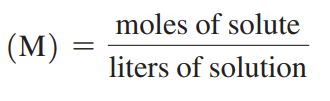Chapter 9: Solutions
0.0(0)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/39
Last updated 4:57 AM on 1/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
Solution
A homogeneous mixture in which the solute formly dispersed in a solvent.
2
New cards
Water
* It is one of the most common solvents in nature.
* It is polar, thus it is a polar solvent.
* It is polar, thus it is a polar solvent.
3
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
Occur between molecules where partially positive hydrogen atoms are attracted to the partially negative atoms.
4
New cards
Hydration
The process of surrounding dissolved ions by water molecules.
5
New cards
electrolytes
When ____ dissolve in water, the process of dissociation separates them into ions forming solutions that conduct electricity.
6
New cards
nonelectrolytes
When ____ dissolve in water, they do not separate into ions and their solutions do not conduct electricity.
7
New cards
Strong electrolyte
There is 100% dissociation of the solute into ions.
8
New cards
Weak Electrolyte
A compound that dissolves in water mostly as molecules.
9
New cards
Equivalent (Eq)
The amount of that ion equal to 1 mole of positive or negative electrical charge.
10
New cards
negative ions
In any solution, the charge of the positive ions is always balanced by the charge of the _____.
11
New cards
Solubility
* It is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved at a certain temperature.
* It is used to describe the amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent
* It is usually expressed in grams of solute in 100 g of solvent.
* It is used to describe the amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent
* It is usually expressed in grams of solute in 100 g of solvent.
12
New cards
Unsaturated solution
The solution does not contain the maximum amount of solute.
13
New cards
Saturated solution
A solution that contains all the solutes that can dissolve.
14
New cards
Recrystallization
A process that occurs when a solution is saturated, the rate at which the solute dissolves becomes equal to the rate at which the solid forms.
15
New cards
supersaturated solution
When a saturated solution is carefully cooled, it becomes a _____ because it contains more solute than the solubility allows.
16
New cards
Henry’s Law
It states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly related to the pressure of that gas above the liquid.
17
New cards
Soluble Salts
Ionic compounds that dissolve in water.
18
New cards
Insoluble Salts
Ionic compounds that do not dissociate into ions in water.
19
New cards
Concentration
The amount of solute dissolved in a certain amount of solution.
20
New cards
Mass percent (m/m)
The mass of the solute in grams for exactly 100 g of solution.
21
New cards
Volume Percent (v/v)
The concentration of the volume of liquids or gases.
22
New cards
Mass/volume percent
The mass of the solute in grams for exactly 100 mL of solution.
23
New cards
Molarity (M)
A concentration that states the number of moles of solute in exactly 1 L of solution.
24
New cards
Dilution
A solvent is added to a solution, which increases the volume.
25
New cards
Solution
* It appears transparent, although it may have a color.
* The particles are so small that they go through filters and through semipermeable membranes.
* The particles are so small that they go through filters and through semipermeable membranes.
26
New cards
Colloidal particles
* These are large molecules, such as proteins, or groups of molecules or ions.
* These are small enough to pass through filters but too large to pass through semipermeable membranes.
* These are small enough to pass through filters but too large to pass through semipermeable membranes.
27
New cards
Suspension
* These are heterogeneous, nonuniform mixtures that are very different from solutions or colloids.
* The particles of these are so large that they can often be seen with the naked eye.
* The particles of these are so large that they can often be seen with the naked eye.
28
New cards
Osmosis
The water molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from the solution with the lower concentration of solute into a solution with a higher solute concentration.
29
New cards
Osmotic Pressure
It prevents the flow of additional water into the more concentrated solution.
30
New cards
Reverse Osmosis
A pressure greater than the osmotic pressure is applied to a solution so that it is forced through a purification membrane.
31
New cards
Isotonic Solutions
A solution that has the same particle concentration and osmotic pressure as that of the cells of the body.
32
New cards
Hypotonic Solutions
A solution that has a lower particle concentration and lower osmotic pressure than the cells of the body.
33
New cards
Hemolysis
The increase in fluid causes the cell to swell, and possibly burst.
34
New cards
Hypertonic Solutions
A solution that has a higher particle concentration and higher osmotic pressure than the cells of the body.
35
New cards
Crenation
A process when the water leaves the cell, it shrinks.
36
New cards
Dialysis
* A dialyzing membrane, permits small solute molecules and ions as well as solvent water molecules to pass through, but it retains large particles, such as colloids.
* It is a way to separate solution particles from colloids.
* It is a way to separate solution particles from colloids.
37
New cards
Mass percent Formula
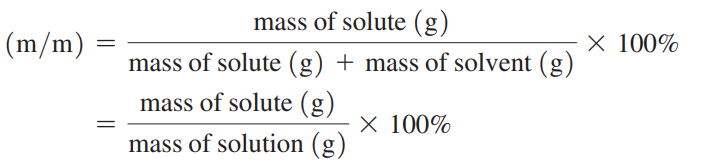
38
New cards
Volume Percent Formula
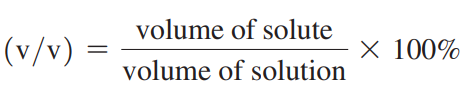
39
New cards
Mass/volume percent formula
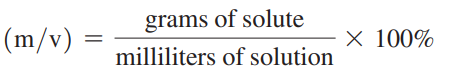
40
New cards
Molarity Formula