Organic Nitrogen compounds
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is the general formula of a primary amine?
RNH2
Describe how to form an amide from a halogenoalkane
Heat with halogenoalkane in a sealed tube with a concentrated ammonia and an ethanol solvent
Why can’t reflux be used to form an amide from a halogenoalkane?
Ammonia is too volatile so it would escape from the reaction vessel
Why is excess ammonia used when forming a primary amine from a halogenoalkane?
So further substitution doesn’t occur.
If ammonia is not in excess then a secondary, tertiary or quaternary amine may form
Describe how to form a primary amine from an amide
Reduction using LiAlH4
Write an equation for the formation of ethylamine from ethanamide
CH3CONH2 + 4[H] ——> CH3CH2NH2 + H2O
Describe how to from a primary amine from a nitrile
Either reduction using LiAlH4 or reduction using Ni catalyst and H2 gas
Write equations for the formation of ethylamine from ethanenitrile
LiAlH4: CH3CN + 4[H] ——> CH3CH2NH2
Ni/H2: CH3CN + 2H2 ——> CH3CH2NH2
Describe how to form phenylamine
Reduction of nitrobenzene with Sn and concentrated HCl. Reflux for 30 minutes
When synthesising phenylamine from nitrobenzene, why is NaOH added after the mixture has been refluxed?
To remove a proton from the -NH3+ group
What is the overall equation for the synthesis of phenylamine?
C6H5NO2 + 6[H] ——> C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
Why are amines basic?
The lone pair on the nitrogen in the amine group can accept a proton/hydrogen ion
What affects the strength of a base?
How easily the lone pair can accept a hydrogen ion
The stability of the ions formed
What is the order of relative basicity between ammonia, ethylamine and phenylamine? (most reactive to least)
Ethylamine, Ammonia, Phenylamine
Why is ethylamine a stronger base than ammonia?
Alkyl groups tend to push away from themselves creating a positive inductive effect
This increases the negative charge of the nitrogen in ethylamine, making the lone pair more attracted to hydrogen ions
The electron pushing effect also spreads the charge more so the ethylammonium ion is more stable than the ammonium ion
Why is phenylamine a weaker base than ammonia?
Phenylamine has one of the p-orbital on the nitrogen overlaps with the pi-bonding system in the ring
This causes the lone pair on nitrogen to be delocalised into the ring, making the lone pair less available to form dative bonds with H+
Why is phenylamine more reactive than benzene?
The -NH2 group in phenylamine activated the benzene ring when the lone pair on the nitrogen is delocalised into the pi system making phenylamine more reactive because of the electron density in the pi system so more electrophiles are attracted
Describe the conditions for the reaction between phenylamine and aqueous bromie
Room temperature
No catalyst
Describe what would be observed when phenylamine reacts with aqueous bromine
Bromine water is decolourised
2,4,6-tribromophenylamine is formed with a white precipitate forms
What is formed in the reaction between phenylamine and nitrous acid when the mixture is warmed?
Phenol, H2O and N2
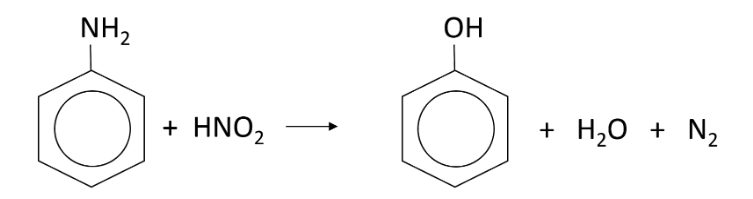
When reacting phenylamine with nitrous acid, why is the nitrous acid typically made in situ and how?
Because it decomposes rapidly
It is made by reacting HCl with sodium or potassium nitrate so phenylamine is added to HCl and NaNO3 at the same time
What is formed from the reaction between phenylamine and nitrous acid when the reaction vessel is below 10 degrees?
A Benezenediazonium ion is formed with water
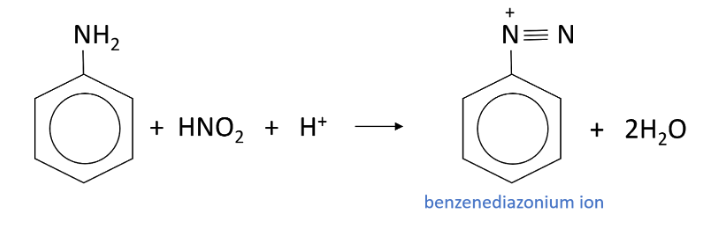
What group does a diazonium ion contain?
N2+ group
Describe the formation of dyes from benzenediazonium chloride and phenol
Phenol is reacted with NaOH to from sodium phenoxide
Sodium phenoxide is cooled in ice ana a cool solution of benzenediazonium chloride is added
A yellow orange precipitate forms and this is the azo compound
What is an azo compound?
A compound containing two benzene rings joined by a nitrogen bridge
What is they type of reaction that occurs when reacting sodium phenoxide and benzenediazonium chloride? List the reagent and conditions
Diazotisation
Reagents: Nitrous acid and HCl
Conditions: Keep below 10 degrees
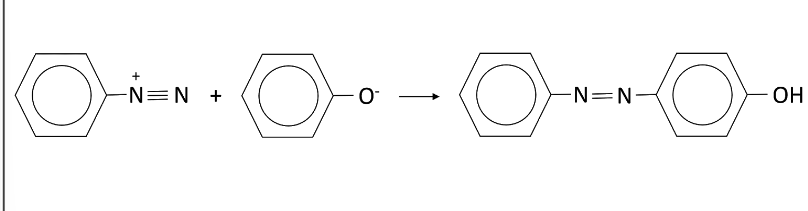
During the formation azo-compounds, at which position does coupling typically take place?
At the 4-position
If the 4-position is occupied, coupling will take place at the 2-position
What functional group do amides contain?
-CONH2
Are amides acidic, neutral or basic?
Neutral
Describe how an amide can be formed from ammonia
React with an acyl chloride and HCl gas is also produced
Write an equation for the reaction between ammonia and propanoyl chloride
If excess ammonia is used, the overall equation is:
CH3CH2COCl + 2NH3 ——> CH3CH2CONH2 + NH4Cl
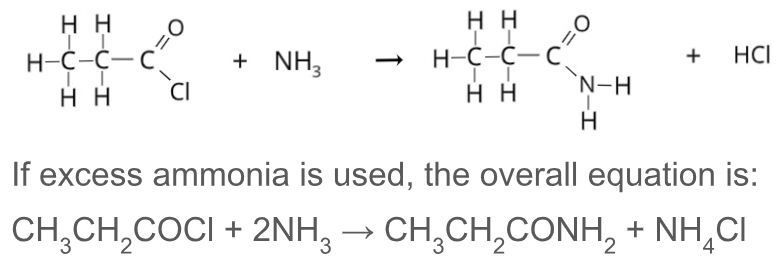
Describe the acid hydrolysis of amide
Upon heating with acid, an amide will be broken down into a carboxylic acid and either ammonium ions or RNH3+ ions
Describe the alkaline hydrolysis of amides
Upon heating with NaOH, an amide will be broken down into a carboxylate salt and either ammonia or an amine
Describe the reduction of amides
LiAlH4 is used with a dilute acid
An amine and water is formed
Write an equation for the reduction of propanamide
CH3CH2CONH2 + 4[H] ——> CH3CH2CH2NH2 + H2O
What functional groups do all amino acids contain?
COOH
NH2
Why can amino acids act as both acids and bases?
The -COOH group can donate a proton
The -NH2 group can accept a proton
What is a zwitterion? How do amino acids from zwitterions?
A zwitterion is an ion containing a positive and negative charge. It has no overall charge
Amino acids form zwitterions when carboxylic acids group donates a proton to the amine group
What happens when an alkali is added to an amino acid zwitterion?
The NH3+ group donates a hydrogen ion to the OH- ions of the alkali to form water. The organic compound isn’t a zwitterion anymore because it only contains a negative charge
What happens when an acid is added to an amino acid zwitterion?
The COO- group accepts a hydrogen ion from the acid. The organic compound isn’t a zwitterion anymore because it only has positive charge
How does a peptide bond form?
During a condensation reaction between amino acids
What is a buffer solution?
A substance that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acids or bases are added
What is electrophoresis?
The separation of ions placed in an electric field between a positive and negative electrode
What must the pH for a specific amino acid to form its zwitterion?
The pH must be the isoelectric point of the amino acid
When the pH is the isoelectric point of the amino acid, why doesn’t this amino acid movie during electrophoresis?
The amino acids forms its zwitterion making it no overall charge, so it is not attracted to the anode or cathode
When do amino acids moves towards the cathode during electrophoresis?
When they are positively charged and may occur when an amino acid has an extra hydrogen in the amine group
When do amino acids moves towards the cathode during electrophoresis?
When they are negatively charged and may occur when an amino acid has lost a hydrogen from the carboxylic acid
What are the factors that affect the rate at which ions move towards electrodes during electrophoresis?
Size of the ion
Charge on the ions
Voltage applied
Temperature
Mass and voltage affect the speed
Charge on the ion and pH affect direction
How is the size of ions related to the speed at which they travel during electrophoresis?
Smaller ions travel faster because there’s less resistance to their movement through the paper fibres
How does using buffer with a LOW pH affect the results when using electrophoresis to separate amino acids?
-COOH groups remain as -COOH
-NH2 groups accept a proton to become -NH3+
All amino acids will be positively charged so they move to the cathode
How does using buffer with a HIGH pH affect the results when using electrophoresis to separate amino acids?
-COOH groups donate a proton to become -COO-
-NH2 groups remain as -NH2
All amino acids will be negatively charged so they move to the anode
What must be done before peptides can undergo electrophoresis? Describe how the molecules are changes
Treat the peptides with SDS and denature them by heating
The secondary and tertiary structures are lost and the molecules become amino acid chains surrounded by negative charges