Biology Exam 2
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
prokaryotic cell
simple cell w/ no membrane-bound organelles. They are unicellular, no nucleus
Eukaryotic cells
membrane-bound organelles which each carry out specific functions. These organelles allow cells of a multi-cellular organism to take o a specific task as a part of a greater whole. has a nucleus
What structures do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common?
cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes
plasma membrane
an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; selectively permeable (in both cells)
fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane; components of plasma membrane as mosaic- phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, carbohydrates
Cytoplasm
the entire region between the nucleus and the plasma membrane
Ribosome
Makes proteins in both cells
Which is bigger prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
eukaryotes are bigger
pili
short, hairlike protein structures on the surface of some bacteria
Flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
capsule
A sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces.
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
nucleoid
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.
cytosol
The soluble portion of the cytoplasm, which includes molecules and small particles, such as ribosomes, but not the organelles covered with membranes.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
organelles don't just float in cells
3 fibers of cytoskeleton
microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
Mircotubules
made of tubulin proteins; arranged into thin, hollow tubes;
Job is to maintain cell shape, cell motility, chromosome movement in cell division, organelle movement
microfilaments
Made of the protein actin; arranged into thin, solid rods;
Job is to maintain cell shape, change cell shape, muscle contraction, cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells, cell motility, division of animal cells
intermdiate filaments
made of different proteins;
Job is to maintain cell shape, anchorage of nuclues and certain organelles, formation of nuclear lamina
what does the nucleus protect
DNA
Chromitin
the DNA and protein components of chromosomes, visible as clumps or threads in nuclei
What are ribosomes made of?
rRNA and proteins (2 subunits: large and small)
why are blood cells red
hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that reversibly binds oxygen.
What are membranes made of?
phospholipids, cholesterol, carbohydrates, proteins
Lysosome
digestive vesicles (recycle) very acidic so it will only work at a low pH so it can't eat a whole cell
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
theory of endosymbiosis
This theory states that cell organelles, like mitochondria, were once tiny, free-living prokaryotic organisms that took up permanent residence inside larger prokaryotic organisms.
Autophagy
A process in which lysosomes decompose damaged organelles to reuse their organic monomers
Peroxisomes
metabolizes vesicles
vesicle
A membrane bound sac that contains materials involved in transport of the cell.
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area
Mitochondria
where cellular respiration occurs. In plants and animals
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis
Centrosome
to organize the cytoskeleton
endomembrane system
starts with nuclear membrane and continues physically with the ER (that is folded on itself). It also has a Golgi apparatus and plasma membrane. Vesicles will move inbetween them
Golgi apparatus
serves as a kind ofpackaging center: Transport vesicles deliver materialsto the cis face.

Plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls (through their pours) that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells.
tight junctions
-Watertight seal between cells
-Plasma membranes fused with a strip of proteins
(animal cell)
desmosome
act like spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells, the cadherins protein connect to intermediate filaments
(animal cell)
gap junction
A type of intercellular junction in animals that allows the passage of materials between cells.
intergal proteins
integrated into membrane structure and hydrophobic membrane-spanning regions interact w/ hydrophobic region of phospholipid bilayer; has hydrophilic region(s) and 1 or + mildly hydrophobic regions
Carbohydrates correlation with Plasma membranes
found exterior surface of cell and bind to glycoproteins or glycolipids, collectively called glycocalyx
What affects membrane fluidity?
Temperatures (increase temps= increase futility)
Saturation of fatty acid tails (cis double bonds in fatty acid tails make membrane more fluid unsaturated also makes more fluid)
Cholesterol (at high temp cholesterol can lower fluidity, at low temp cholesterol can increase fluidity)
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell; substances move from higher concentration to lower concentration
simple diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. uses no energy. small, nonpolar molecules can diffuse across plasma membrane
facilitated transport (diffusion)
diffusion with the help of transport proteins. Can be channels for material or carriers. does not require extra energy
channel proteins
have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or ions can use as a tunnel
carrier proteins
bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
hypertonic solution
a solution that causes a cell to shrink because of osmosis (water leaves)
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution (water goes in)
how is hypertonic and hypotonic different between animal and plant cells
in hypertonic the cell and plasma membrane shrink away from cell wall. In hypotonic solution it does not burst, instead it would just be pushed against cell wall.
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
primary active transport
3 Na attach along with an ATP that causes the Na to go to other side and one P to stay attached then 2 K attach and go to other side with the P flying off
secondary active transport
Form of active transport which does not use ATP as an energy source; rather, transport is coupled to ion diffusion down a concentration gradient established by primary active transport.
electronchemical gradient
on outside Low [K] but high [Na]. inside plasma membrane high [K] but low [Na]
proton pump
An active transport protein in a cell membrane that uses ATP to transport hydrogen ions out of a cell against their concentration gradient, generating a membrane potential in the process.
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes.
receptor-mediated endocytosis
The movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of membranous vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in; enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances.
Gibbs free energy
change in free energy, energy available to do work. measure of stability (the less of gibbs free energy the more stable it is)
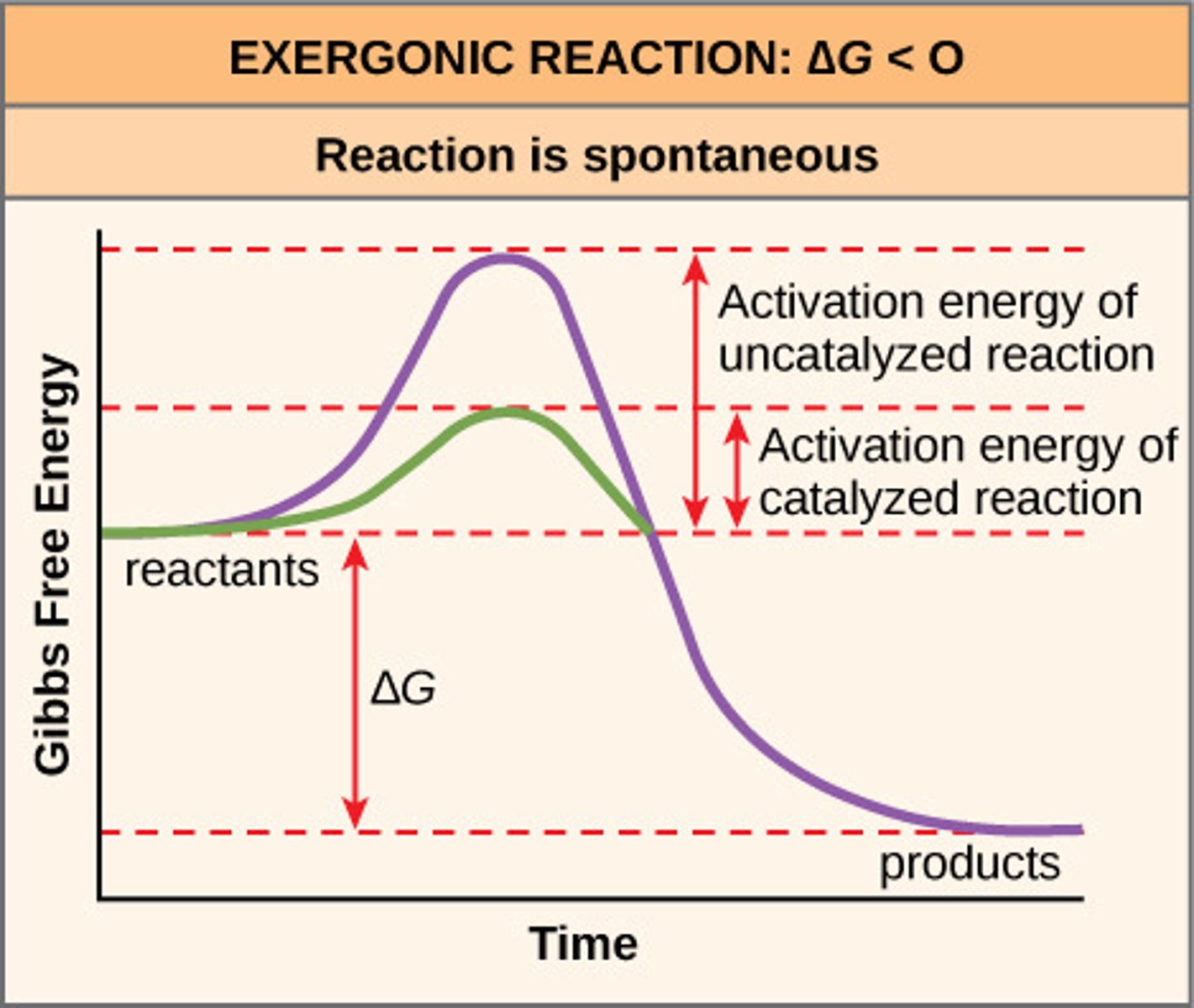
spontaneous reaction
has a negative change in free energy. a reaction that will happen on its own
exergonic reaction
spontaneous. energy released
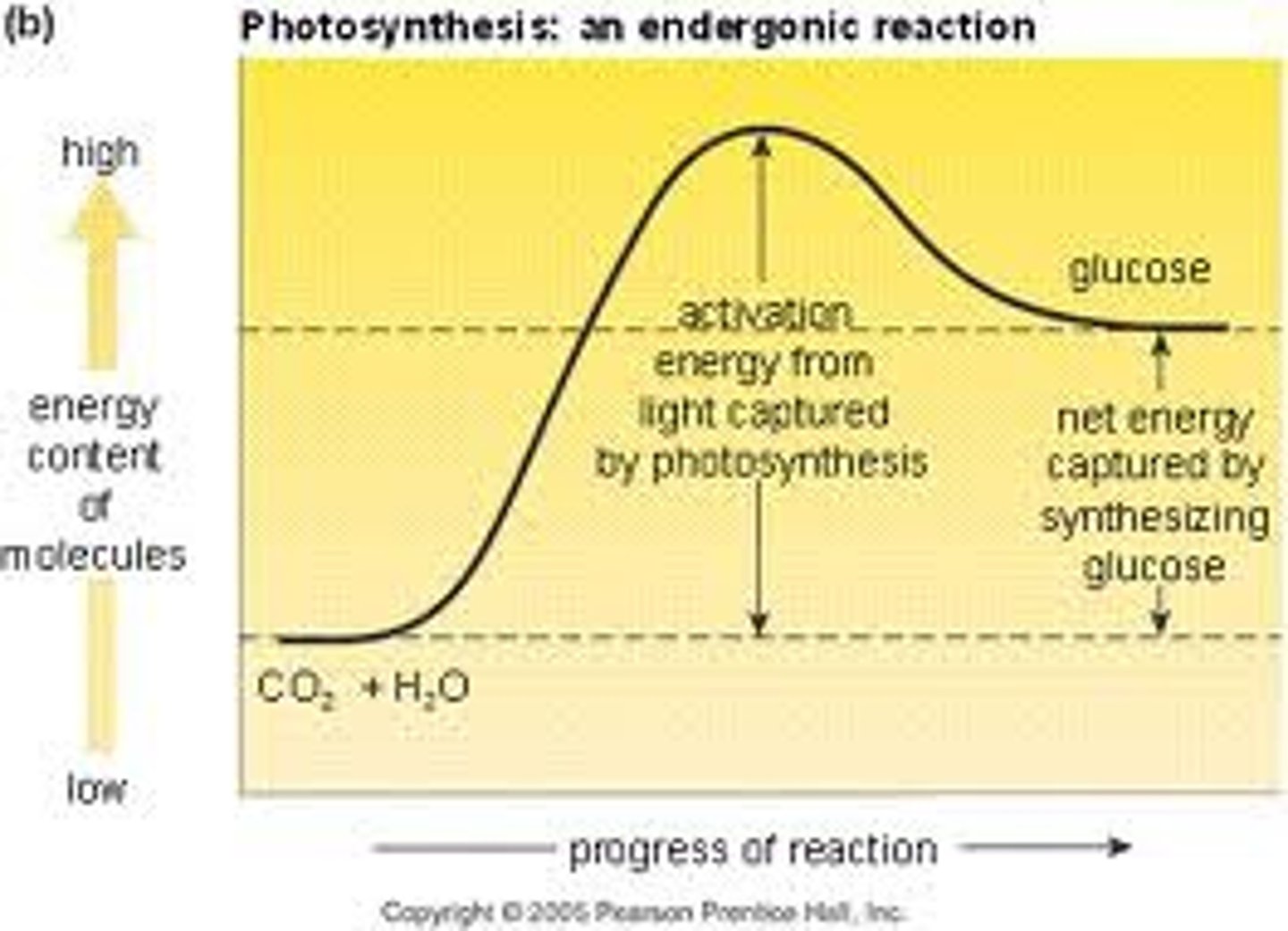
endergonic reaction
non-spontaneous. energy required
endergonic reaction graph
exergonic reaction graph
Hydrolysis of ATP
Releases 7.3 kcal/mole energy to do work. Reaction favors formation of products. Energy liberated is used to drive a variety of cellular processes.
What is the purpose of energy coupling? in hydrolysis of ATP
it makes the overall reaction exergonic.
enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. Is used to lower activation energy. not a product not a reactant and cant change the free energy.
How are enzymes regulated by the cell?
by noncompetitive and competitive inhibition, allosteric change, feedback inhibition, gene expression, cellular localization and activators
redox reaction
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another; also called oxidation-reduction reaction.
oxidized
loss hydrogens
reduction
gain hydrogen
Compare substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation
both their ultimate production is ATP
substrate-level phosphorylation
The enzyme-catalyzed formation of ATP by direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism.
oxidative phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; the third major stage of cellular respiration.
What is the role of NAD+ and FAD in cellular respiration?
function as electron shuttles. keep going
What is the reduced and oxidized form of both of these coenzymes? for NAD+ and FAD
NAD+ is reduced when it goes to NADH. NADH is oxidized when it goes to NAD+.
FAD is reduced when it goes to FADH2. FADH2 is oxidized when it goes to FAD.
Glycolysis
-takes place in the cytosol.
-the inputs are glucose.
-Outputs are 2 molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH
-The glucose oxidizes.
-NAD+ reduces
Transcription of gene in nucleus → translation of mRNA in cytosol(cytoplasm) on free ribosomes → release of protein
Pyruvate oxidation
-takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
-the inputs are pyruvate.
-the output is 1carbon dioxide, 1 NADH, and acetyl CoA
-NAD+ reduces.
-pyruvate oxidizes
Citric Acid Cycle
-takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- input: Acetyl-CoA
-output: 2carbon dioxide, 3NADH, 1FADH2, and 1ATP
-isocitrate is oxidized
-NADH and FADH2 are reduced
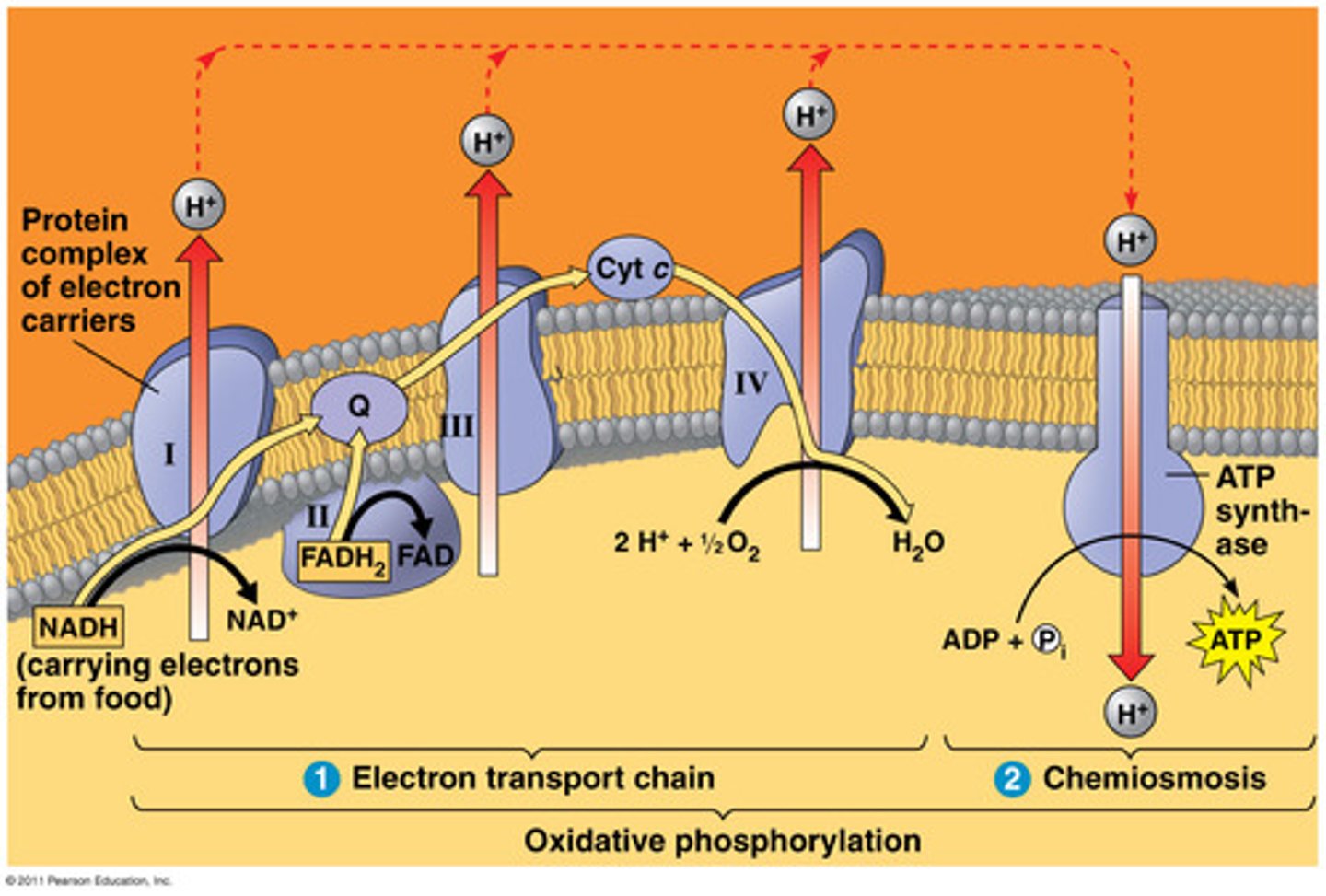
Electron Transport chain
-takes place in inner mitochondrial membrane
-input: NADH, H+, ADP, FADH2, O2
-output: NAD+, 26 ATP, FAD, H2O
-NADH and FADH2 are oxidized
-hydrogen is reduced
ETC within the thylakoid membrane
moves protons across the thylakoid membrane into the lumen. the energy is used from the electrons
ATP synthase
a channel protein that makes ATP from protons moving down their concentration gradient. The hydrogen ions will flow down (from high to low) and use the energy it makes to make ATP
two types of fermentation
alcoholic and lactic acid
What is the purpose of fermentation
to recycle back NADH to NAD+ (back to glycolysis)
lactic acid fermentation
When pyruvate has no where to go so the 2 NADH get there oxygens taken off and go with NAD+
alcohol fermentation equation
pyruvic acid→ acetaldehyde + NADH → ethanol NAD⁺
When in cellular respiration is the presence or absence of oxygen a deciding factor in which path to take?
glycolysis
where in the mitochondria the citric acid cycle and ETC take place
high H+ is the top and low H+ is at bottom
What are in the inputs and outputs for the light reactions of photosynthesis?
inputs: H2O, light, NADP+, ADP and Pi
outputs: O2, ATP, NADPH
general photosystem
composed of a reaction center surrounded by numerous light harvesting complexes
What is the difference between Photosystem I and Photosytem II?
the reactions of photosystem II occur in the Calvin cycle, whereas the reactions of photosystem I occur outside of the Calvin cycle
pigments
absorb specific wavelengths of visible light. It is there to absorb light energy
thylakoid membrane
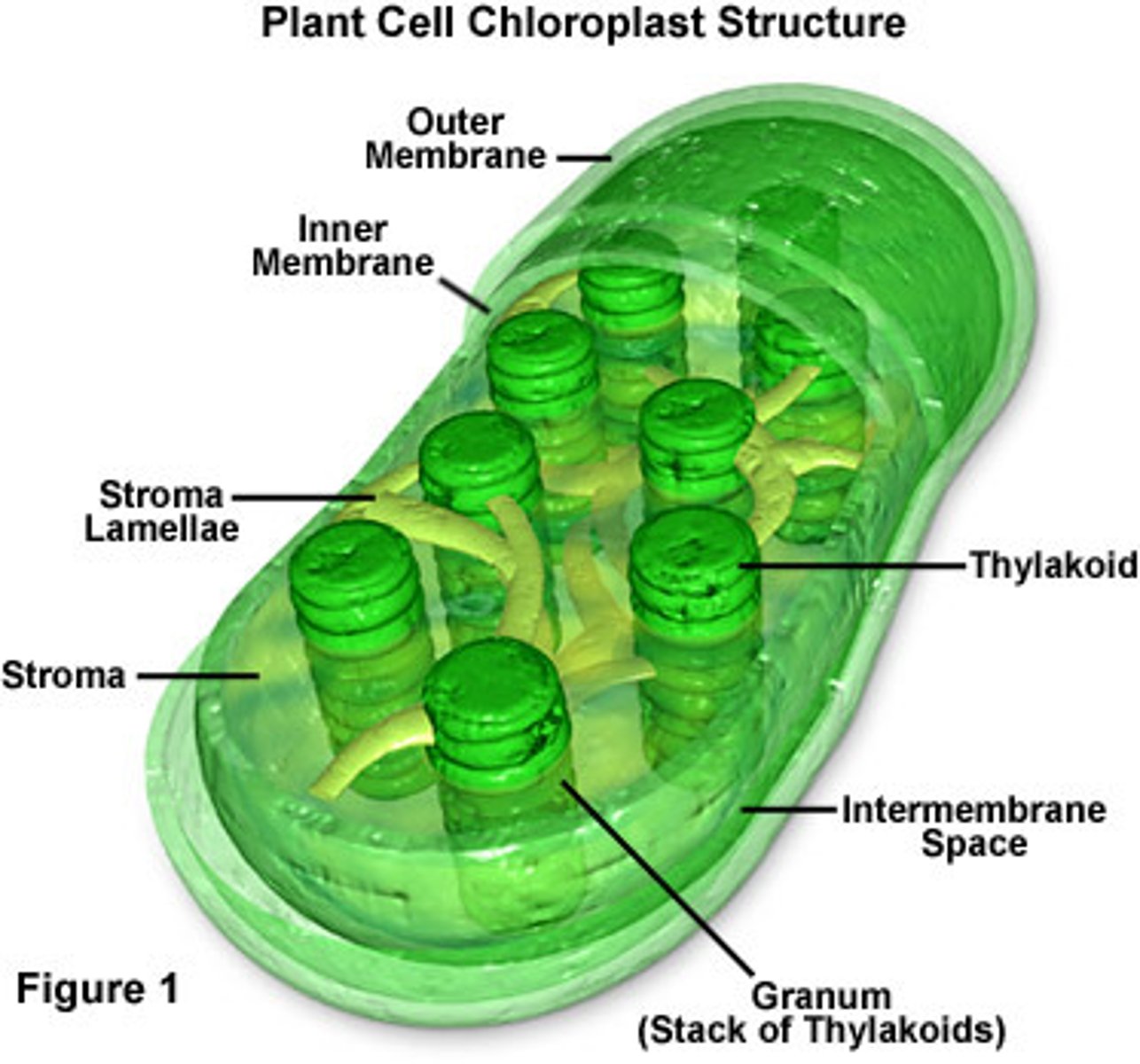
the path of electron through the light reactions
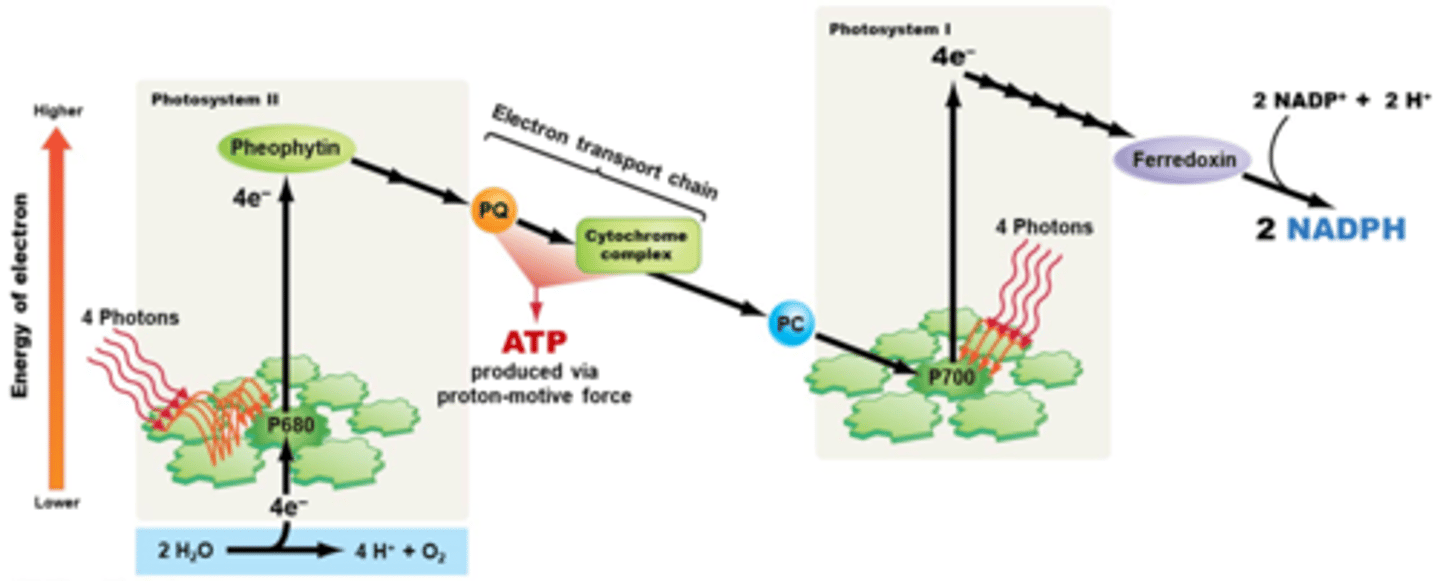
What are the inputs and outputs for the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis?
inputs: CO2, ATP, NADPH
output: ADP, NADP+
What are the three steps of the Calvin cycle
carbon fixation (takes 6 ATP), reduction (reduce 6 NADPH), regeneration (take 3 ATP)