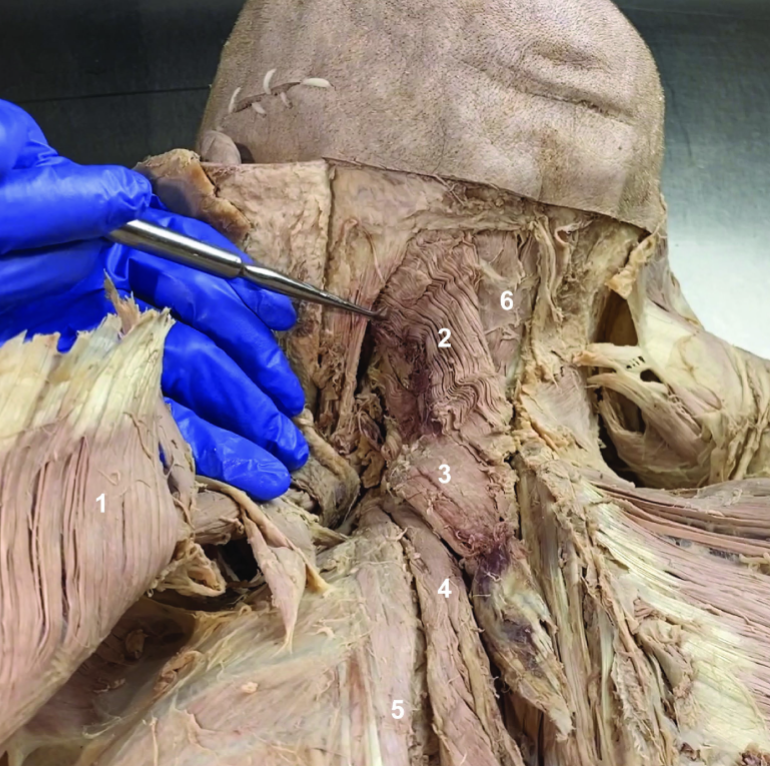
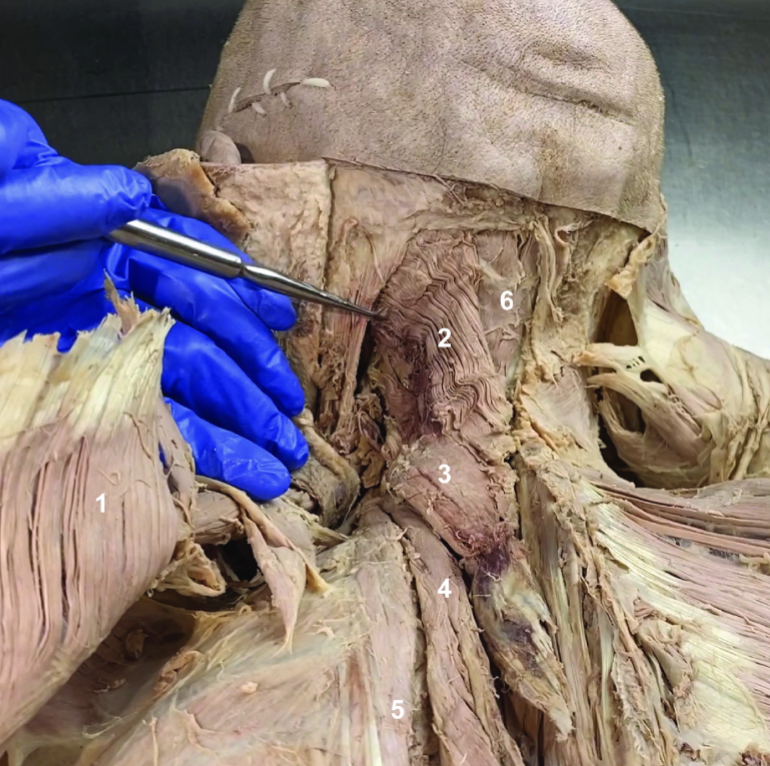
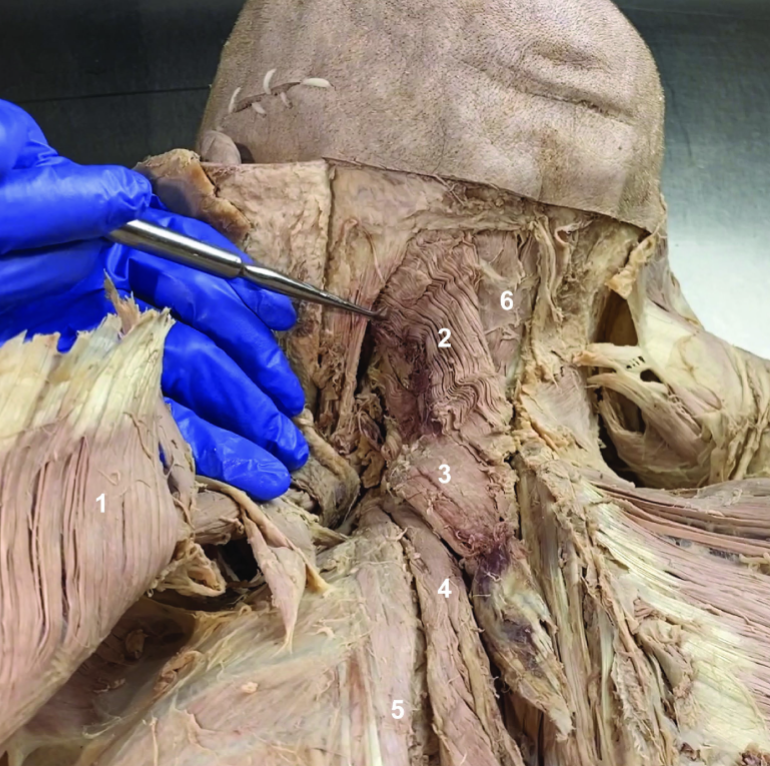
ID structure
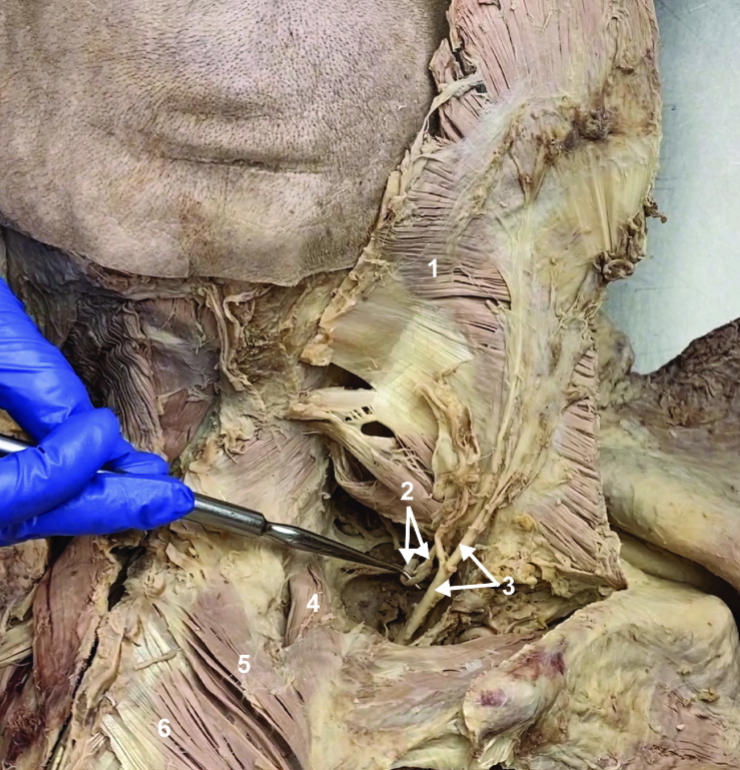
Spinal accessory n. (CN XI)
ID structure
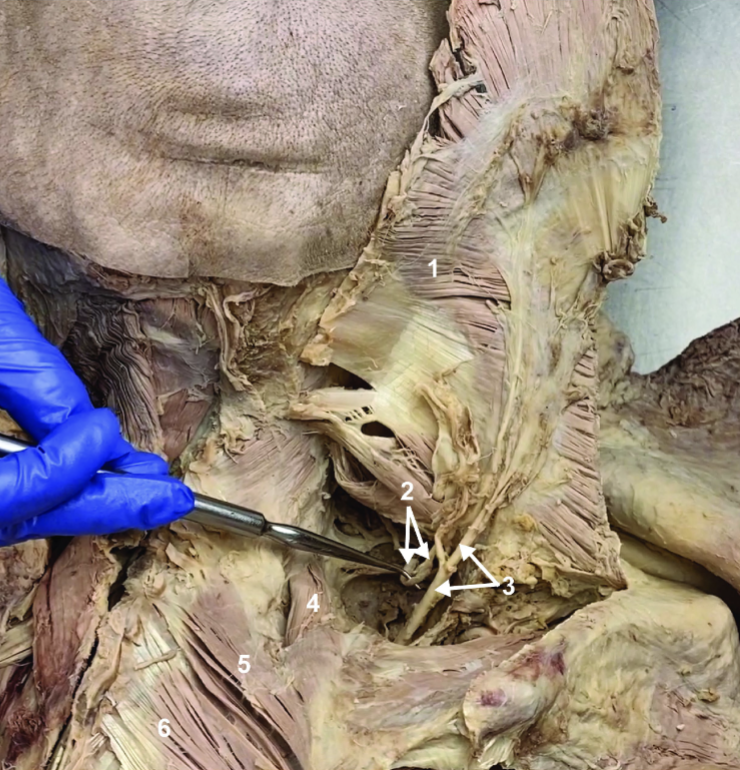
Transverse cervical a.
ID structure
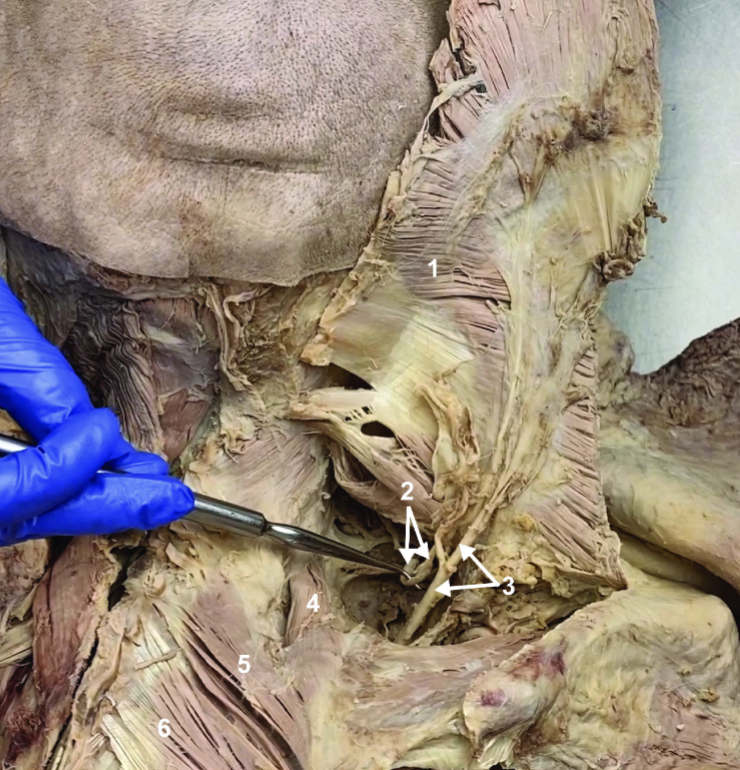
Levator scapulae
ID structure
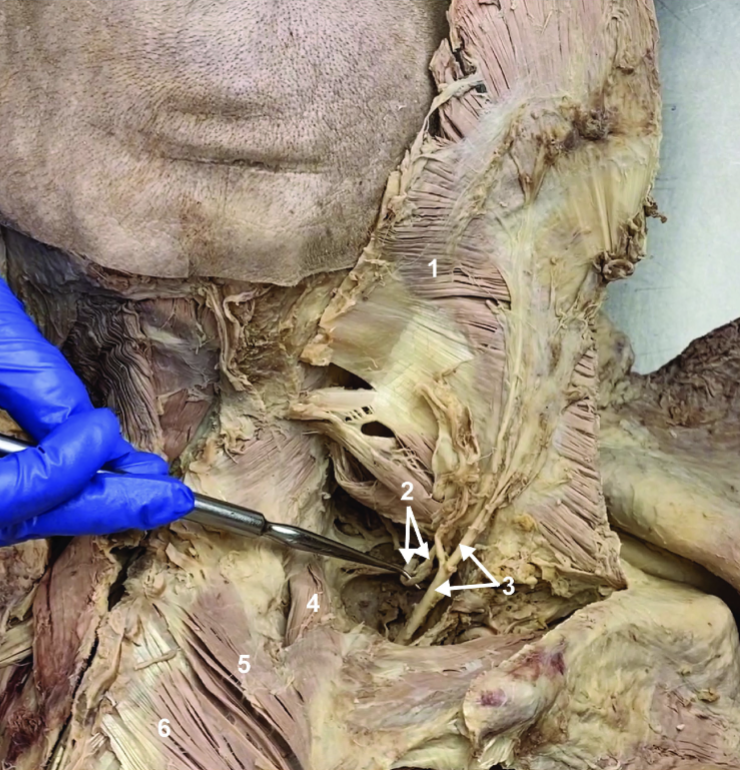
Rhomboid minor
ID structure
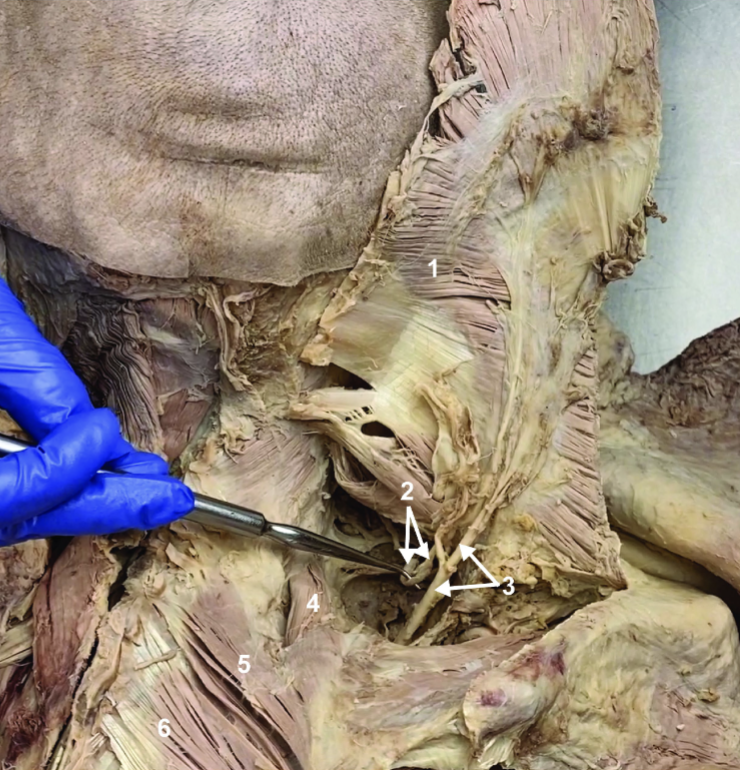
Rhomboid major
ID structure
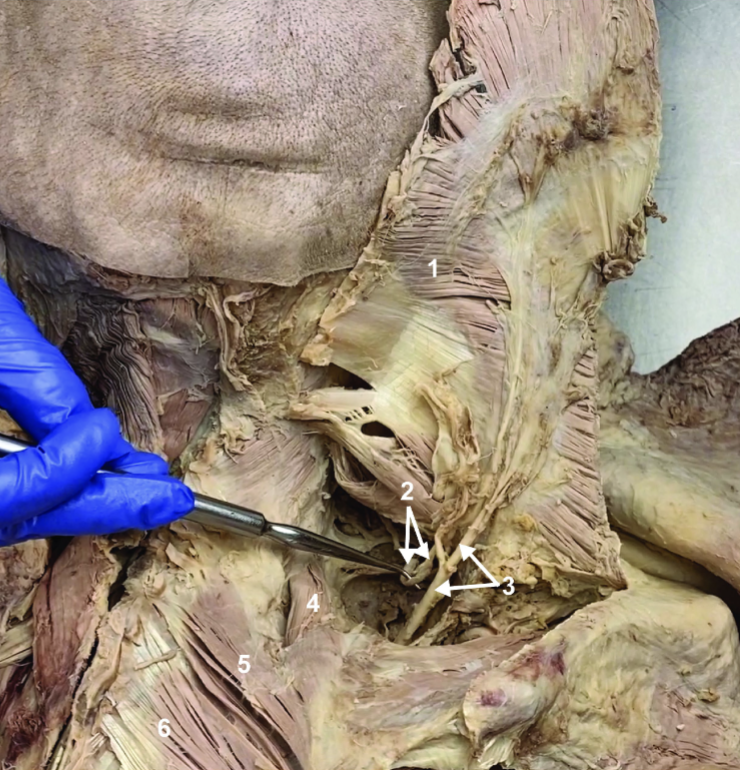
Rhomboids (reflected)
ID structure
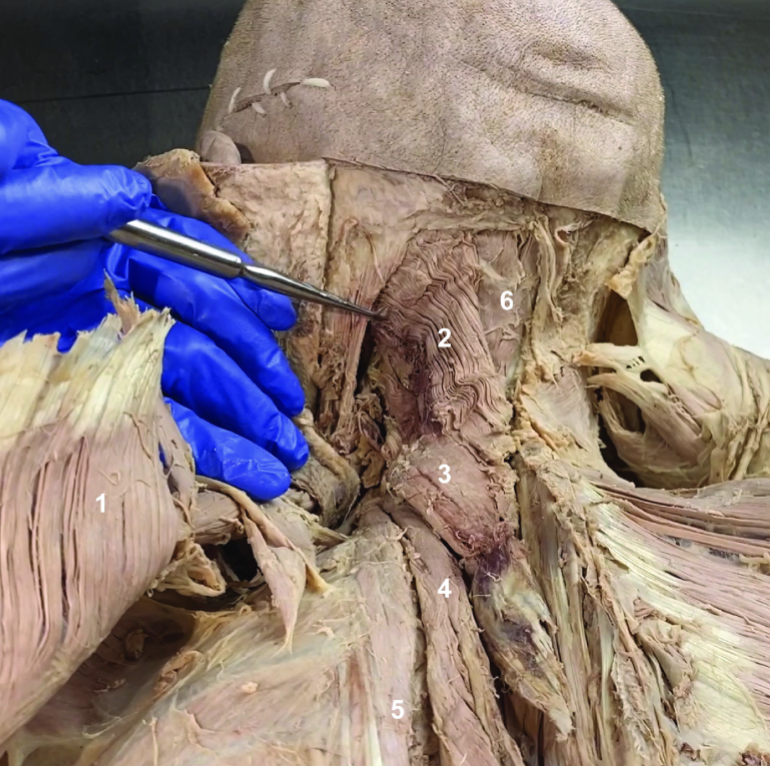
Splenius capitis
ID structure
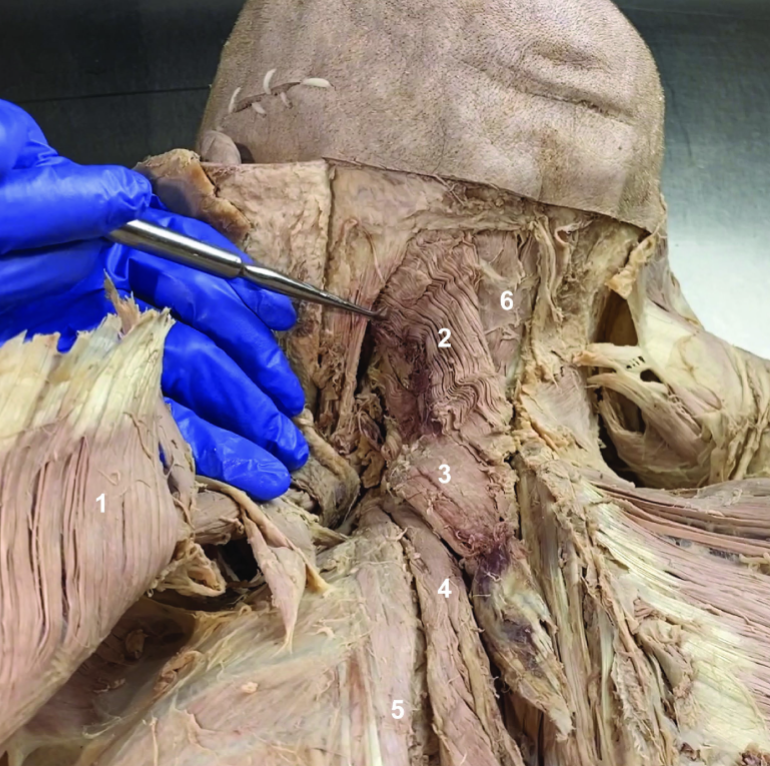
Splenius cervicis
ID structure
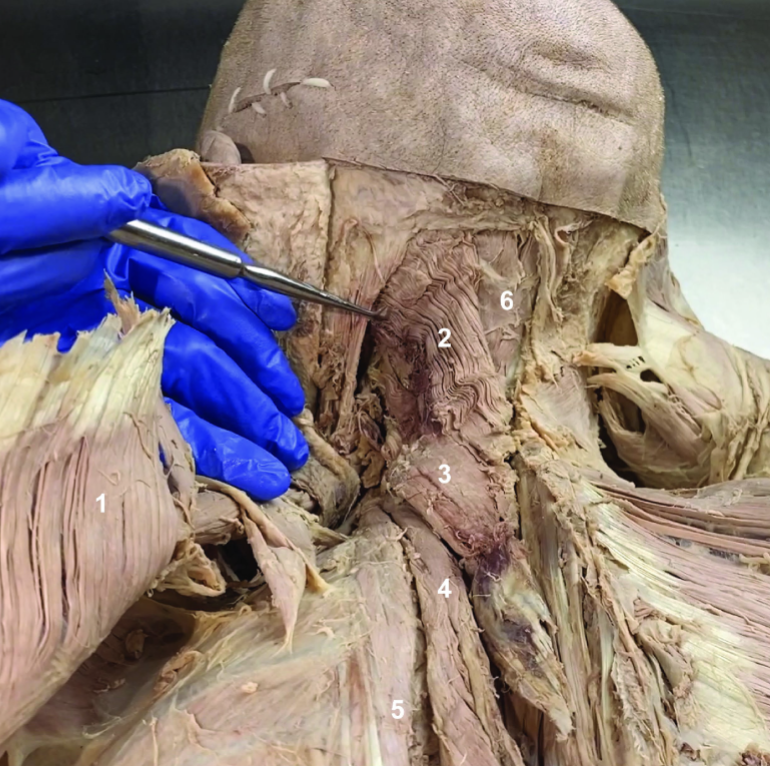
Longissimus
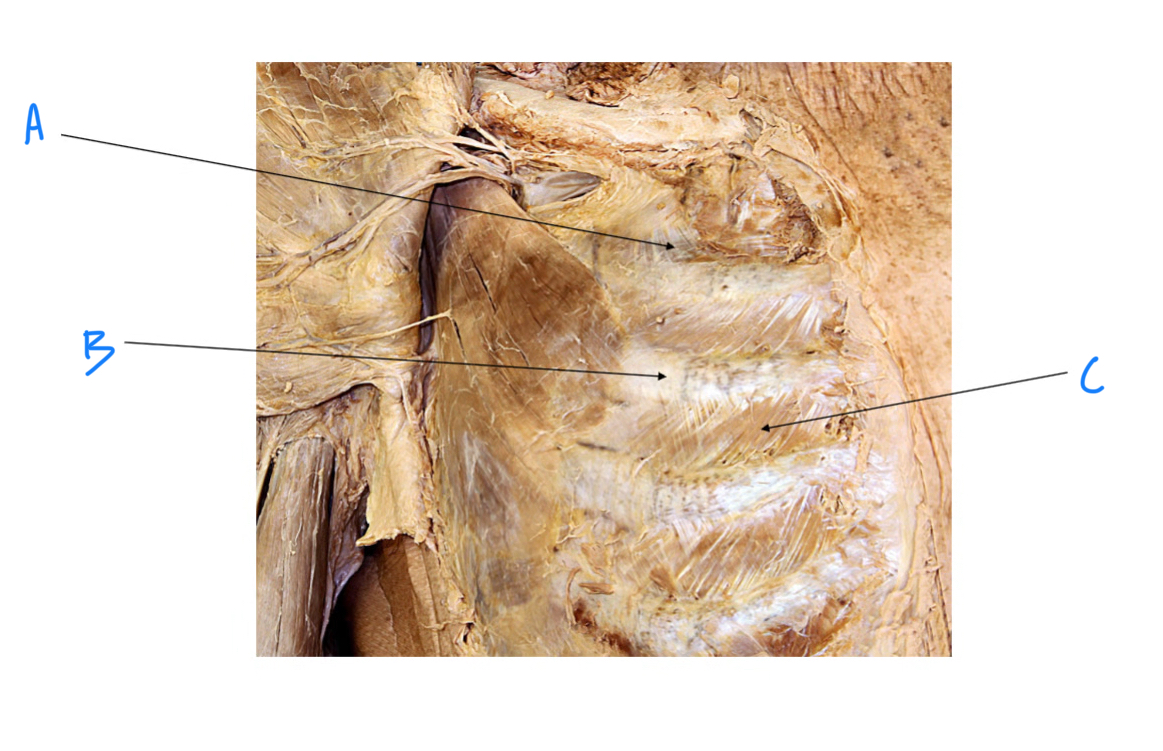
ID structure
Iliocostalis
ID structure
Semispinalis capitis
ID structure
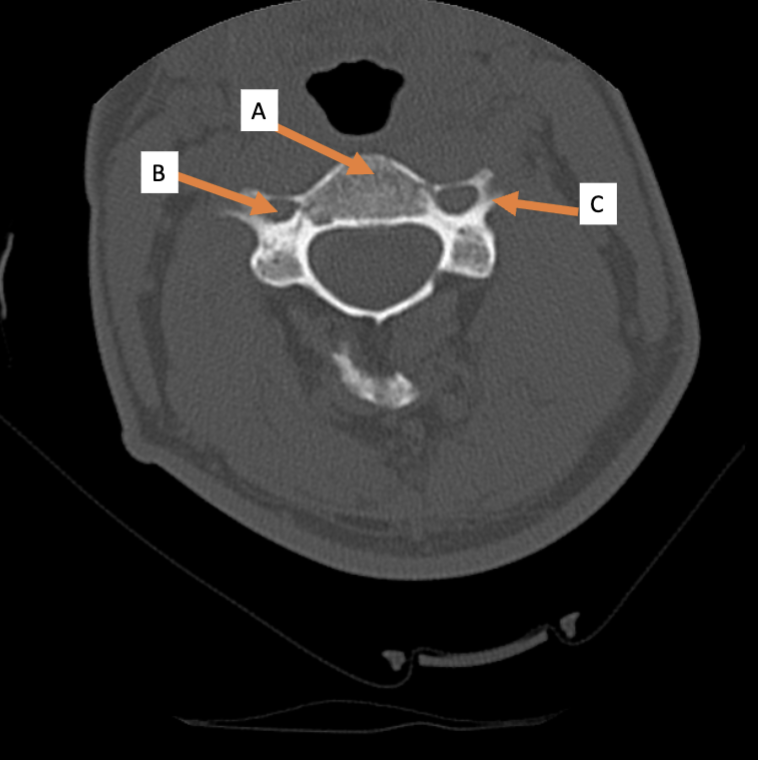
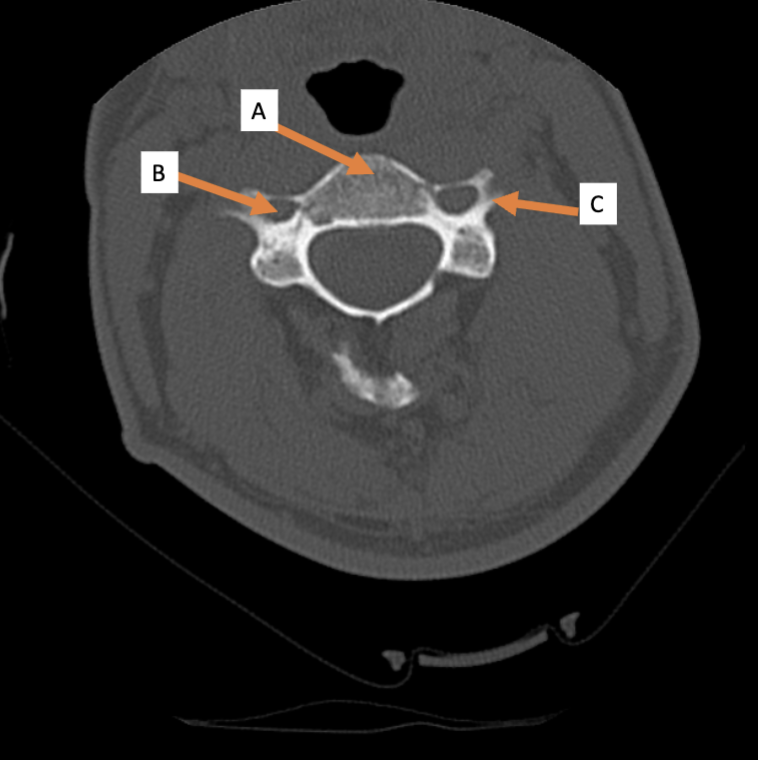
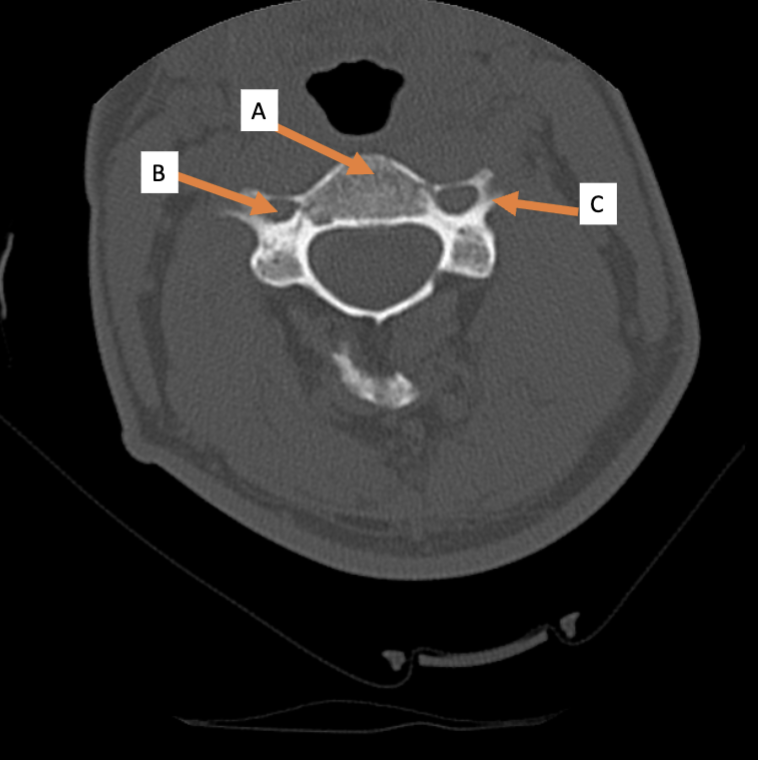
7; 12; 5
How many vertebrae are there in the cervical region? Thoracic? Lumbar?
C1 (atlas); C2 (axis)
Which cervical vertebra doesn’t have a body? Which cervical vertebra has a dens?
Erector spinae
If you bend over from a standing position to pick up an object off the floor, which muscles actively contract to allow you to stand up again?
Epidermis, dermis, superficial fascia, deep fascia, trapezius, rhomboids, erector spinae (likely iliocostalis)
Name in order from superficial to deep tissue layers, including the first 2 muscle layers that would be pierced by a knife wound entering medial to the scapula and adjacent to the scapular spine.
Superficial fascia
Which type of fascia stores fat
Dermis
Given the renewal of cells that occur in one of the layers of the skin, into which layer of skin do you think pigment is injected when making a tattoo.
Dorsal rami provide SM to the deep back m., pass through the superficial back m. without supplying innervation, exit the muscle changing name to posterior cutaneous n. and supplying SS to the overlying skin
How does a posterior cutaneous n. differ from a dorsal ramus
Tension lines formed elastic fibers in the dermis, clinically relevant because they influence wound gaping and healing
What are Langer’s lines and why are they clinically relevant?
External intercosal m.
A. Identify
Costochondral joint
B. Identify
Internal intercostal m.
C. Identify
Internal thoracic (mammary) a.
A. Identify
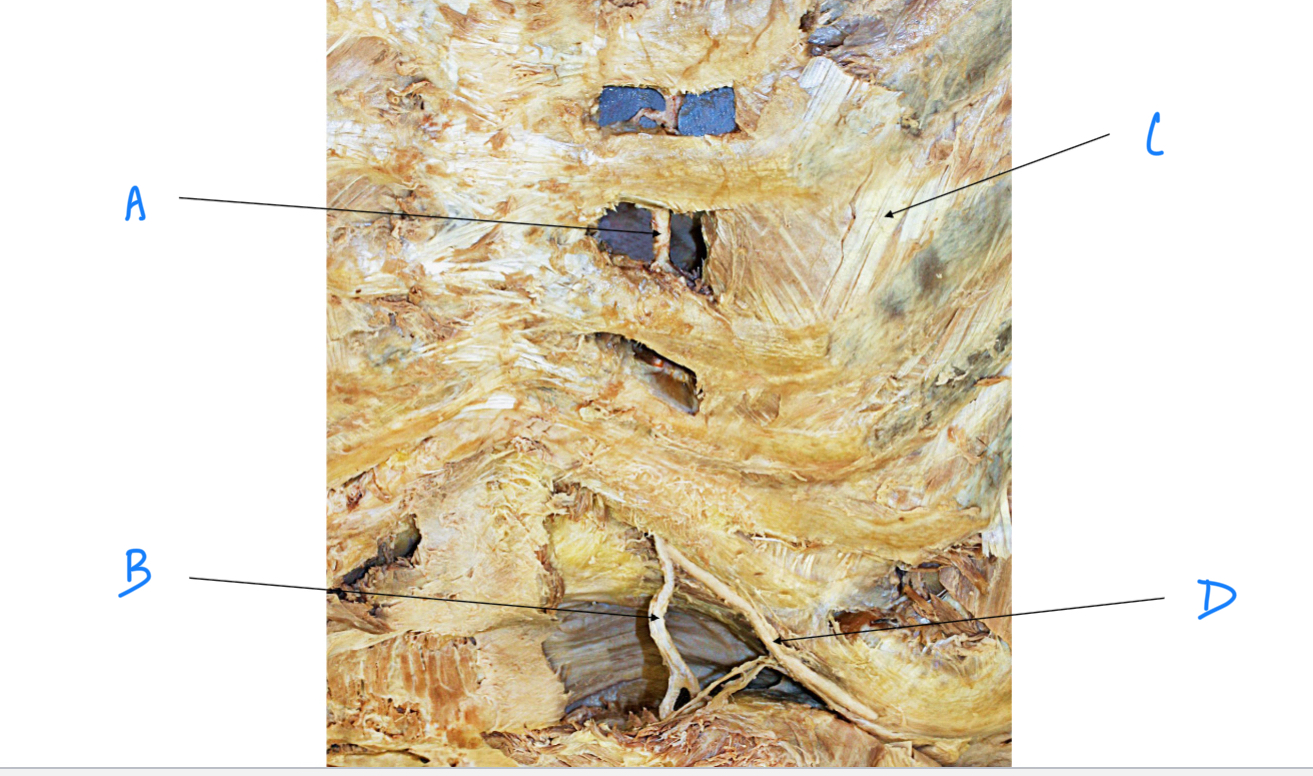
Superior epigastric a.
B. Identify
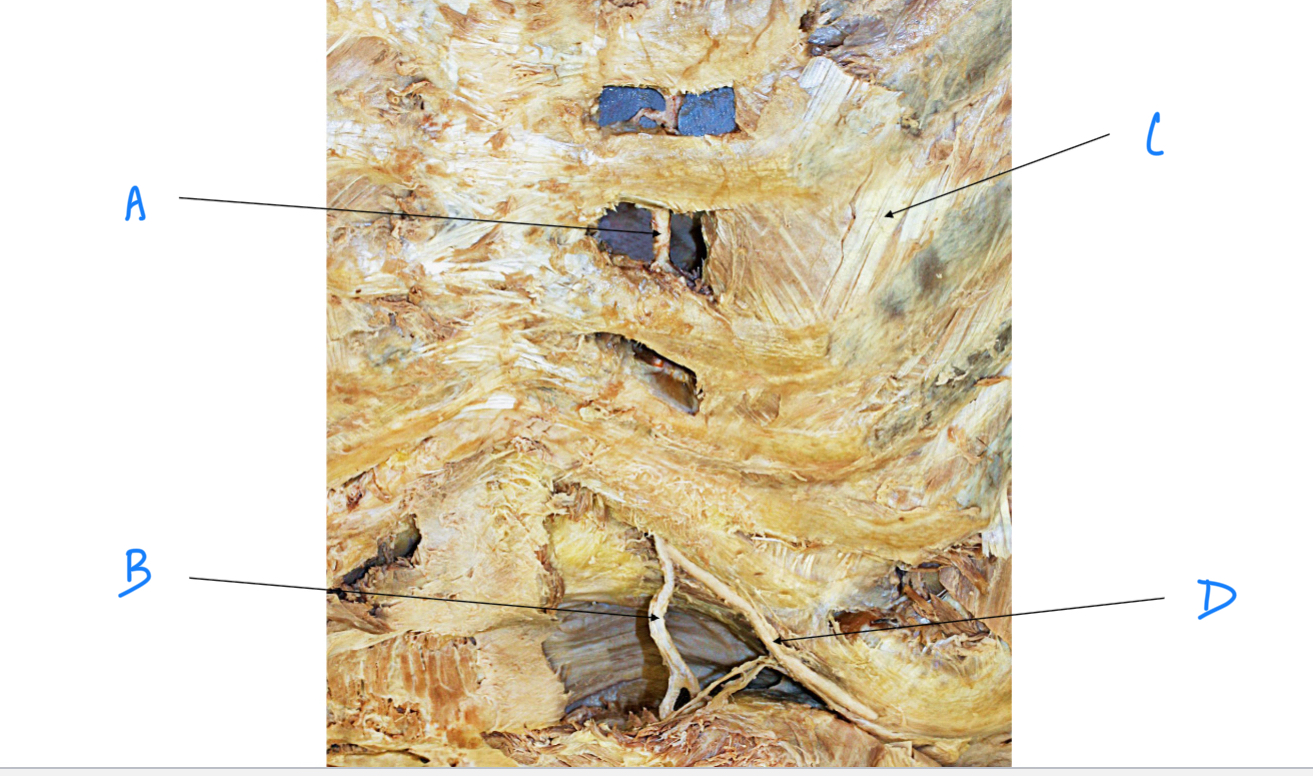
Musculophrenic a.
D. Identify
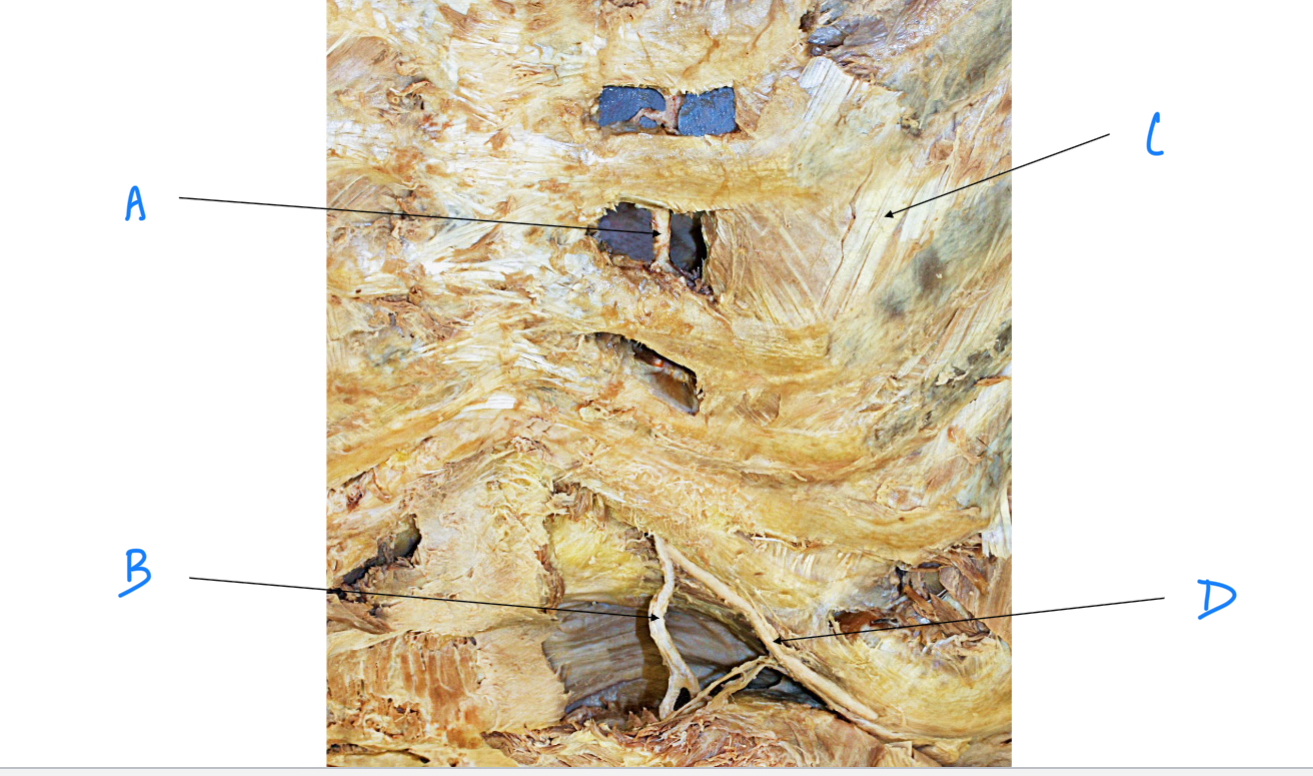
External intercostal m.
C. Identify
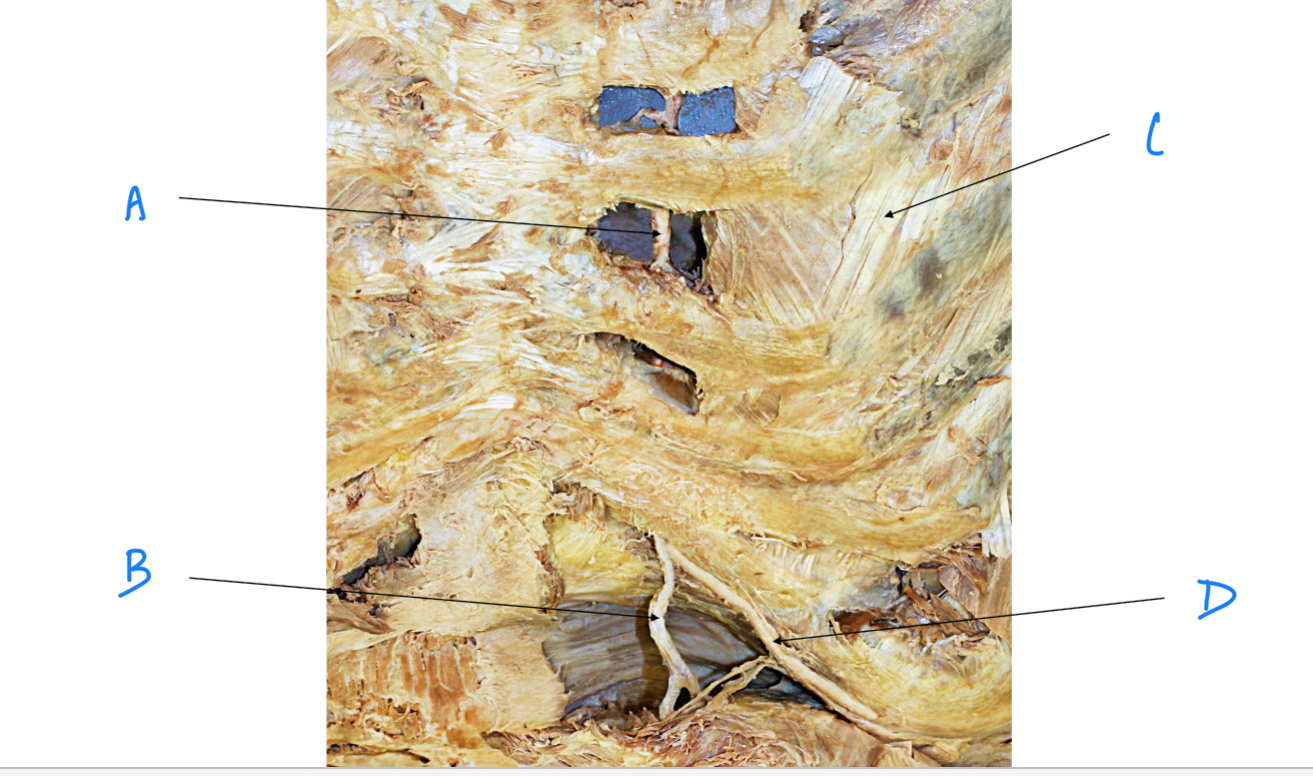
Sternum, thoracic vertebrae, R and L ribs
Which bony structures from the walls of the thoracic cavity
Strip of skin innervated by a SS axons associated with a pair of spinal nerves
Define a dermatome.
DRG, Spinal n., Dorsal ramus, Posterior cutaneous n.
Shingles is reactivation of latent varicella zoster virus that is found in DRG, causing blistering on the skin in a dermatomal pattern. In a patient who has lesions on the back just lateral to the posterior midline, what is the pathway taken by the virus?
T4
Which DRG was originally infected in a case of shingles involving a horizontal strip of skin that intersects the nipple?
Yes
Do dermatomes overlap
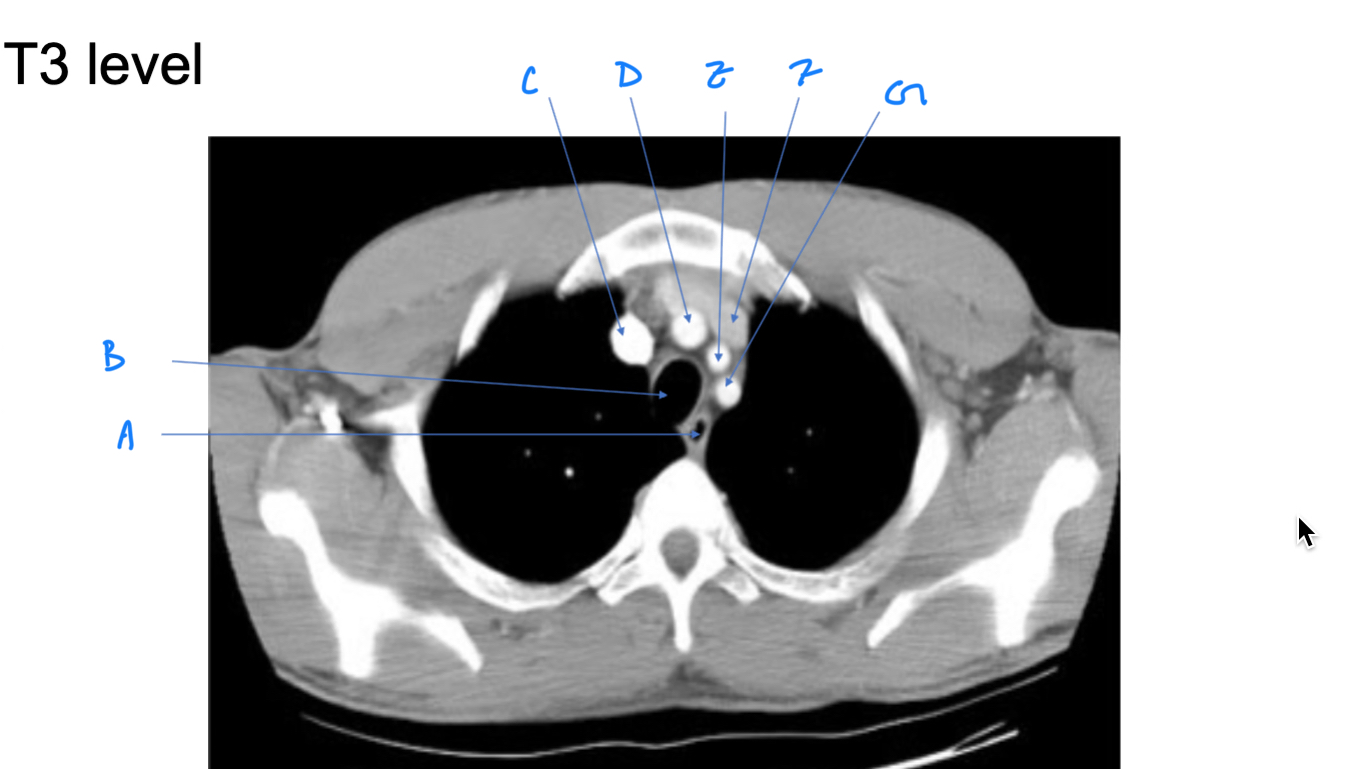
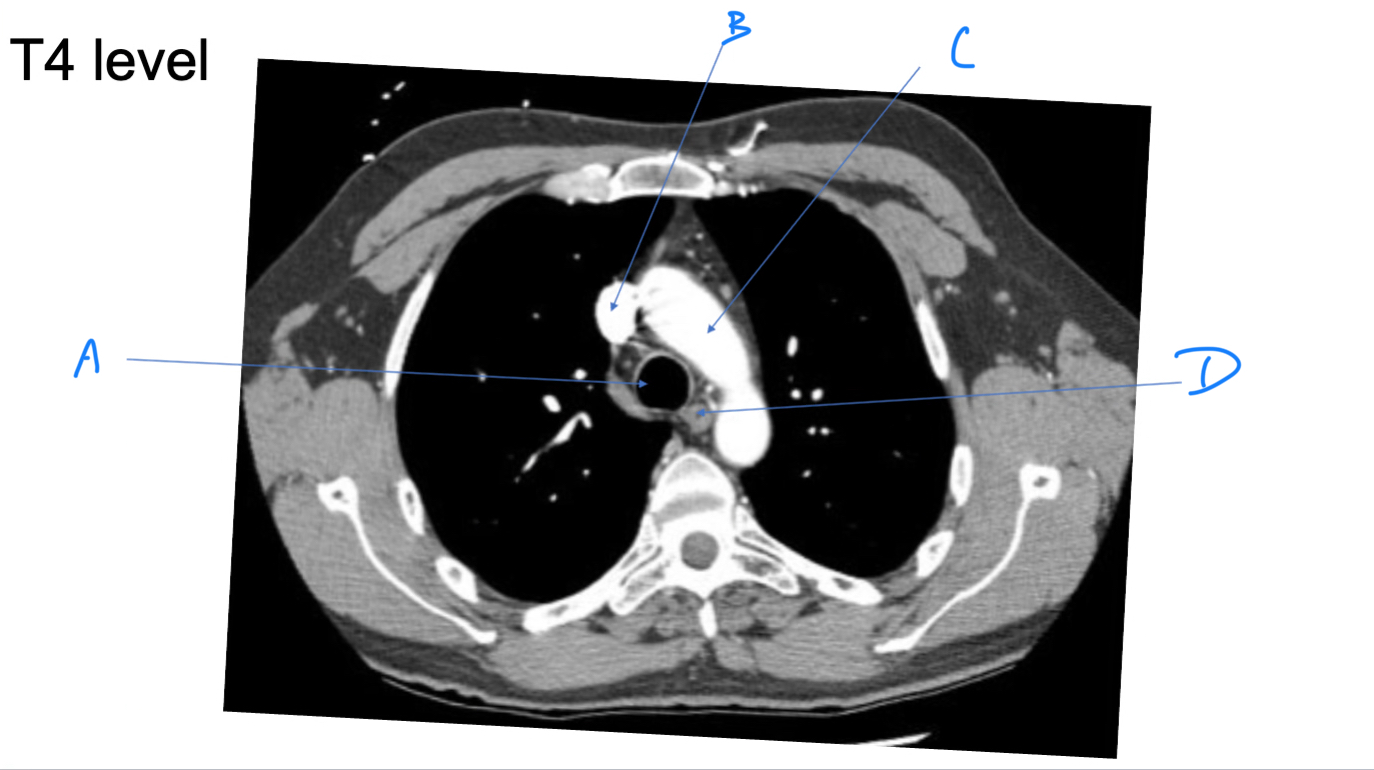
Esophagus
A. Identify
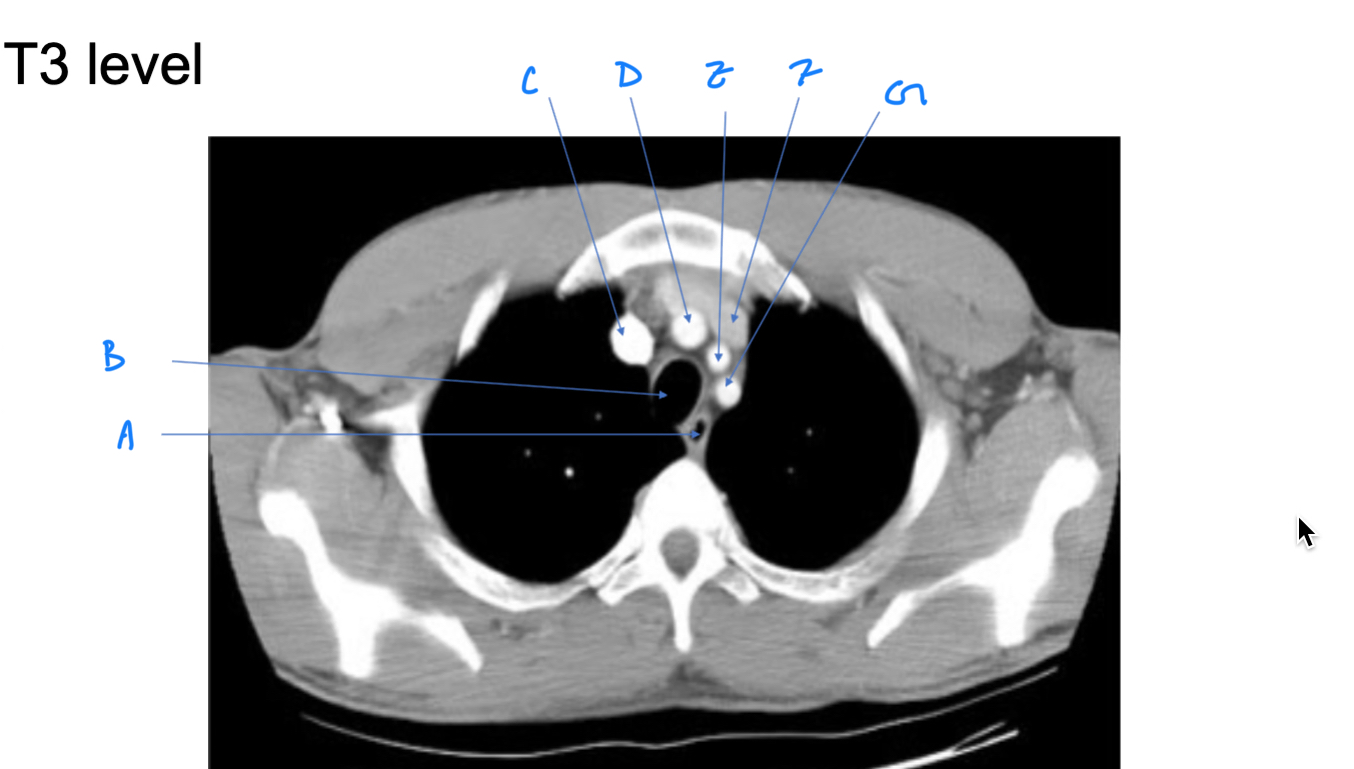
Trachea
B. Identify
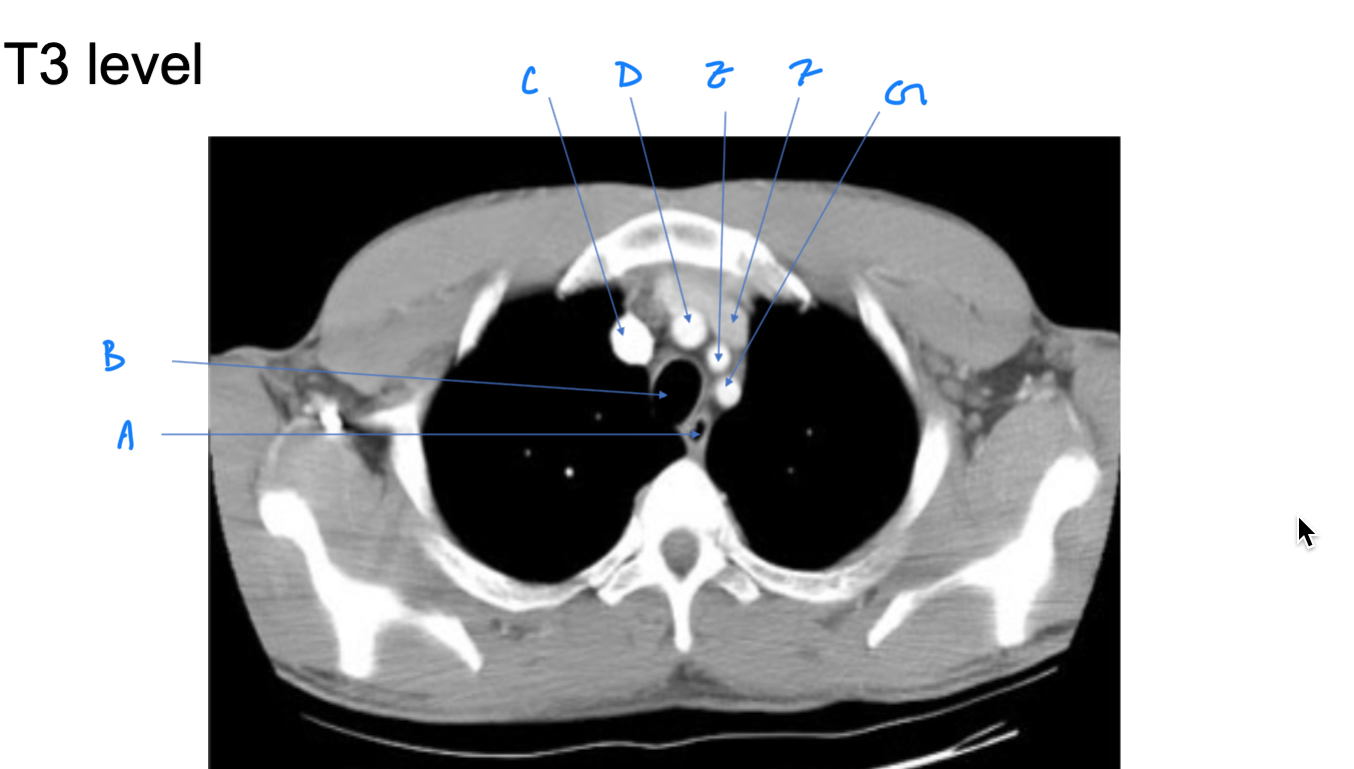
R Brachiocephalic v.
C. Identify
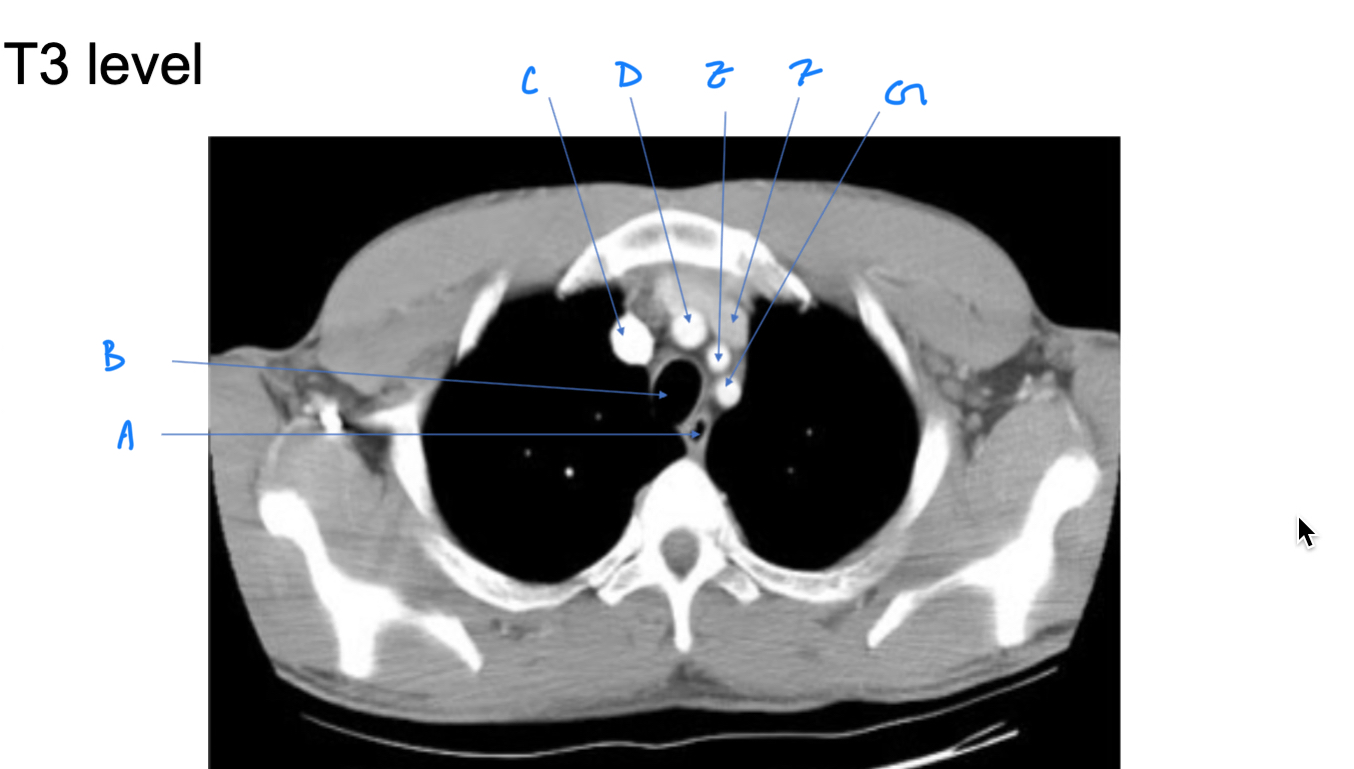
Brachiocephalic trunk
D. Identify
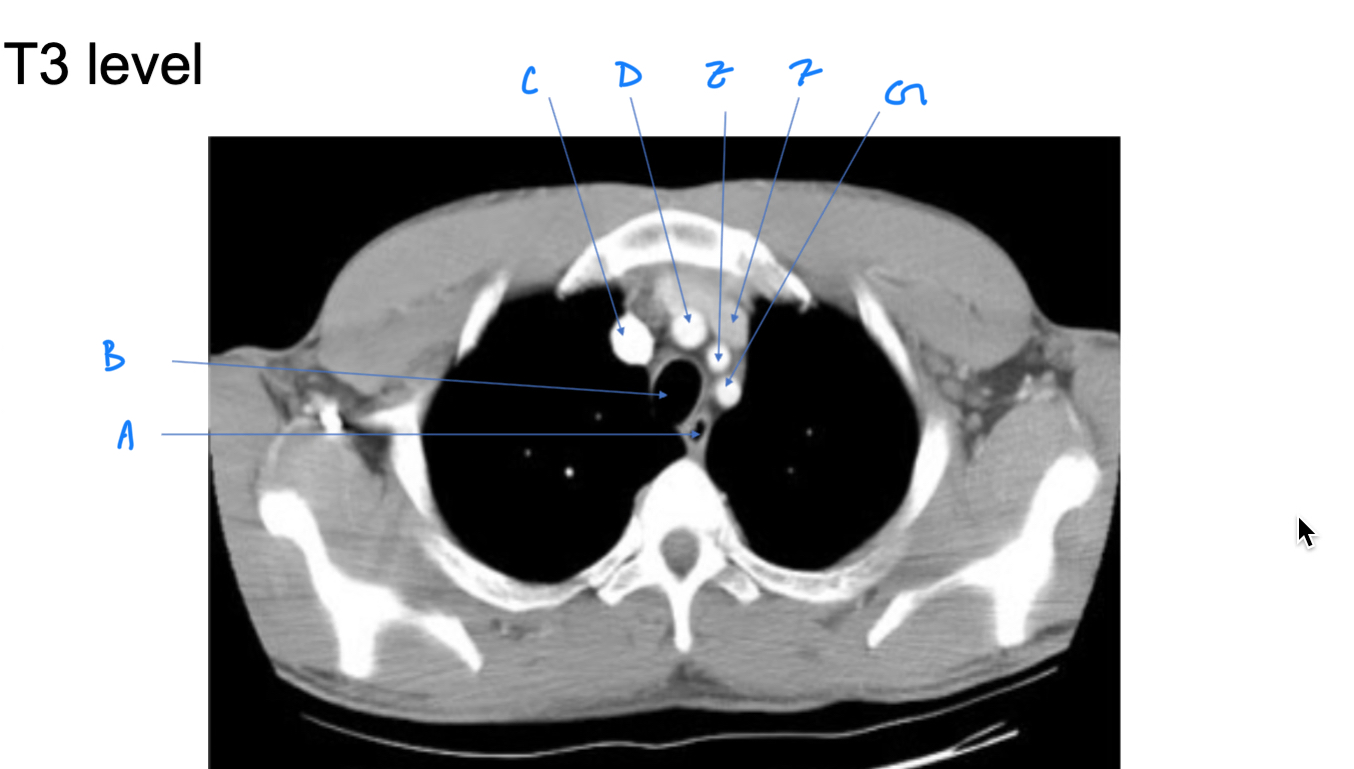
L CCA
E. Identify
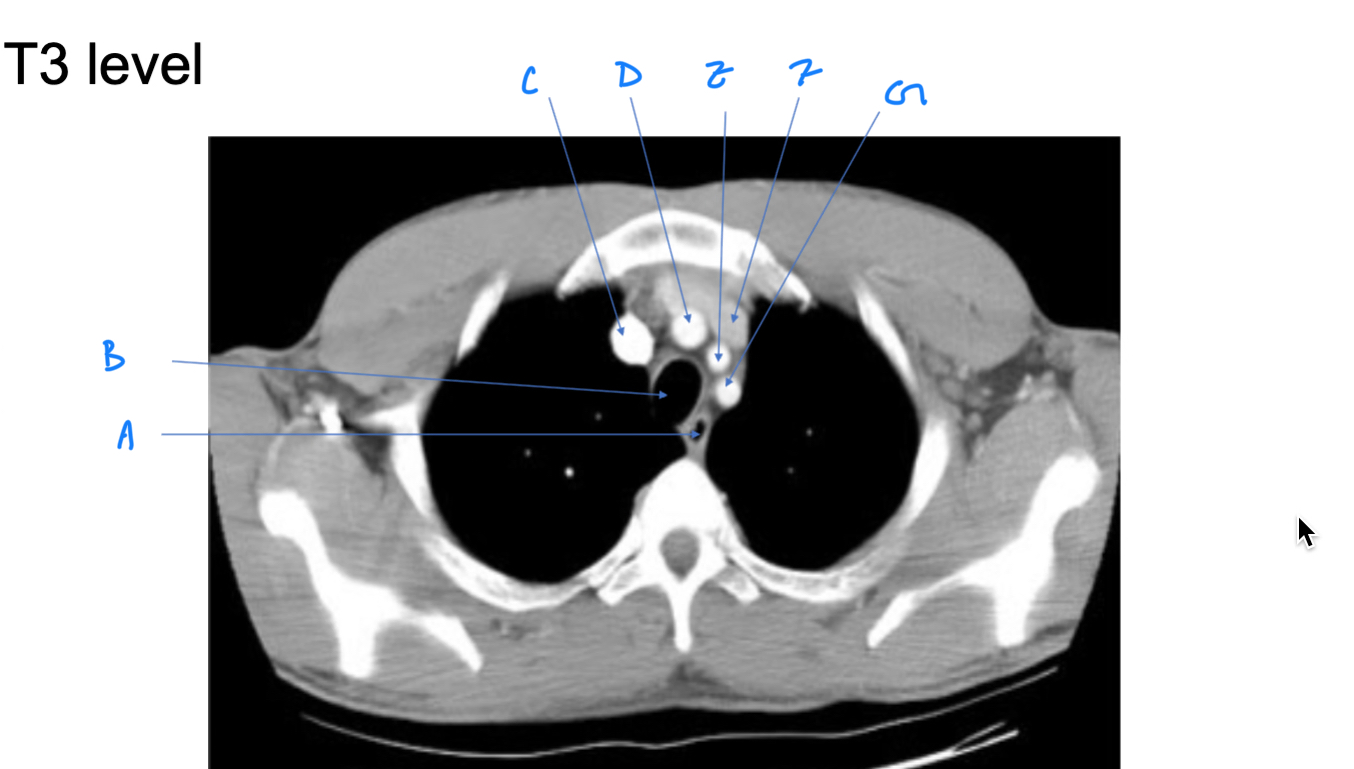
L Brachiocephalic v.
F. Identify
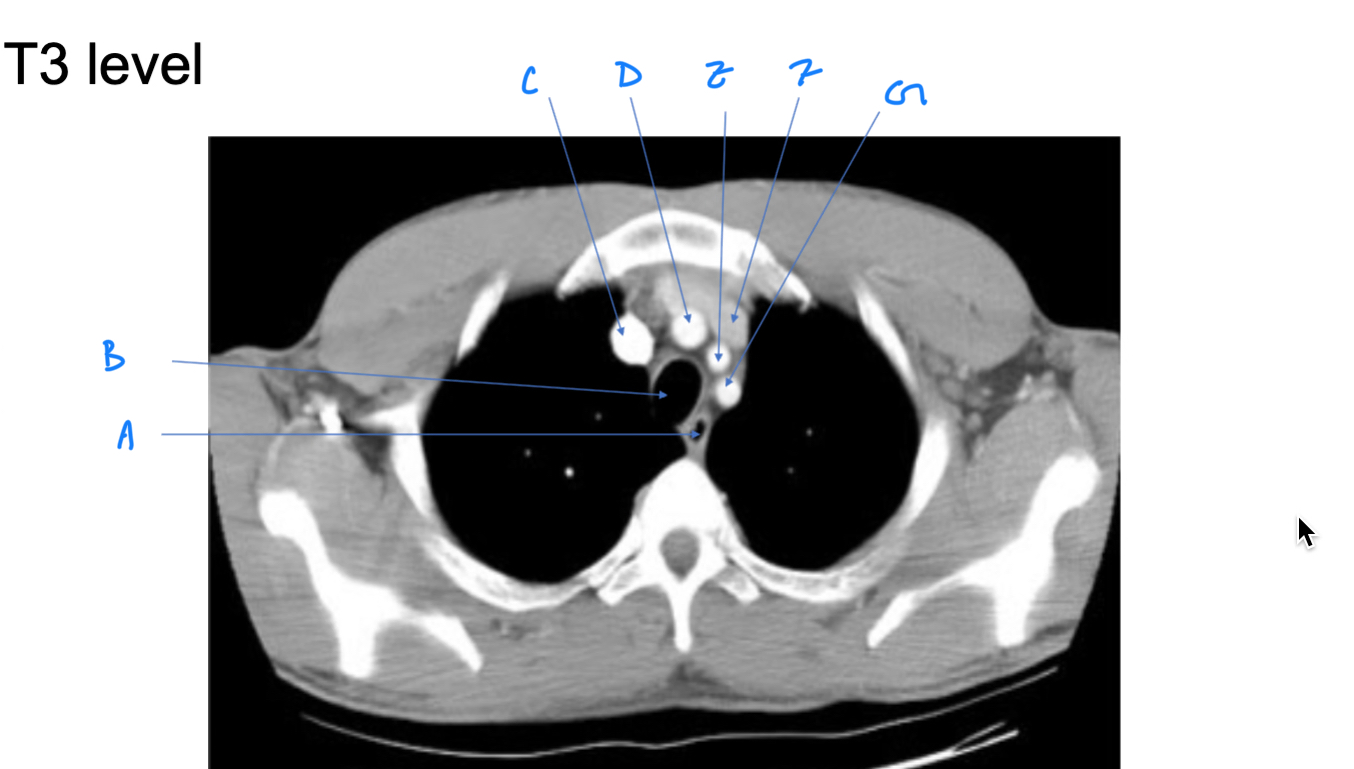
L Subclavian a.
G. Identify
Trachea
A. Identify
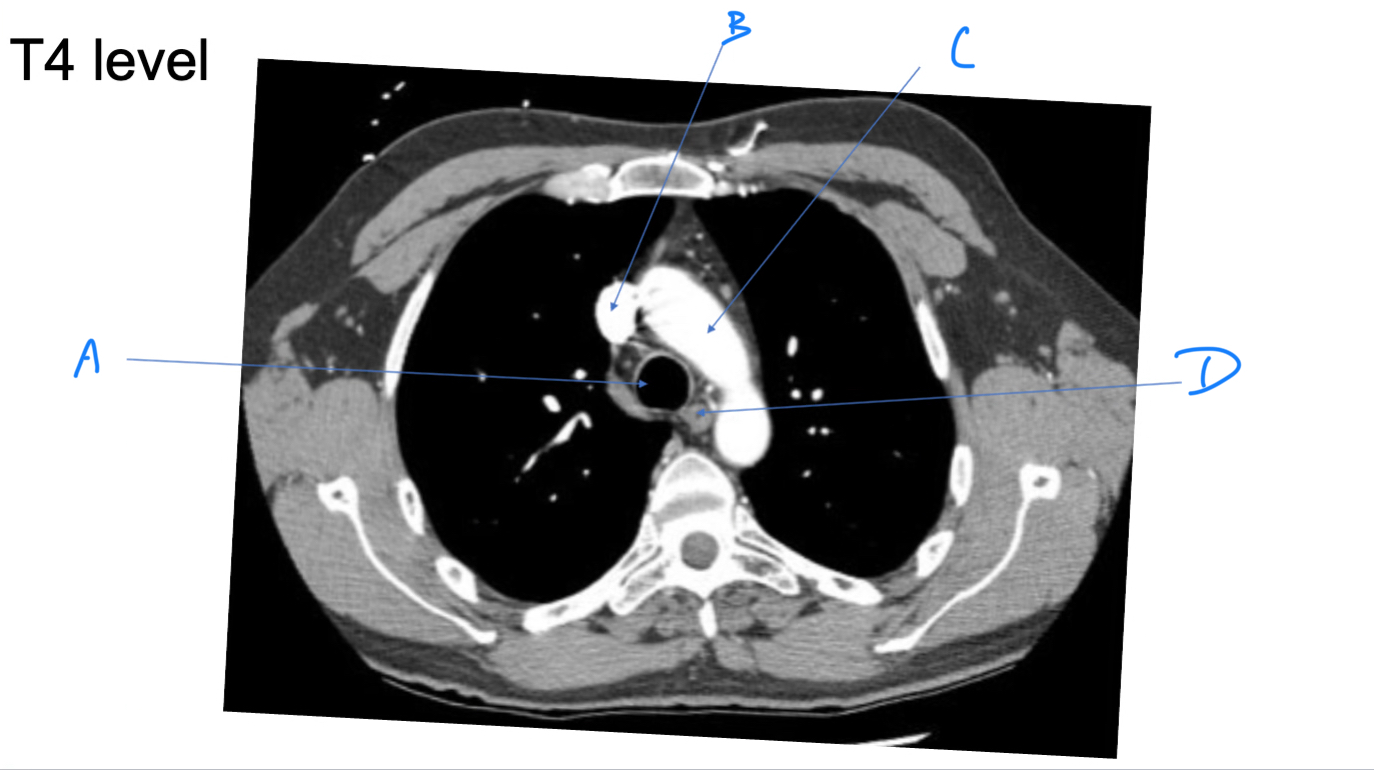
Superior vena cava (SVC)
B. Identify
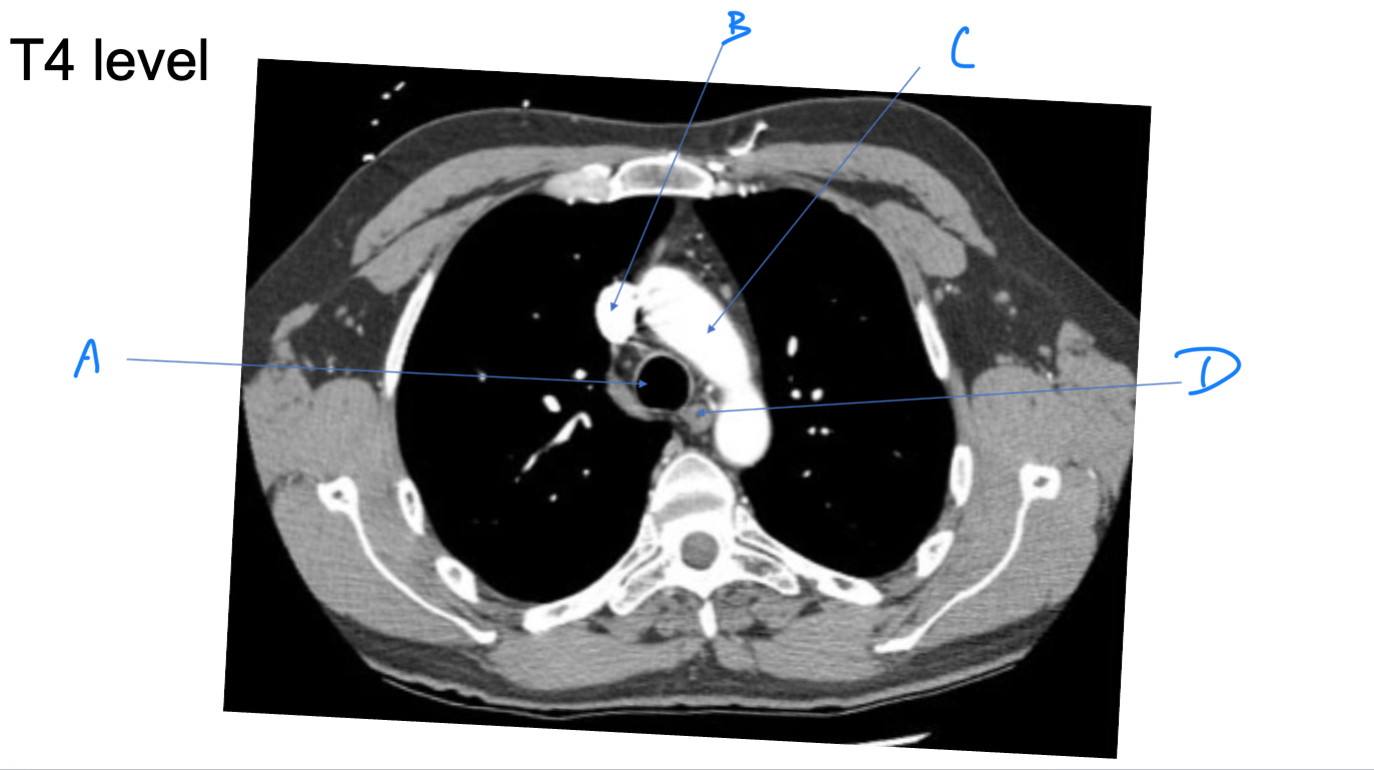
Arch of aorta
C. Identify
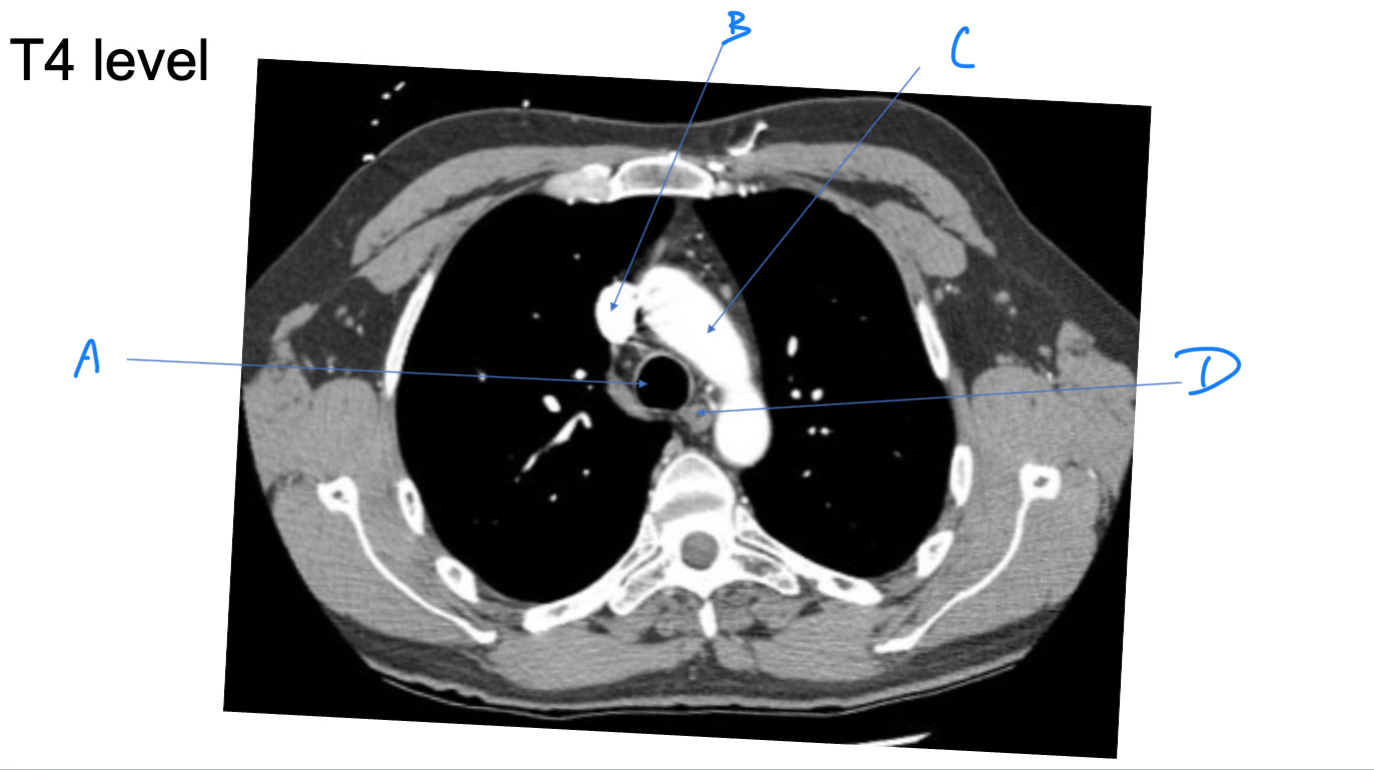
Esophagus
D. Identify
L5; vertical course of the n. roots in the cauda equina and the height of the intervertebral foramina (higher because of larger vertebral bodies)
Which spinal n. is most likely impinged when the intervertebral disk between L4 and L5 protrudes postereolaterally to the right? What features of the lumbar vertebrae and spinal n. informed your answer?
31; 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal
How many spinal cord segments are there and how are they spread across the vertebral regions
Somatosensory and sympathetic post-ganglionic
LA is applied approximately 2 finer breadths to the R of the spinous process of the C7 vertebrae to minimize any pain associated with a procedure. What types of axons are found in the n. that supplies the skin at the region?
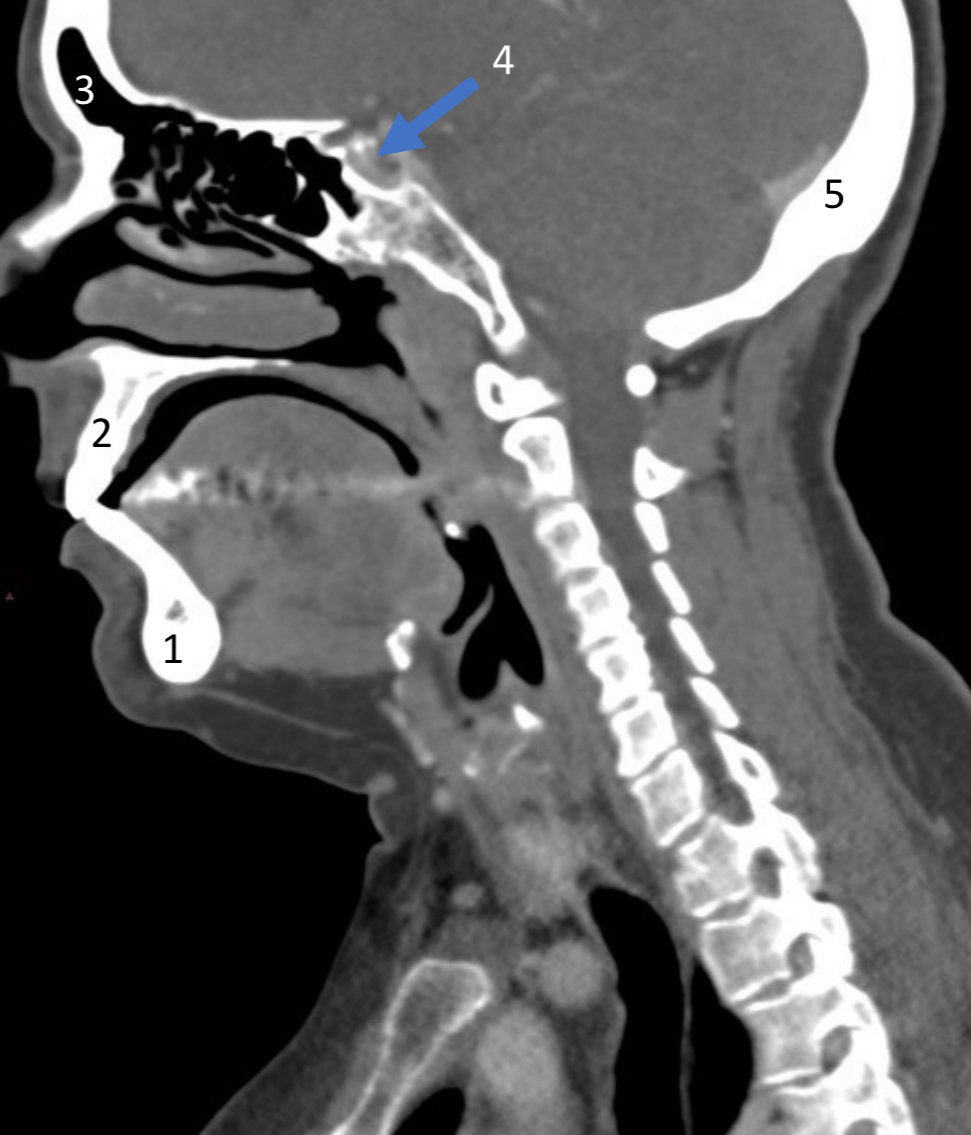
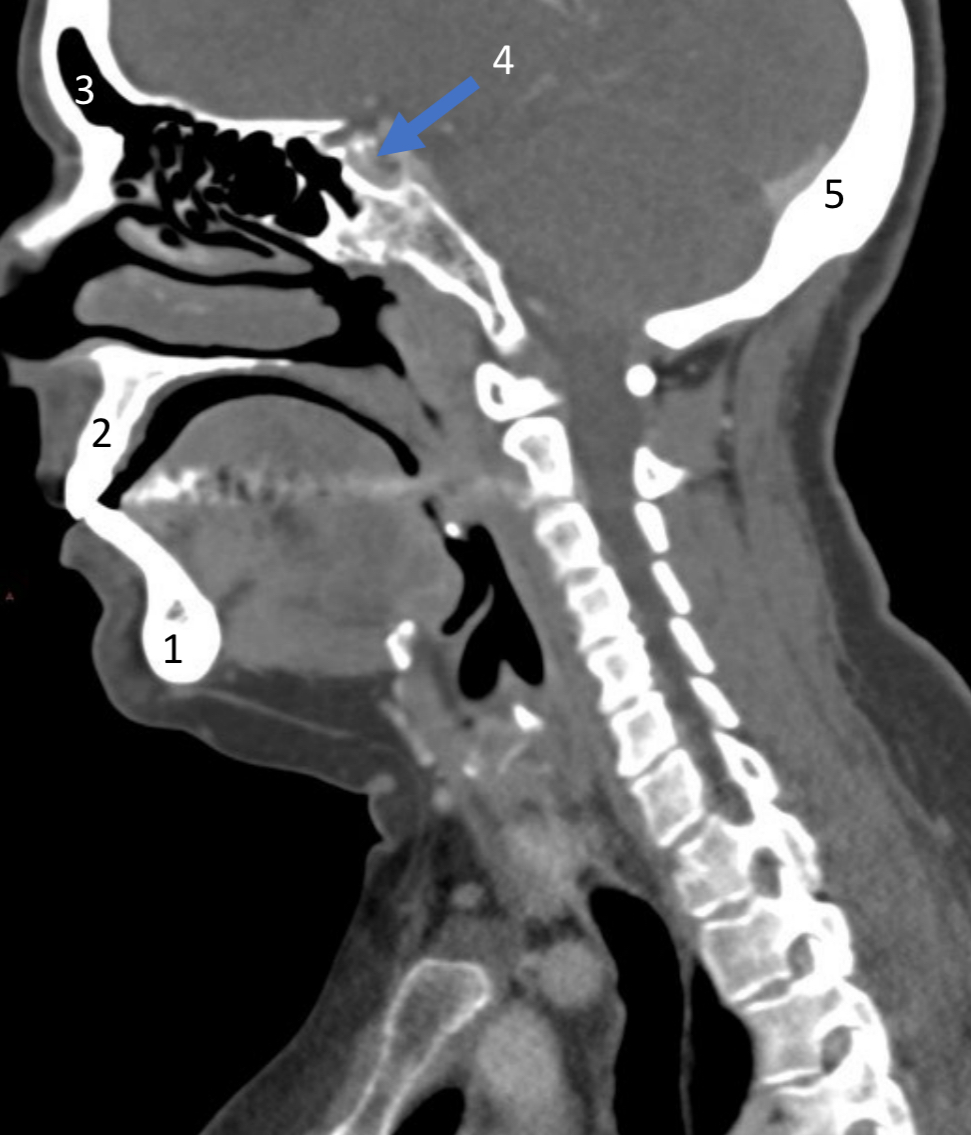
Mandible
ID bone
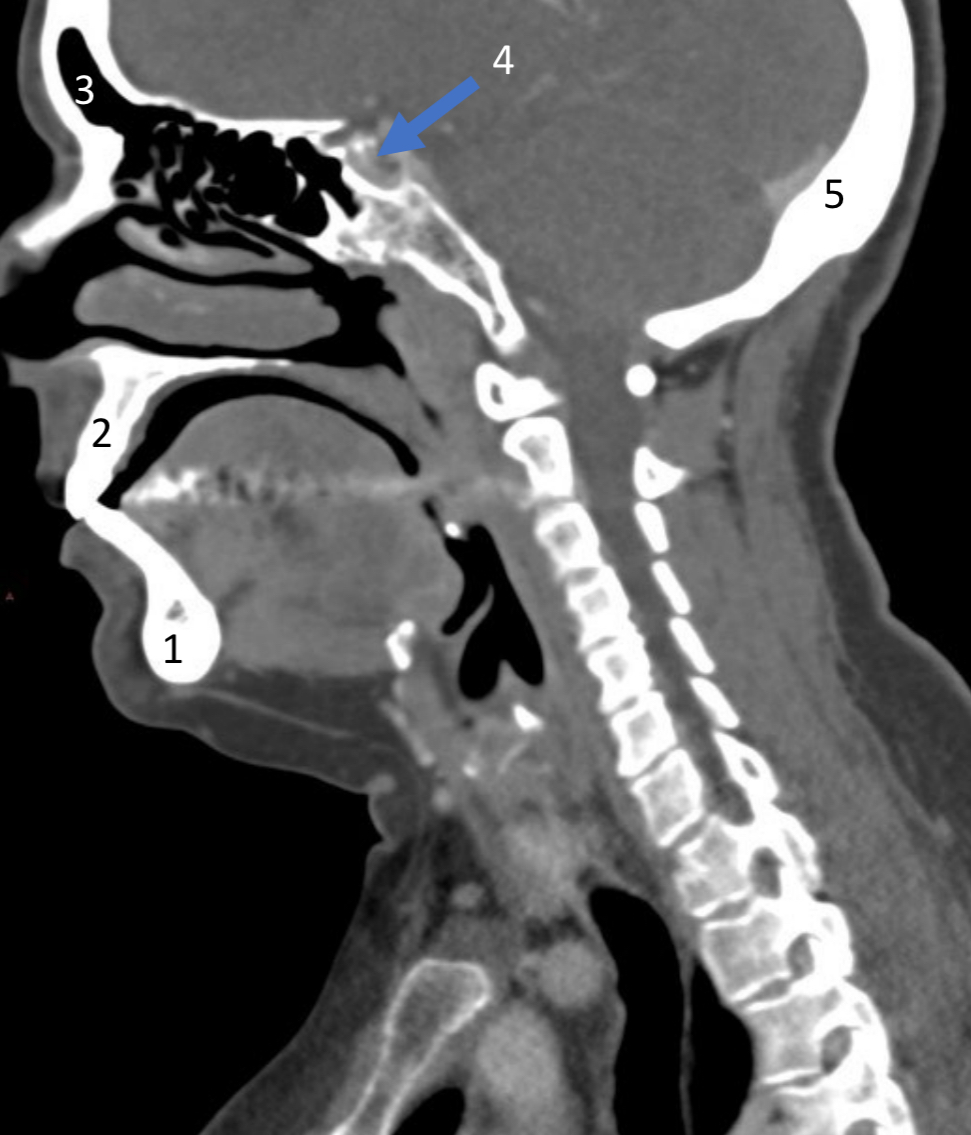
Maxilla
ID bone
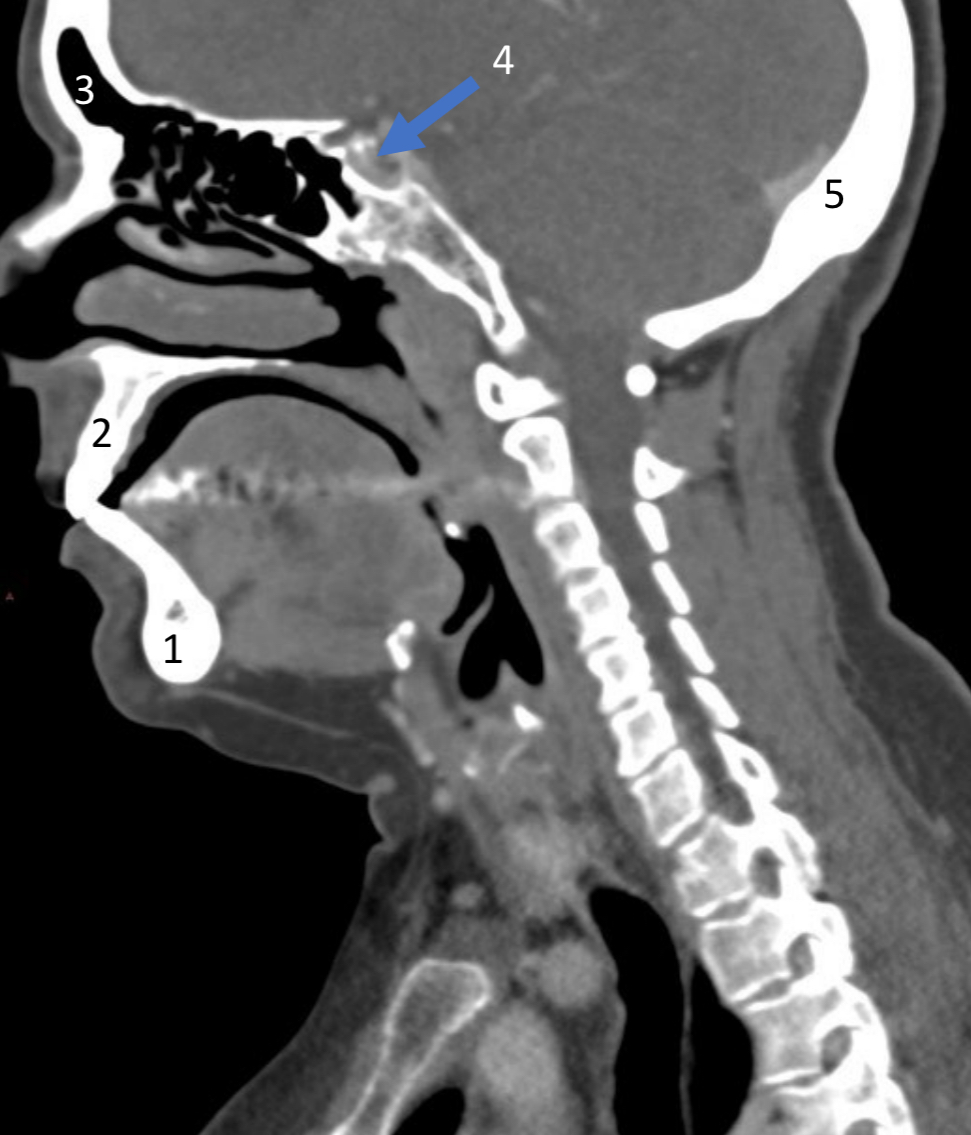
Frontal sinus
ID structure
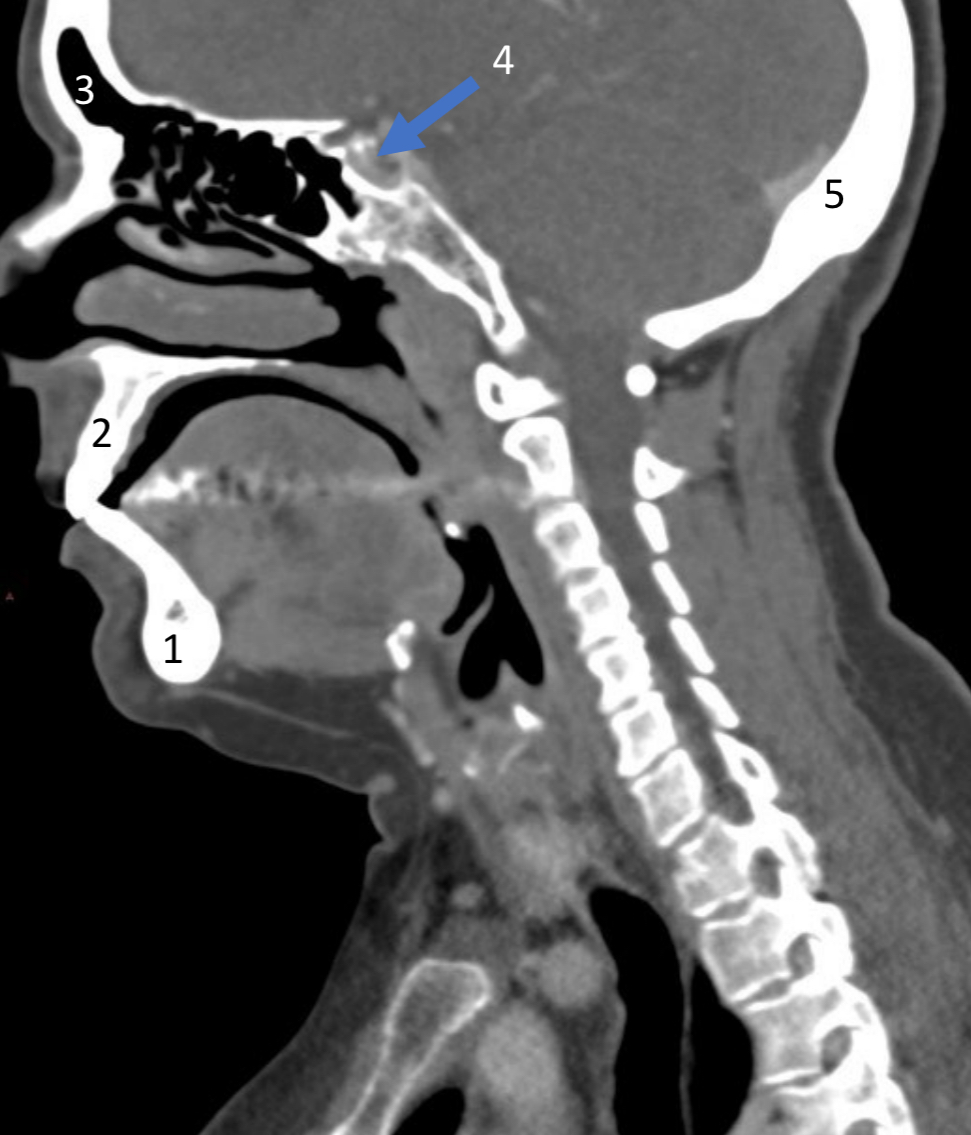
Pituitary fossa
ID structure
Occipital
ID bone
Lambdoid suture
ID structure
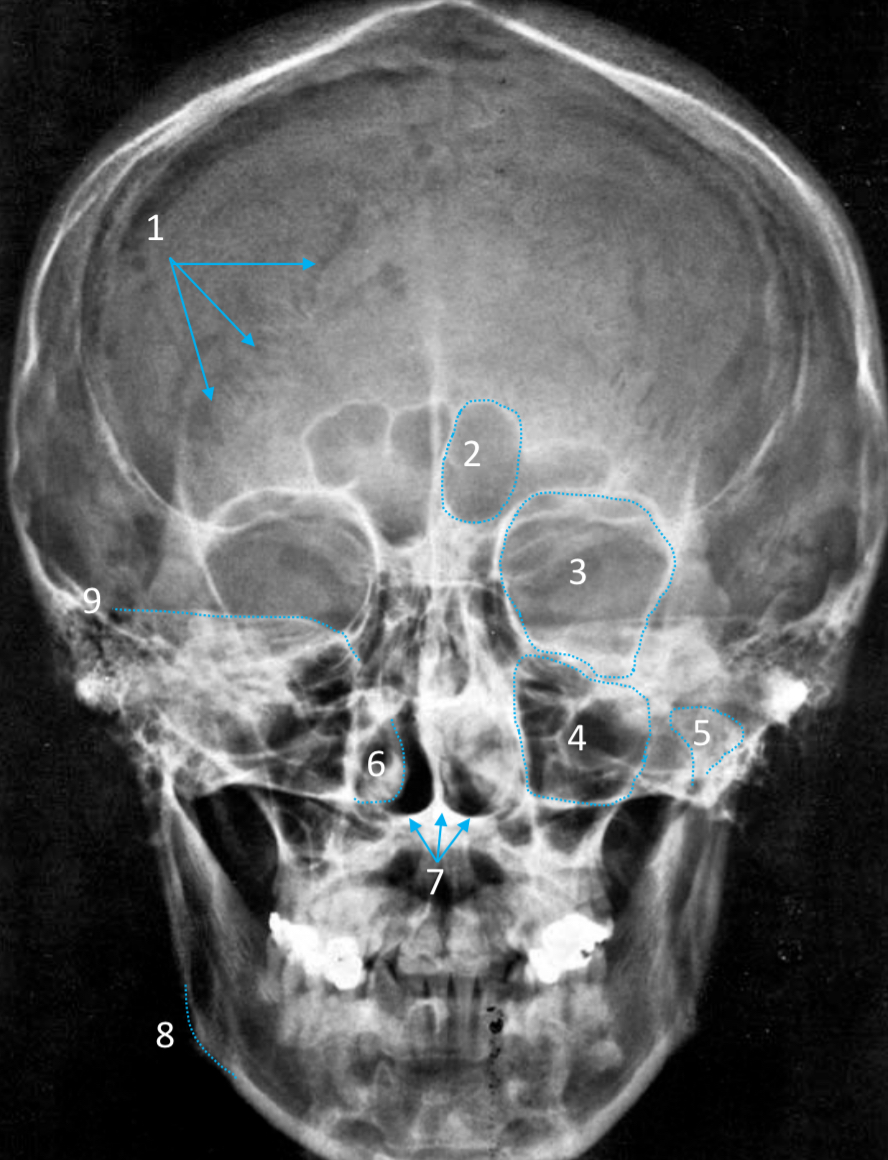
Frontal sinus
ID structure
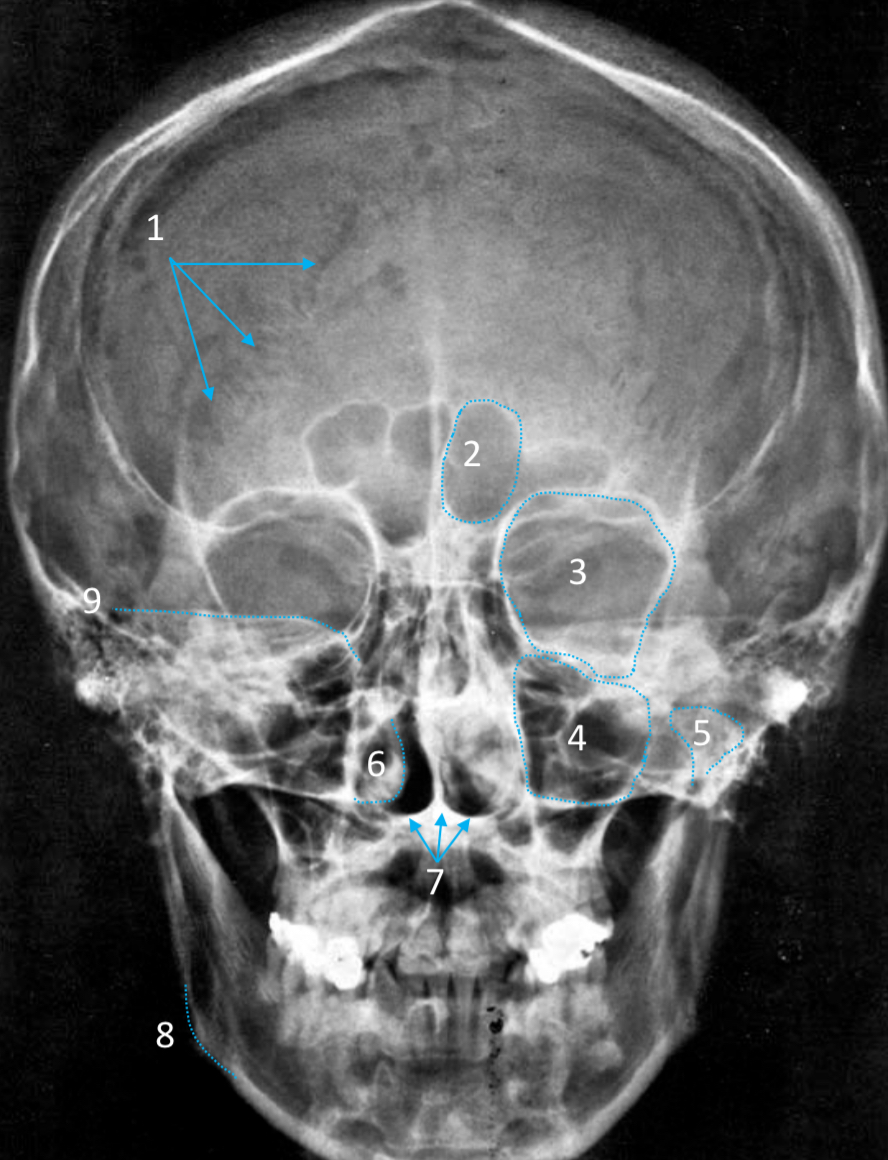
Orbital margin
Orbit
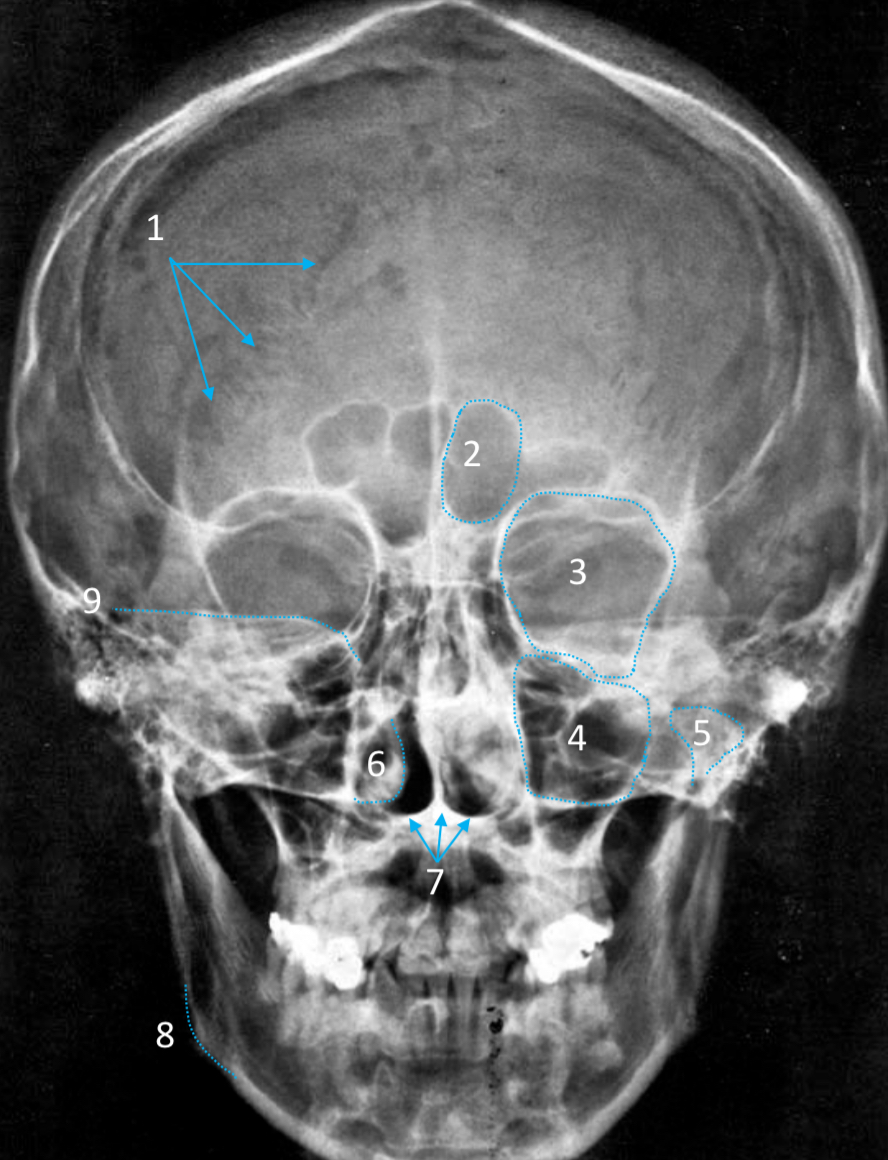
Maxillary sinus
ID structure
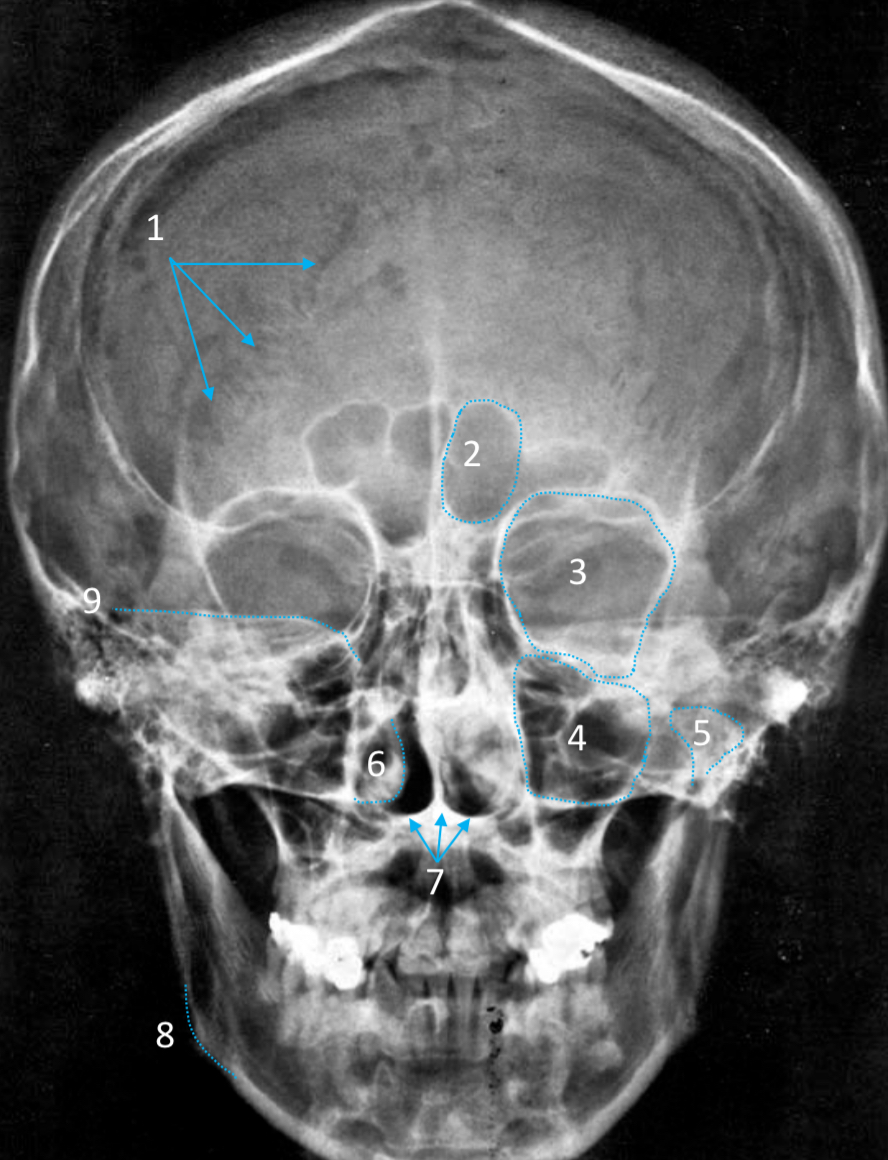
Mandibular condyle
ID structure
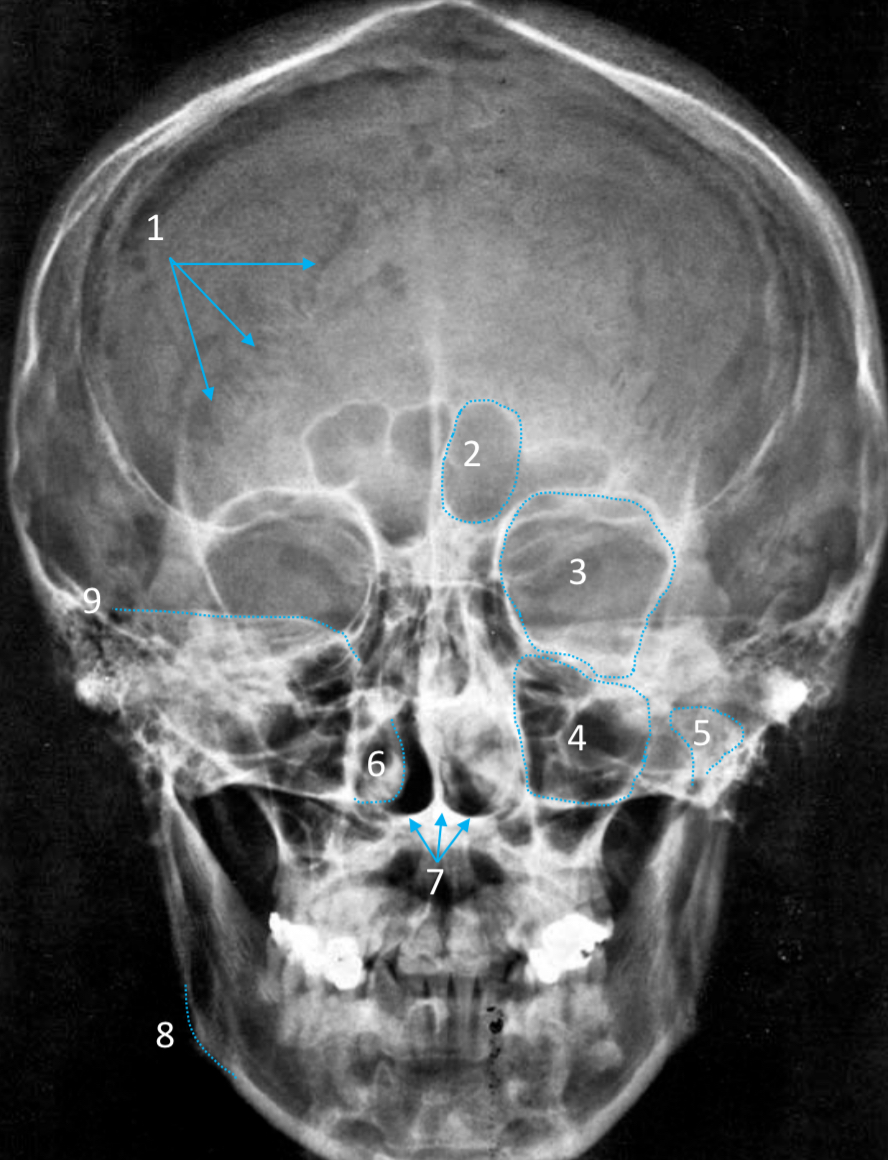
Inferior nasal concha
ID structure
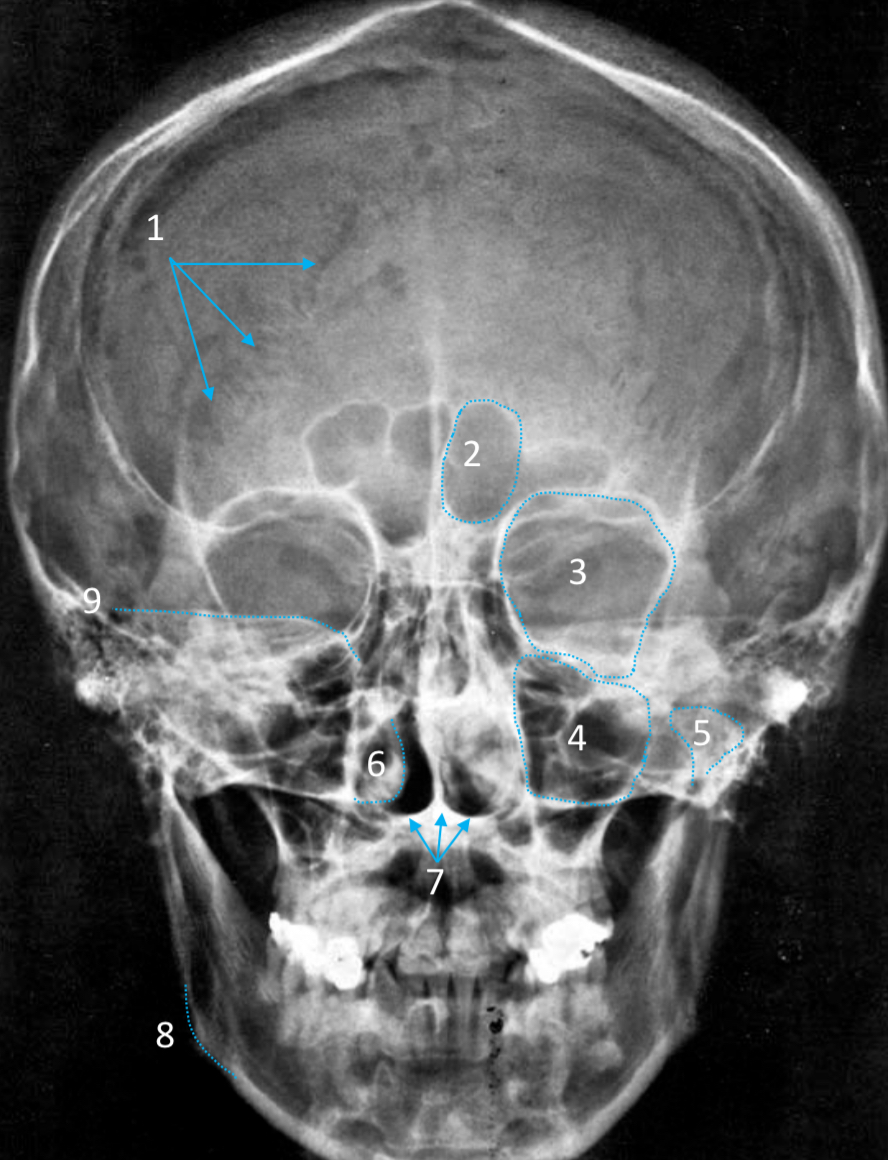
Hard palate
ID strucutre
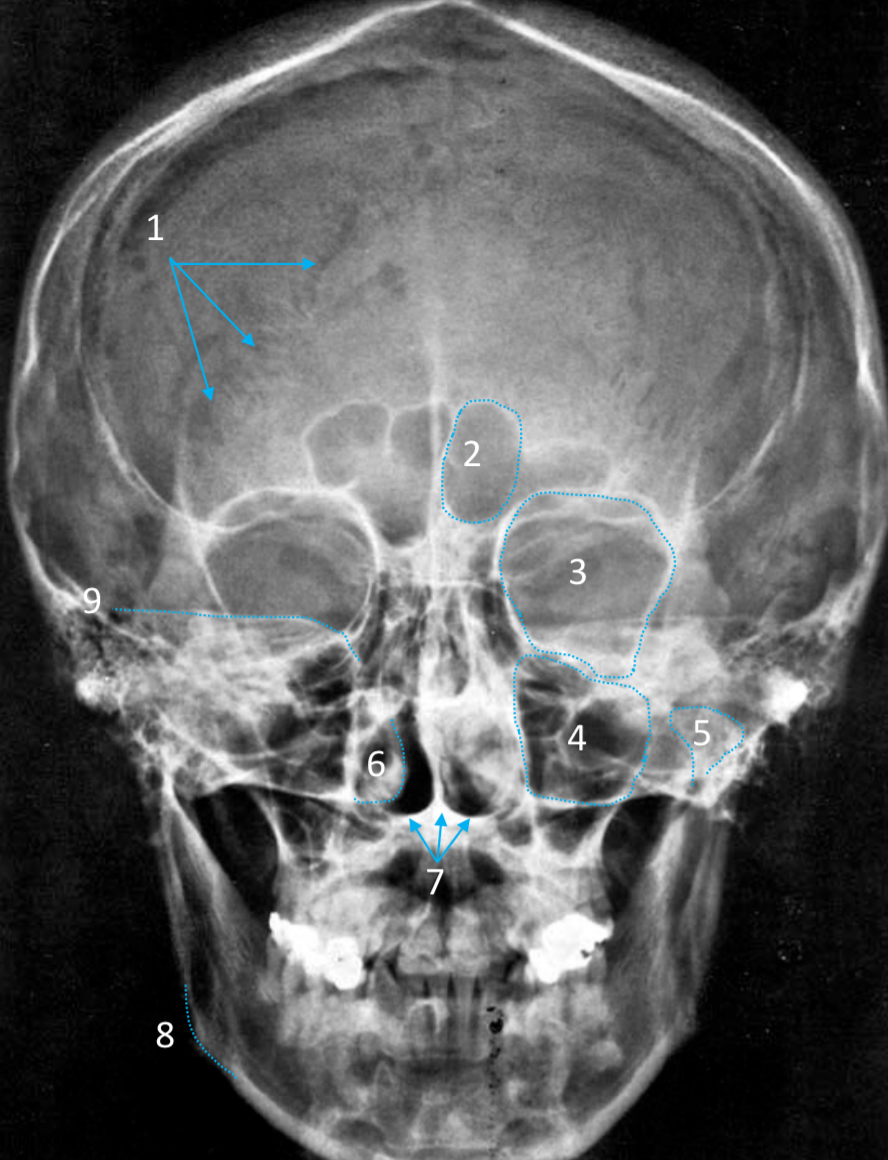
Gonial angle
ID strucutre
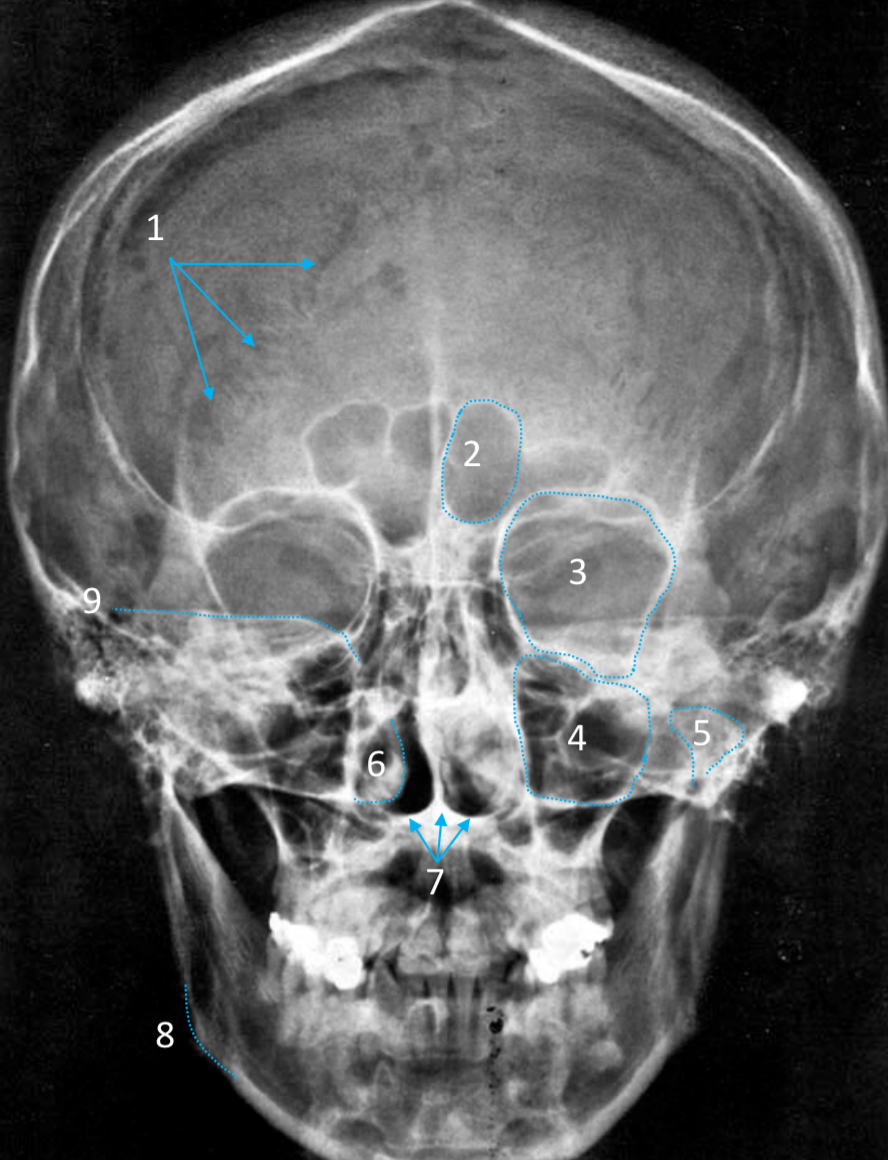
Petrous ridge
ID structure
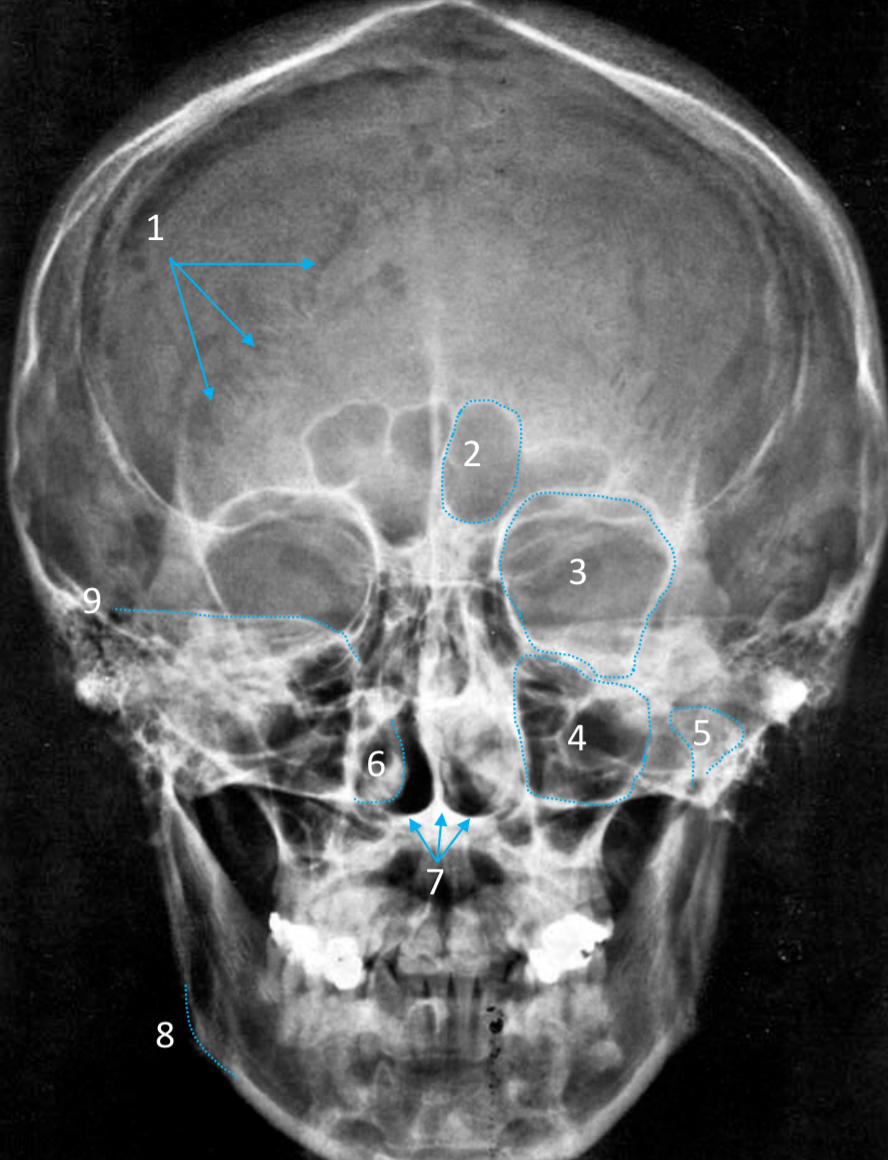
Groove of middle meningeal a.
ID structure
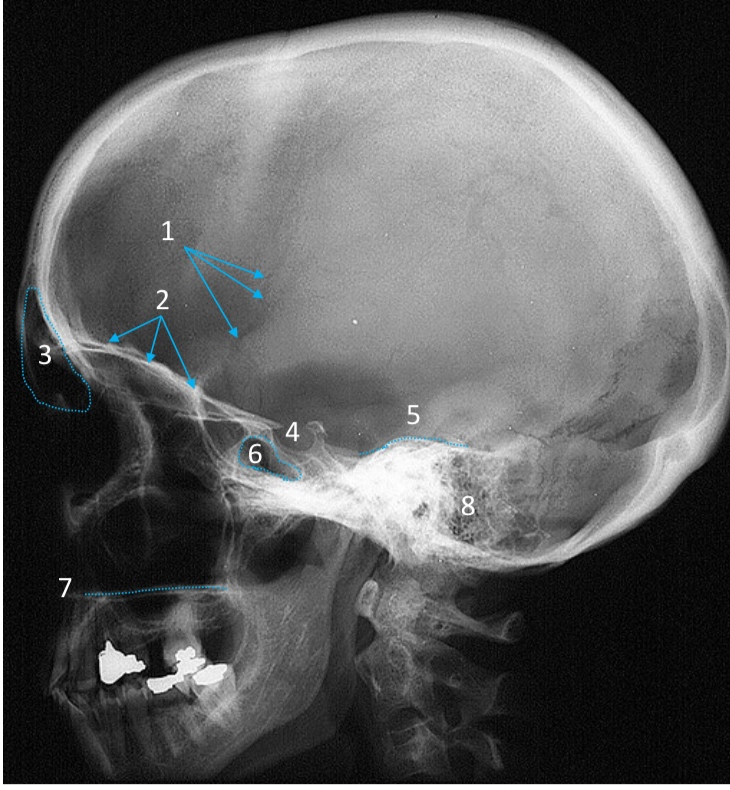
Roof of orbit
ID structure
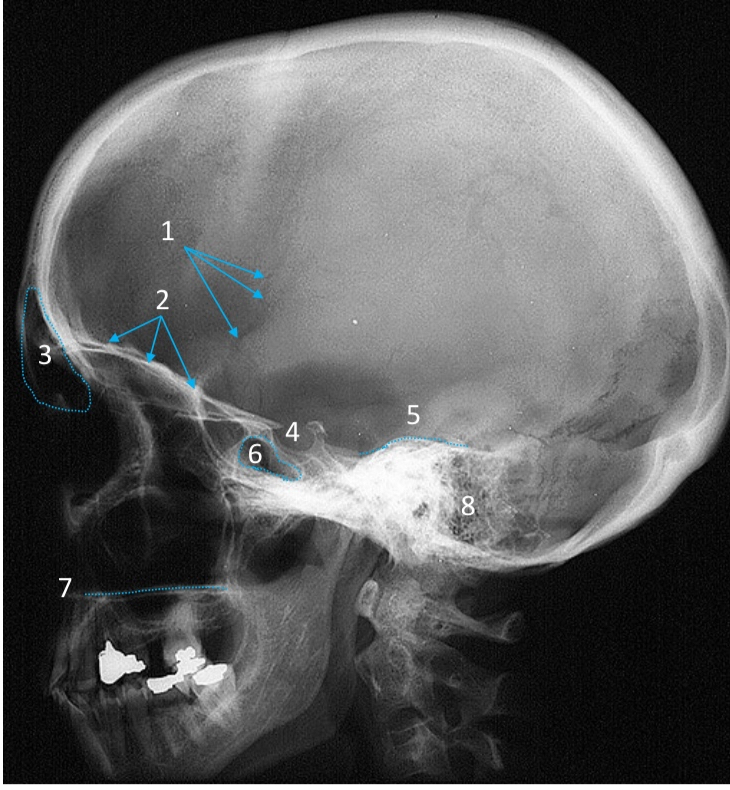
Frontal sinus
ID structure
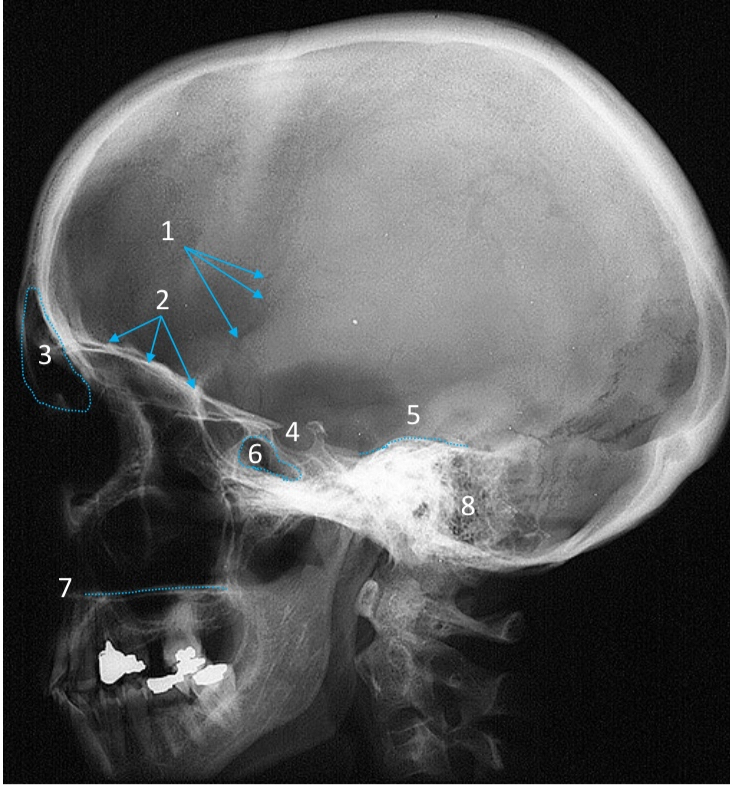
Pituitary fossa
ID structure
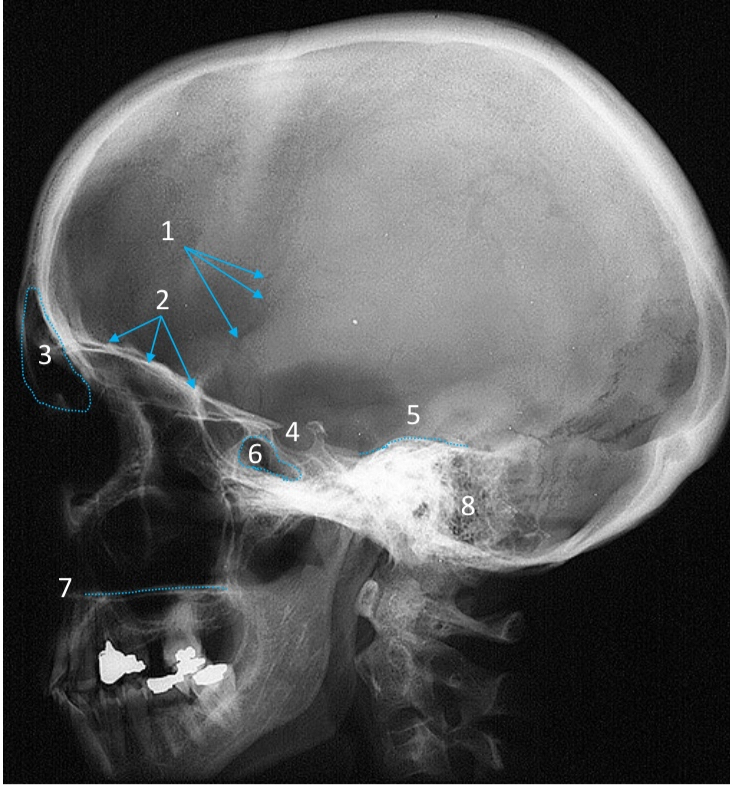
Petrous ridge
ID structure
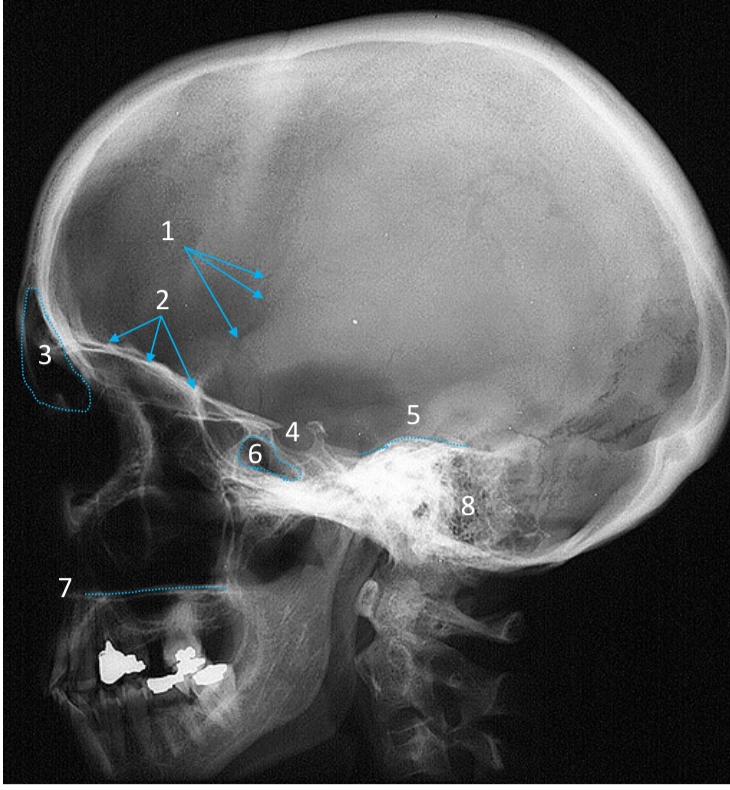
Sphenoid sinus
ID structure
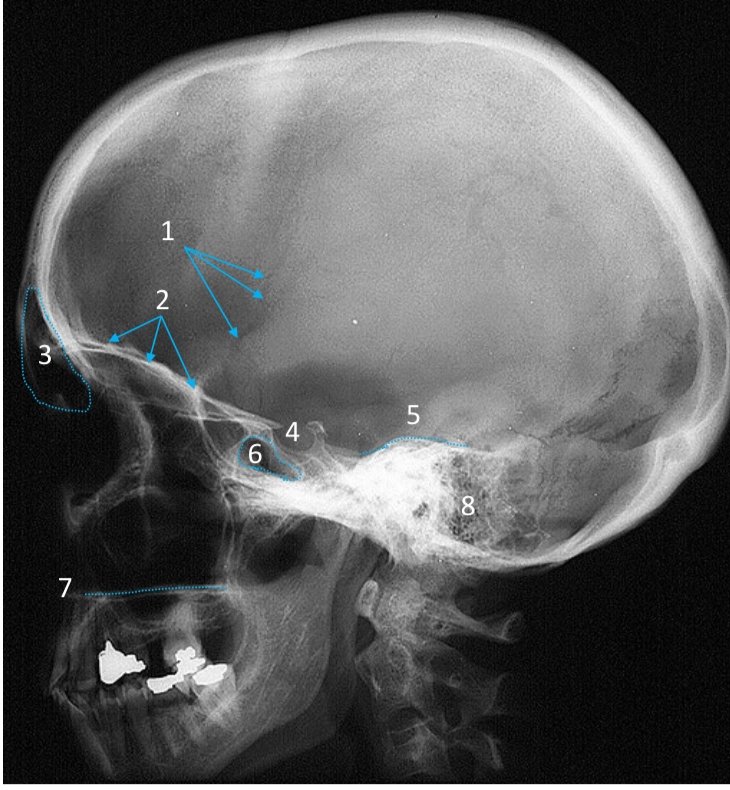
Hard palate
ID structure
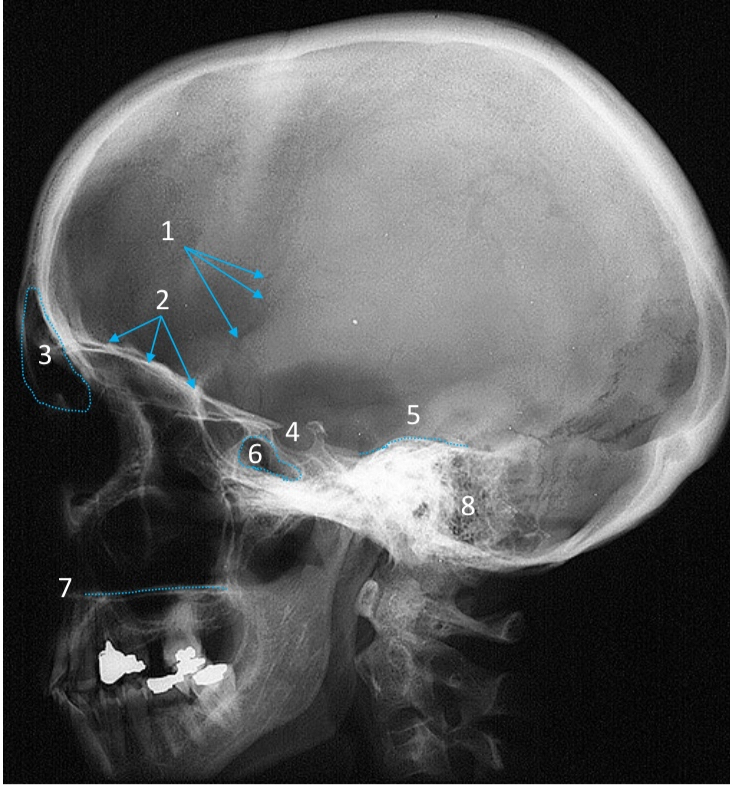
Mastoid air cells
ID structure
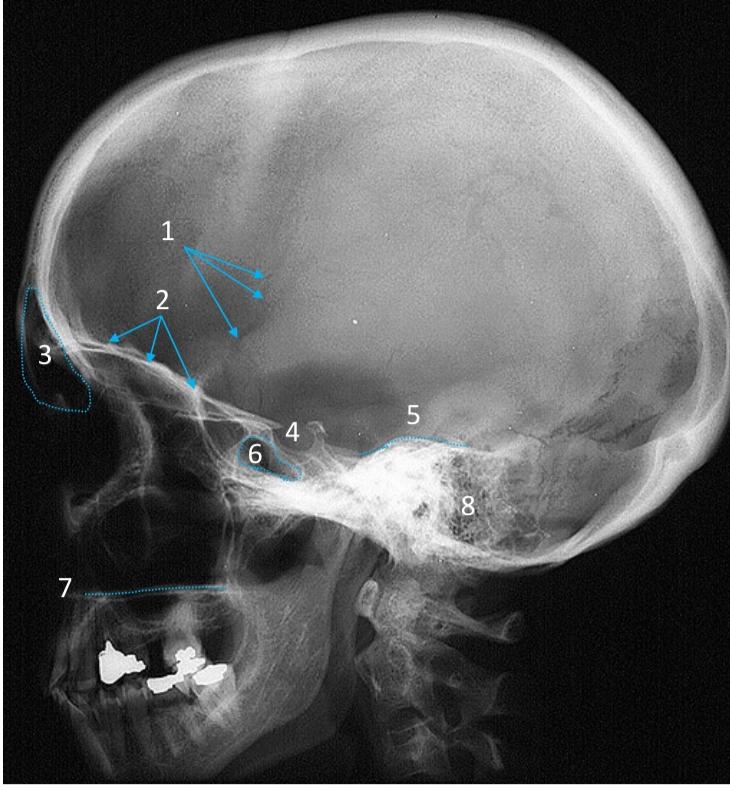
Zygomatic arch
ID structure
Mandibular condyle
ID structure
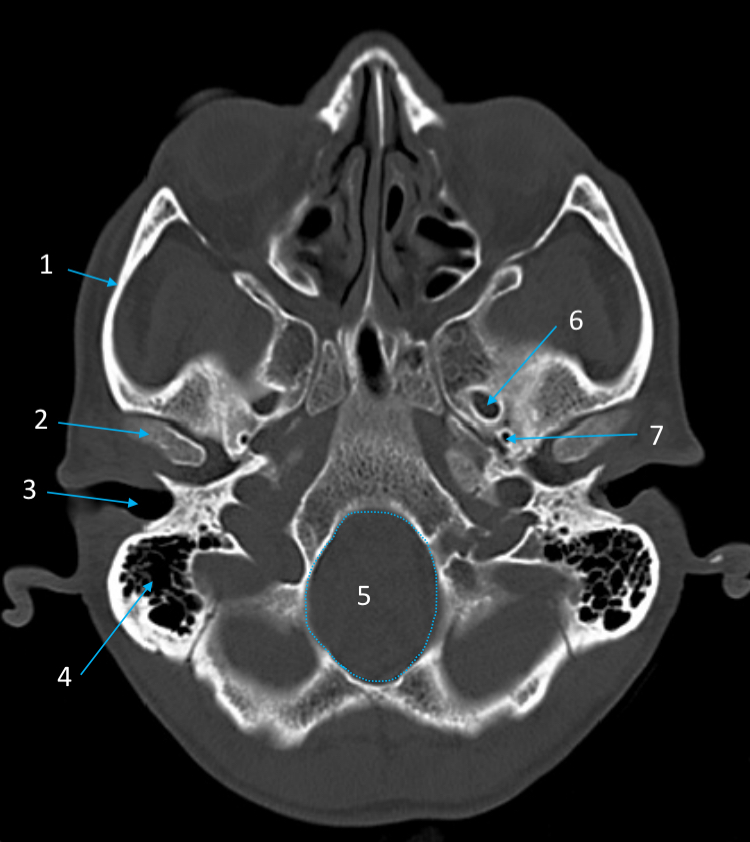
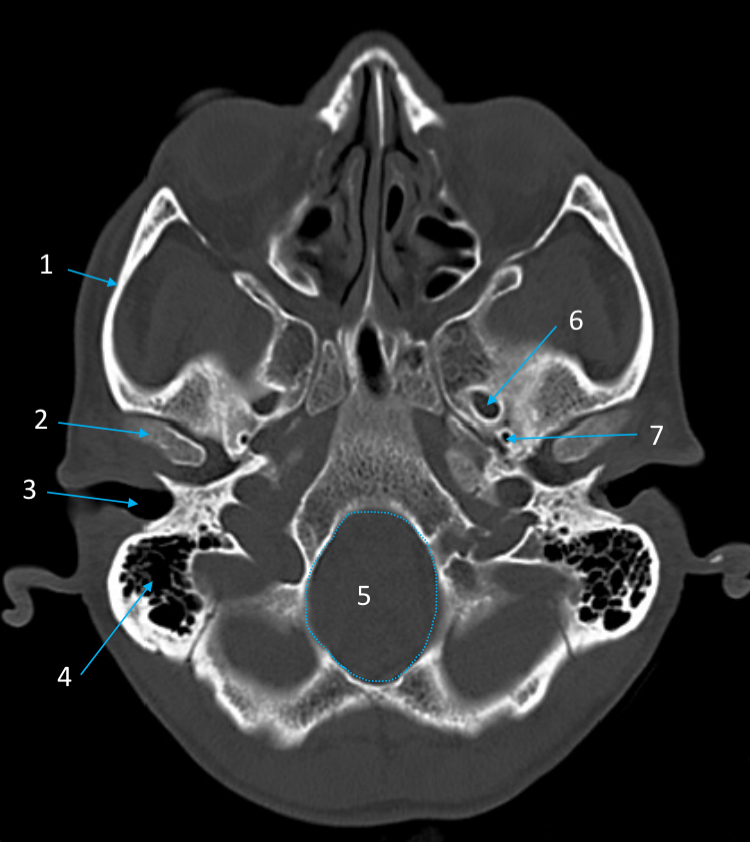
External auditory meatus
ID structure
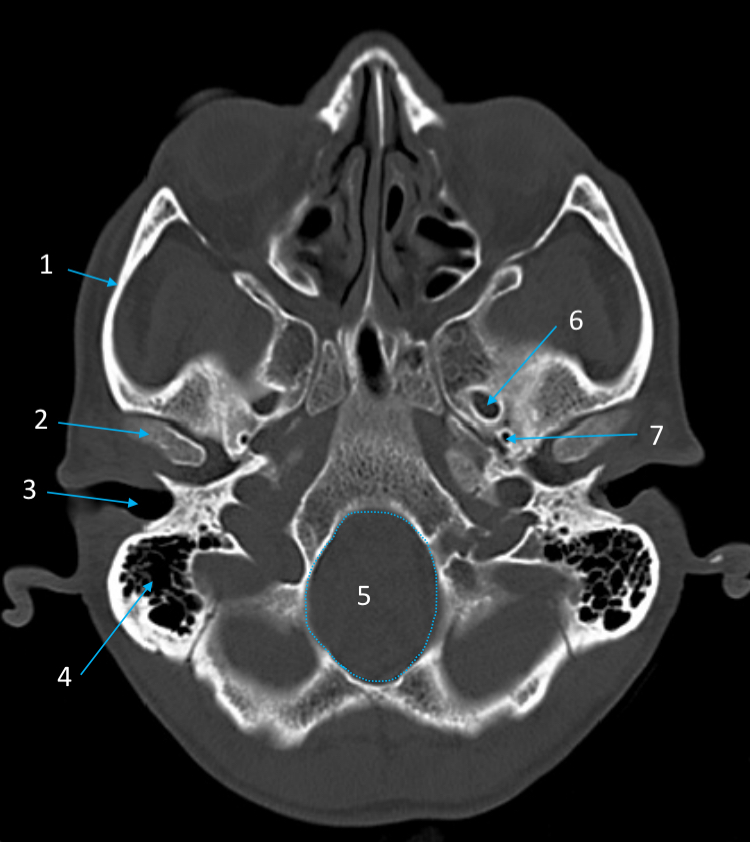
Mastoid air cells
ID structure
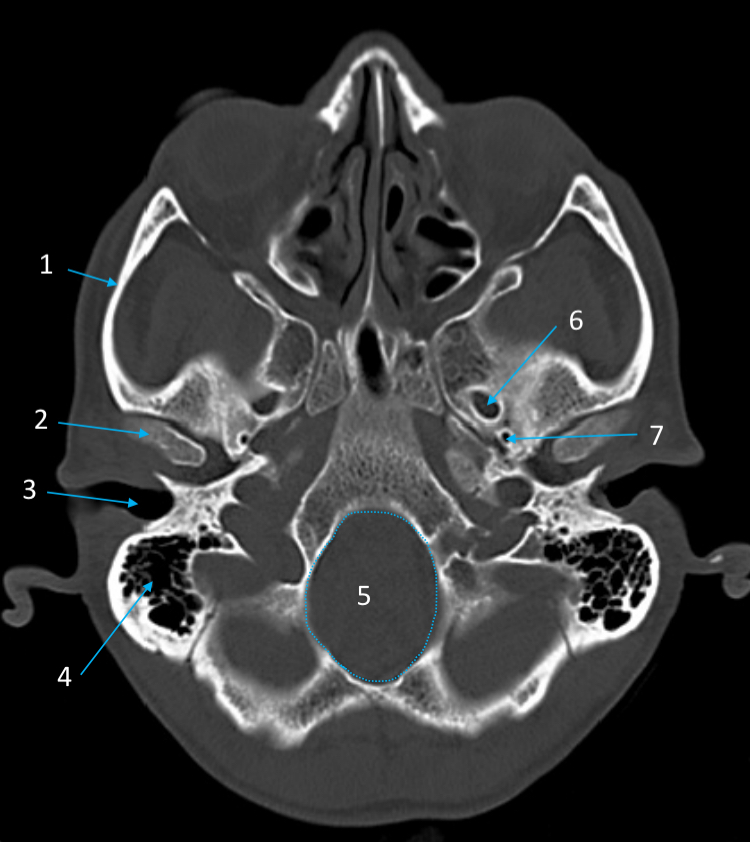
Foramen magnum
ID structure
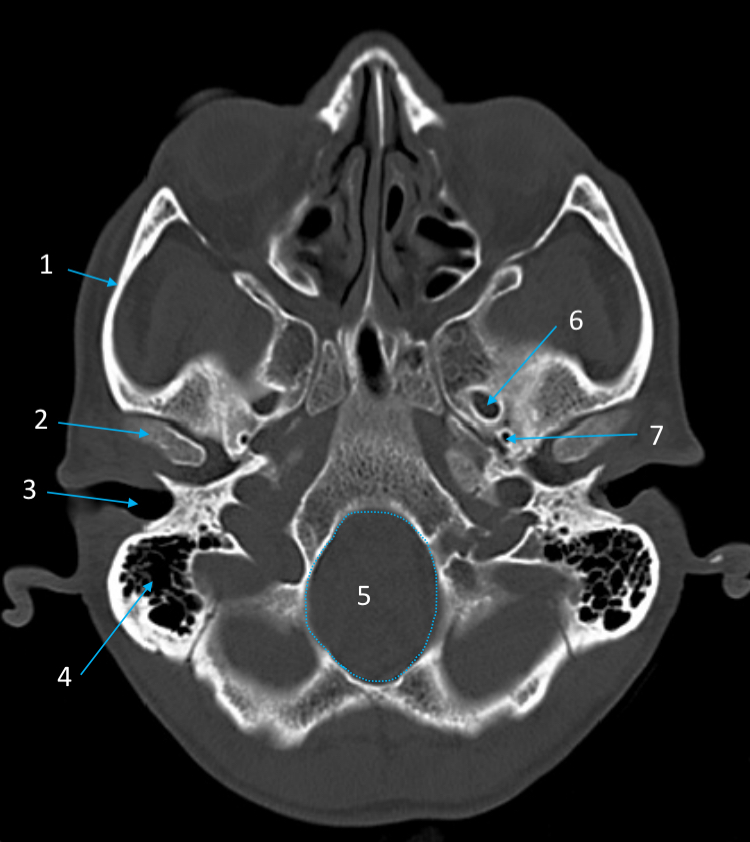
Foramen ovale
ID structure
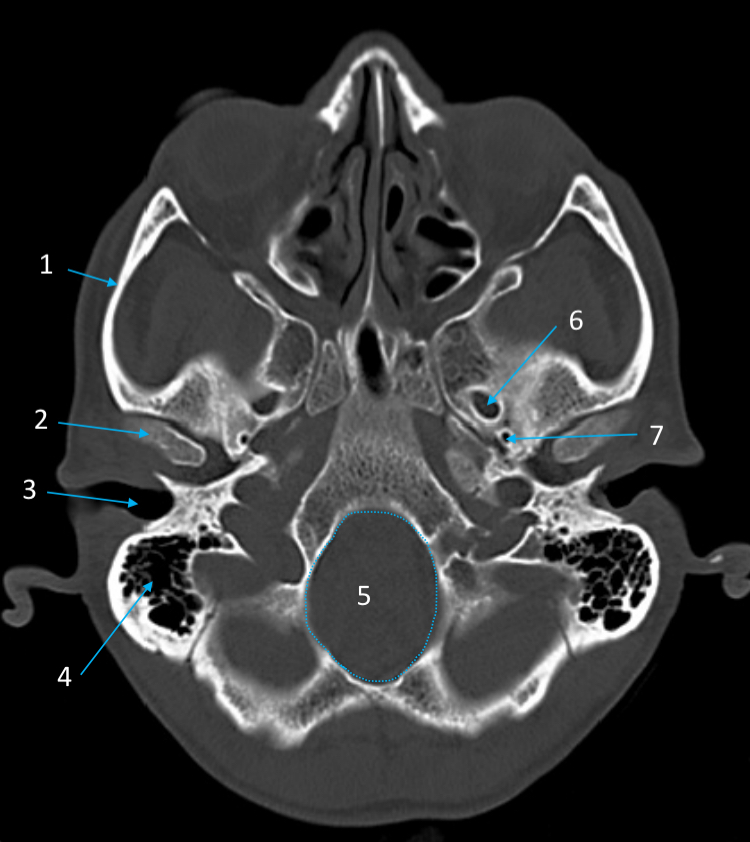
Foramen spinosum
ID structure
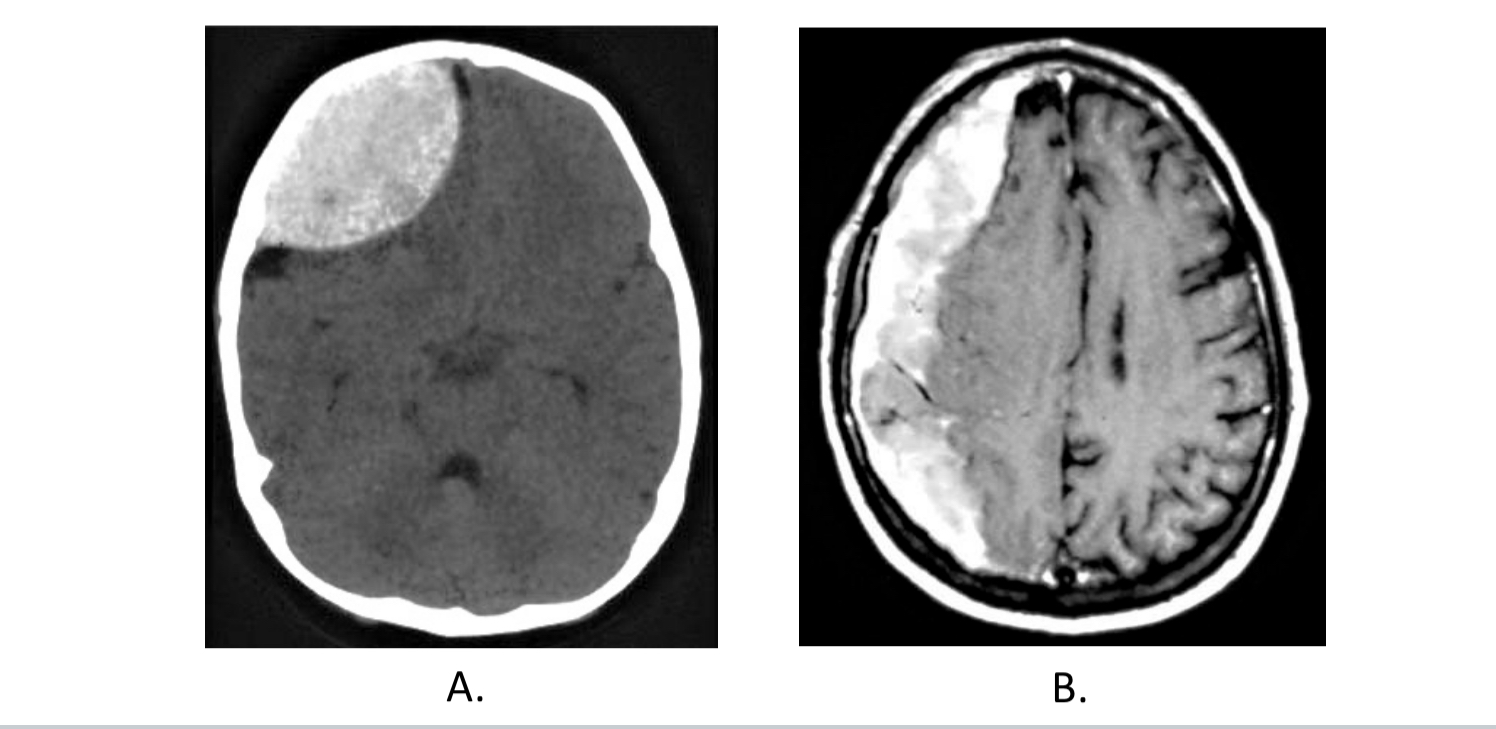
A. Epidural hematoma; B. Subdural hematoma
What are these two conditions?
Cribiform plate
ID structure
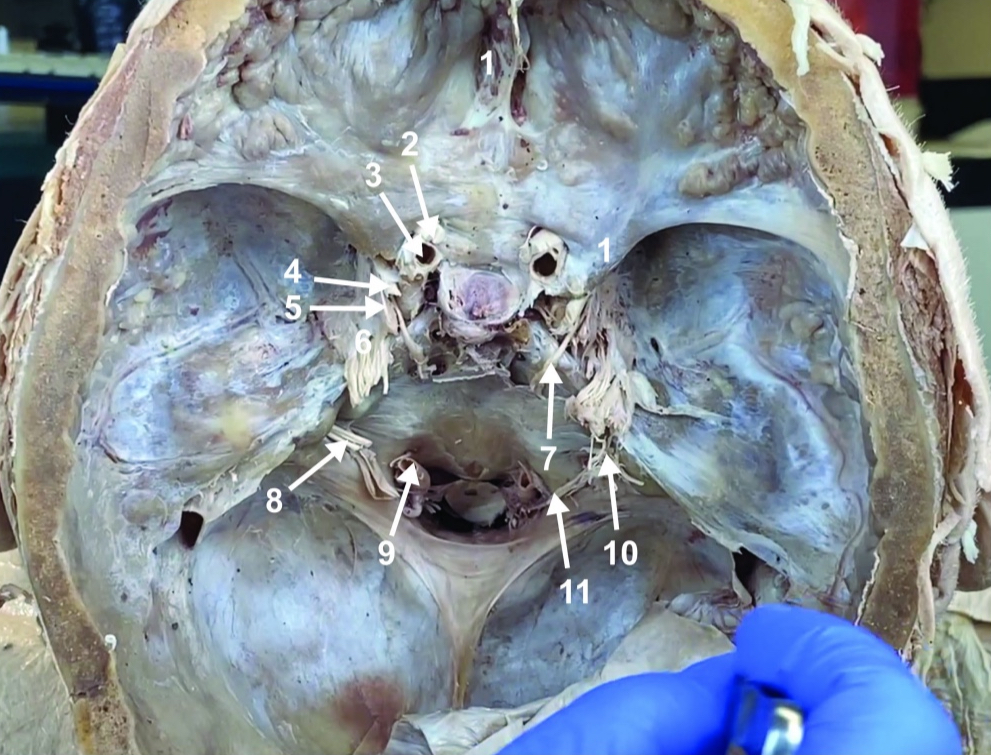
Optic n. (CN II)
ID structure
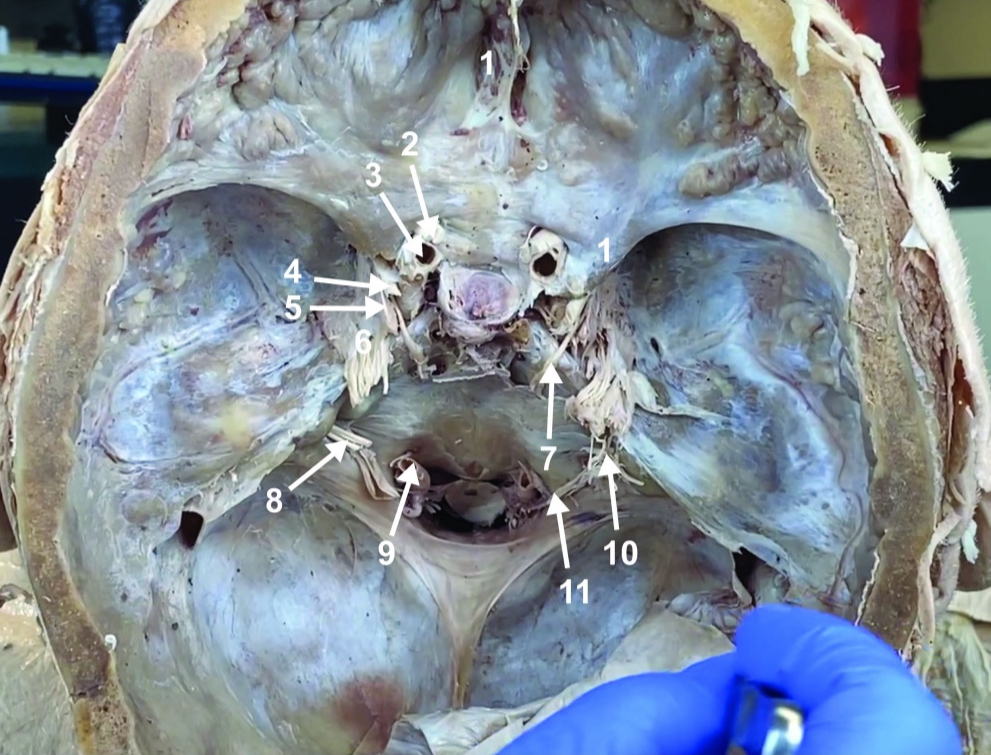
Internal carotid a. (ICA)
ID structure
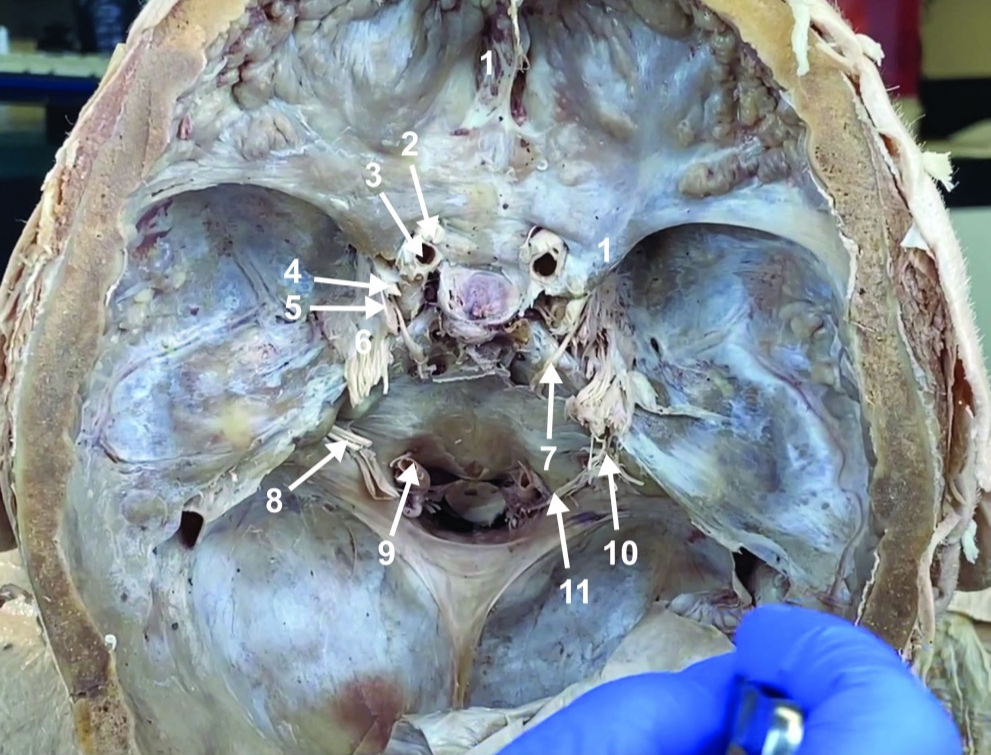
Occulomotor n. (CN III)
ID structure
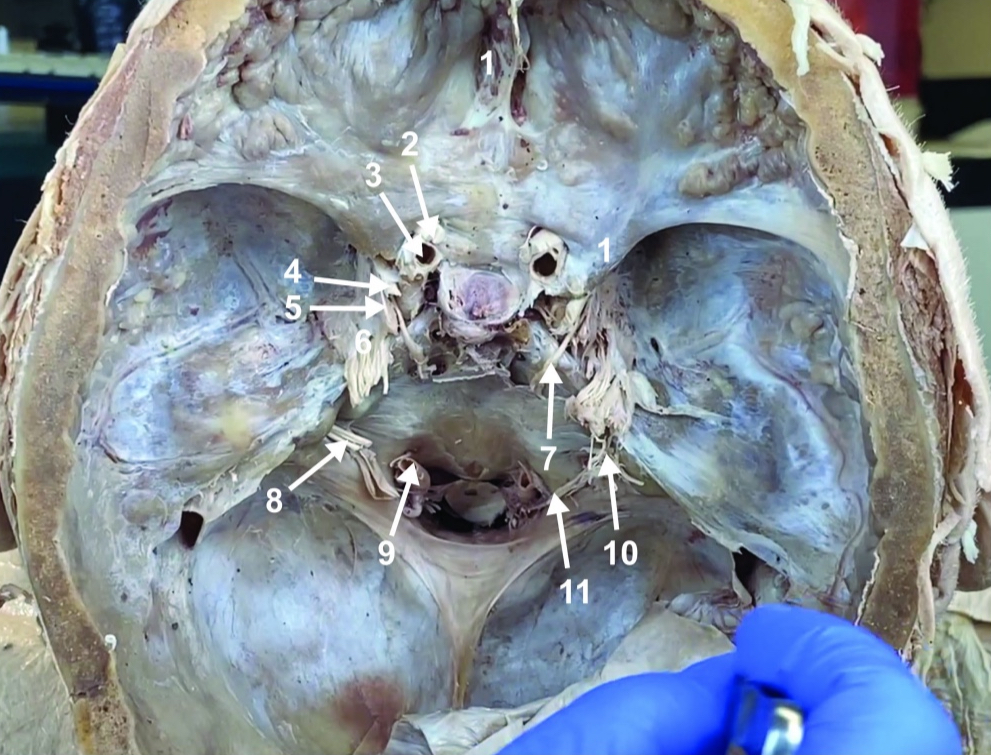
Trochlear n. (CN IV)
ID structure
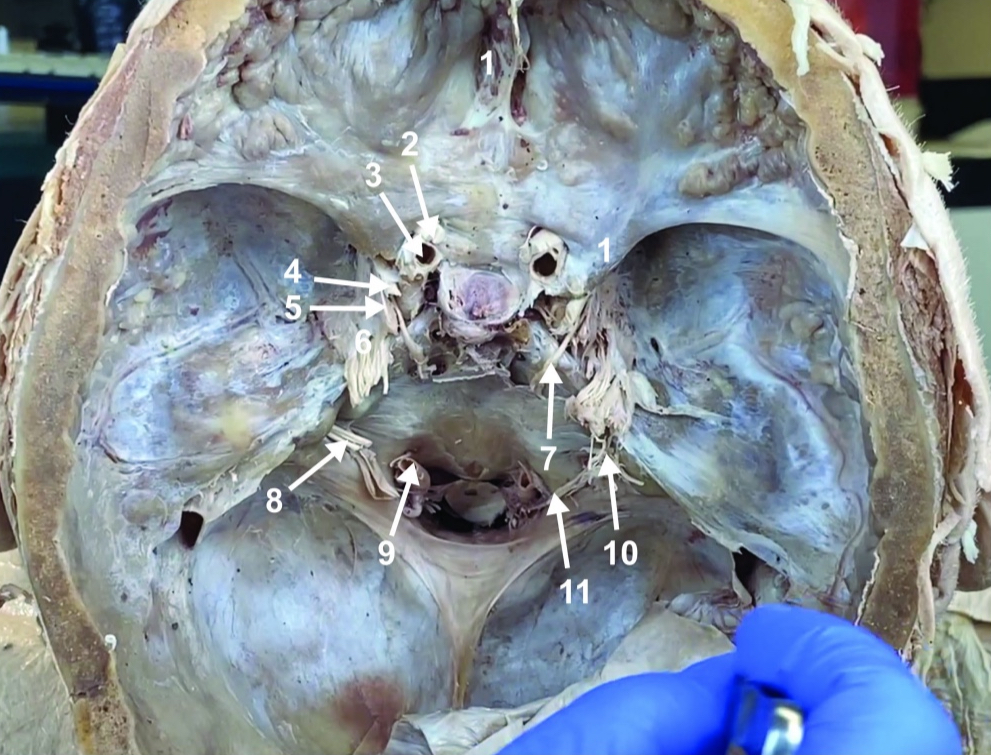
Trigeminal n. (CN V)
ID structure
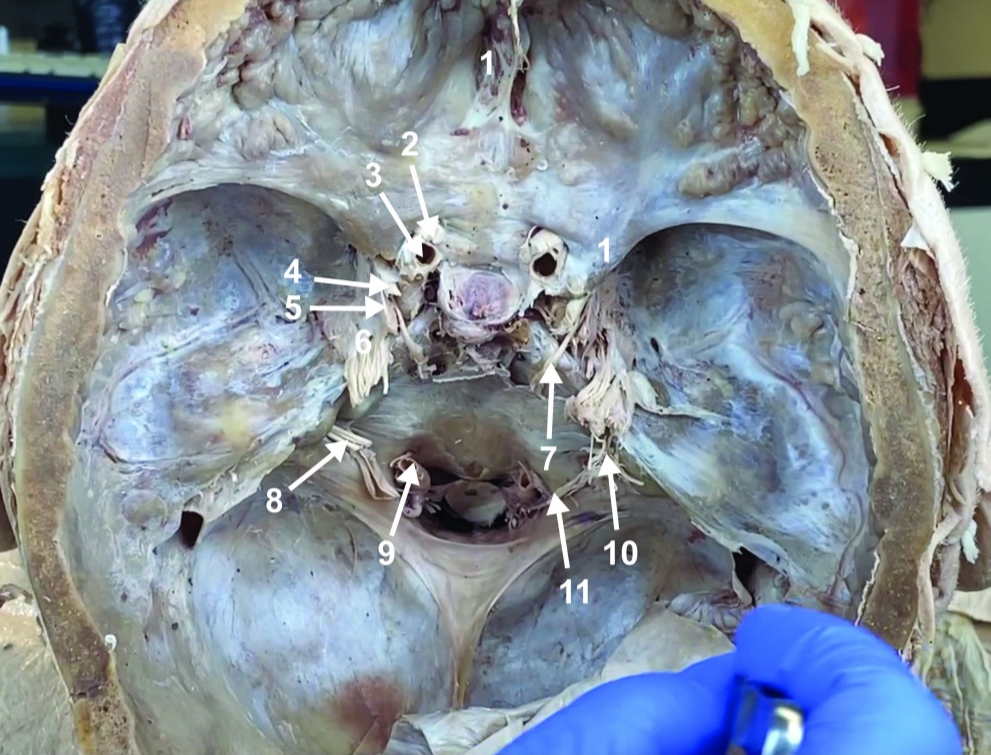
Abducent n. (CN VI)
ID structure
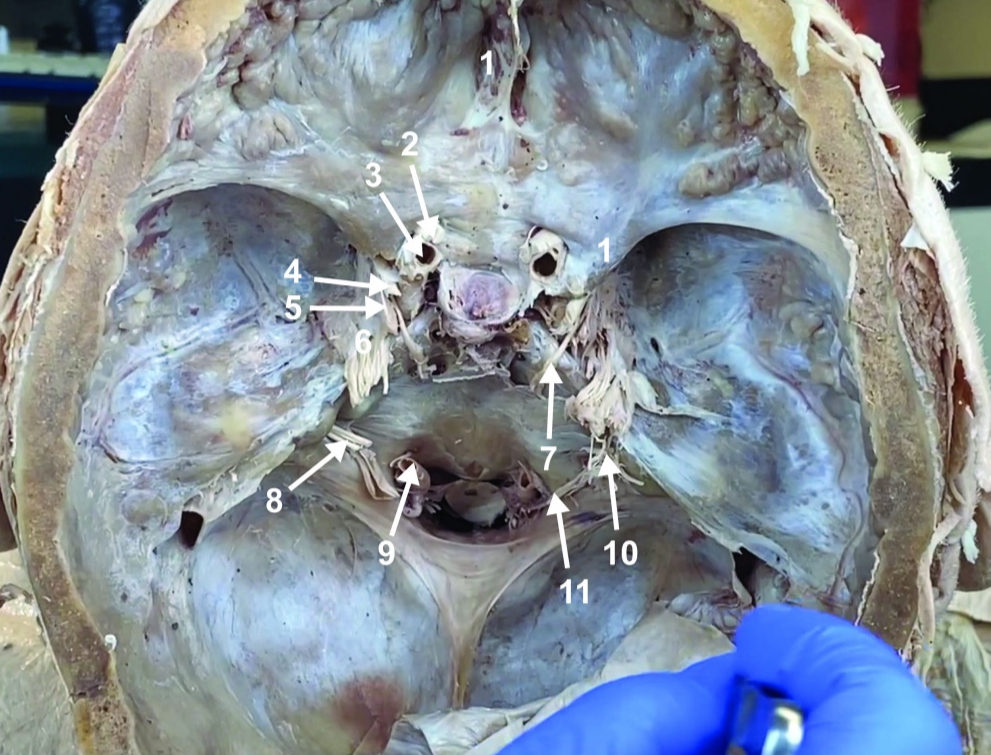
Facial and vestibulocochlear n. (CN VII and VIII)
ID structure
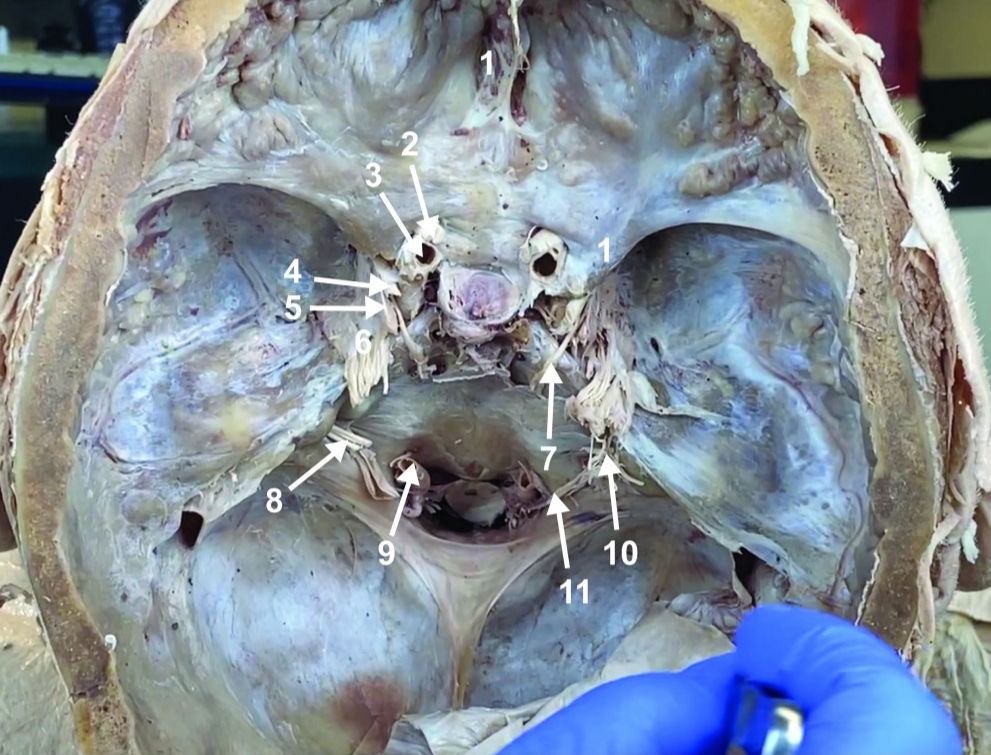
Vertebral a.
ID structure
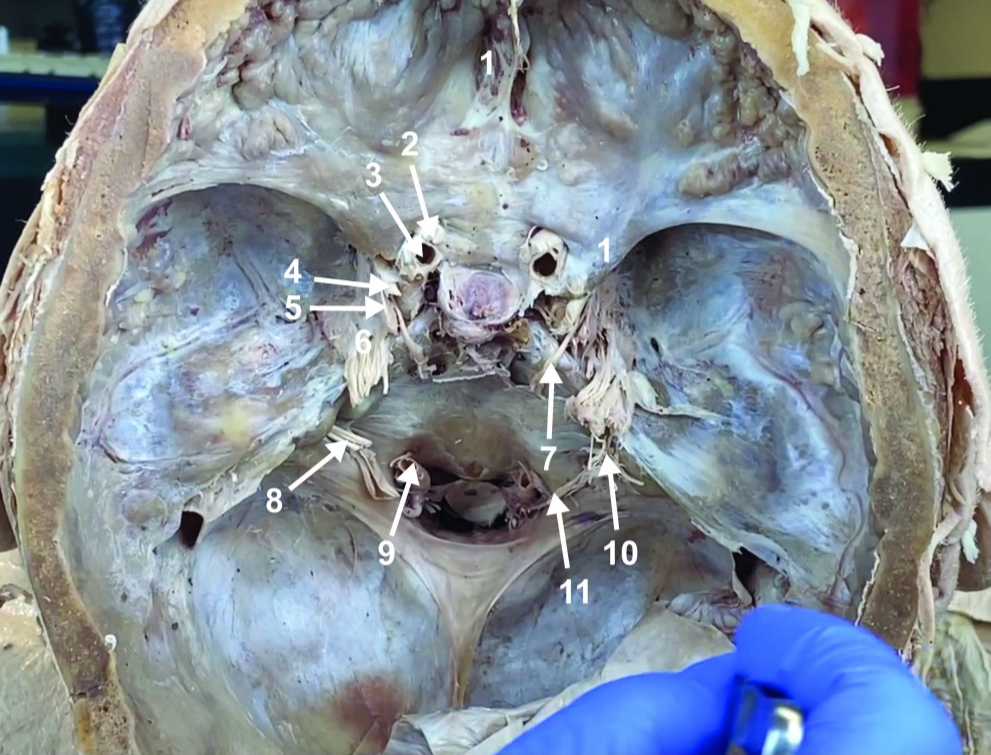
Glossopharyngeal and vagus n. (CN IX and X)
ID structure
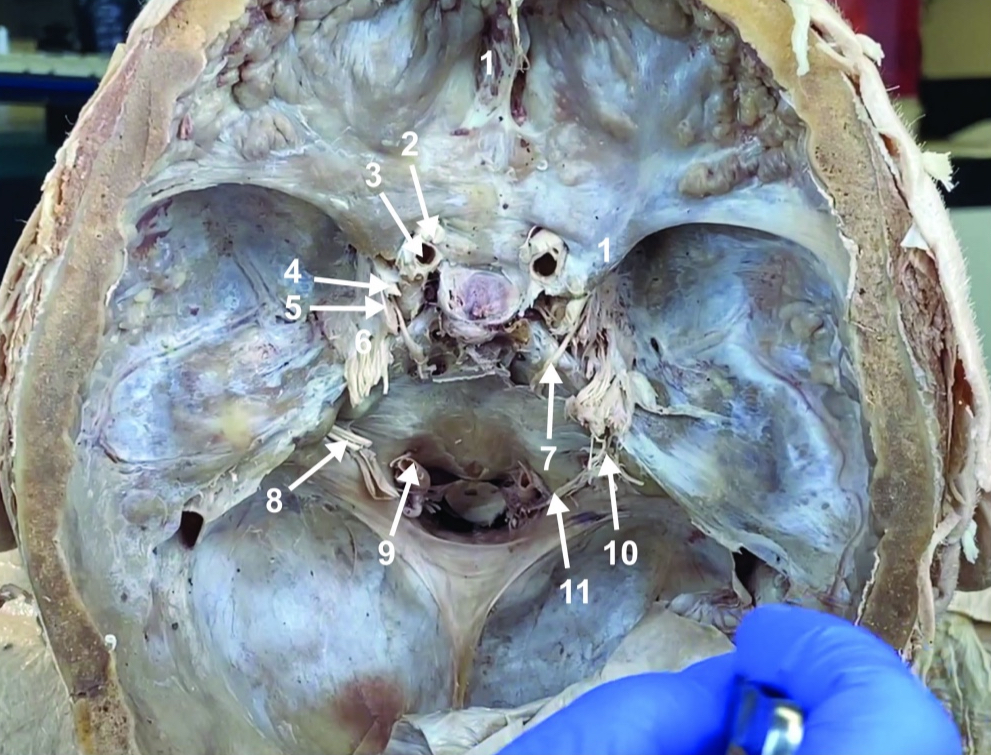
Root of spinal accessory n. (root of CN XI)
ID structure
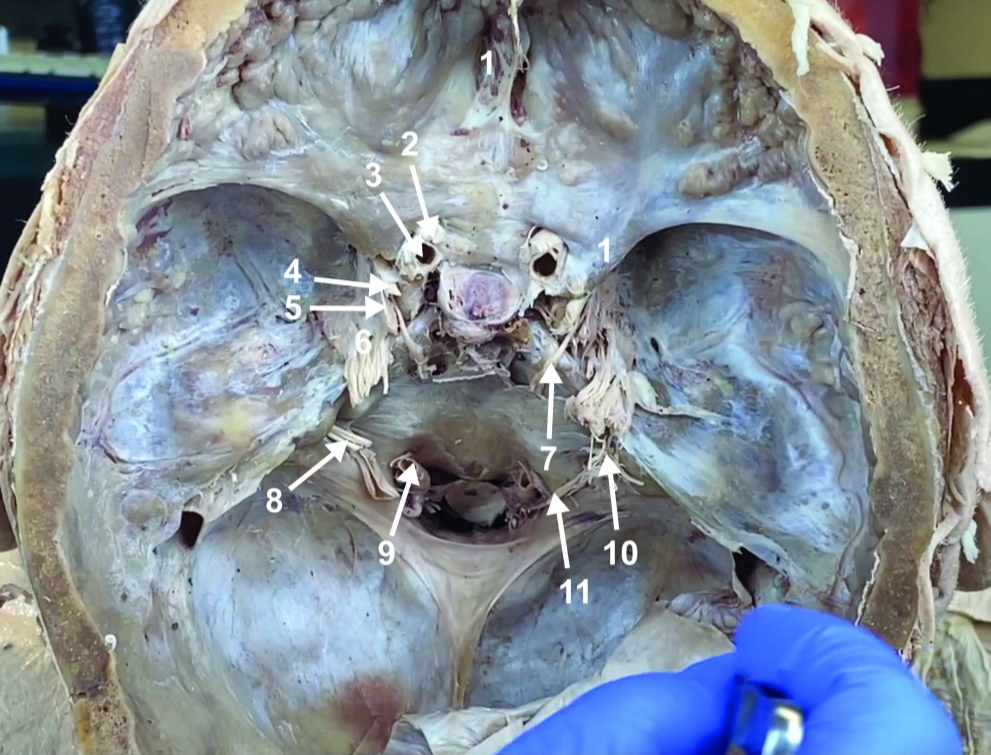
Ophthalmic division of CN V (CN V1)
ID structure
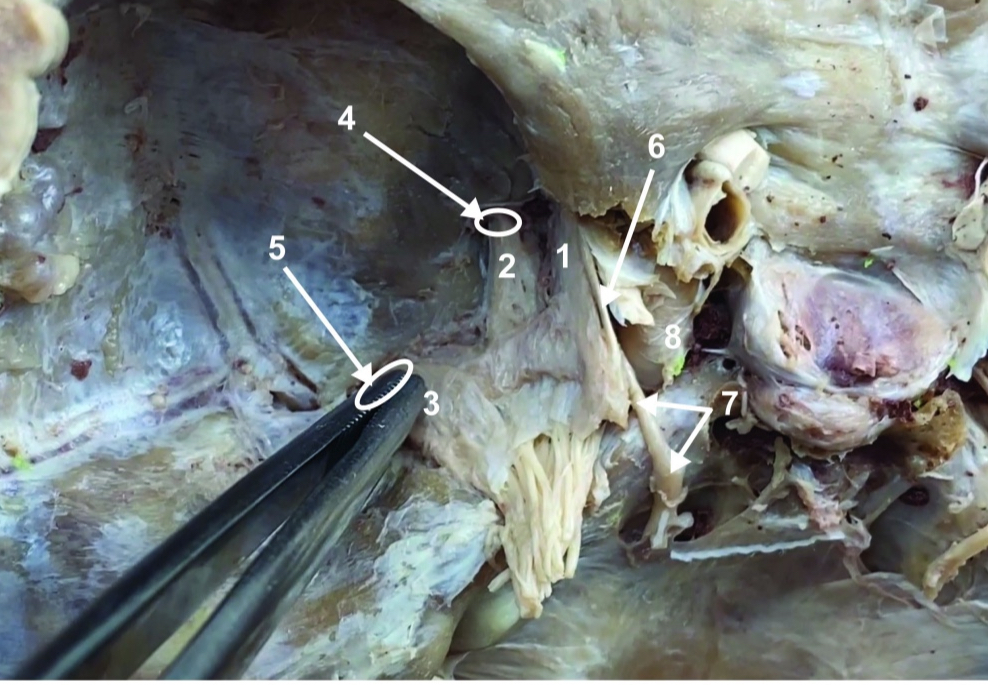
Maxillary division of CN V (CN V2)
ID structure
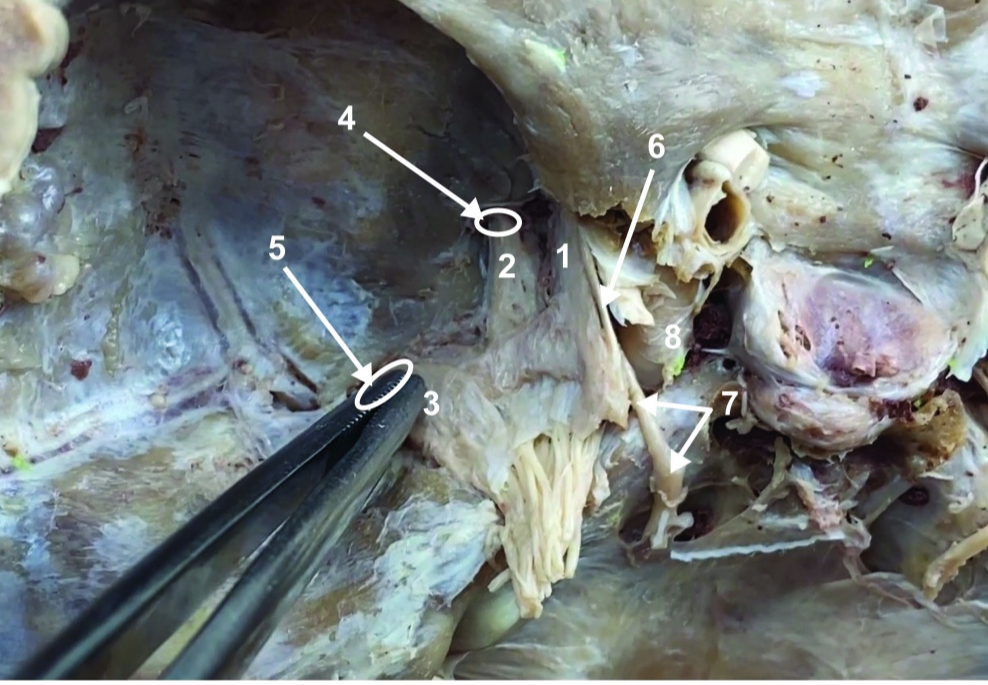
Mandibular division of CN V (CN V3)
ID structure
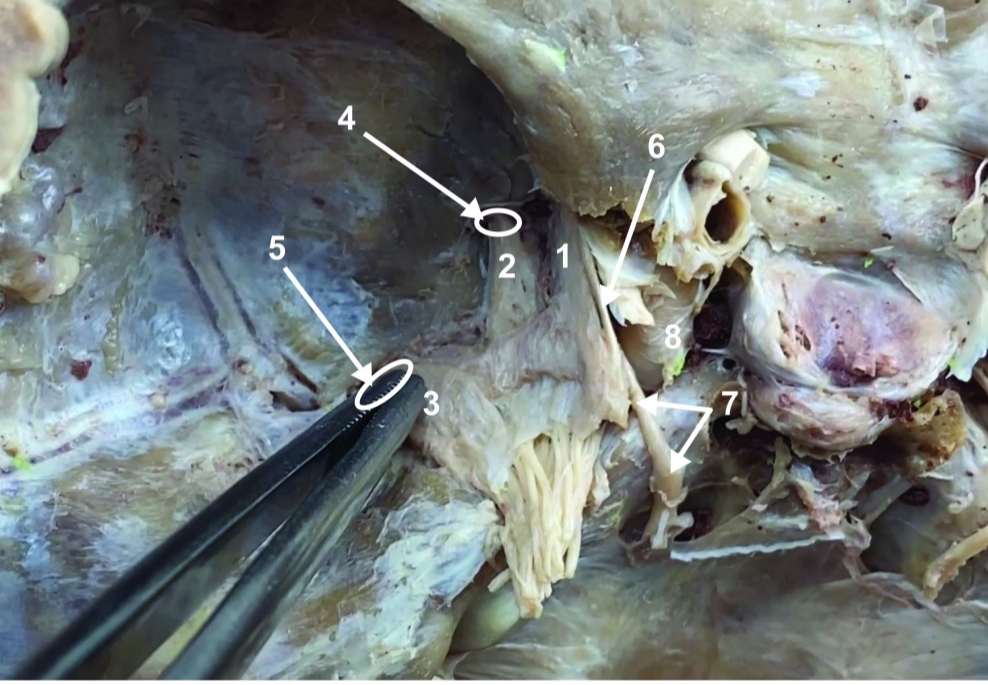
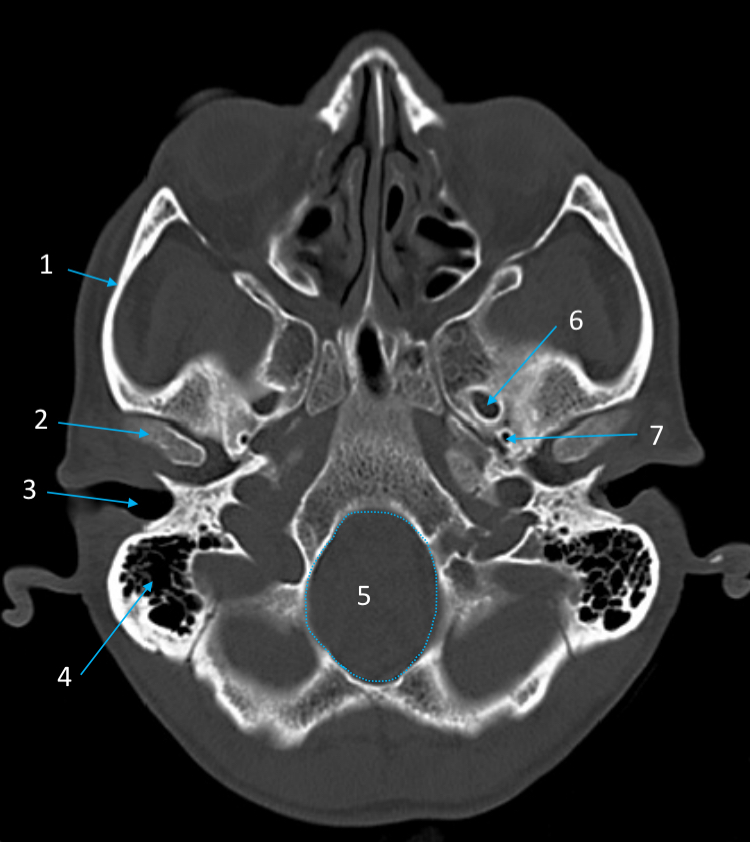
Foramen rotundum
ID structure
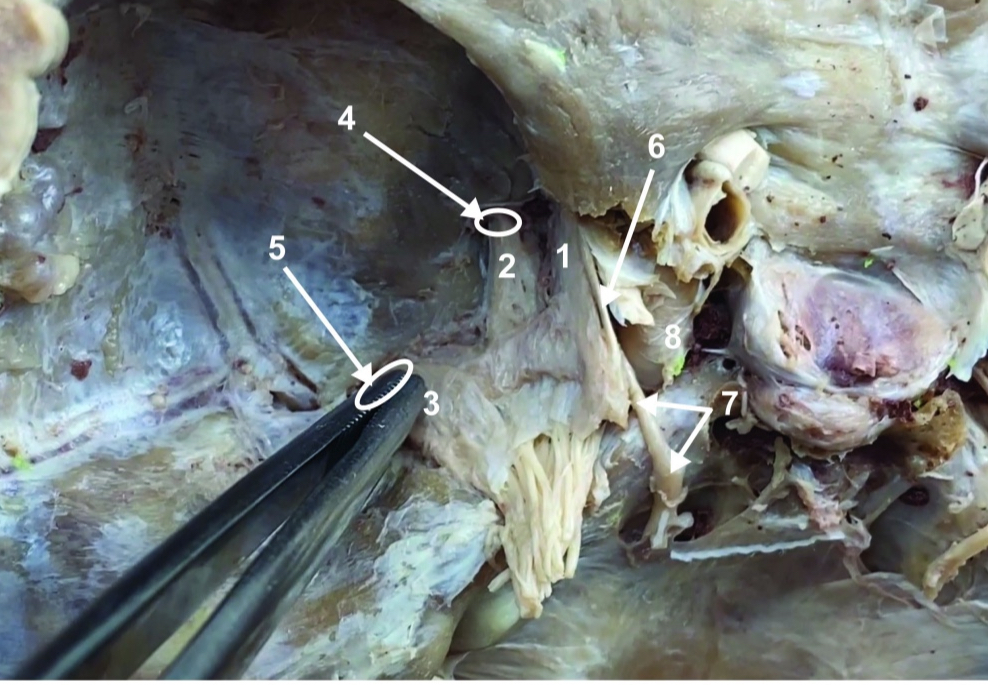
Foramen ovale
ID structure
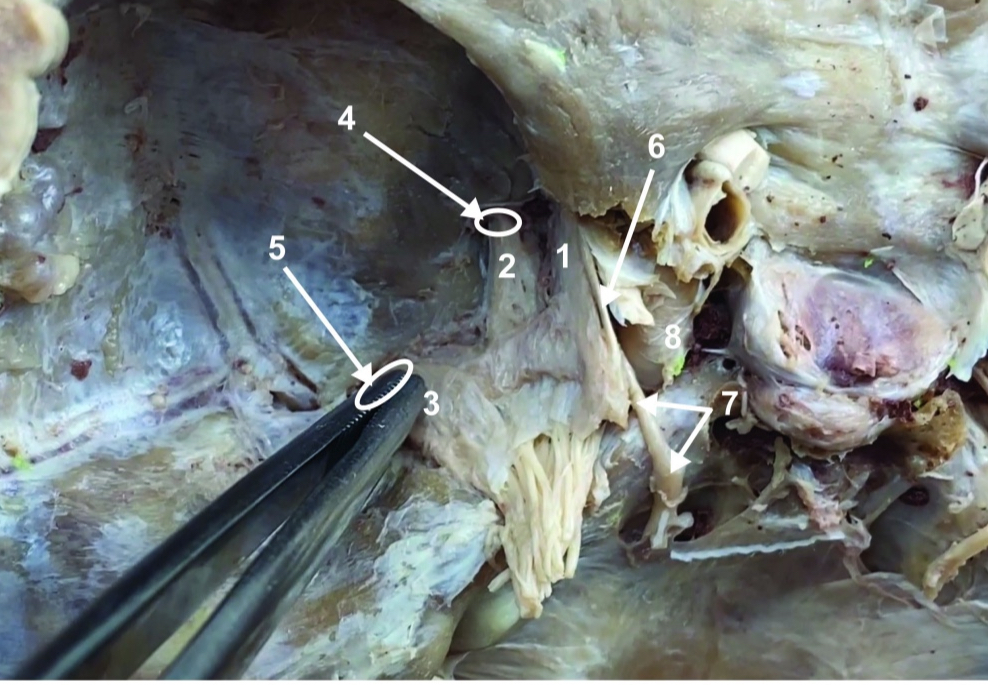
Trochlear n. (CN IV)
ID structure
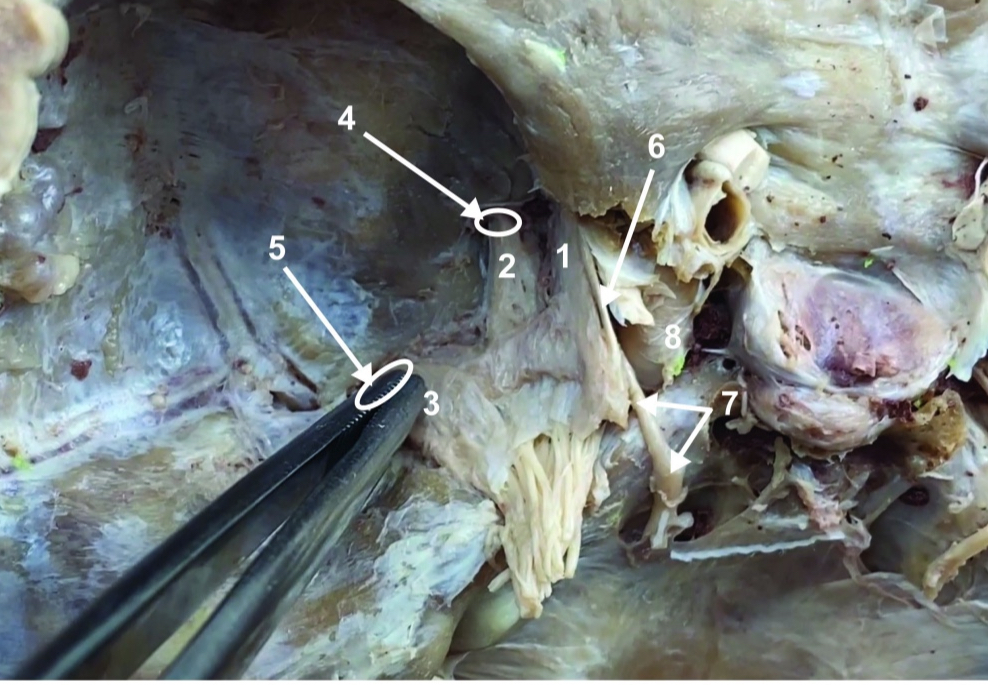
Abducent n. (CN VI)
ID structure