Micro Lab Results and Media
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What does purple staining mean on a gram-stain?
Gram positive
What does pink staining mean on a gram-stain?
Gram negative
What kind of medium are blood agar plates?
enriched, differential, contain blood
What does blood agar plates test for?
hemolysins damaging/lysing red blood cells
What kind of medium is a mannitol salt agar plate?
selective, differential, high salt concentration (7.5% NaCl)
How to do gram stain? (ingredients used)
Crystal violet, iodine, decolorizer, safranin
Crystal 1 min, water, iodine 1 min, water, decolorizer until clear, immediately with water, safranin for 1 min, water, blot dry.
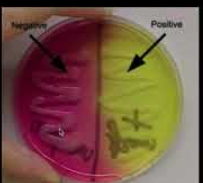
What does the positive result mean?
fermenter of mannitol
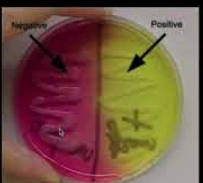
What does the negative result mean?
does not ferment mannitol but tolerates salt
What type of medium is a MacConkey agar plate?
selective (bile salt and crystal violet) and differential medium (pH indicator), shows fermentation of lactose
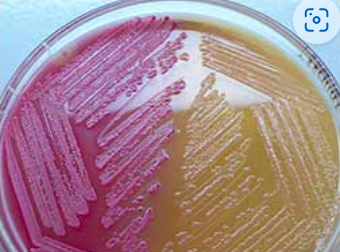
What does yellow mean on a MacConkey agar?
negative, non-lactose fermentation (along with colorless colonies)
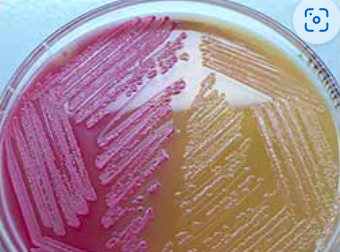
What does pink mean on a MacConkey agar?
positive, lactose fermenter (pink colonies)

What is an obligate aerobe?
microbe that requires oxygen for growth and survival
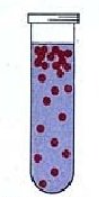
What is a facultative anaerobe?
microbes use oxygen for aerobic respiration but can grow without it
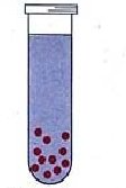
What is an obligate anaerobe?
microbe unable to grow in presence of oxygen

What is an aerotolerant anaerobe?
microbes that dont use oxygen to produce ATP but can tolerate/grow in presence of oxygen.

What is a microaerophile?
microbes use oxygen for energy production but in low amounts
What is an BHI agar used for?
determining aerotolerance of microbe
What kind of medium is a BHI (deep) agar?
enriched
What is UV light used for?
kill microbes
What kind of test is a nitrate test?
to look for nitrate reduction (denitrification)
After adding reagents A and B to nitrate test and turns red, what does this result indicate?
positive, nitrite present
After adding reagents A and B, as well as Zn2+ and HCl, and is red?
Negative, NO3 still present
After adding reagents A and B, as well as Zn2+ and HCl, and is clear/yellow?
positive, NO3 reduced to N2O or N2
What kind of medium is a DNase test?
differential medium and used to determine what organisms hydrolyze DNA

What result on a DNase test agar does this indicate?
negative for hydrolyzing DNA, no clearing around bacteria, green colored agar throughout
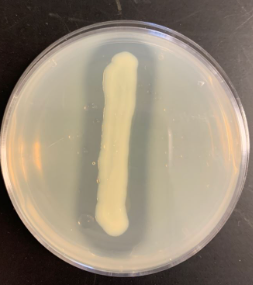
What result does this indicate on casein agar?
positive result, hydrolyzes ccasein

What result does this indicate on casein agar?
negative result, no hydrolysis of casein
What type of medium is a casein agar?
nutrient
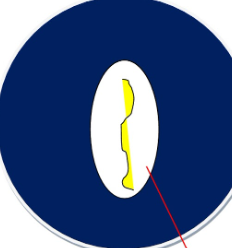
what result does this mean on this starch agar?
positive, starch hydrolysis occurs
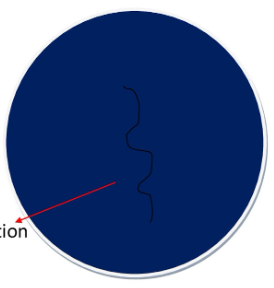
what result does this mean on this starch agar?
negative, no starch hydrolysis occurs
What kind of medium is a starch agar?
differential
What does the phenol red test provide?
differentiate gram negative enteric bacteria

What result does this mean in a phenol red tube?
negative carbohydrate fermentation and no gas produced

What result does this mean in a phenol red tube?
drop in the pH because of the production of the acid by the fermentation of the carbohydrate

What result does this mean in a phenol red tube?
ferment carbohydrate and gas production
What does the IMViC and SIM test do?
SIM (sulfur, indole, motility) methyl red- voges proskauer, cirate,

What result A does this mean in a SIM test?
motile, hydrogen sulfide -, indole +

What result B does this mean in a SIM test?
non-motile, hydrgoen sulfide -. indole -

What result C does this mean in a SIM test?
motile, hydrogen sulfide -, indole -

What result D does this mean in a SIM test?
motile, hydrogen sulfide -, indole -

What result E does this mean in a SIM test?
motile, hydrogen sulfide +, indole+

MR test results? Yellow tube
negative

MR test results? Red tube
positive
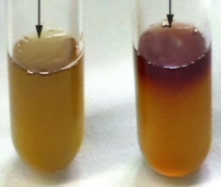
VP test result for yellowish
negative
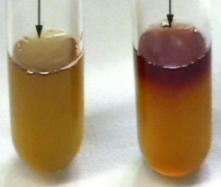
VP test result for pink
positive

citrate result? green
negative

Citrate result? blue
positive