Memory
1/86
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What does coding mean?
The way information is transformed into a format that can be stored and retrieved from memory
What is a piece of research that supports coding?
Baddely (1966) - looked at how information is coded in different stores. ppts had a list of words to remember
Group 1 - acoustically similar words - words sounded similar. Group 2 - acoustically dissimilar words - words sounded different
Group 3 - semantically similar words - words with similar meanings. Group - semantically dissimilar words - words with different meanings
ppts had to recall in correct order - when they had to do immediate recall, tended to do worse with acoustically similar words - suggests STM relies on acoustic encoding (how words sound)
When they recalled words after 20 mins, ppts had difficulty recalling semantically similar words - suggests LTM relies on semantic encoding
What does Capacity mean?
the amount of information that can be held in a memory store
What is a piece of research that supports Capacity?
Jacobs (1887) - developed a technique to measure digit span
researcher gives 4 digits then ppt is asked to recall them in correct order out loud, if correct researcher reads out 5 digits and so on until ppt cannot recall order correctly
this determines individuals digit span
found that mean span for digits across all ppts was 9.3, mean span for letters was 7.3
What was contradictory research for Jacobs Capacity research?
Miller - made observations of everyday practice - noted things come in sevens - 7 days of the week etc
this reduces internal validity of Jacobs’ research as it suggests the span of the STM is about pus or minus 2
he also found that we can recall 5 words as well as 5 letters
What does Duration of STM mean?
The limited capacity memory store - the duration is between 18 and 30 seconds
What is a piece of research that supports the duration of STM?
Peterson + Peterson - tested 24 undergrad students. each student took part in 8 trials - on each trial, student was given consonant syllable to remember and was also given a 3-digit number, student was then asked to count backwards from that number until told to stop
counting backwards was to prevent mental rehearsal of consonant syllable
What dies the Duration of LTM mean?
The permanent memory store - can store memories for up to a lifetime
What is a piece of research supporting the Duration of LTM?
Harry Bahrick - studied 392 ppts form Ohio who were aged between 17 and 74. high school yearbooks were obtained from the participants - recall was tested in various ways
1: photo recognition test consisting of 50 photos some from ppts high school yearbooks. 2: free recall test where ppts recalled all names of their graduating class
ppts who were tested within 15 years of graduation were 90% accurate
after 48 years, recall declined to about 70%
free call: after 15 years - 60% accurate dropping to 30% after 48 years.
What is a limitation of research into capacity?
lack of control in the study
Jacob’s research was conducted in 1887, before the use of computers meaning the numbers would have to be read out by researcher
their tone, volume and speed may have changed each time
this is a limitation because the study lacks reliability and these may have acted as extraneous variables
What is a strength of research into the duration of STM? (Bahrick’s study)
high external validity
real life meaningful memories were studied. when studies on LTM have been conducted with meaningless pictures to be remembered, recall rates were lower
the downside of real life research is that confounding variables are not controlled, such as the fact that Bahrick’s ppts may have looked at their yearbook photos and rehearsed their memory over the years.
What is a limitation of research into the duration of STM?
the stimulus material was artificial
trying to memorise consonant syllables does not reflect most real life memory activities where what we are trying to remember is meaningful
so we might say this study lacked external validity
however, we do sometimes try to remember fairly meaningless things such as phone numbers, so the study is not totally irrelevant
What is the Multi-Store Model of Memory?
An explanation of memory that sees information flowing through a series of storage systems.
What is the first part of the MSM?
The sensory store
What is the second step of the MSM?
Attention
What is the third step of the MSM?
Short term store (STM)
What is the last step of the MSM?
Long term store (LTM)
What is the sensory store?
Sensory stimulus from the environment will pass through the sensory register e.g. sights, smells, sounds
Within the sensory register there are 5 stores fro each of the senses. the main stores are iconic (visual info) and echoic (auditory info. the coding is modality specific and said to be raw or unprocessed information
unknown (but supposedly unlimited)
What is short term memory?
known as limited capacity store of memory of 7 plus or minus 2 chunks of information - limited duration of about 20 seconds
information coded acoustically. maintenance rehearsal occurs when something is repeated over + over again - only way info can be kept in STM. info is lost if not rehearsed. longer rehearsal leads to the information to pass to the LTM
What long term memory?
The permanent memory store (duration) - capacity thought to be unlimited. information is coded semantically. memories that have been rehearsed for a long period of time are stored in LTM
when we want to recall from our LTM we have to transfer it back to the STM by a process called retrieval. no memories are recalled straight from LTM
What is a strength of the MSM?
case study support
Clive Wearing suffered an illness which affected his hippocampus and caused him to suffer from amnesia
CW is unable to form new memories, failing to transfer information from the short term to long term, suggesting this component is not functioning
however, he is able to retrieve e.g his wife’s name
this is a strength of the MSM, supporting the validity of the separate existence of short term and long term memory stores
What is a limitation of the MSM?
case studies suggesting its too simplistic
HM suffered an injury as a child which caused him to have to least 10 seizures a day. he had an operation to remove his hippocampus to reduce the number the number of epileptic seizures
this affected HM’s memory as he could not remember the name of the doctor who helped him but he could improve the star tracing task he conducted multiple times. this suggests that there are declarative and procedural memories
this is a limitation of the MSM as it doesn’t consider the fact that there are different types of LTM
however, this is a case study and cannot be generalised to everybody who suffers with a memory disorder.
Why did Tulving create the model?
The MSM is too simplistic and rigid. There are 3 LTM stores rather than just one which all contain different information.
What are the types of memory?
declarative and non-declarative
semantic and episodic
procedural
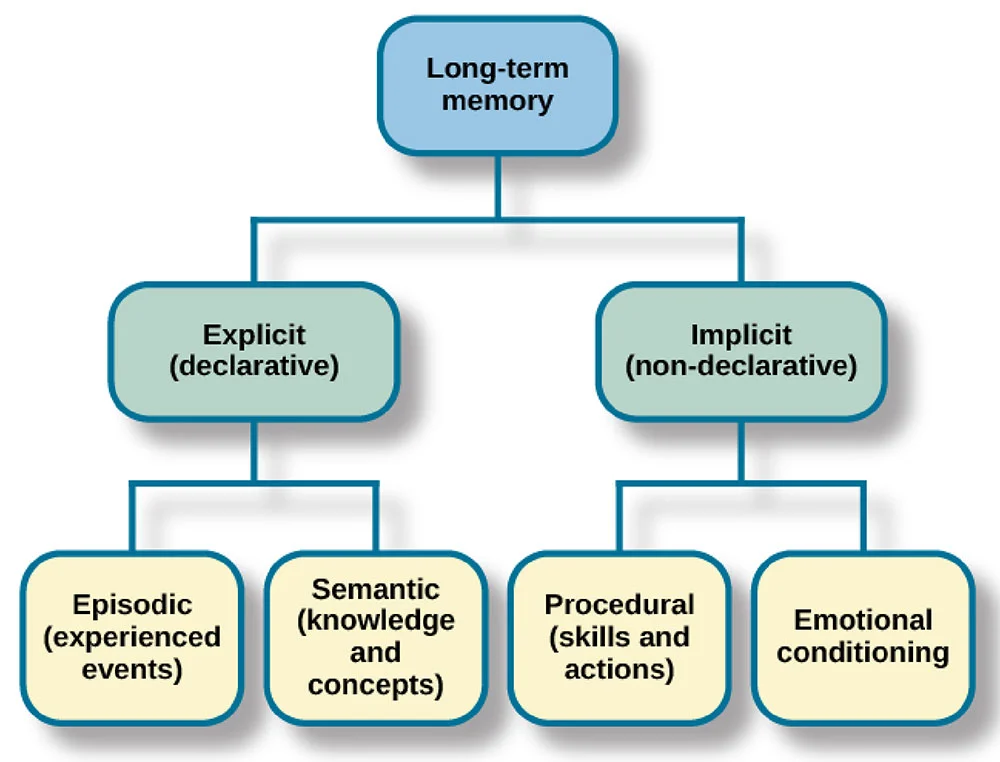
What does the episodic memory contain?
The ability to recall events from our lives e.g your last visit to the dentist, the last concert you went to, what you had for breakfast this morning
Why is the episodic memory complex?
they are time stamped - memories are recalled based on when they happened
an episode will include several elements - people, places objects and events
you have to make a conscious effort to recall episodic memories - it can take time
What does the Semantic memory mainly contain?
Knowledge of the world
What else does the semantic memory contain?
the stored knowledge can be about anything
understanding of key concepts
these memories are not time stamped
semantic memories are always being added to
What does procedural memory mainly contain?
The memory for actions, skills or how to do anything e.g driving or riding a horse
What else does the procedural memory contain?
these kinds of memories can be recalled without conscious awareness
the ability to do such things relies on procedural memory
some of the actions that are processed by procedural memory can be hard to explain to others e.g how to ride a bike
What is a strength of types of long term memory? (nomothetic + idiographic)
it takes a nomothetic and idiographic approach
in creating universal laws of cognitive processes, including the different types of long term memories we all possess, it takes a nomothetic approach
however, in the use of case studies, such as HM and Clive Wearing, it takes an idiographic approach, studying one person in as much detail as possible to gain an in depth understanding
this is a strength as it is able to combine the positives pf both approaches to understand memory
What is another strength of types of long term memory? (case study support)
case study support
HM suffered an injury as a child which caused him yo have at least 10 seizures a day, he had surgery to remove his hippocampus to reduce the number of seizures
this affected HM’s memory as he could not remember the name of the doctor who operated on him, but he could improve at the star tracing task he conducted multiple times
this is a strength as it increases the validity of the idea
What is the last strength of types of long term memory? (brain scan evidence)
brain scan evidence
research has shown that different parts of the brain are active when accessing episodic, semantic and procedural memory
Episodic memory has been associated with the hippocampus and temporal lobe, semantic memory is associated with the temporal lobe and procedural memory is associated with the cerebellum and motor cortex
this is a strength as it suggests that different brain regions are responsible for the different types of LTM, supporting the idea that our LTM is made up of 3 different categories
What does the Working Memory Model explain?
The WMM is a model of how the STM is organised and how it functions. it focuses on the part of the mind that is active when we are temporarily storing and manipulating information
The MSM is too simplistic, this is why the WMM was developed
What does the central executive do?
An attentional process
monitors incoming information
makes decisions and directs info to a specific slave system
limited storage capacity and can deal with any sensory modality
What does the visuospatial sketchpad do?
stores visual and/or spatial information when required
limited capacity - about 3 to 4 objects
divided info - visual cache - stores visual data e.g colour and shape. inner scribe - records arrangement of objects in the visual field
What does the Episodic buffer do?
temporary store for information - integrates visual, spatial and verbal information
maintains a time sequence - records events that are happening
limited capacity of 4 chunks
What does the Phonological loop do?
processes auditory information - the coding for this slave system is acoustic
subdivided into: the phonological store - stores acoustic data for limited period, inner ear - the articulary rehearsal system - allows maintenance rehearsal repeating sounds or words in a loop. capacity around 2 seconds
What is a strength of the WMM? (dual task performance)
supporting evidence from dual task performance studies
this supports the separate existence of the visuospatial sketchpad. Baddeley showed that ppts had more difficulty doing 2 visual tasks (tracing a light and scribing he letter f) than doing both visual and verbal at the same time
this is because both slave systems are competing with each other
this is a strength of the WMM as it supports the separate existence of the phonological loop and the visuospatial sketchpad
What is a limitation of the WMM? (lack of clarity)
lack of clarity over the central executive
cognitive psychologists suggest that this component of the WMM is unsatisfactory and does not really explain anything
Baddeley recognised this when he said ‘it was the most important but least understood component of the working memory’. the central executive needs to be more clearly specified than just being simply ‘attention’. for example some psychologists suggest it may consist of separate components
this is a limitation of the WMM as it lacks validity as not all the components have been fully explained
What is another strength of the WMM? (case study evidence)
case study evidence
Shalice and Warrington completed a case study of a patient, KF, who suffered brain damage
he had poor STM ability for verbal information but he could process visual information normally presented visually ie he had difficulty with sound but her could recall digits and letters
this is a strength for the WMM because it suggests that there is at least one store for auditory information and one store for visual information, in the case of KF his phonological loop had been damaged but his visual spatial sketchpad was still functioning.
What is interference?
A process that affects memory recall in which specific memories interfere with the retrieval of other memories
What is proactive interference?
Old information prevents new information from being recalled.
What is retroactive interference?
New information prevents an old piece of information from being recalled.
Describe Keppel and Underwood’s study on proactive interference.
Aim - to investigate the effect of proactive interference on LTM
Method - ppts presented with meaningless 3 letter consonant trigrams at different intervals. to prevent rehearsal, ppts had to count backwards in threes before recalling
Results - ppts typically remembered trigrams that were presented first
Conclusion - proactive interference occurred as memory for earlier consonants interfered with memory for new consonants
Describe Baddely and Hitch’s study on retroactive interference.
Aim - to investigate retroactive interference in everyday memory
Method - rugby players who played every match + some who missed matches due to injury - length of time form start to end of season. players were asked to recall names of teams played against earlier in season
Results - players who played most games forgot more games than those who had fewer games.
Conclusion - this was result of retroactive interference as the learning of new info interfered with memory of old info.
What is a strength of research into retroactive interference? (high ecological validity)
high ecological validity
they used real life memories involving rugby players, asking them to recall teams they played earlier in the season.
this involves ppts actual memories of events and accounts for time taken between learning and recall
this is a strength as we can be sure this type of forgetting happens in the real world not just a lab
however, research into proactive interference is unable to so this as ppts are being assessed on artificial study, which doesn’t leave a gap between learning and retrieval
What is a limitation of research into interference? (insight)
it only provides insight into similar information
the results of B + H demonstrate retroactive interference in rugby players trying to recall team names from earlier in the season and K + U demonstrate proactive interference when trying to learn 3 letter consonant trigrams
both of these examples highlight interference effects of similar information
this is a limitation ad research is limited in its real world application and are unable to explain forgetting in other situations
What is retrieval failure?
forgetting occurs when we don’t have the necessary cues to access memory. when information is placed in memory, associated cues are stored at the same time so that we can retrieve the information
What is context dependent failure?
Environmental/external cues are missing at the time of retrieval which were present at the time of transfer from STM to LTM
What is state dependent failure?
Emotional state/internal cues are missing at the time of retrieval which were present at the time of transfer from STM to LTM
Describe research into context dependent failure
Method - 18 ppts - 13 male, 5 female. from a university diving club they were divided into 4 conditions. 1- learning words on land + recalling on land. 2- learning on land + recalling underwater. 3- learning underwater + recalling underwater. 4- learning underwater + recalling on land. repeated measures.
results - words learned underwater better recalled. underwater + learned on land better on land
Conclusion - environmental cues improve recall
Describe research into state dependent failure
Method - ppts tasked with learning list of words from text then asked to recall later. 4 conditions, 1- learned words after taking antihistamine + recall after taking AH. 2- learned words without taking AH and recall without taking AH. 3- learn words after taking AH and recall without AH. 4- learn words without AH and recall after taking AH
Results - in conditions were learning and recall matched, memory improved and when physiological state of ppts different recall was worse
Conclusion - when physiological/emotional cues are presented at time of transfer are missing at time of retrieval, state dependent forgetting is likely to occur
What is a limitation of research into context dependent forgetting?
G + B used repeated measures design
during their experiment, each diver took part in all four conditions. it could be possible that the divers worked out aim of experiment and displayed order effects. by 4th trial, ppts recall may have improved as a result of completing experiment multiple times
with a sample of just 18 divers, conclusions drawn should be treated with caution
this is a limitation because context examined in their study is extreme and provides little insight
What is a strength of explanations for forgetting?
practical application
understanding that cues being absent at time of retrieval compared to transfer can create forgetting allows police forces to use this info when interviewing eyewitnesses
the cognitive interview has as a result been created by psychologists to overcome forgetting that can take place in a police interview.
What is a limitation of theories into forgetting?
nomothetic approach
research into forgetting is usually done on a small sample with similar characteristics which is then generalised to all humans
an idiographic approach to investigating forgetting using ppts of different ages and cultures may give more insight into this complex phenomenon
this is a limitation as by trying to create universal laws about forgetting, it may not be applicable to all ages or cultures
How can anxiety have a negative impact on EWT?
When someone becomes over-aroused, this then negatively affects out attention as it reduces our ability to attend to cues in a situation.
What is the weapon focus effect?
We can get tunnel vision where all of our attention is drawn to the threat and we miss other important details.
How can anxiety have a positive impact on EWT?
When the fight or flight response is triggered, which causes an increase in arousal, this increase in arousal increases alertness and dilates pupils, which allows for people to attend to cues in situations.
Describe Yuille and Cutshall’s study
Procedure - investigated effect of anxiety in a real life shooting. 21 witnesses originally interviewed by police and 13 witnesses took part in study, 4-5 months later
Findings - witnesses were asked to rate anxiety on a scale, those who reported high anxiety were 88% accurate, and those who reported low anxiety were 77% accurate. the witnesses were accurate in their accounts 5 months later - little change found in testimonies. all major details remained same
Conclusion - these results refute weapon focus effect and results of Johnson and Scott show that IRL cases of extreme anxiety - accuracy of EWT is not affected
What does Yerkes-Dodson law state?
There is an optimum level of anxiety for accurate EWT - people who are not at all stressed and people who are very stressed will be less accurate eyewitnesses than those who are under a moderate amount of stress.
What is a limitation of research into the positive effects of anxiety on EWT?
the measurement of the independent variable
in the yuille and cutshall study, ppts were asked to rate their anxiety on a scale of 1-7, the issue is that this is very personal and subjective, everybody experiences anxiety differently, someone may say that they were not stressed but the same incident could have caused a higher level stress for someone else
this is a limitation as it means that when measuring the effects of anxiety on EWT it is very hard to measure anxiety objectively across all ppts
furthermore as the research took place 4-5 months after the real life shooting, ppts may misremember how anxious they were affecting the internal validity of the findings
What is a limitation of research into the negative effects of anxiety on EWT?
lacks ecological validity
Johnson + Scott’s study took place in the reception area outside a lab this means that ppts may have anticipated something was going to happen
this is a limitation because it could have affected the accuracy of their judgements
however other research refute the finding of J + S and suggest that their results do not represent real life cases of anxiety
What is a limitation of research into the effects of anxiety on EWT?
ethical issues
ppts were deceived about the nature of experiment and not protected from harm. J + S exposed some of the ppts to a man holding a bloody knife, which could have caused extreme anxiety
this is a limitation as the ppts may have left the experiment feeling stressed
furthermore, the researchers had to cause anxiety to measure the effect it had on EWT
How do you improve the accuracy of EWT using the cognitive interview - Report Everything
How - witnesses are encourage to include every detail of the event even if it seems irrelevant
Why - trivial details may trigger other important memories that may act as cues - witnesses are retrieving episodic and semantic long term memories - which is aided by trying to retrieve as much information as possible using any cues they can - context + state dependent
How do you improve the accuracy of EWT using the cognitive interview - Reinstate the context
How - witnesses should return to original crime scene in their mind and imagine the environment and their emotions
Why - this technique is based on context-dependent failure - by getting witnesses to recall every detail, this may help them retrieve more information based on cues they made in that environment
How do you improve the accuracy of EWT using the cognitive interview - Reverse the order
How - events should be recalled in a different chronological order
Why - prevents people from reporting what they expect to happen and to focus on the actual event, also prevents dishonesty - this avoids witnesses relying on schema and encourages witnesses to use cues from context to help accurately retrieve information
How do you improve the accuracy of EWT using the cognitive interview - Change perspective
How - witness recalls events another perspective e.g. how the event would appear to another witness
Why - the aim is to disrupt expectations or schemas about the event - schemas about an event can create expectations and this can affect the accuracy of recall - changing perspective makes a witness see both context and state of the incident differently - this may allow them to use more cues from the context
What is a limitation of the cognitive interview? (time consuming)
time consuming
police forces need to undergo extensive training to ensure they can properly hep witnesses improve accuracy
for example, they would need to be supported in how to assist witnesses reinstate the context to help trigger cues in memory - this can be time consuming and expensive to already stretched police forces
this is a limitation as it means the proper version of the cognitive interview may not be used, reducing its effectiveness
What is a strength of the cognitive interview?
research supporting its effectiveness
Fisher et al researched the effectiveness - 16 experienced detectives recorded a selection of their interviews using standard interview technique. the detectives were divided into 2 groups. 1- trained to use cognitive interview, control group trained to use standard interview
after training interviews were recorded + analysed, trained detectives elicited 46% more info after cognitive interview training in comparison to control group - over 90% was found to be accurate
these results support the findings of Fisher, using real police interviews provide support for the effectiveness of the cognitive interview
What is another limitation of the cognitive interview? (environmental reductionism)
environmental reductionism
there could be many explanations for difficulties that victims and eyewitnesses experience in recalling an event apart from the technique that is actually used to interview them
for example the research does not address a possible culture bias, in that the researchers and the ppts are from a western culture but the results are taken to apply to all cultures