Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
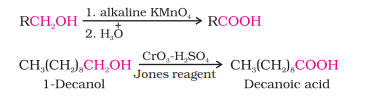
From Primary Alcohols and Aldehydes
Easily oxidized to carboxylic acid by using KMnO4 in neutral, alkaline or acidic medium
Or K2Cr2O7 and CrO3 in acidic medium (Jones’ Reagent)
Aldehydes can be oxidized by using a mild oxidizing agent like Tollen’s reagent
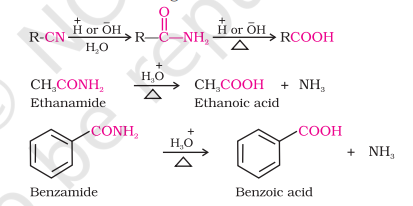
From Nitriles and Amides
Nitriles are hydrolyzed to amides in the presence of catalysts like OH- and H+
Mild reaction conditions help stop the reaction at amide stage
From Alkylbenzenes
Alkylbenzenes vigorously oxidize with chromic acids or acidic/alkaline KMnO4
During oxidation, the chain gets oxidized with -COOH group but the aromatic nucleus remains intact
Only 1* and 2* alkyl chains are oxidized due to presence of benzylic hydrogen
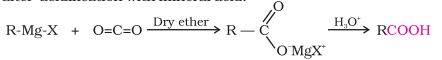
From Grignard’s Reagent
Grignard Reagent reacts with dry ice (CO2) in ethereal solution to produce salts of carboxylic acids, which on acidification with mineral acids give corresponding carboxylic acids
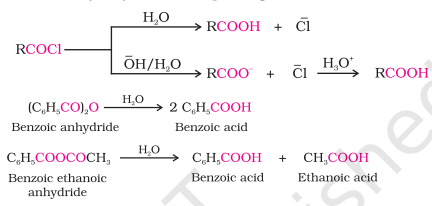
From Acyl Halides and Anhydrides
Acyl halides, on being hydrolyzed with water give corresponding carboxylic acid
When hydrolyzed with an aqueous base, give us carboxylate ion that on acidification gives corresponding acid
Anhydrides when hydrolyzed with water give corresponding carboxylic acid
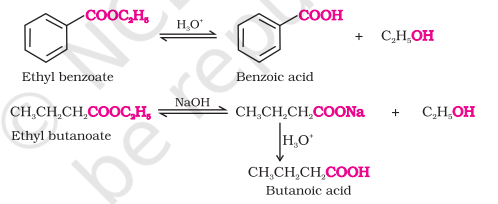
From Esters
Acidic hydrolysis : Directly gives us carboxylic acids
Basic hydrolysis : Gives carboxylates that on acidification get converted to carboxylic acids