biology Yr 11 final exam IB
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:47 PM on 5/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
antibodies
y-shaped proteins with binding sites produced by plasma cells in response to the presence of an antigen
2
New cards
antigens
molecules the body identifies as foreign based on surface proteins and molecules
3
New cards
disease modes of transmission
vectors (from another species)
vertical (mother to fetus)
vertical (mother to fetus)
4
New cards
antibiotics
compounds blocking growth and reproduction of bacteria. only works on bacteria. targets structures only bacteria have (eg, cell wall)
5
New cards
vaccines
injections containing weakened/killed pathogens. stimulate immune system and prompt the body to produce antibodies to the disease.
6
New cards
eukaryotes
eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles with DNA. all living organisms except bacteria.
7
New cards
prokaryotes
bacteria, unicellular, simplistic.
\
\
8
New cards
prokaryote vs prokaryotic
prokaryote = the organism
prokaryotic = type of cell
prokaryotic = type of cell
9
New cards
viruses
not made of cells and require a host. particles of nucleic acid, protein and lipids. are the core of DNA/RNA. coated in a protein called capsid.
10
New cards
pathogen
organism or agent able to cause disease
11
New cards
internal fertilization vs external fertlization
internal - fusion of gametes inside the body of a parent
external - fusion of gametes outside the body of a parent.
external - fusion of gametes outside the body of a parent.
12
New cards
mitosis
form of cell division that produces 2 genetically identical daughter cells.
diploid (2n) = full set of chromosomes in each cell.
\
diploid (2n) = full set of chromosomes in each cell.
\
13
New cards
reasons for mitosis
maintenance (repair/replacement)
organism growth
organism growth
14
New cards
SRY - gene
located on y-chromosome
causes gonads to secrete testosterone causing male development.
causes gonads to secrete testosterone causing male development.
15
New cards
zygotes
fertilised cell (egg and sperm)
16
New cards
gametes
reproductive cell of an animal or plant (egg and sperm)
a body cell divides so there is half the genetic info in the process of meiosis.
a body cell divides so there is half the genetic info in the process of meiosis.
17
New cards
mRNA
molecule containing the instructions or recipe that directs the cells to make a protein using its natural machinery.
18
New cards
how many chromosomes does DNA have?
* 46 chromomes
* 23 pairs
* 23 pairs
19
New cards
what is a chromosome
a structure found inside the nucleus of a cell.
20
New cards
type of neurons
motor, sensory, relay
21
New cards
motor neuron
communicate info from the brain to tissues and organs throughout the body allowing for movement
22
New cards
sensory neuron
take sensory info from environment
23
New cards
relay neuron
the majority. transmit info from between sensory and motor neurons.
24
New cards
nodes of ranvier
gaps between the myelin sheaths. electric impulses traveling down the axon are able to jump between the nodes
25
New cards
function of nerve fibers
transmit signals over long distances very quickly. to facilitate this, nerve axons are covered by an insulating lipid myeling sheath protected by schwann cells.
26
New cards
cell body
contains the nucleus and majority of the organelles and cytoplasm.
27
New cards
axon
long, narrow ‘arm’ that carries electric signals
28
New cards
dendrites
short, balanced fibres that receive and transmit signals to other cells.
29
New cards
neurons
cells that transmit electrical signals to/from the brain and muscle/glands.
30
New cards
effector
a body part that carries out a response to the stimulus
31
New cards
how do neurons transmit info?
in the form of impulses
32
New cards
spinal chord
sends an impulse to the appropriate effector which will cause the response to the stimulus.
33
New cards
brain
receives nerve impulses from receptors that have detected a stimulus.
34
New cards
chemoreceptor
responds to specific chemicals
35
New cards
temp receptors
respond to changes in temp
36
New cards
photo (light) receptors
respond to changes in light energy
37
New cards
receptor
specialised sensory cell that can detect a stimulus in an organisms environment. send signals to the CNS
38
New cards
function of the nervous system
detects, relays and co-ordinates info about an organisms internal and external environment
39
New cards
nervous system structure
CNS - brain + spinal chrod
PNS - attached to CNS, nerves and receptors
PNS - attached to CNS, nerves and receptors
40
New cards
heterozygous
different alleles
41
New cards
trait
a characteristic a parent can pass on to an offspring. is controlled by the proteins made from DNAs instructions
42
New cards
asexual reproduction
produces genetically identical clones. comes from one parent
43
New cards
sexual reproduction
process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote (genetically different offspring.)
44
New cards
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism. written in letters and represents alleles inherited.
45
New cards
phenotype
expressed genotype, physical looks
46
New cards
DNA full name
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
47
New cards
where is DNA found?
in the nucleus of a eukaryote.
in the cytoplasm of a prokaryote
in the cytoplasm of a prokaryote
48
New cards
what does DNA do?
controls all activities of a cell
49
New cards
whats DNA made of?
nucleic acid made of smaller building blocks called nucleotides
50
New cards
parts of a nucleotide
1. deoxyribose structure (5 carbons, pentagon)
2. phosphate group
3. nitrogen base
51
New cards
nitrogenous bases
Adenine + thymine
Cytosine + Guanine
Cytosine + Guanine
52
New cards
what is a gene
a segment of DNA. each gene controls a different trait. humans have over 20,000 genes.
53
New cards
genomes
a list of all ATGC bases coded into our chromosomes. whole genetic info of an organisms. used in GMOs
54
New cards
homozygous
same allele
55
New cards
heredity
set of traits an organism receives from it’s parents
56
New cards
alleles
a pair of two or more genes at a given area of a chromosome.
57
New cards
homeostasis
biological state of equilibrium. the nervous and endocrine systems are responsible from maintianng it.
58
New cards
gonads
develop into either testes or ovaries
59
New cards
meiosis
produces gametes
4 genetically unique daughters.
haploid (n) = half the number of chromosomes in daughter cells
4 genetically unique daughters.
haploid (n) = half the number of chromosomes in daughter cells
60
New cards
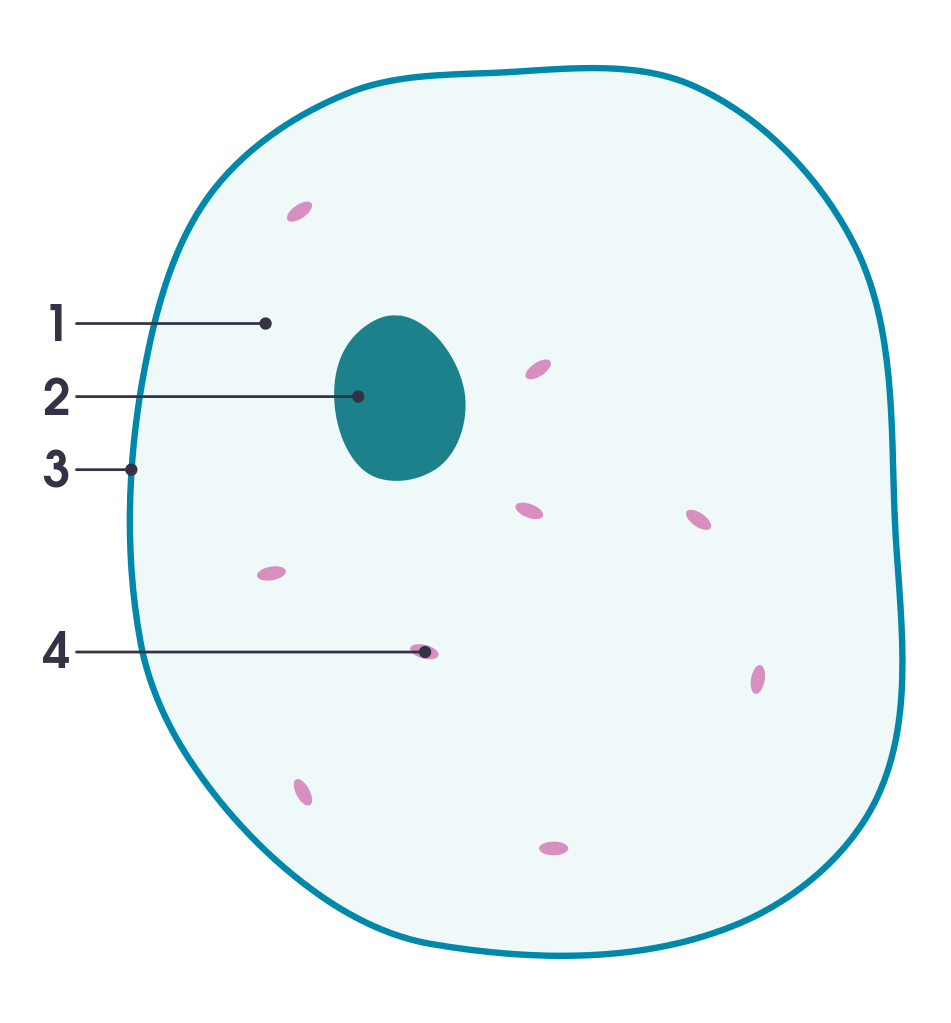
cell strcuture
1. cytoplasm
2. nucleus
3. cell membrane
4. mitochondrion
61
New cards
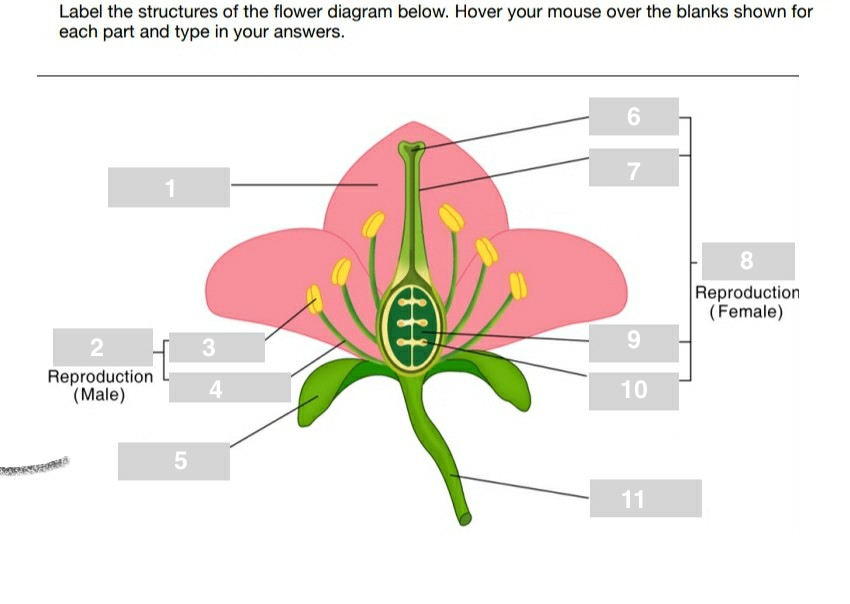
parts of a flower
1. petal
2. stamen
3. anther
4. filament
5. sepal
6. stigma
7. style
8. pistil
9. ovary
10. ova (eggs)
11. stem
62
New cards
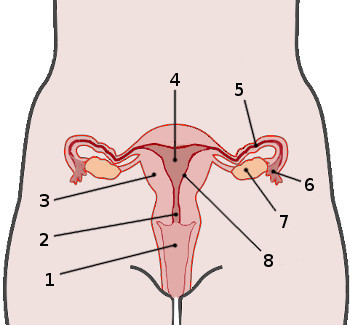
female reproduction
1. vagina
2. cervix
3. myometrium
4. uterus
5. fallopian tube
6. -
7. ovary
8. endometrium
63
New cards
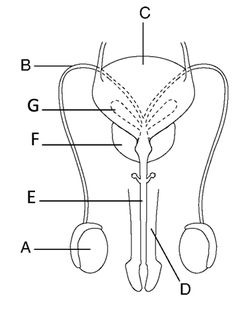
male reproduction
a. testicles
b. vas deferens
c. bladder
d. glans
e. epyidimus
f. prostate
g. seminal vesicle
b. vas deferens
c. bladder
d. glans
e. epyidimus
f. prostate
g. seminal vesicle