3.1 Enzymes
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Enzymes
proteins that catalyze(speed up) reactions by lowering the activation energy(the initial input of energy to start a reaction)
not consumed by a reaction
they do this by bringing reacting molecules close together in the correct position, enzyme active sites can be charged which can alter the substrate to promote catalysis, or they can change the shape of the substrate
some enzymes consist of only polypeptide chains, while others require cofactors
Enzyme-Substrate complex
enzymes act on substrates, and substrates bind to compatible active sites
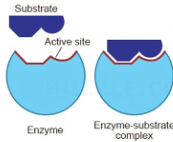
Substrates
a specific reactant that an enzyme acts upon to catalyze a biochemical reaction
Active site
area for substrate to bind
enzymes can only mediate a reaction if the substrate is compatible(the shape and charge) with the active site
when a substrate binds to the active site, both the enzyme and the substrate will change shape slightly, which helps to position the substrate so bonds can be broken/formed easier
Enzyme function
enzymes break down complex molecules and also build complex molecules
Cofactors
non protein molecules that bind to enzymes and assist enzyme function
some are metallic ions(iron, copper, zinc, etc)
others are small organic compounds called coenzymes, which assist enzymes in catalysis and act as electron carriers during reactions