AP Microecon 3.1-3.4 Study Guide
1/61
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is the production function?
the relationship between quantity of inputs used to make a good and the quantity of output of that good
total product
total output produced by a firm
Average Product
total product/units of variable input (aka labor)
Marginal Product
the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input
What is the relationship between Total Product and Marginal Product
Marginal product is the slope of the total product (also known as the derivative)
What is the relationship between Average Product and Marginal Product
When MP is above AP it pulls AP up. When MP is below AP it pulls AP down. It is like AP is your GPA and MP is the grade you get in one class
When MP is increasing, what is TP doing
Increasing at an increasing rate
When MP is decreasing, what is TP doing
Increasing at a decreasing rate
When MP is negative, what is TP doing
TP is decreasing
Where is TP maximized
When MP = 0
Why does MP go up at the beginning?
Specialization causes additional inputs to increase production
Why does MP then start to decrease
Diminishing Marginal Returns
What is Diminishing Marginal Returns
As you add more variable inputs to fixed input, the production you get from additional inputs will be less and less. Imagine the paper chain, and by adding more workers, without adding additional staplers, then the additional workers will not add much to the paper chain.
What is the relationship between Marginal Product and Marginal Cost
They are the inverse (or mirror) of each other. When MP is increasing, MC is decreasing and vice versa
fixed input
an input whose quantity is fixed for a period of time and cannot be varied
What is a variable input
an input whose quantity the firm can vary at any time
what is the difference between the short run and long run?
In the short run at least one input is fixed. In the long run all inputs are variable
What is meant by plant capacity
A firm's maximum level of production in the short run
Where is Average Product Maximized?
Where Marginal Product = Average Product
What is fixed cost
A cost that must be paid when a firm's output is zero. A cost that is the same at all output levels (e.g. rent)
What is variable cost
a cost that varies with the level of output. As you add more materials and workers to produce more product your variable cost will increase
What is Total Cost
fixed cost + variable cost
What is Marginal Cost
the cost of producing one more unit of a good
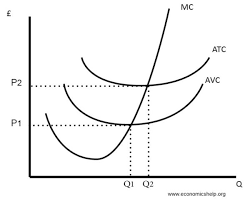
What is the shape of the Marginal Cost curve?
Nike Swoosh - it initially goes down due to specialization, but then starts to rise due to diminishing marginal product
What is Average Fixed Cost?
fixed cost divided by the quantity of output
What is the shape of the Average Fixed Cost curve?
always decreasing - it should be approaching the x-axis as output increases
What is Average Variable Cost
variable cost divided by the quantity of output
What is the shape of the Average Variable Cost curve?
U-Shaped
What is Average Total Cost?
total cost divided by the quantity of output
What is the shape of the Average Total Cost curve?
U-shaped
What is the gap between the ATC and AVC curves? Why does it shrink over time?
The gap between ATC and AVC is average fixed cost, and as AFC is consistently getting smaller, the gap between ATC and AVC shrinks with more output
Why is the ATC curve shaped the way it is?
It first goes down as AFC is decreasing, but then increases due to diminishing marginal product
What is the relationship between MC and AVC
When MC is below AVC it is pulling AVC down, and when MC is above AVC it is pulling AVC up.
Where does MC cross AVC
At the AVC curve's minimum
What is the relationship between MC and ATC
When MC is below ATC it is pulling ATC down, and when MC is above ATC it is pulling ATC up.
Where does MC cross ATC?
at the ATC curve's minimum
What is the difference between long run and short run for the cost curves?
All costs are variable in the long-run. No long-run fixed costs
What is the shape of the long-run ATC curve?
U-Shaped
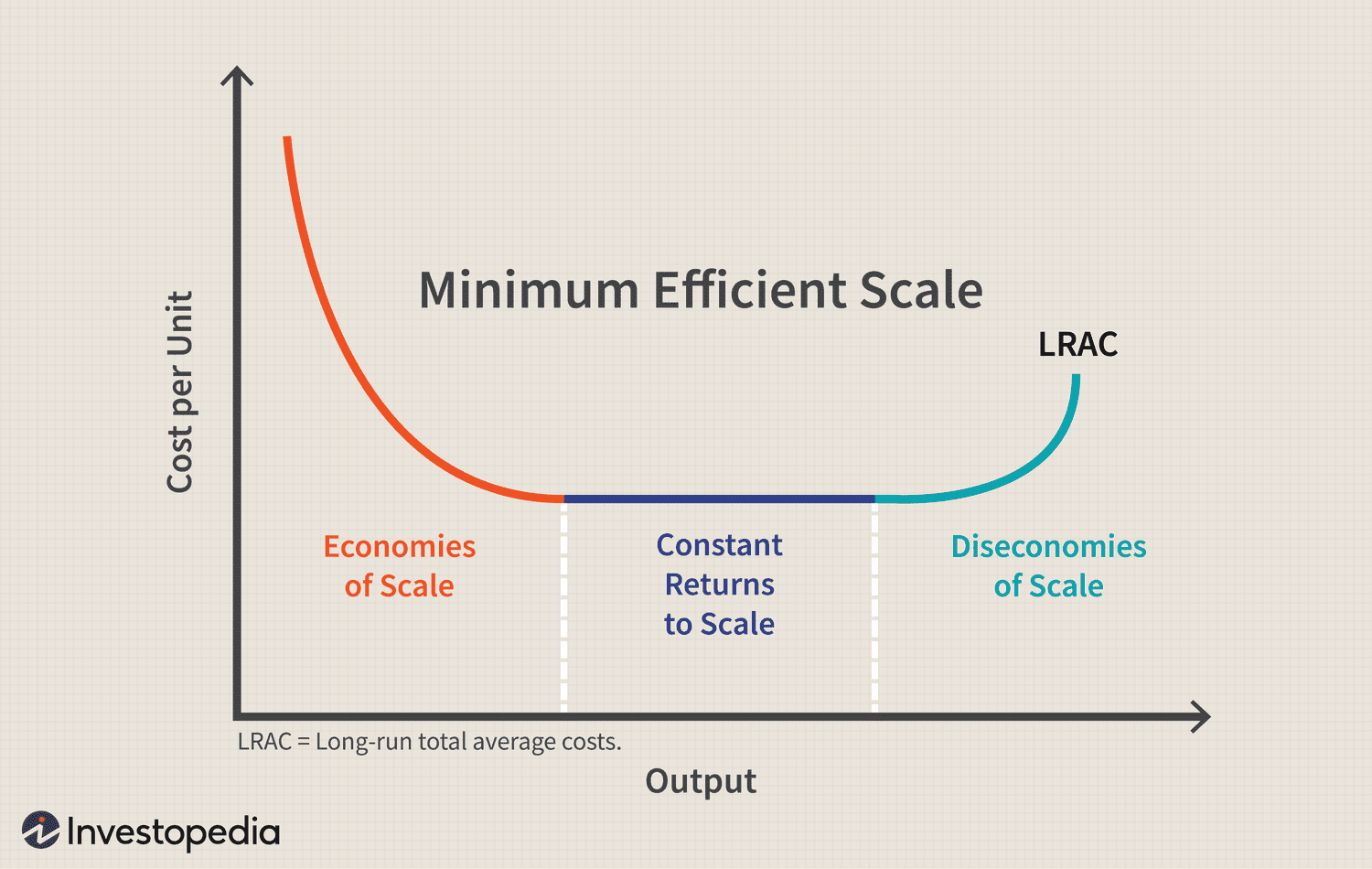
What is the downward portion of the long-run ATC curve?
Economies of Scale
What is Economies of Scale?
when the average cost of producing a good or service falls as the quantity produced increases
What causes Economies of Scale?
Specialization and taking advantage of bigness. If you have all the capital in place to produce a product at a low marginal cost, running all those machines to produce more and more product will bring down your average total cost
What is constant returns to scale?
the property whereby long-run average total cost stays the same as the quantity of output changes
Where is constant returns to scale found on the long-run ATC curve?
The flat portion at the bottom of the curve
What is the upward sloping portion of the long-run ATC curve?
Diseconomies of Scale
What is Diseconomies of Scale
the property whereby long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increases
What causes Diseconomies of Scale?
Larger businesses difficult to coordinate
As a business gets larger, communication becomes more difficult
Workers might feel less a part of the business
What is increasing returns to scale?
When output increases at a greater rate than inputs (aka Economies of Scale) If you double inputs but more than double outputs
What is decreasing returns to scale?
When output increases at a smaller rate than adding inputs (aka Diseconomies of Scale) If you double inputs but outputs increase do not double
Where is Minimum Efficient Scale found
At the bottom of the long-run ATC curve. It is when Economies of Scale stops and constant returns to scale sets in.
Where should a firm produce in the long-run?
At a place where long-run ATC is minimized
What causes cost curves to move up?
An increase in costs - taxes, labor costs, materiel costs, etc.
What causes cost curves to move down?
A decrease in costs - lower taxes, lower labor costs, lower material costs, etc.
explicit cost
Money spent on inputs for a business - labor, capital, natural resources, etc.
What is implicit cost?
the monetary value of an opportunity cost (e.g. I could earn $30,000 being an tutor, but have instead decided to be an Uber driver)
Accounting Profit
total revenue minus total explicit cost
Economic Profit
total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs
Normal Profit
Covers the explicit costs and forgone income (zero economic profit)
Production Function Graph
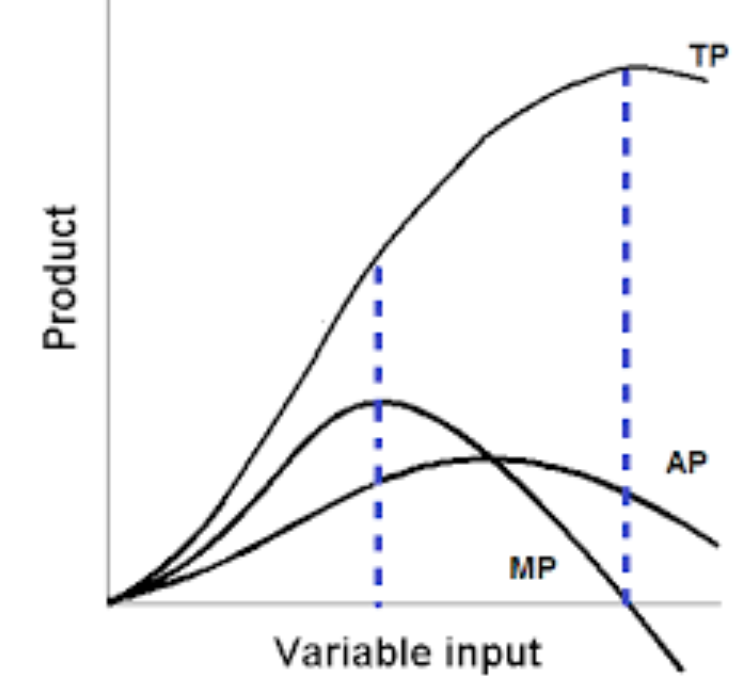
Short Run Production Function Graph
Long Run Average Total Cost Curve