Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nervous System Lab
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
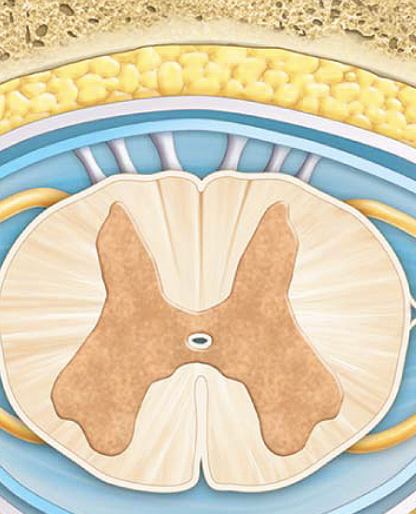
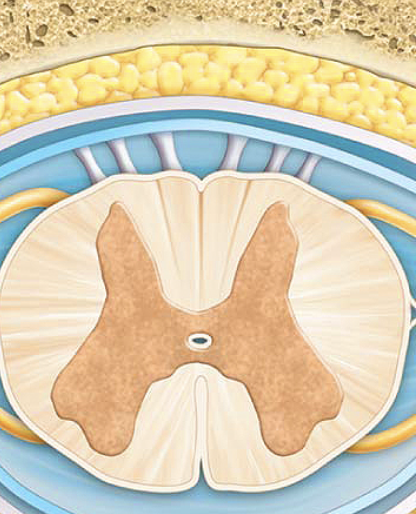
Anterior (ventral)
Posterior (dorsal)
ceiling/back
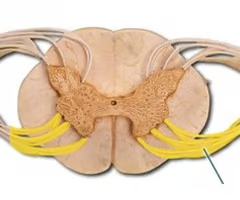
gray horns
what is the red butterfly called
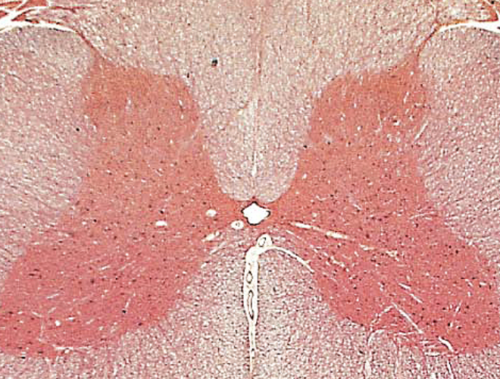
anterior gray horns
floor of grey horns
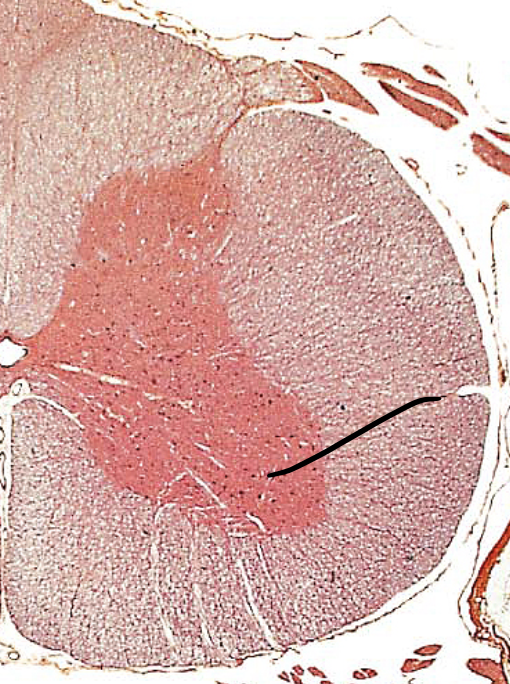
lateral gray horns
middle of gray horns

posterior gray horns
ceiling of gray horns
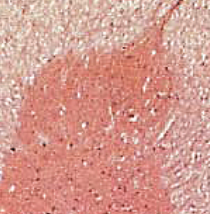
white columns
each side of the spinal cord has three funiculi (columns): dorsal (posterior) funiculus, lateral funiculus, and ventral (anterior) funiculus, which are further divided into tracts
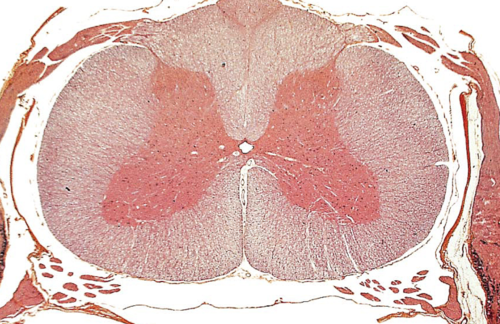
anterior funiculi
floor of white column
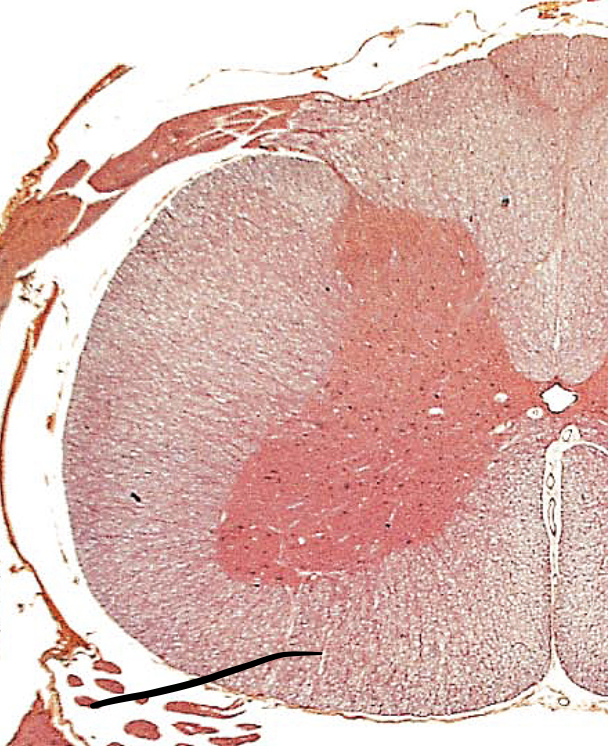
lateral funiculi
middle of white column
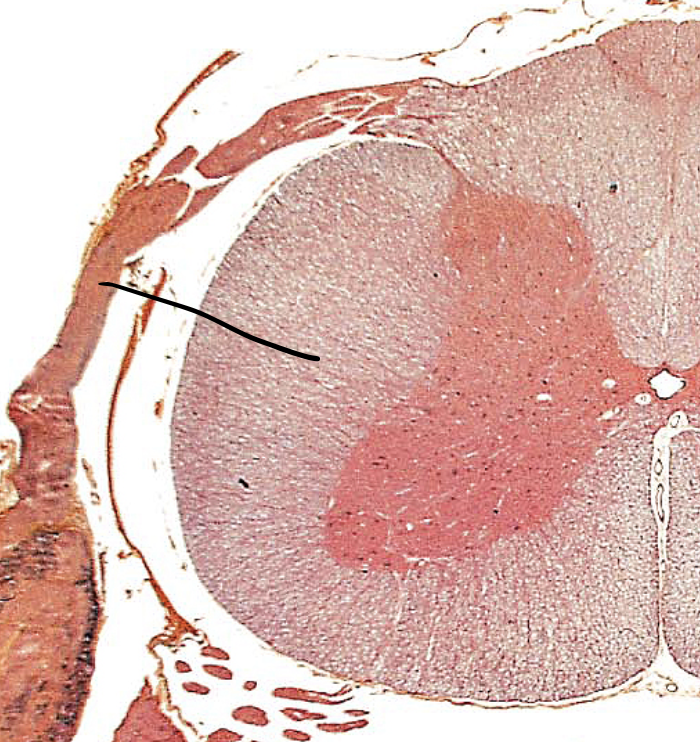
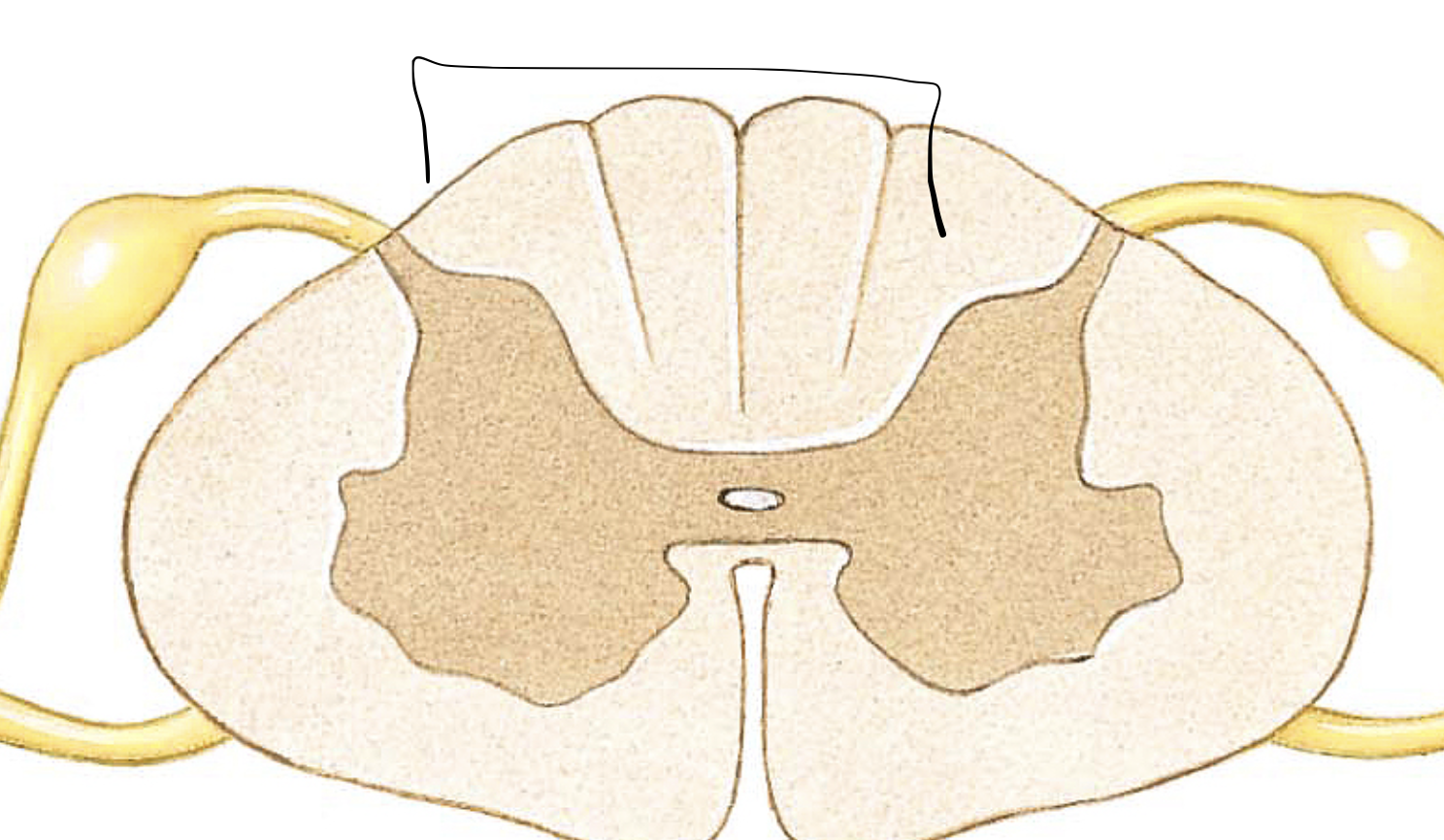
posterior funiculi
ceiling of white columns
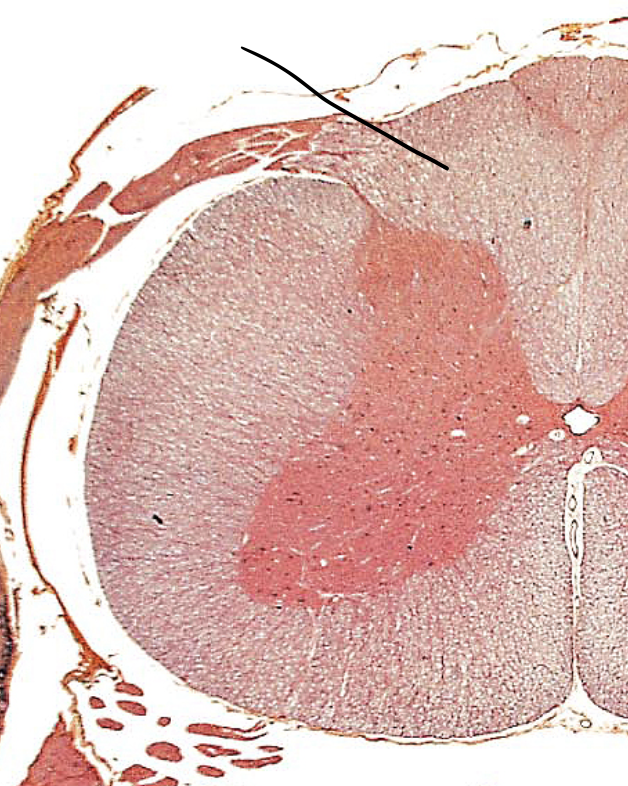
central canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord and inferior medulla oblongata

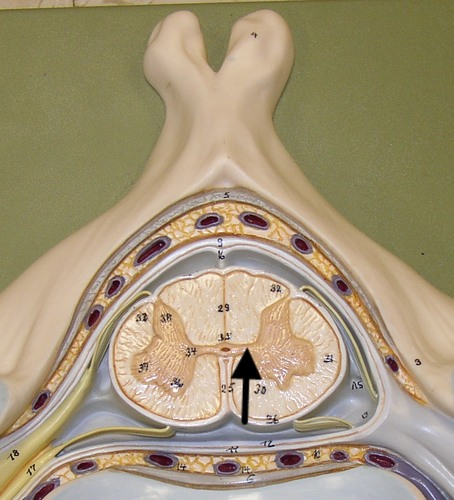
gray commissure
connects masses of gray matter; encloses central canal
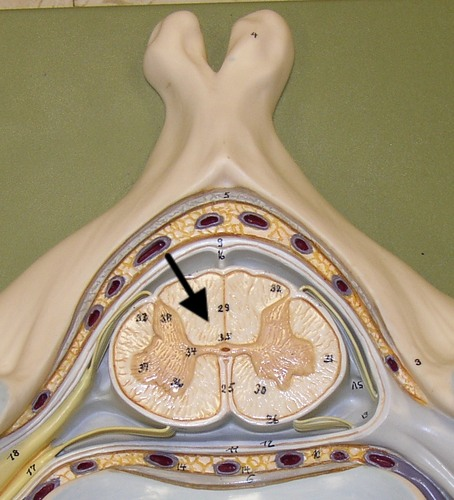
white commissures
connects the white matter of the right and left sides of the spinal cord
anterior median fissure
a groove along the anterior midline of the spinal cord that incompletely divides it into symmetrical halves
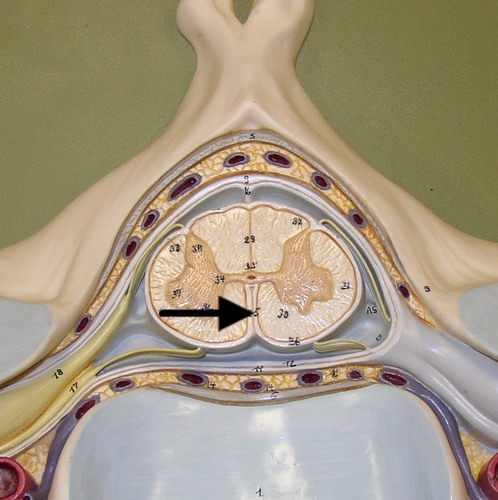
posterior median sulcus
a shallow vertical groove dividing the spinal cord throughout its whole length in the midline posteriorly.
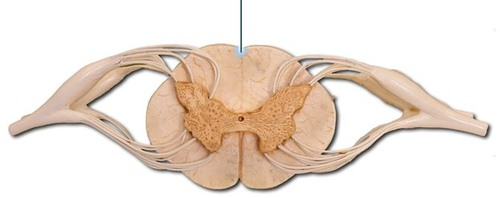
meninges
three layers of connective tissue in which the brain and spinal cord are wrapped/ The WHOLE LAYER
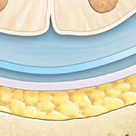
epidural space
The yellow stuff on TOP Cushion of fat and network of veins in space between vertebrae and spinal dura mater
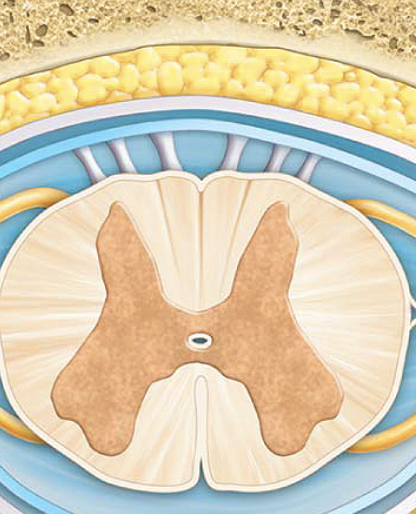
dura mater
pink layer
arachnoid mater
the light blue layer
subarachnoid space
The spaces between the purple/ The blue
pia mater
The first top layer/ under the purple stuff

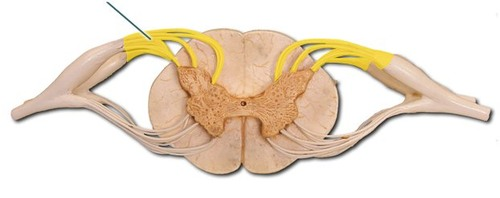
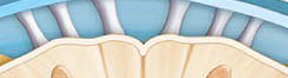
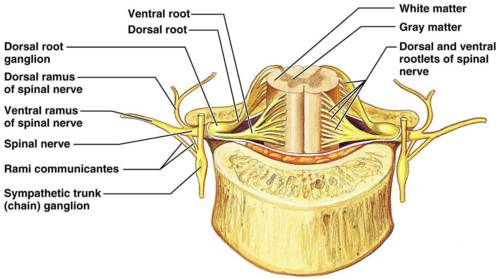
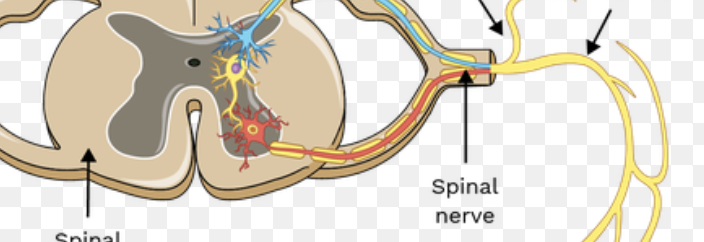
dorsal root
the sensory branch of each spinal nerve
dorsal root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons

ventral root
the basal branch of each spinal nerve; carries motor neurons
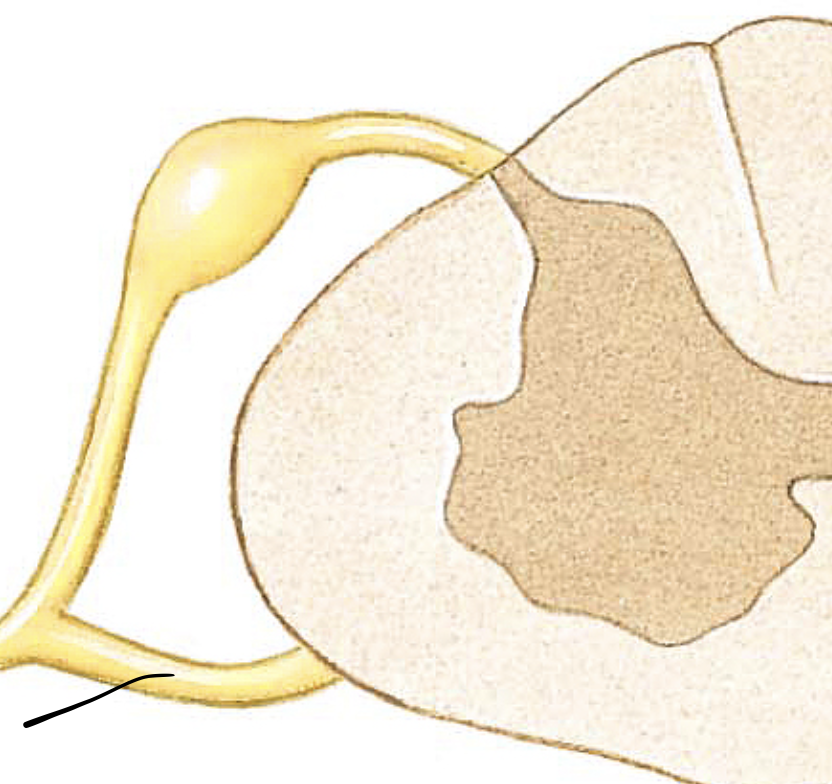
spinal nerve
a peripheral nerve attached to the spinal cord. Motor and Sensor nerve.

rami
branches of spinal nerves
dorsal ramus
the division of posterior spinal nerves that transmit motor impulses to the posterior trunk muscles and relay sensory impulses from the skin of the back
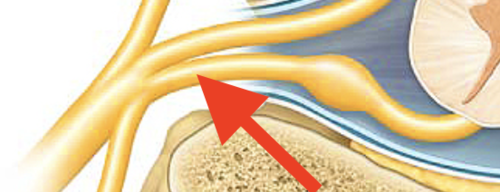
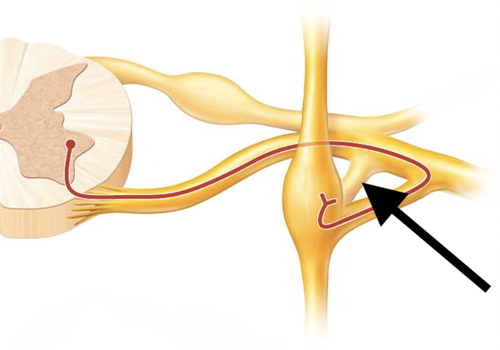
ventral ramus
what. is the second arrow pointing at?
gray rami communicantes
Carry unmyelinated postganglionic sympathetic axons from trunk to all spinal nerves
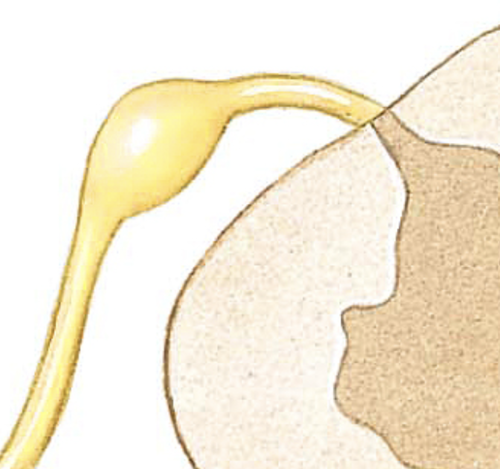
sympathetic trunk
nerve running along each side of the vertebral column
sympathetic trunk ganglia
big yellow thing
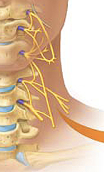
cervical plexus
C1-C5 supplies neck and phrenic nerve to the diaphragm
brachial plexus
network of interlacing nerves found in the upper arm area
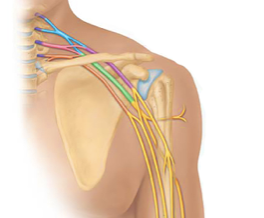
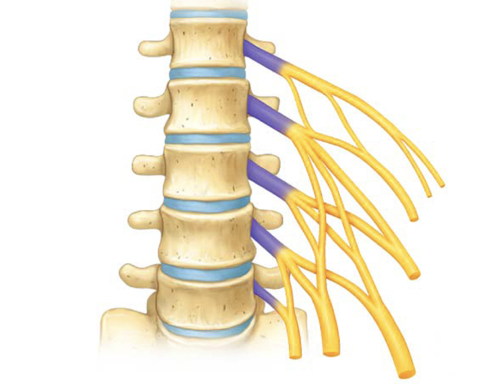
lumbar plexus
lower back nerves
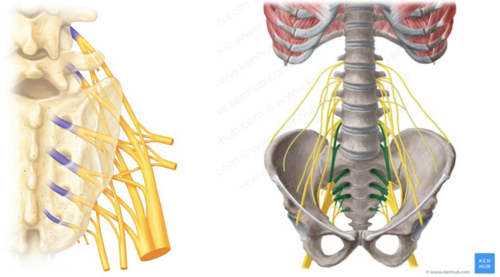
sacral plexus
Serves the buttock, lower limb, pelvic structures, and perineum
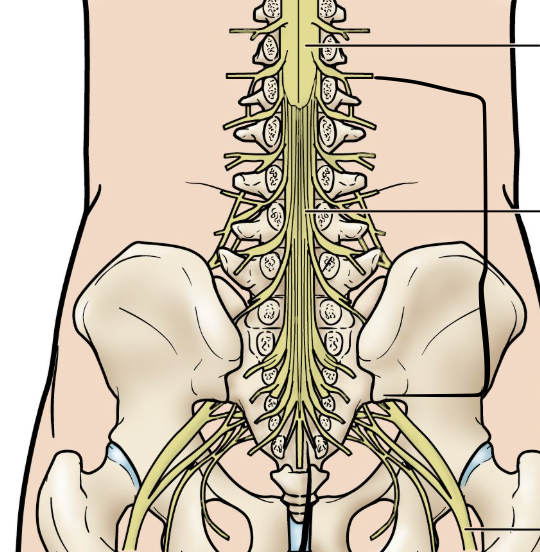
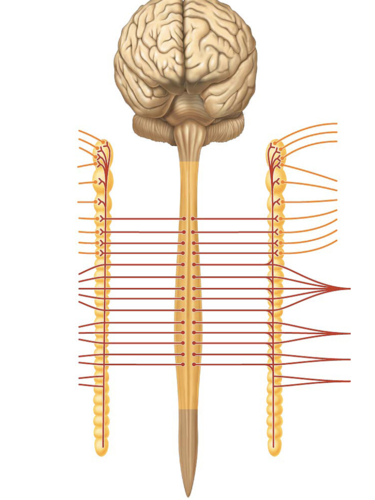
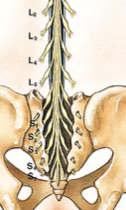
cauda equina
"horse's tail", a fan of nerve fibers below the spinal cord
median nerve
Sensory-motor nerve that is smaller than the ulnar and radial nerves and that, with its branches, supplies the arm and hand.
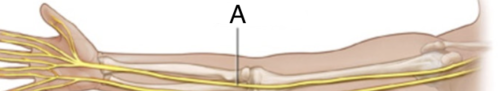
ulnar nerve
Sensory-motor nerve that, with its branches, affects the little-finger side of the arm and palm of the hand.
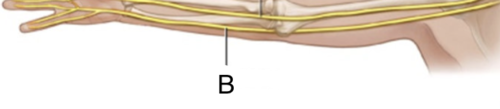
radial nerve
Sensory-motor nerve that, with its branches, supplies the thumb side of the arm and back of the hand.
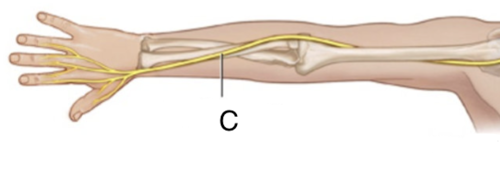
femoral nerve
L2-L4
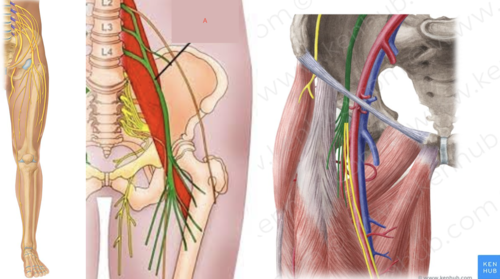
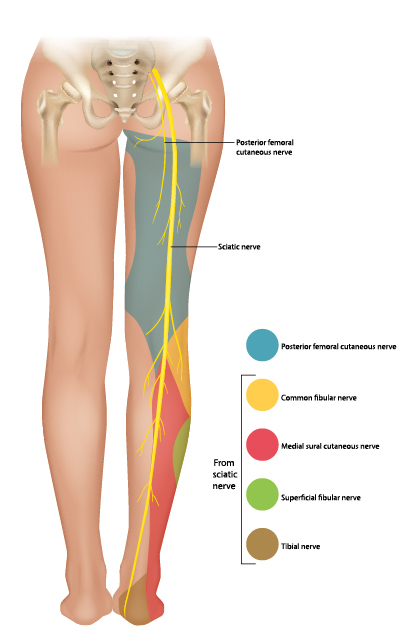
sciatic nerve
S1-S3
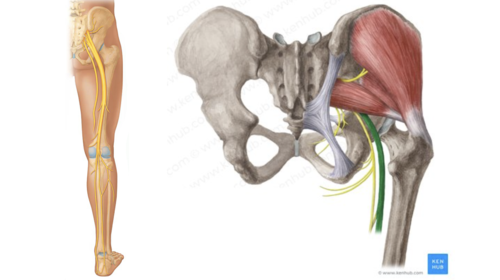
intercostal nerves
nerves between the ribs
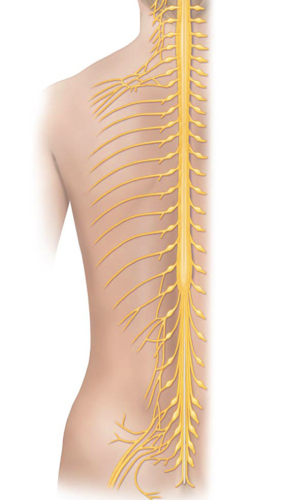
Pia mater
The orange outer layer
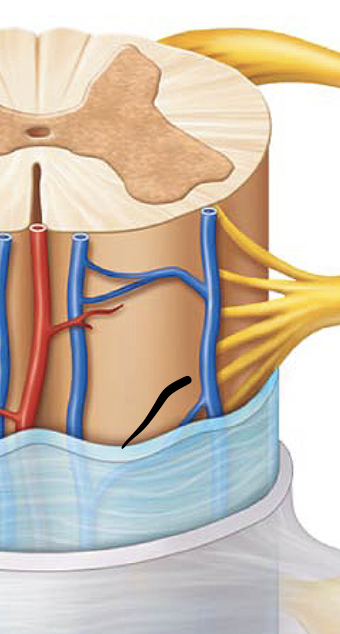
subarachnoid space
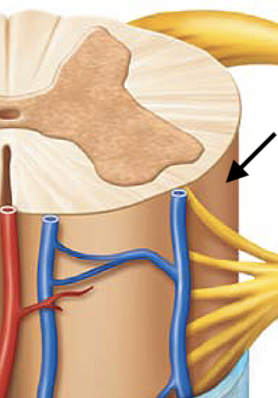
arachnoid mater
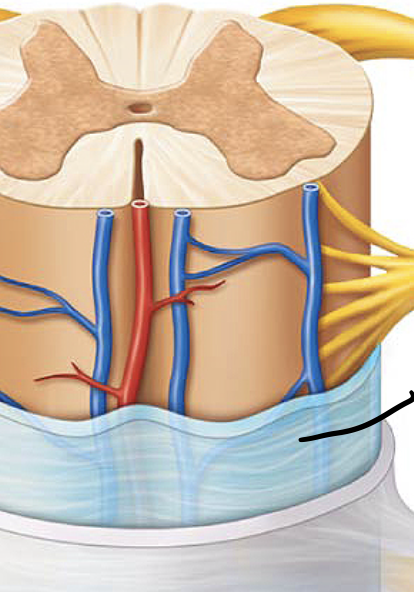
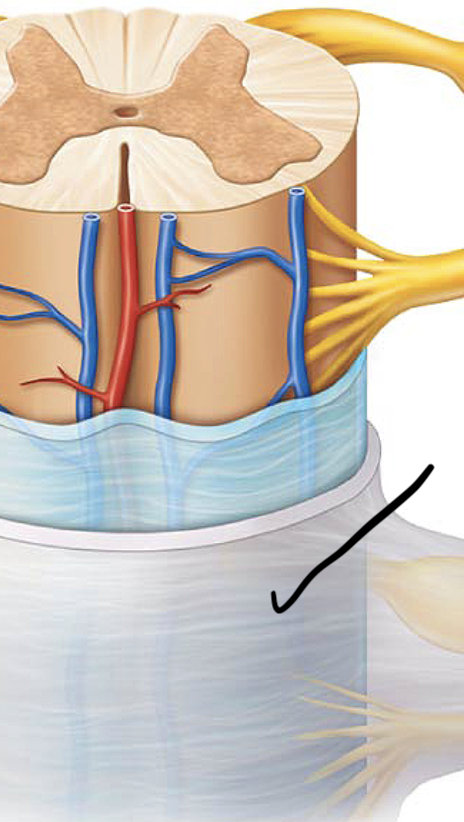
Dura mater
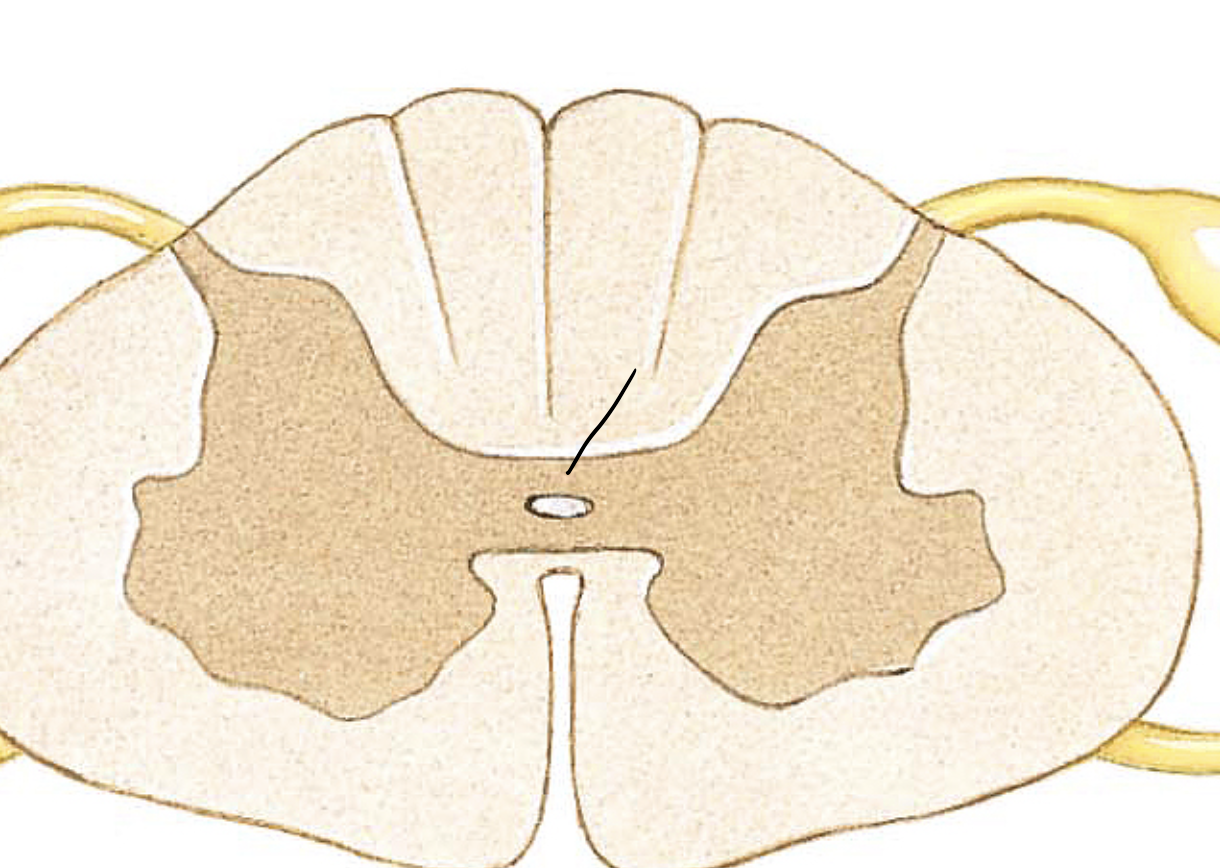
Gray commissure
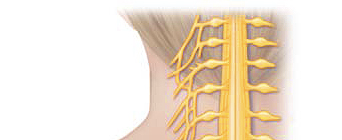
cervical plexus
Brachial plexus
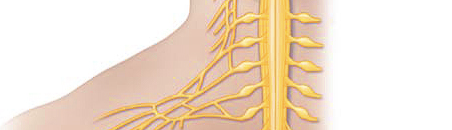
lumbar plexus
L1-L4
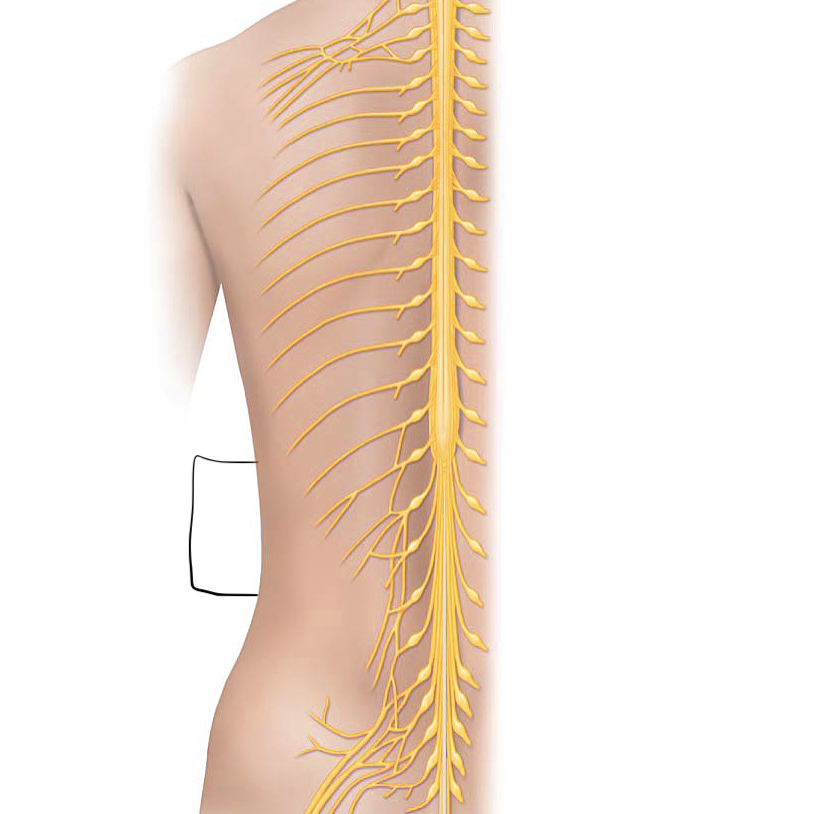
sacral plexus
L4-S4
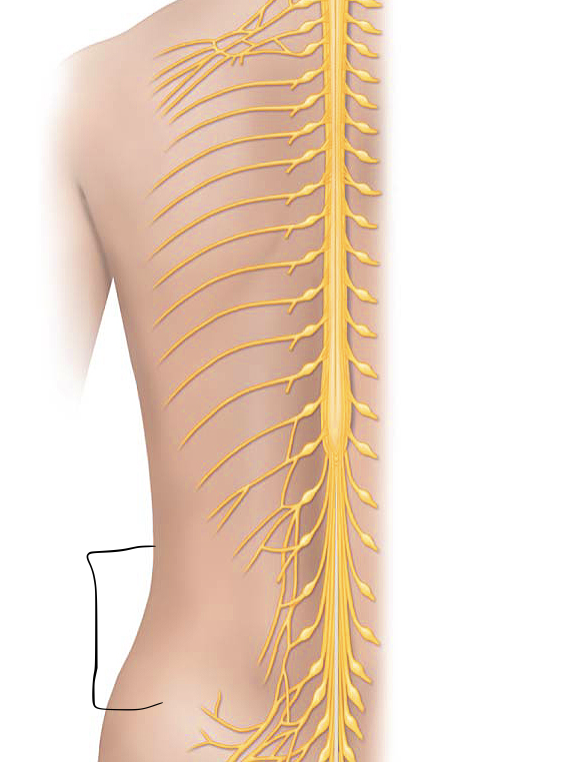
ventral ramus
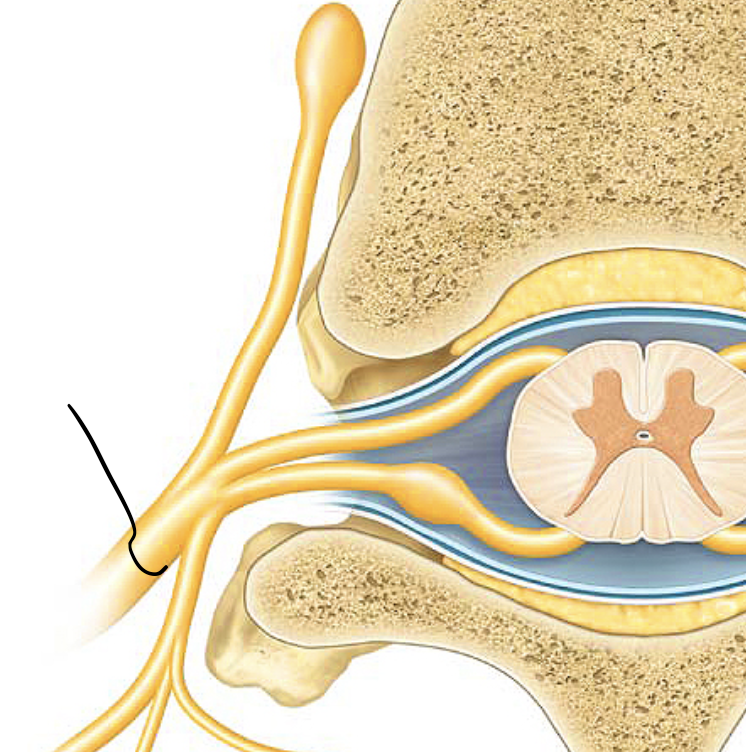
dorsal ramus
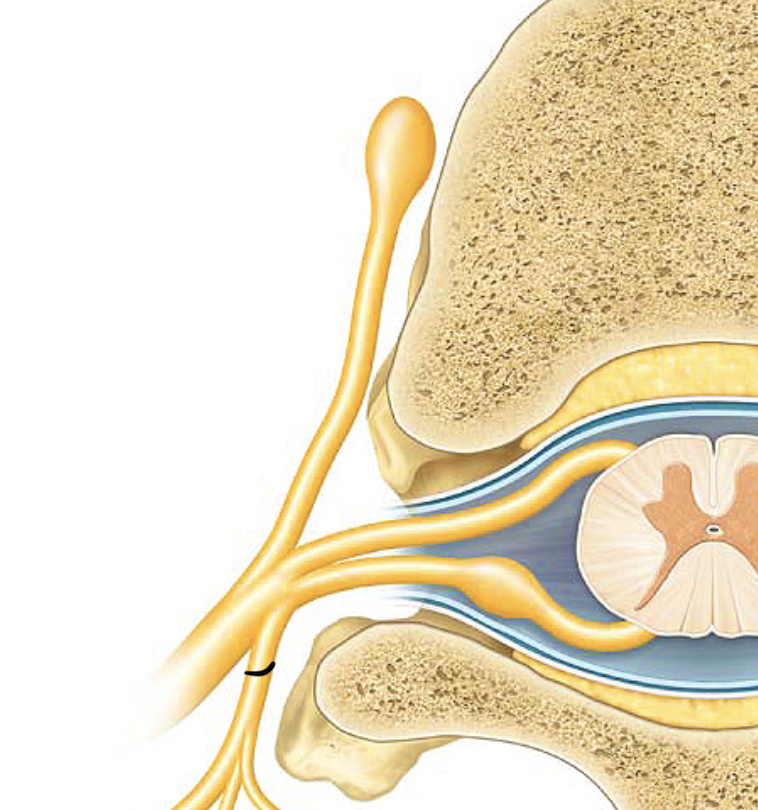
ventral root
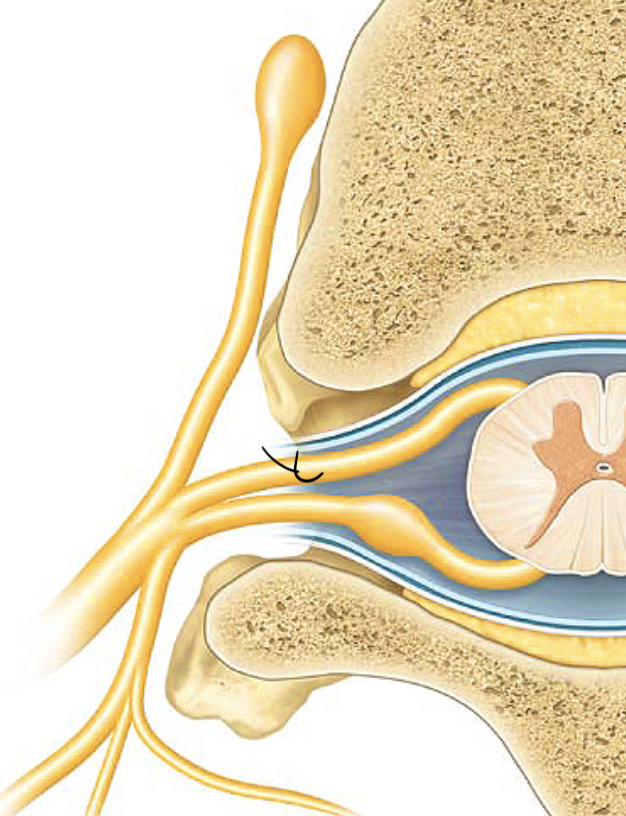
ventral root
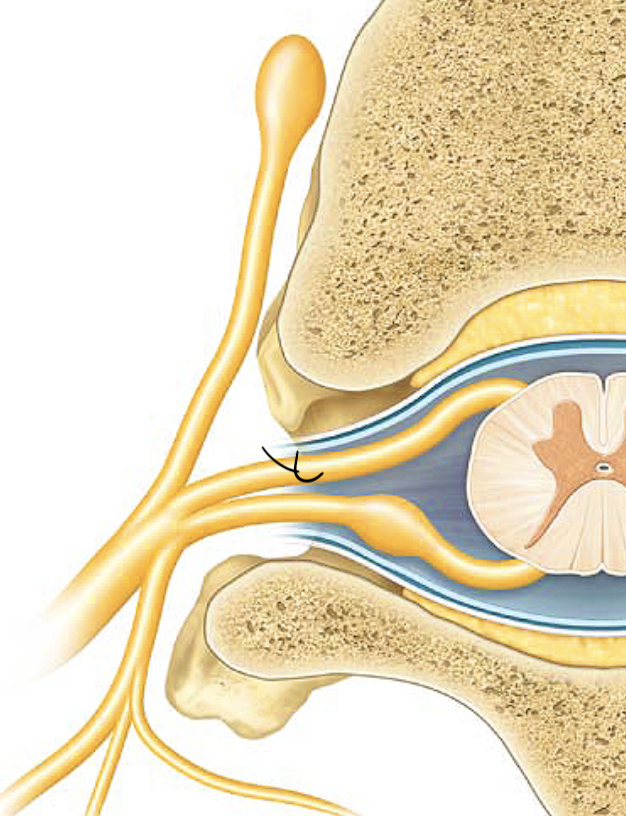
posterior funiculi
sciatic nerve
cauda equina