alcohols chapter 15 oxford aqa
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
uses of alcohols
solvents , intermediates in reactions, cosmetics, alcoholic drinks, antifreeze
general formula
CnH2n+1 OH
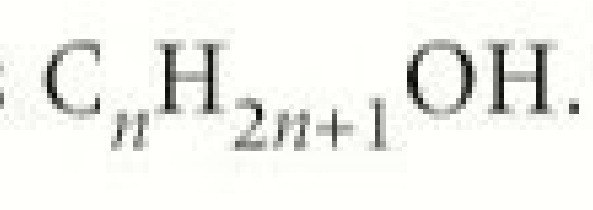
naming alcohols
suffix: alkane + ol
e.g propan-2-ol or methanol
which alchohol is used in antifreeze
ethane,1,2diol
what factors affect reactivity of alcohols
polarity
strength of bonds
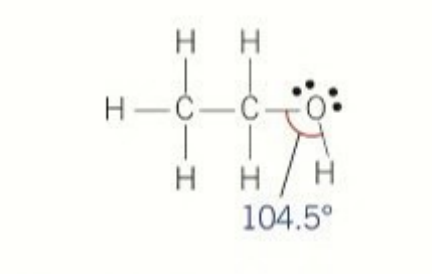
shape of alcohols
tetrahedron because there are 2 lone pairs on O
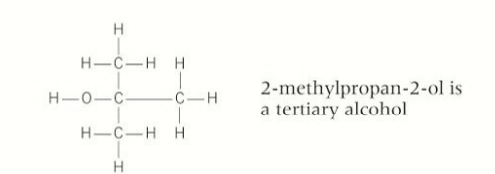
classification of alcohols
primary
secondary
tertiary
carbons in a primary alcohol
1 carbon bonds to the OH- functional group
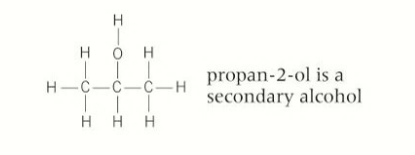
carbons in a secondary alcohol
2 carbons bonded to the OH- functional group
carbons in a tertiary alcohol
3 carbons bonded to the OH- fucntional group
physical properties
hydrogen bonding
higher MP/BP than alkanes
Similar relative molecular mass to alkanes
solubility of alcohols
soluble in water =short chain
insoluble in water = long chain
complete combustion of alcohols
burn completely in the presence of oxygen
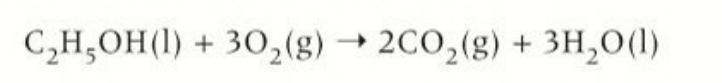
uses of alcohols
fuel
methylated spirits
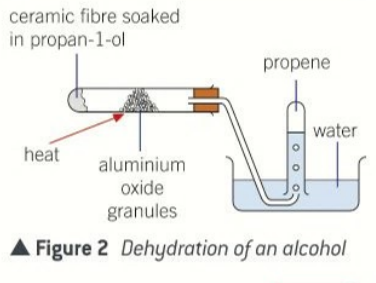
elimination reactions in alcohol
dehydration where a small molecular leaves the alcohol to form water
dehydration step
forming an alkene
reagents used for dehydration
excess concentration sulfuric acid
alminium oxide as a catalyst
condition for dehydration of alcohol
600 kelvins
mechanism for dehydration
oxygen lone pair attack h+ proton
oxygen cation gains an electron
forming H2O and an alkene
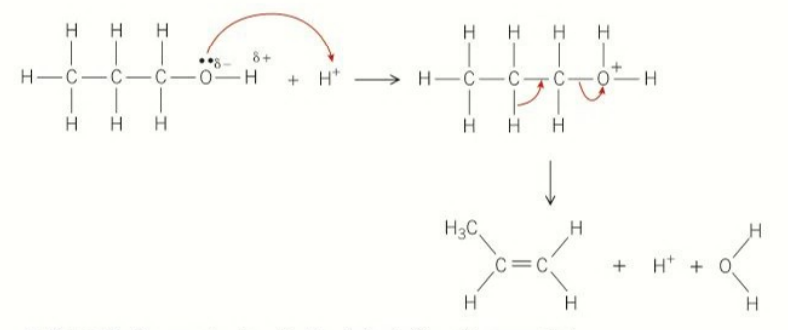
isomeric alkenes
Dehydration of longer chain alcohols can produce a mixture of alkenes which can exhibit E / Z isomerism with a number of different products
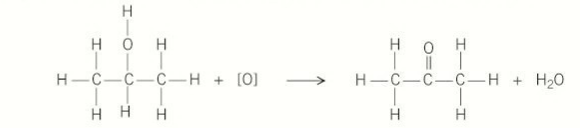
products formed when primary alcohols are oxidised
aldehydes
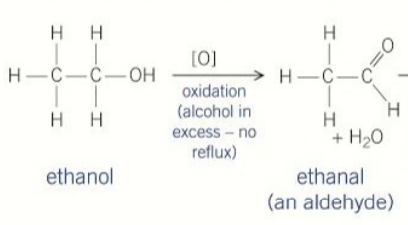
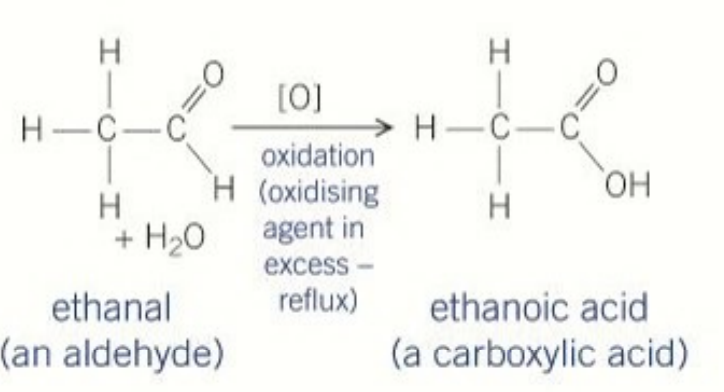
second oxidation of primary alcohols(aldehydes)
carboxylic acid
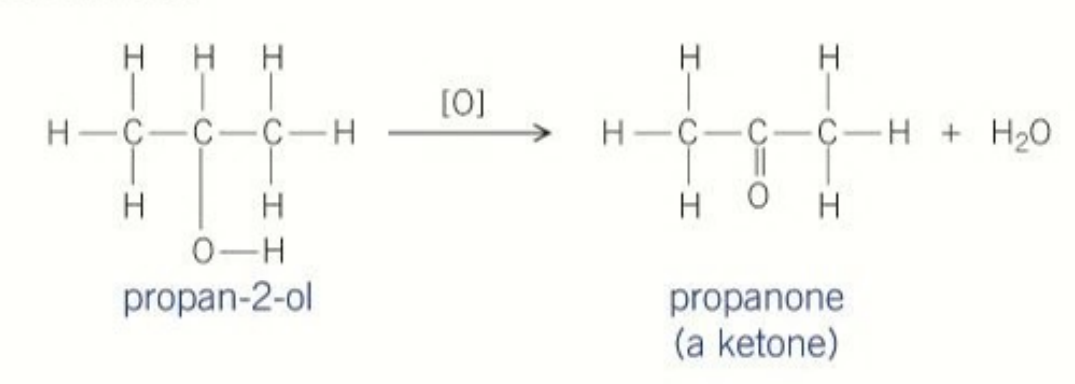
oxidation of secondary alcohol products
ketones
oxidation of tertiary alcohols
no product formed because they are not easily oxidised
reagents used in the first oxidation of ethanol
concentrated sulfuric acid potassium dichromate
role of sulfuric acid
proton donor/oxidising agent
why are anti bumping granules are added
gentle boiling
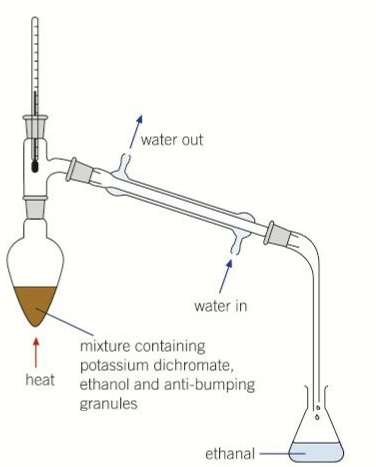
why is a pear shaped flask used
even distribution of heat
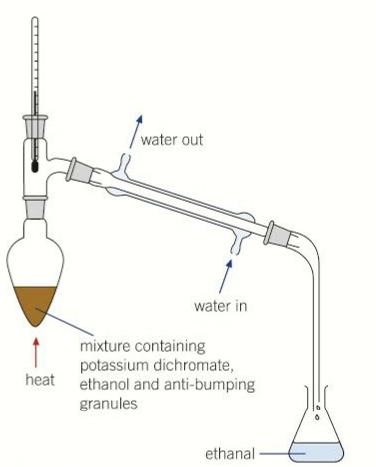
what happens during distillation of alcohols
ethanal evaporates and gets condensed in the condenser and is collected in a flask that gets cooled in ice
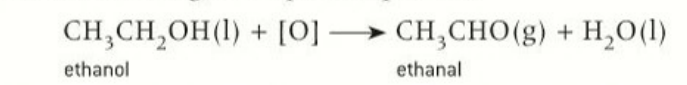
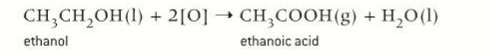
product formed when oxidising ethanol in reflux
carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid)
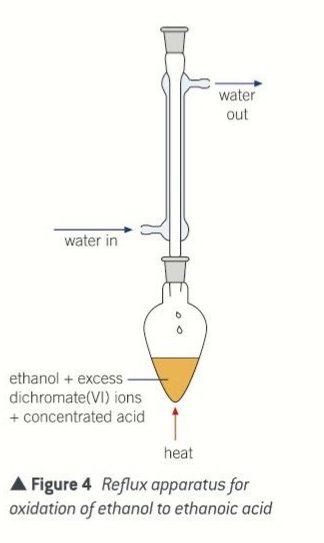
reflux
the ethanol vapour condenses back into the same flask until fully oxidised
reagents used for reflux
excess sulfurix acid and excess potassium dichromate
conditions for reflux
291k or 118 degrees celsius
symbol equation for reflux of ethanol
(O) is the oxidising agent
ethanol + 2O → ethanoic acid + water
apparatus used for reflux
pear shaped flask
condenser
tubes
blue flame bunsen burner
product formed when oxidising secondary alcohols
ketones
similarities of aldehydes and ketones
carbonyl group or C=O bond
aldehydes
at the end of the hydrocarbon chain
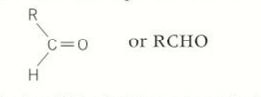
ketones
in the middle of the hydrocarbon chain
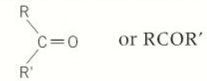
suffix for ketone
-one
suffixe for aldehydes
-al
test for aldehydes
gentle oxidation until an acid is formed
test for ketones result when oxidised
no visible change
silver mirror test
positive: colourless to silver
negative: no visible change in colour
what does the tollens silver mirror test for
aldehydes
colour change of fehling’s test
positive: blue → brick red of CuO (aldehyde present)
negative: remains blue (ketone present)
what does fehling’s test contain
blue Cu+ ions

role of the copper ions
gentle oxidising agent