Unit 4 Chemistry Past Paper Questions
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
1
New cards


2
New cards


3
New cards

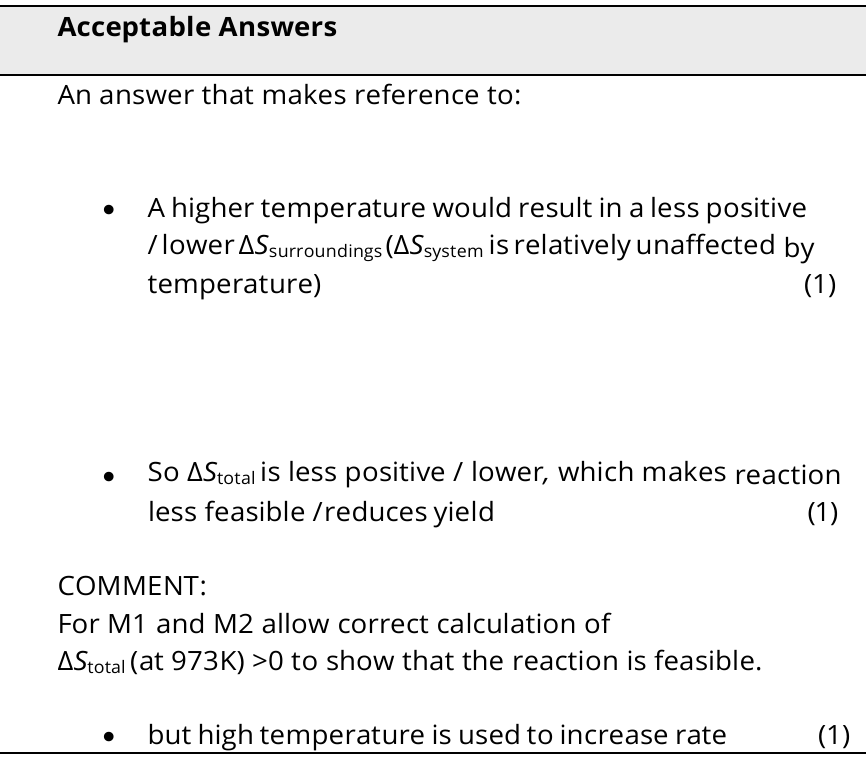
4
New cards
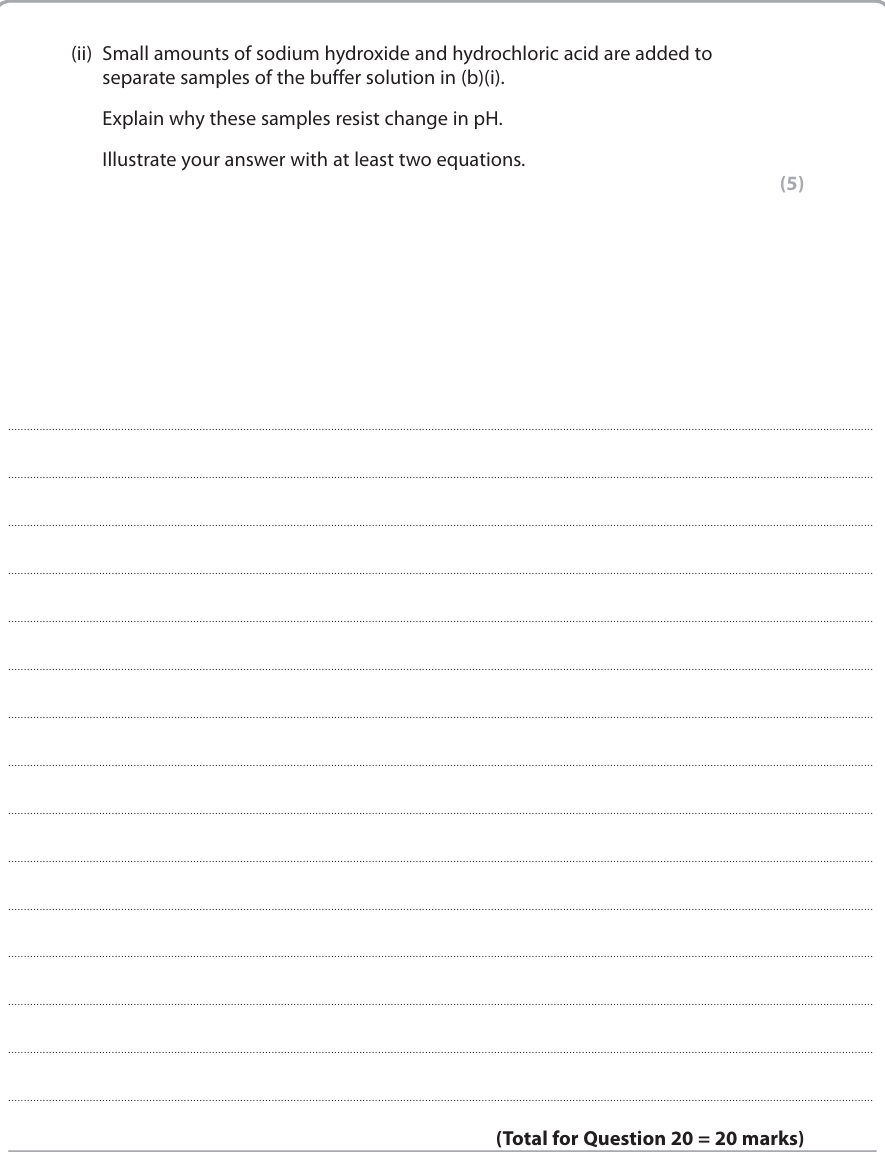

5
New cards


6
New cards


7
New cards


8
New cards
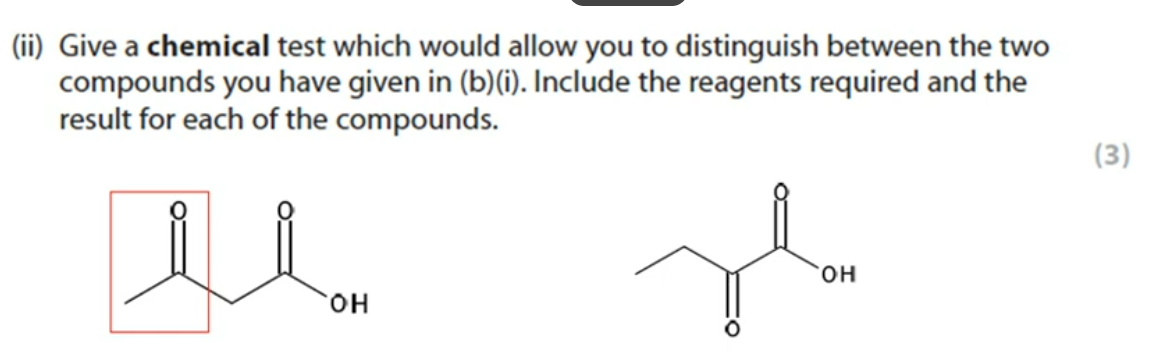
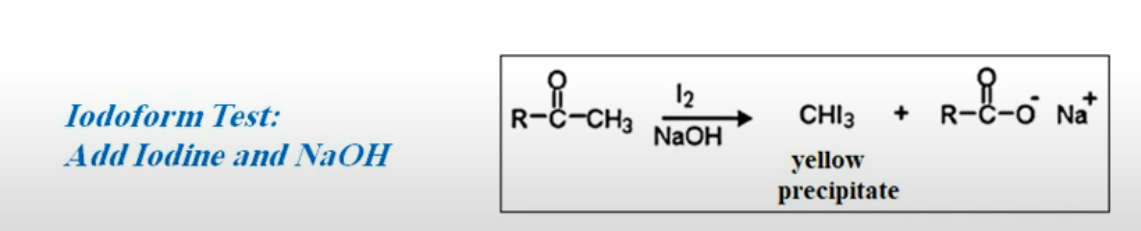
9
New cards
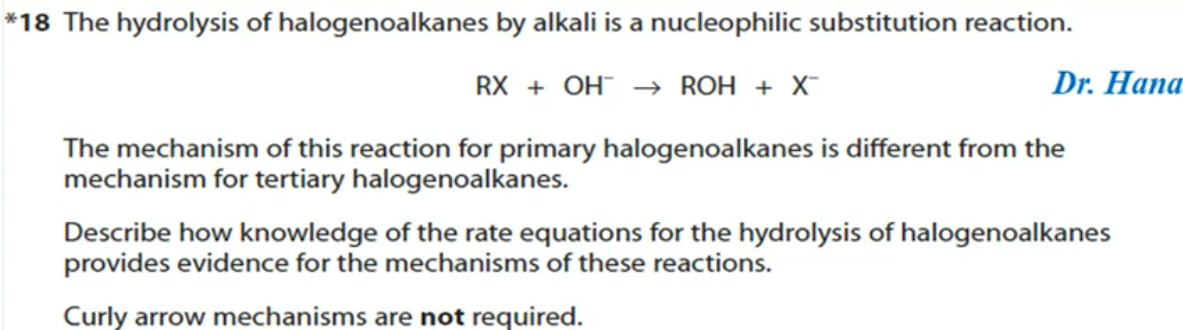
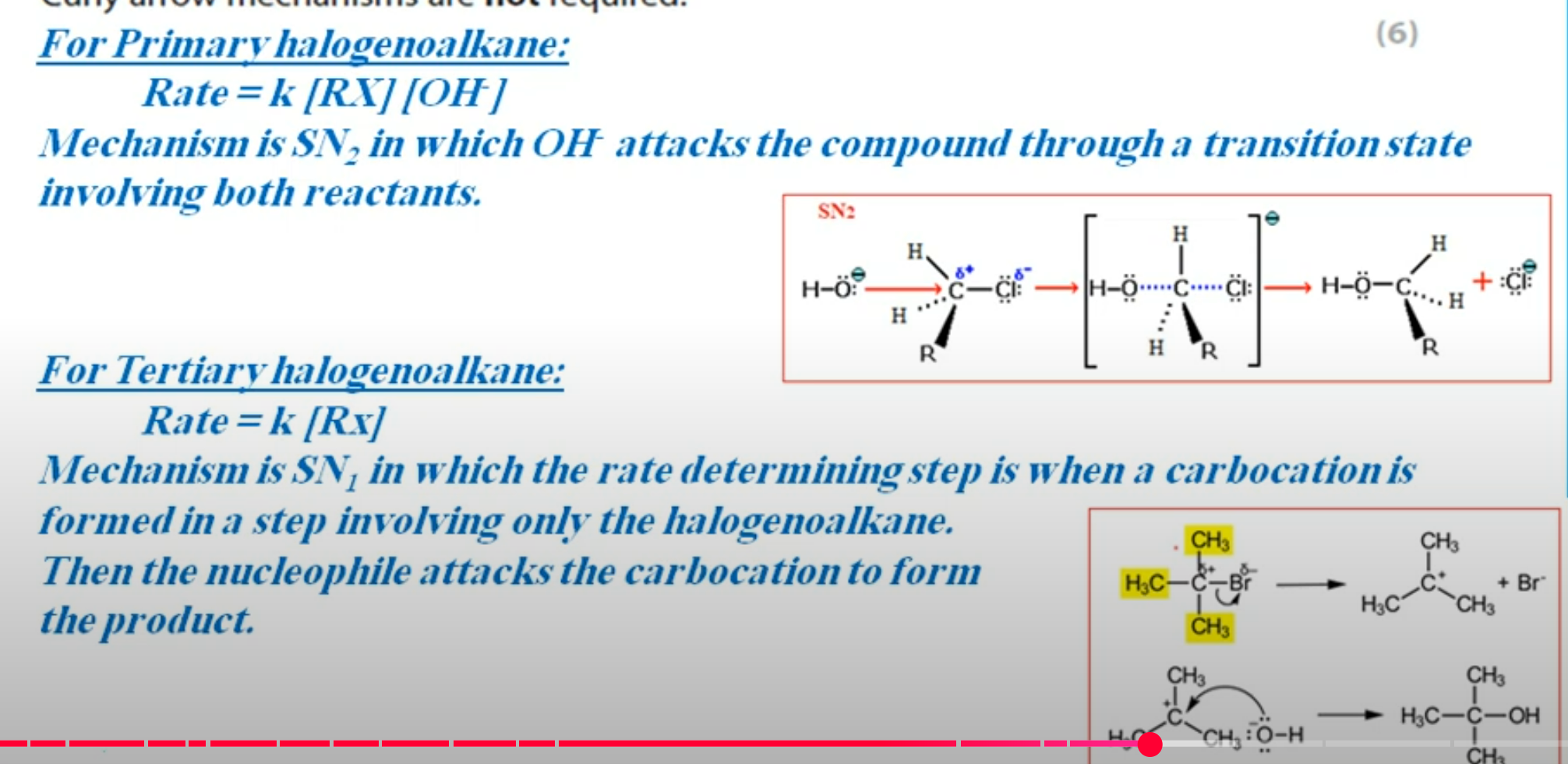
10
New cards


11
New cards

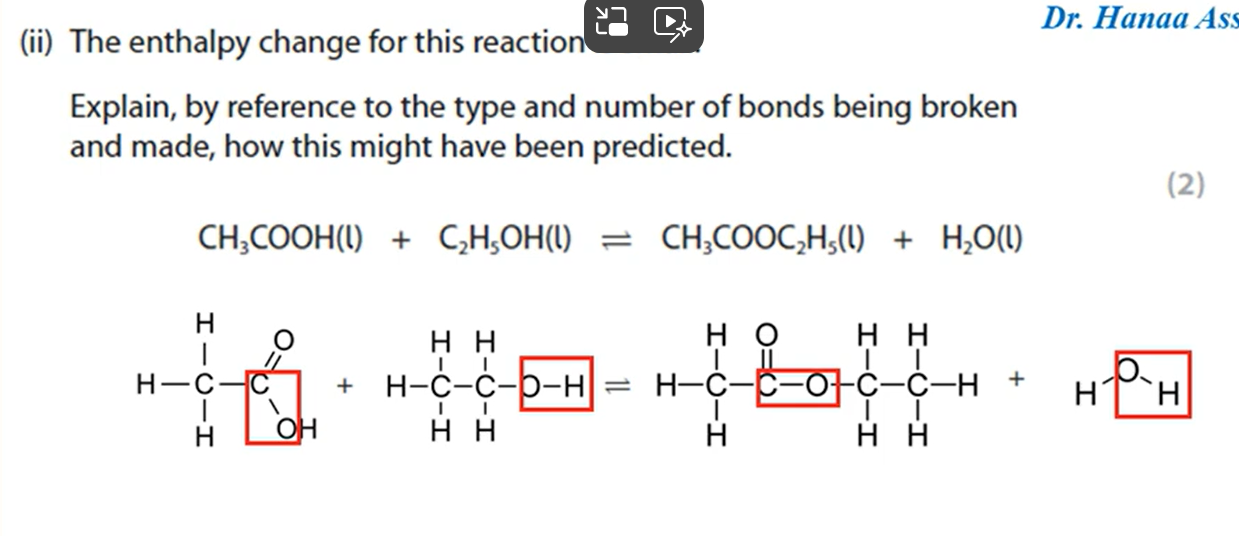
12
New cards
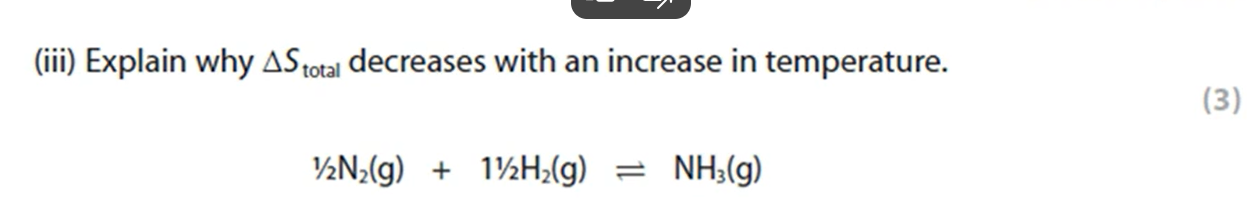
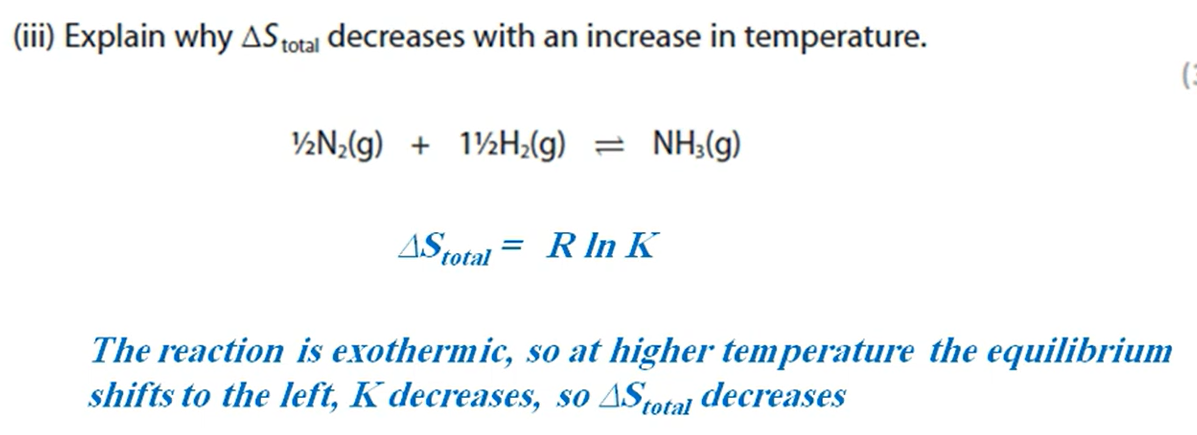
13
New cards
Why would a product of a reaction not be optically active even though it contains a chiral carbon atom? (3 marks)
The nucleophile can approach from above and below the plane of the compound equally to form a racemic mixture of two enantiomers.
These enantiomers will rotate the plane of polarised light in opposite directions and cancel each other’s motion out, leading to no optical activity.