Gastrointestinal System
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Achalasia
Esophageal obstruction due to the inability of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax
Manifestations of a patient with achalasia
Coughing
Heartburn
Weight loss
Chest pain
Regurgitation
What modality best demonstrates achalasia and what is the radiographic appearance?
Fluroscopy (UGI)
Tapering of the distal 1-3cm of the esophagus
Rat tail or bird beak
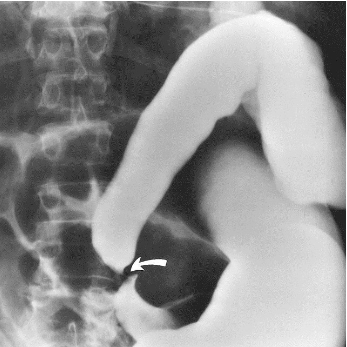
name the pathology
Achalasia
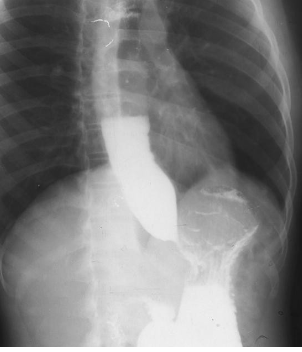
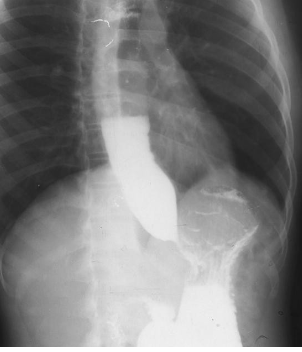
Name the pathology
Ascites
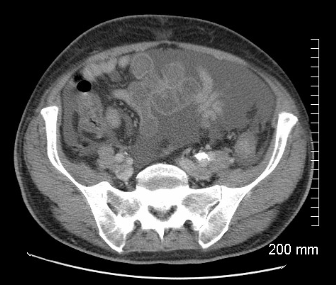
What is the transition point of a SBO
The point where bowel returns to normal
What can cause a LBO
Carcinoma (usually)
Diverticulitis
Volvulus
Which is more dangerous, LBO or SBO?
SBO, develops faster and creates more gastric disturbance
Why is carcinoma of the stomach difficult to detect?
Symptoms overlap with many non-cancerous pathologies:
Poor appetite
Pain
Feeling of fullness
Heartburn
Nausea
Swelling and edema of abdomen
How is stomach carcinoma diagnosed?
Endoscopy usually
UGI: single or double contrast
CT: with or without for staging or to see if cancer has spread
Stomach carcinoma radiographic appearance (UGI)
Diffuse thickening, narrowing and thickening
Ulceration and ittegulatiy
Gastric wall infiltration
Polypoid mass
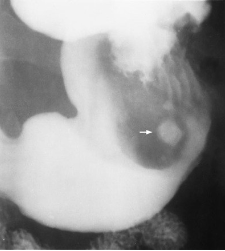
Name the pathology
Carcinoma of the stomach
What are cholelithiasis made of?
Gallstones made of cholesterol or pigment
Only 20% contain enough calcium to detect on x-ray
Best modality to view the gallbladder?
US
What x-ray would be done for cholelithasis? What will the radiographic appearance be?
KUB, stones visible if they contain calcium
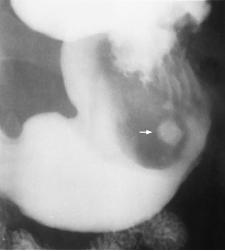
Name the pathology
Cholelithasis
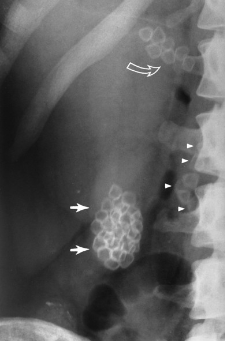
What is cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gall bladder usually caused by gall stone impaction
Cirrhosis
Deterioration of healthy liver tissue, formation of scar tissue. The result is a decreased ability for blood to flow and inability to produce proteins and bile or process nutrients, hormones, drugs and toxins.
What are the most common causes of cirrhosis?
Hep C
fatty liver disease
Alcohol consumption
Clinical manifestations of cirrhosis
Asymptomatic
Jaundice
Bruising easily
Lethargy
Itching (bile salts in skin)
Poor appetite
Portal hypertension
Ascites
What modalities are used to diagnose cirrhosis and what is the radiographic appearance?
KUB - hazy due to ascites
CT - fatty infiltrate in liver, portal vein involvement, ascites/fluid collection, atrophy of liver, decreased attenuation of liver
US - coarse nodules (scar tissue)
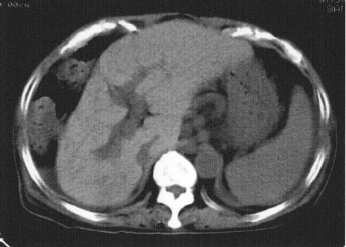
Name the pathology
Cirrhosis - atrophy of right lobe
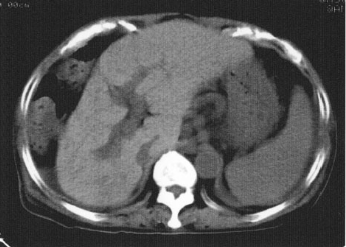
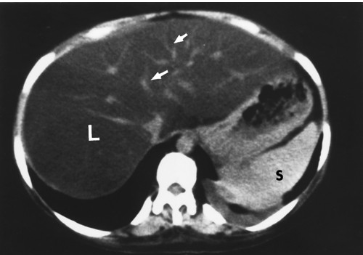
Name the pathology
Cirrhosis - decreased attenuation of liver surrounded fy hepatic fat

Colorectal cancer risk factors
50-70 years old
men (X2 more likely)
Ulcerative colitis
Family history
Colorectal cancer manifestations
Constipation
Diarrhea
Bloody stool
Narrow stool
Pain
Weight loss
Nausea
What modalities are used for colorectal cancer and what is the radiographic appearance?
CT - colonography, lesion larger than 2cm with apple-core or napkin ring appearance, bowel wall thickening, mets, lymphadenopathy
Fluoro - Double barium enema, apple core lesion
US - tumor invasion of lymph tissue
PET - nodular metastasis
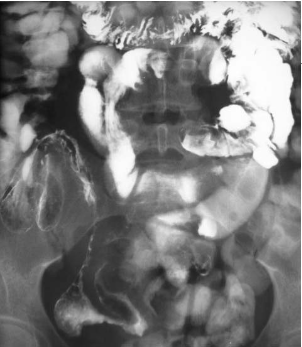
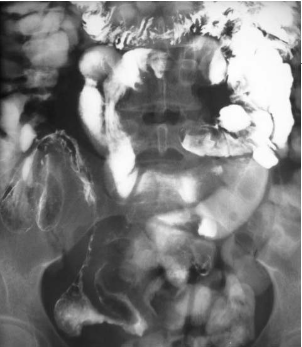
Name the pathology
Colorectal cancer - apple core lesion
Where is colorectal cancer most commonly found?
Rectum
Crohn’s disease
Chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, especially the colon and ileum
Chron’s disease demographic
Young adults
Chron’s disease manifestations
Pain
Nausea
Weight loss
Uncontrollable diarrhea
Lack of energy
Arthritis
Eye inflammation
Mouth sores
Skin disorders
Attacks and remissions
Radiographic appearance of chrons disease
Thick mucosal folds
Cobblestone appearance
String sign, skip lesions
Ulcerations, fistula formations
Dirty fat mesenteric appearance
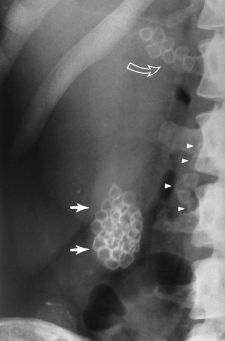
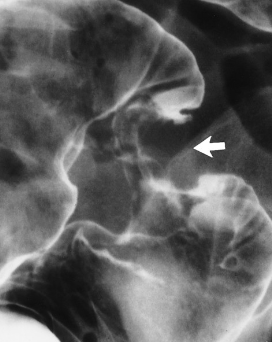
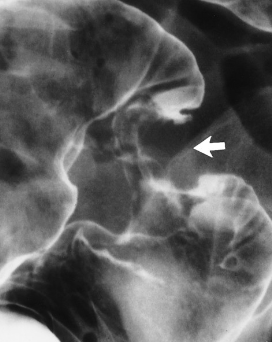
Name the pathlolgy
Chron’s disease - string sign
Diabetes mellitus
Inability to produce or use insulin, cannot metabolize glucose
Type 1 diabetes
Insulin dependant, childhood, rare
Type 2 diabetes
Non insulin dependant, adult, common
Manifestations of diabetes mellitus
Polyurea (peeing)
Polydipsia (thirsty)
Polyphagia (hungry)
Fatigue
Weight changes
Infections
Slow healing
Vision issues
Sliding hernia
Stomach and lower esophagus slide into chest
Paraesophageal hernia
Part of stomach squeezes through hiatus and sits beside esophagus
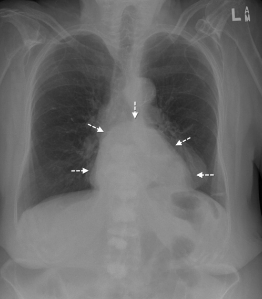
Name the pathology
Hiatal hernia
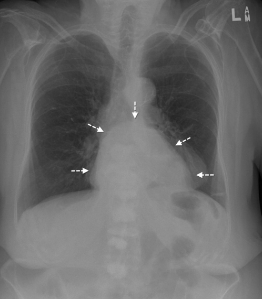
Diaphragmatic hernia
Hole in diaphragm causing organs to move into chest. Surgical correction at an early age
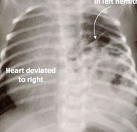
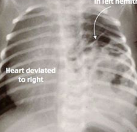
Name the pathology
Diaphragmatic hernia
Inguinal hernia
Abdominal organs protrude through abdominal muscles
What is the danger of inguinal hernias?
Organs trapped outside of abdominal cavity, twisting and impaction leads to necrosis
Diverticulosis
Diagnosis of diverticula - one or more found
Atresia
The closing or absence of a passage or lumen
Risk factors for esophageal carcinoma
Men
Alcohol use
Smoking
Radiographic appearance of esophageal carcinoma
Irregular wall, mucosal destruction, absent mucosal folds
CT - wall thickening greater than 3mm
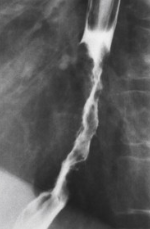
Name the pathology
Esophageal carcinoma
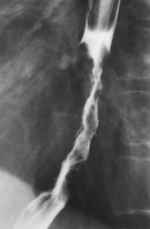
What causes esophageal varices
Portal hypertension from increased venous pressure, often the result of cirrhosis
Radiographic appearance of esophageal varices
Filling defects, wall thickening
Rosary bead sign
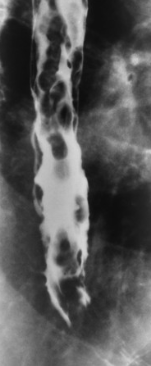
Name the pathology
Esophageal varices - rosary beads
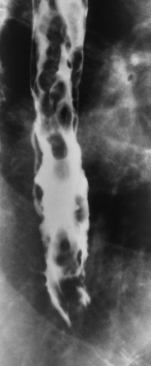
How is reflux best demonstrated on a UGI?
Valsalva maneuver or trendelenburg
Hemangioma
Bright red birthmark, cluster of blood vessels under the skin
Manifestations of liver hemangioma
Almost always asymptomatic
bloating and discomfort
loss of appetite
fullness
Hepatitis
Inflammatory disease of the liver caused by viral infection or toxin exposure
Types of hepatits
Hep A - self-contained, good prognosis
Hep B - healthcare workers are susceptible, 90% recovery
Hep C - chronic, cause cirrhosis, 50% will develop hepatocellular carcinoma
Hep E - self - limited, from ingesting feces
Hepatitis imaging modalities and appearance
CT - contrast can show lobulated liver
MRI - diffuse enhancement
US - nodules
Ileus
Failure of peristalsis causing an obstruction, no bowel sounds
Liver cancer appearance
CT - mass with irregular contour, contrast uptake, invasion of hepatic and portal venous system
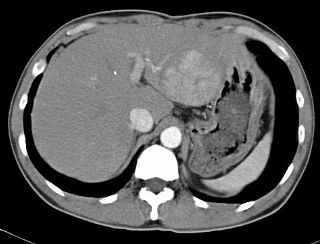
Name the pathology
Liver carcinoma
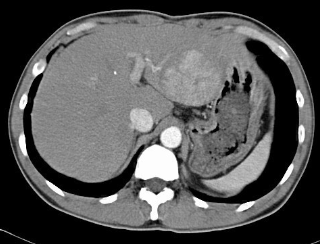
Radiographic appearance of pancreatic cancer
CT - tumor, ductal dilation, invasion of adjacent tissues
US - tumor 2cm or greater with irregularity
Pancreatic cancer prognosis
Less than 2% survicve
Pancreatitis causes
Excessive alcohol, gallstones
Pancreatitis
Inflammatory process of pancreas, protein and lipid digesting enzymes activate and destroy pancreas
Acute vs chronic pancreatitis
Acute: sudden, life-threatening often caused by binge drinking or gallstone misplacement
Focal enlargment
Chronic: long term inflammation causing permanent damage, chronic alcohol use, scar tissue
Calcifications, enlarged pancreas, ductal dilation
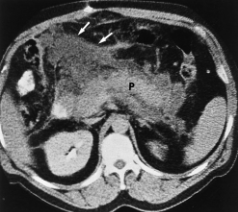
Name the pathology
Acute pancreatitis - diffuse enlargement with fatty obliteration
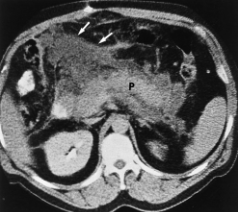
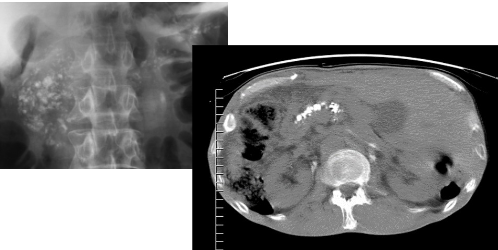
Name the pathology
Chronic pancreatitis - diffuse calcifications
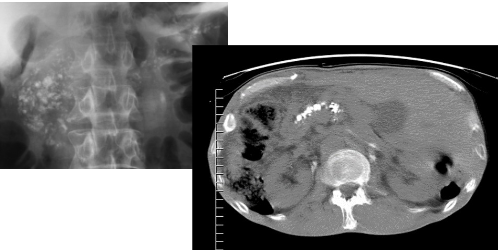
Most common location of peptic ulcers
Duodenal bulb
Imaging for pneumoperitoneum
LLD - air along liver
Ulcerative colitis radiographic appearance
Lead pipe sign
Loss of haustra
Ulcerative colitis location
Large bowel, often rectosigmoid
Radiographic difference between chrons and ulceratice colitis
Chrons - skip lesions
UC - continuous lesions
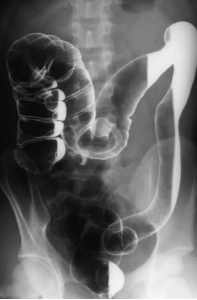
Name the pathology
Ulcerative colitis
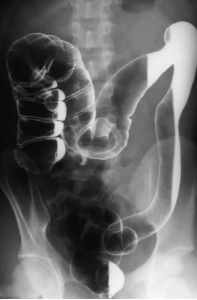
Radiographic appearance of volvulus
Cecal volvulus - barium fills colon to cecum
Sigmoid - coffee bean / beak appearance
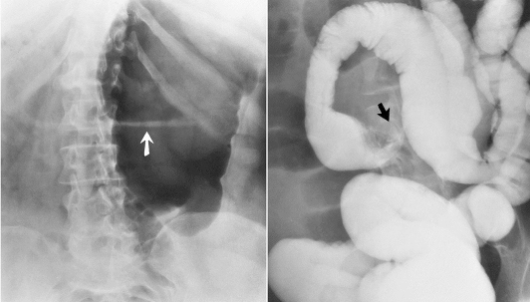
Name the pathology
Cecal volvulus
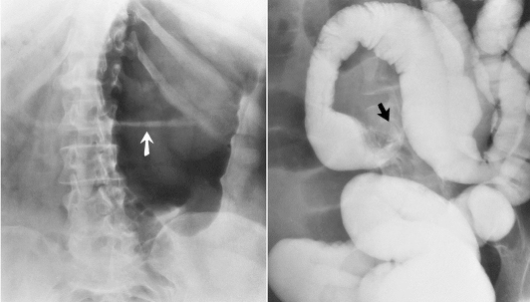
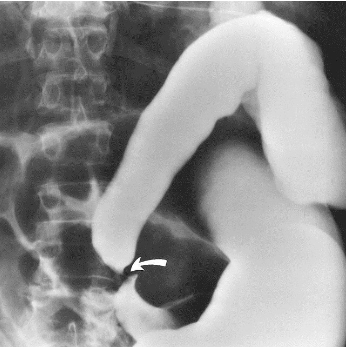
Name the pathology
Sigmoid volvulus