Chapter 8: Receivables, Bad Debt Expense, and Interest Revenue
4.7(3)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/49
Last updated 7:46 AM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
It encourages the customer to buy more goods or services, so revenue goes up.
An advantage of extending credit is:
2
New cards
Increase in wage costs, bad debt expense, and delays receipt of cash
Disadvantages to extending credit includes:
3
New cards
Increase is wage costs
________ is caused by having to hire more employees to see if someone is credit worthy, see how much money people owe, and to collect from customers.
4
New cards
Bad debt costs
________ is due to the fact that sometimes people don't pay what they owe.
5
New cards
Delays receipt of cash
________ means cash may be received in 30-60 days.
6
New cards
bad debt
When accounts receivables aren't fully paid off, it results in ________.
7
New cards
"net realizable value"
Accounts Receivable is recorded at the value that is expected to be collected, aka ________.
8
New cards
expense recognition principle (matching)
You must record Sales Revenue and Bad Debt Expense in the same period of the sale. This is called ________.
9
New cards
allowance method
A(n) ________ is estimating bad debts that may not be collected and adjusting these estimations later.
10
New cards
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
________ is a contra account to Accounts Receivable and has a normal credit balance.
11
New cards
written off
When an account can not be collected, the account must be ________.
12
New cards
Income Statement
Write offs DO NOT appear on the ________.
13
New cards
Debit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Credit Accounts Receivable
Credit Accounts Receivable
Journal entry for write offs:
14
New cards

\
Net Receivable Value =
15
New cards
Debit Accounts Receivable
Credit Sales Revenue
Credit Sales Revenue
Journal entry to record sales on account:
16
New cards
Debit Bad Debt Expense
Credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Journal entry to record estimate for bad debts:
17
New cards
Percentage of Credit Sales Method
Aging of Accounts Receivable
Aging of Accounts Receivable
The two methods to calculate the estimate of bad debt:
18
New cards
Percentage of Credit Sales Method
________ is also known as the Income Statement Account. It estimates Bad Debt Expense for the period, but is not precise.
19
New cards
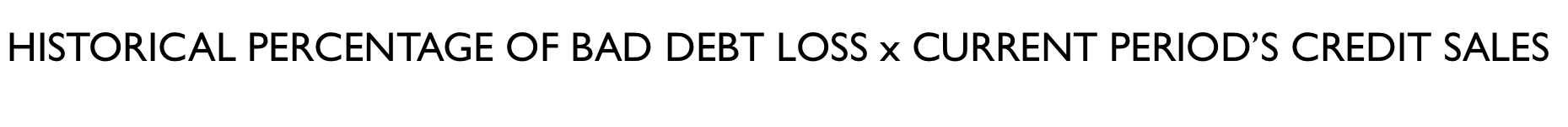
\
Equation for estimating bad debt expense (% of Credit Sales Method):
20
New cards
Aging of Accounts Receivable
________ is also known as the Balance Sheet Method. It estimates the ending balance in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. It is more accurate.
21
New cards
The steps for the Aging of Accounts Receivable
Prepare an aged listing of accounts receivable.
Estimate the bad debt loss percentages for each category.
Compute the total estimated bad debts.
Estimate the bad debt loss percentages for each category.
Compute the total estimated bad debts.
22
New cards
Revising estimates
________ is when a company revises their bad debt estimates for the current period.
23
New cards
Accounts recovery
________ is reviving written off accounts.
24
New cards
recovery
There are always 2 journal entries for a ________.
25
New cards
Debit Accounts Receivable
Credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Journal entry for reversing the write off (first recovery entry):
26
New cards
Debit Cash
Credit Accounts Receivable
Credit Accounts Receivable
Journal entry for the collection of the account (second recovery entry):
27
New cards
notes receivable
A ________ is reported when a promissory note is used for a transaction. It has a stronger legal claim.
28
New cards
charge interest
Notes receivables ________ from the date they are created to when they are due.
29
New cards
maturity date
The day the Notes Receivable is due is called the ________.
30
New cards
Loaning money.
Receiving extended payment.
Switching from Accounts Receivable to Notes Receivable.
Receiving extended payment.
Switching from Accounts Receivable to Notes Receivable.
A company may use a Notes Receivable for:
31
New cards

\
Equation for calculating interest =
32
New cards
Principal
The amount of the Note Receivable.
33
New cards
Interest Rate
The interest percentage charged on the note.
34
New cards
Time Period
The amount of time covered in the interest.
35
New cards
Debit Notes Receivable
Credit Cash
Credit Cash
Journal entry for establishing a Note Receivable:
36
New cards
Debit Interest Receivable
Credit Interest Revenue
Credit Interest Revenue
Journal entry for accruing interest earned but not received (use interest formula):
37
New cards
Debit Cash
Credit Interest Receivable
Credit Interest Revenue
Credit Interest Receivable
Credit Interest Revenue
Journal entry for recording interest payments received (adjusting journal):
38
New cards
Debit Cash
Credit Note Receivable
Credit Note Receivable
Journal entry for the principal payments received:
39
New cards
receivables turnover analysis
A(n) ________ helps see the effectiveness of a companys credit- granting and collection activity.
40
New cards
increase
Selling goods or services make the receivables balance ________.
41
New cards
decrease
Collecting the money from customers makes the receivables balance _______.
42
New cards
Receivables turnover
________ is the constant selling and collecting cycle.
43
New cards
receivables turnover ratio
The ________ indicates how many times the cycle is repeated during the accounting period.
44
New cards
A higher ratio means a faster collection of receivables.
Low ratios mean companies give their customers too long of a period to pay.
Low ratios mean companies give their customers too long of a period to pay.
Higher vs lower receivables turnover ratio
45
New cards
Days to collect
________ is the number of days to collect receivables. A higher ratio means it takes more days to collect. We want a low ratio.
46
New cards

\
Equation for Receivable Turnover Ratio:
Receivable Turnover Ratio =
Receivable Turnover Ratio =
47
New cards

365/Receivables Turnover Ratio
Equation for Days to Collect:
Days to Collect =
Days to Collect =
48
New cards
Credit cards
________ speed up cash collection and make it less likely to receive bad checks from customers.
49
New cards
Credit terms
________ is an agreement between the buyer and seller about the timings and payment to be made for the goods bought on credit.
50
New cards
factor
A ________ is when you sell outstanding accounts to a different company. By doing so, your company is paid for the receivables it sells to the factors. A factoring fee must be considered.