Chem Exam 4 stuff to memorize
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Ionic Bond
A type of chemical bond formed through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Covalent Bond
A type of bond where two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
Lattice Energy
The energy released when ions in a gaseous state form an ionic solid.
Born-Haber Cycle
A thermochemical cycle that relates the lattice energy of an ionic solid to other thermodynamic quantities.
Electronegativity
A measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
Dipole Moment
A measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule.
Lewis Structure
A diagram representing the arrangements of electrons in a molecule.
Resonance Structure
One of two or more valid Lewis structures for a molecule that cannot be represented accurately by a single structure.
Formal Charge
The charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, calculated based on the number of valence electrons.
Bond Energy
The energy required to break a bond between two atoms.
VSEPR Theory
A model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs.
Intermolecular Forces*
*Forces that occur between molecules, which influence the physical properties of substances.
Hydrogen Bonding*
A strong type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs between molecules containing hydrogen bonded to highly electronegative atoms*
Vapor Pressure
The pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases at a given temperature.
Boiling Point
The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the external pressure surrounding the liquid.
Sublimation
The process by which a solid turns directly into a vapor without passing through a liquid phase.
Phase Diagram
A graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure.
Heat of Fusion
The amount of energy required to convert a unit mass of a solid into a liquid at its melting point.
Critical Temperature
The highest temperature at which a substance can exist as a liquid.
Molecular Geometry
The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
Sigma Bond
A type of covalent bond formed by the direct overlap of atomic orbitals.
Pi Bond
A type of covalent bond formed by the lateral overlap of atomic orbitals.
Ionic Bond
A type of chemical bond formed through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Covalent Bond
A type of bond where two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
Lattice Energy
The energy released when ions in a gaseous state form an ionic solid.
Born-Haber Cycle
A thermochemical cycle that relates the lattice energy of an ionic solid to other thermodynamic quantities.
Electronegativity
A measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
Dipole Moment
A measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule.
Lewis Structure
A diagram representing the arrangements of electrons in a molecule.
Resonance Structure
One of two or more valid Lewis structures for a molecule that cannot be represented accurately by a single structure.
Formal Charge
The charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, calculated based on the number of valence electrons.
Bond Energy
The energy required to break a bond between two atoms.
VSEPR Theory
A model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs.
Intermolecular Forces*
*Forces that occur between molecules, which influence the physical properties of substances.
Hydrogen Bonding**
**A strong type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs between molecules containing hydrogen bonded to highly electronegative atoms.
Vapor Pressure
The pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases at a given temperature.
Boiling Point
The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the external pressure surrounding the liquid.
Sublimation
The process by which a solid turns directly into a vapor without passing through a liquid phase.
Phase Diagram
A graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure.
Heat of Fusion
The amount of energy required to convert a unit mass of a solid into a liquid at its melting point.
Critical Temperature
The highest temperature at which a substance can exist as a liquid.
Molecular Geometry
The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
Sigma Bond
A type of covalent bond formed by the direct overlap of atomic orbitals.
Pi Bond
A type of covalent bond formed by the lateral overlap of atomic orbitals.
Electron Domain
The total number of lone pairs and bonding locations surrounding a central atom.
Linear Geometry
A molecular arrangement with two electron domains, typically resulting in a 180^\circ bond angle.
Trigonal Planar
A molecular arrangement with three electron domains, typically resulting in 120^\circ bond angles.
Tetrahedral
A molecular arrangement with four electron domains, typically resulting in 109.5^\circ bond angles.
Trigonal Bipyramidal
A molecular arrangement with five electron domains, featuring bond angles of 90^\circ and 120^\circ.
Octahedral
A molecular arrangement with six electron domains, typically resulting in 90^\circ bond angles.
Bent Geometry
A non-linear molecular shape that occurs when lone pairs on the central atom push bonding pairs closer together.
Lone Pair Repulsion
The principle that lone pairs occupy more space and exert stronger repulsive forces than bonding electron pairs.
Electron Geometry
The arrangement of all electron domains (both bonding pairs and lone pairs) around a central atom.
Molecular vs. Electron Geometry
Electron geometry considers all electron domains, while molecular geometry describes only the spatial arrangement of the atoms, ignoring the 'invisible' lone pairs.
Trigonal Pyramidal
A molecular geometry resulting from four electron domains where one is a lone pair; the bond angles are typically slightly less than 109.5^\circ.
Seesaw Geometry
A molecular geometry resulting from five electron domains where one is a lone pair occupying an equatorial position.
T-shaped Geometry
A molecular geometry resulting from five electron domains where two are lone pairs.
Square Pyramidal
A molecular geometry resulting from six electron domains where one is a lone pair.
Square Planar
A molecular geometry resulting from six electron domains where two are lone pairs located opposite each other.
Hybrid Orbitals
Orbitals formed by mixing atomic orbitals (s, p, d) to describe the bonding in polyatomic molecules.
sp3 Hybridization
The mixing of one s and three p orbitals, corresponding to a tetrahedral electron geometry.
Intermolecular forces…
Exist between different molecules
Dispersion Forces/ London Forces
-happen because fluctuations in electron distribution
-all molecules exhibit dispersion forces
-dispersion forces increase with molar mass
-longer molecule stronger dispersion force
Dipole Dipole Forces…
Exist between polar molecules
Hydrogen Bonding
Strong attraction between hydrogen atom in one molecule and highly electronegative atom in another
Ion Dipole
Mix between ionic compound with polar compound
What is the phase change from Solid to liquid?
Melting / Fusion
What is the phase change from Solid to gas?
Sublimation
What is the phase change from liquid to gas?
Vaporization
What is the phase change from liquid to solid?
Freezing
What is the phase change from gas to solid?
deposition
What is the phase change from gas to liquid?
Condensation
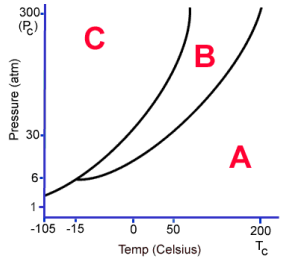
What phase is C?
Solid
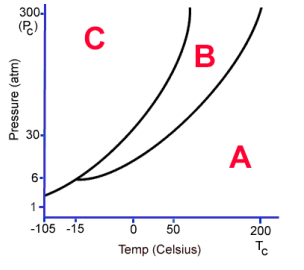
What phase is B?
Liquid
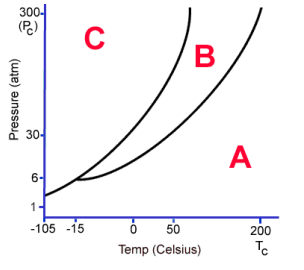
What phase is A
Gas
2 Electron groups, 0 Lone pairs, 180 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Linear, and Linear
3 electron groups, 0 lone pairs, 120 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Trigonal planar, and Trigonal planar
3 electron groups, 1 lone pair, less than 120 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Trigonal Planar, and Bent
4 Electron groups, 0 lone pairs, 109.5 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Tetrahedral, and Tetrahedral
4 Electron groups, 1 lone pair, less than 109.5 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Tetrahedral, and Trigonal pyramidal
4 Electron groups, 2 lone pairs, less than 109.5 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Tetrahedral, and Bent
5 electron groups, 0 lone pairs, 120 and 90 bond angles - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Trigonal bipyramidal, and Trigonal bipyramidal
5 electron groups, 1 lone pair, less than 120 and 90 bond angles - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Trigonal bipyramidal, and Seesaw
5 electron groups, 2 lone pairs, less than 120 and 90 bond angles - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Trigonal bipyramidal, and T-shaped
5 electron groups, 3 lone pairs, less than 120 and 90 bond angles - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Trigonal bipyramidal, and Linear
6 electron groups, 0 lone pairs, 90 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Octahedral, and Octahedral
6 electron groups, 1 lone pair, less than 90 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Octahedral, and Square pyramidal
6 electron groups, 2 lone pairs, less than 90 bond angle - What is the Electron and molecular geometry?
Octahedral, and Square planar
Formal charge formula
Formal Charge = (Valence Electrons) - (Bonds) - (Dots)
Bond energy
Bond Enthalpy
What periodic trend is more electronegative?
Up and right
What periodic trend is less/ or decreasing in electronegativity ?
Left and down
Molecular v. Electron geometry
Molecular geometry excludes lone pairs
What does symmetry mean when determining polarity?
nonpolar - cancels out dipole movements
What is a chemical bond according to Valance bond theory?
According to Valence Bond (VB) Theory, a chemical bond, specifically a covalent bond, forms from the overlap of two half-filled atomic orbitals from different atoms, creating a shared region where the two valence electrons pair up with opposite spins, holding the atoms together through mutual attraction to this shared electron density. This overlap results in either stronger sigma (σ) bonds (head-on) or pi (π) bonds (sideways), defining single, double, and triple bonds.
What hybridization corresponds to Linear electron geometry?
sp
What hybridization corresponds to Trigonal Planar electron geometry?
sp2
What hybridization corresponds to Tetrahedral electron geometry?
sp3
What hybridization corresponds to Trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry?
sp3d
What hybridization corresponds to Octahedral electron geometry?
sp3d2