Chapter 5: Work, Energy and Power
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Energy & Momentum
Work
Power
Speed
Work–Kinetic Energy Theorem
Conservative Forces
Nonconservative Forces
Gravitational Potential Energy
Spring Force
Hooke’s Law
Elastic Potential Energy
Unification of Gravitational and Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic Potential Energy
Equilibrium Points
Turning Points
12th
Last updated 2:22 PM on 3/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
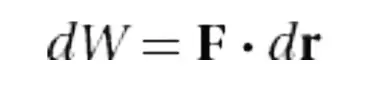
Work by One Force
2
New cards
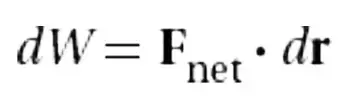
Work due to multiple forces
3
New cards
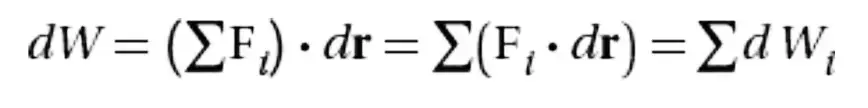
Work due to multiple forces expanded
4
New cards
Joule
The unit of work and energy
5
New cards
scalar
Because work is equal to the dot product of the net force and the displacement vector, it is a \__________ whose magnitude and sign are determined by the component of the net force parallel to the direction of motion.
6
New cards
Work
the change in an object’s kinetic energy due to the action of a given force.
7
New cards
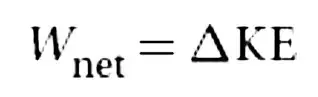
Work–kinetic energy theorem
8
New cards
Work–kinetic energy theorem
This is the first and most fundamental of a number of equations we will soon derive relating various types of work and energy. This theorem is a restatement of Newton’s laws, and it is always valid.
9
New cards
Energy
never created or destroyed; it merely changes form.
10
New cards
Conservative forces
Are involved in reversible energy conversions, where we can get our kinetic energy back.
11
New cards
Nonconservative forces
Are involved in irreversible energy conversions; though the total energy is always conserved, energy is converted to forms from which we cannot recover
12
New cards
Conservative forces
kinetic energy ⇒ potential energy ⇒ kinetic energy
13
New cards
Nonconservative forces
kinetic energy ⇒ sound, heat, etc. ⇒ cannot be easily recovered
14
New cards
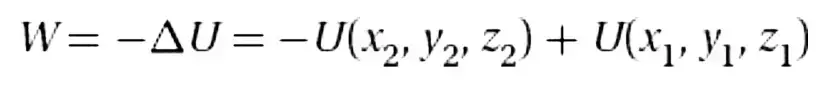
General definition of a potential energy function
15
New cards
zero
Based on the above equation, when the starting and ending points of the motion are the same, the net work must always be \_________
16
New cards

Gravitational potential energy
17
New cards
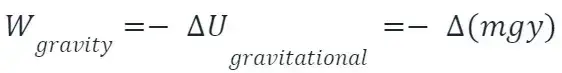
Work done by gravitational force
18
New cards
spring constant
The proportionality constant k , called the \_____________ or force constant, is a property of the particular spring.
19
New cards
negative
The direction of the spring force is opposite the displacement, as indicated by the \______ sign.
20
New cards
restoring force
Because the force always tries to restore the spring to its relaxed state, whether it has been stretched or compressed, it is called a \_______________ .
21
New cards
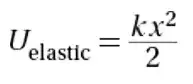
Elastic Potential Energy
22
New cards
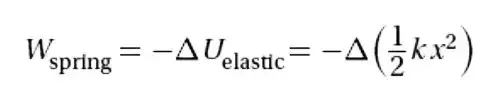
Work Done by Spring Force
23
New cards

general form of the energy conservation equation
24
New cards
Power
The rate at which a force does work on a system
25
New cards
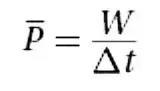
Average power
26
New cards
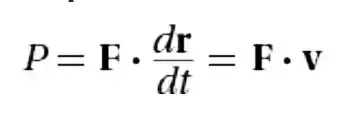
Constant power
27
New cards
Watt
Unit of power
28
New cards
Turning Points
All the energy is potential energy, so the object is temporarily at rest.
29
New cards
Equilibrium Points
Points at which the force is zero
30
New cards
Stable equilibrium points
Points where, if the object is given a small nudge, it will remain close to the equilibrium point, oscillating within an “energy well”.
31
New cards
Unstable equilibrium points
Points where, if the object is given a small displacement, it will end up far away from the equilibrium point
32
New cards
Neutral equilibrium points
Points where the U(x) curve is completely flat, so if the particle is given a little nudge, it will continue to move with a constant velocity.