Glycopeptides MedChem
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Where are enterococci present?
Ubiquitous in nature - everywhere and widely distributed, in GI and GU tract as normal flora
What enterococci are most prominent in humans?
E. Faecium and E. Faecalis
What are E. Faecium and E. Faecalis mostly prevalent in?
Nosocomial pathogens - pathogens that cause infections in a healthcare setting and associated with UTI, wound infection and bacteremia
What antibiotics cannot be used for enterococci?
B-lactams - less susceptible
What risk can cephalosporins have on infection?
Increase risk for enterococcal infection
What can inappropriate use of B-lactams and cephalosporins lead to when enterococci present?
Abx kills healthy flora and enterococci will replace this
How do enterococci acquire high level resistance?
Horizontal genetic transfer - PBPs mutated
What are some resistance mechanisms of enterococci?
Reduced PBP binding affinity, reduced peptide binding affinity, efflux pumps, low uptake of aminoglycosides
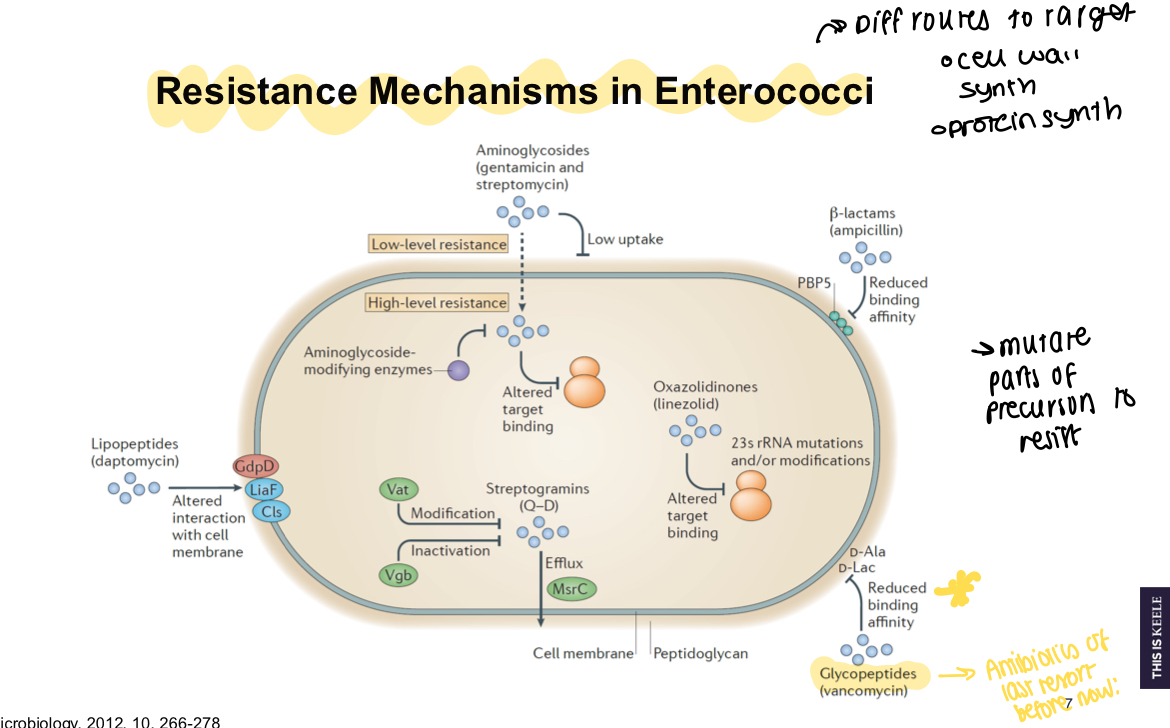
What 2 key things is glycopeptide resistance linked to for glycopeptide resistant enterococci?
Thickened peptidoglycan layer in MRSA and vanA gene cluster
Why are resistant infections such as glycopeptide resistant enterococci difficult to treat?
Many are multi-drug resistance e.g., VRE, gram positive bacteria also transfer resistance
What has isolated glycopeptide enterococci resistance been linked to the veterinary use of?
Avoparcin
What is avoparcin?
Used as growth promoters in veterinary use and can increase livestock resistance
What antibiotic is avoparcin similar to?
Vancomycin
What is the general trend with increasing vancomycin use?
Used more for MRSA but also increases resistance
What region of vancomycin is key for activity?
Peptide region
Aside from the peptide region, what is the function of the rest of the vancomycin molecule?
Helps to fold the drug into the right conformation for activity
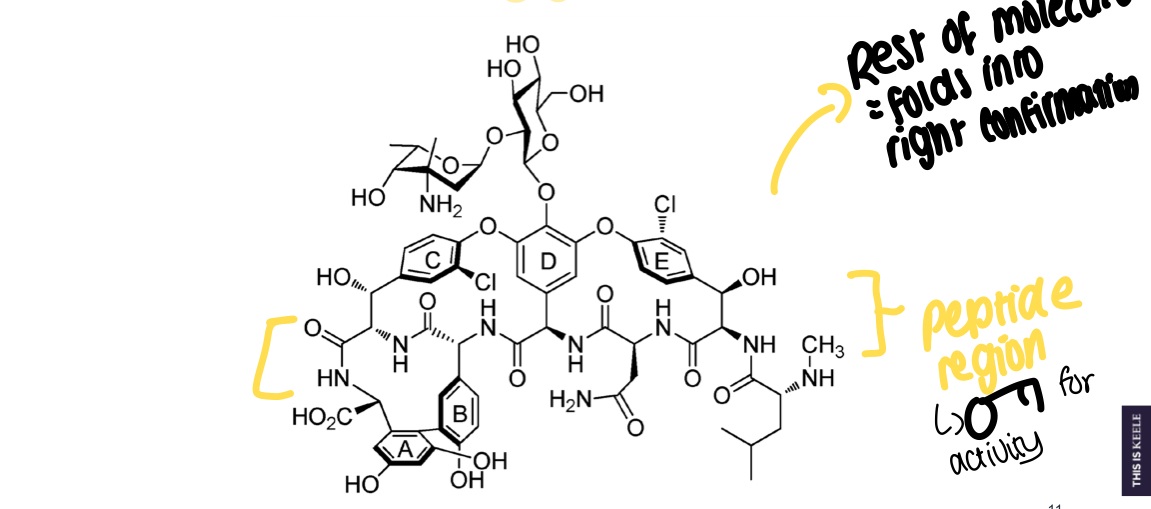
What family of Abx is vancomycin apart of?
Glycopeptides
How does vancomycin work?
Binds to D-Ala-D-Ala in peptidoglycan precursors and prevents transglycosylation and transpeptidation
What bacteria is vancomycin active against?
ONLY gram positive
Why is vancomycin inactive against gram negative bacteria?
Too big and polar to cross gram negatives outer membrane
What is vancomycin primarily used for?
MDR infections, C. Diff infections
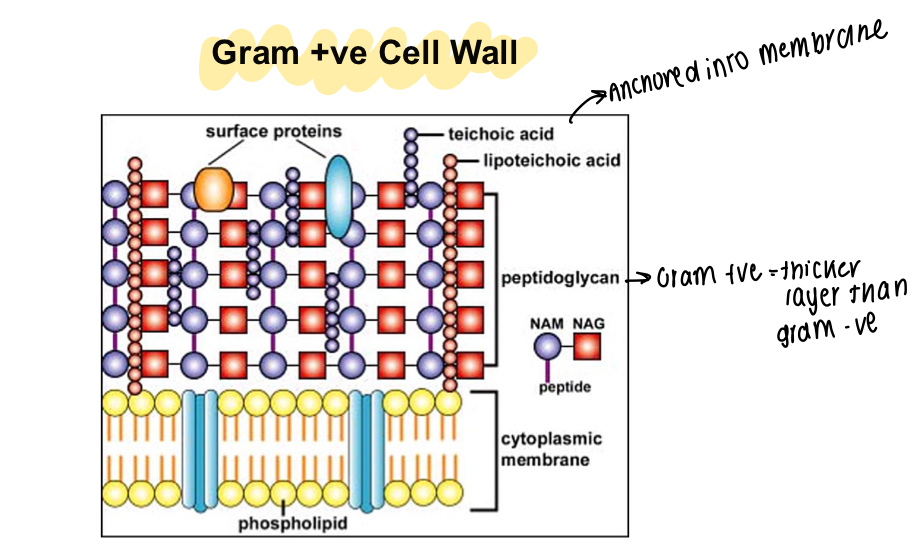
What are the characteristics of a gram positive cell wall?
Acids anchored into the membrane, thick peptidoglycan cell wall
Why do gram positive bacteria have a thicker peptidoglycan cell wall?
Crosslink consists of 5 glycine residues between L-Lysine and D-alanine, also more flexible
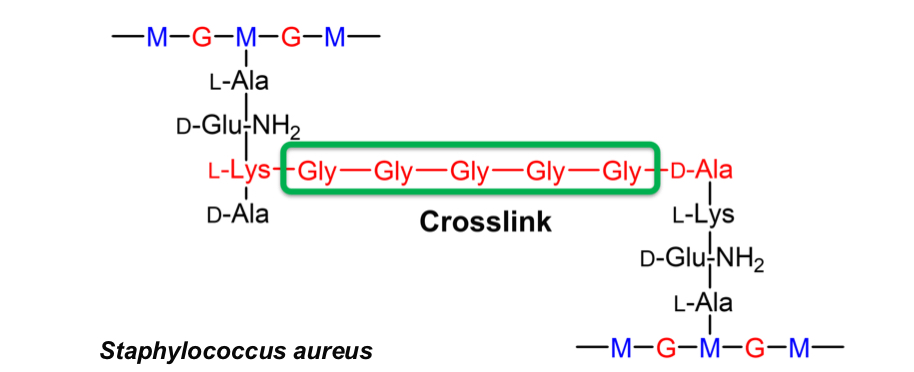
What part of D-alanine is cleaved off to make a peptidoglycan bridge?
Amide group
How many hydrogen bonds does vancomycin make with the cell wall?
FIVE!!!!
What type of bonds does vancomycin make with the cell wall?
Hydrogen bonds
What is the MOA of vancomycin?
Forms H-bonds from its peptide backbone when in the right conformation and binds strongly
What can happen when 2 vancomycin molecules are near one another when acting against bacteria?
Associate to one another via hydrogen bonds and can bind to 2 different alanine residues to increase the effects potency
What amino acid mutation do vancomycin resistance bacteria mutate?
D-Ala-D-Ala terminates to D-Ala-D-Lac (lactic acid)
What is the effect of D-Ala becoming D-Lac to vancomycin’s activity?
Can only form 4 hydrogen bonds and has a lower affinity, less energetically favourable
What vancomycin resistance bacteria change D-Ala to D-Lac?
VanA, B, D, F
What vancomycin resistant bacteria change D-Ala to D-Ser?
VanC, E, G
What is the functional group change when D-Lac is formed?
Ester formed instead
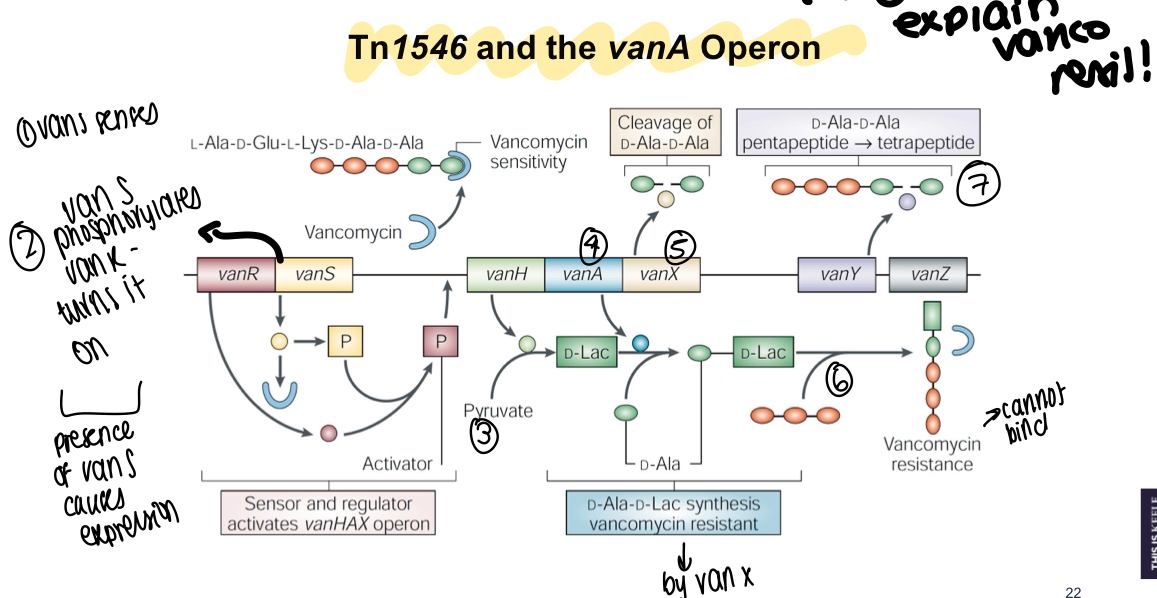
What transposon is key for VRE?
Tn1546
What must happen to Tn1546 to convey resistance?
Must be incorporated into a genome or plasmid - cannot individually/independently replicate
What resistance does Tn1546 bring about?
High-level VanA vancomycin resistance - switch to D-Lac
What does Tn1546 encode for?
9 polypeptides in 4 functional groups
What are the 4 functional group changes that Tn1546 encodes for?
Transposition functions - ORF1, ORF2
Regulation of resistance gene expression - VanR, VanS
Glycopeptide resistance - VanH, VanA, VanX
Accessory proteins - VanY, VanZ

What is another name for ORF1?
Transposase
What is another name for ORF2?
Resolvase
What is another name for VanR?
Regulator
What is another name for VanS?
Sensor
What is another name for VanH?
Dehydrogenase
What is another name for vanA?
Ligase
What is another name for vanX?
Dipeptidase
What is another name for vanY?
Carboxypeptidase
How does vanA/ligase work?
Catalyses ester bond formation between D-Ala and D-Lac and produces D-Ala-D-Lac
What is the role of VanH?
Reduces pyruvate to D-Lac - VanA’s substrate, also affects precursor cross-linking to growing peptidoglycan processed by PBPs
What is the role of VanX?
Hydrolyses D-Ala-D-Ala by cleaving alanine residue but cannot hydrolyse D-Ala-D-Lac
How are vanA, H and X regulated at a transcriptional level?
Regulated at transcriptional level by VanR-vanS, transmit a signal in response to vancomycin presence
What component of regulation senses vancomycin presence?
VanR
What is the role of VanY?
Auxillary protein that catches D-Ala terminal that escaped previous hydrolysis from VanX
What is the role of VanZ?
Low-level resistance to teicoplanin
What is a diagram showing the vanA operon and Tn1546?
How can VRSA be controlled?
Cycling Abx, appropriate prescribing
What can decreased susceptibility to VRSA be due to?
Increased peptidoglycan levels and precursors