Glycogen Metabolism: Structure, Pathways, and Regulation in Biochemistry
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is the basic structure of glycogen?
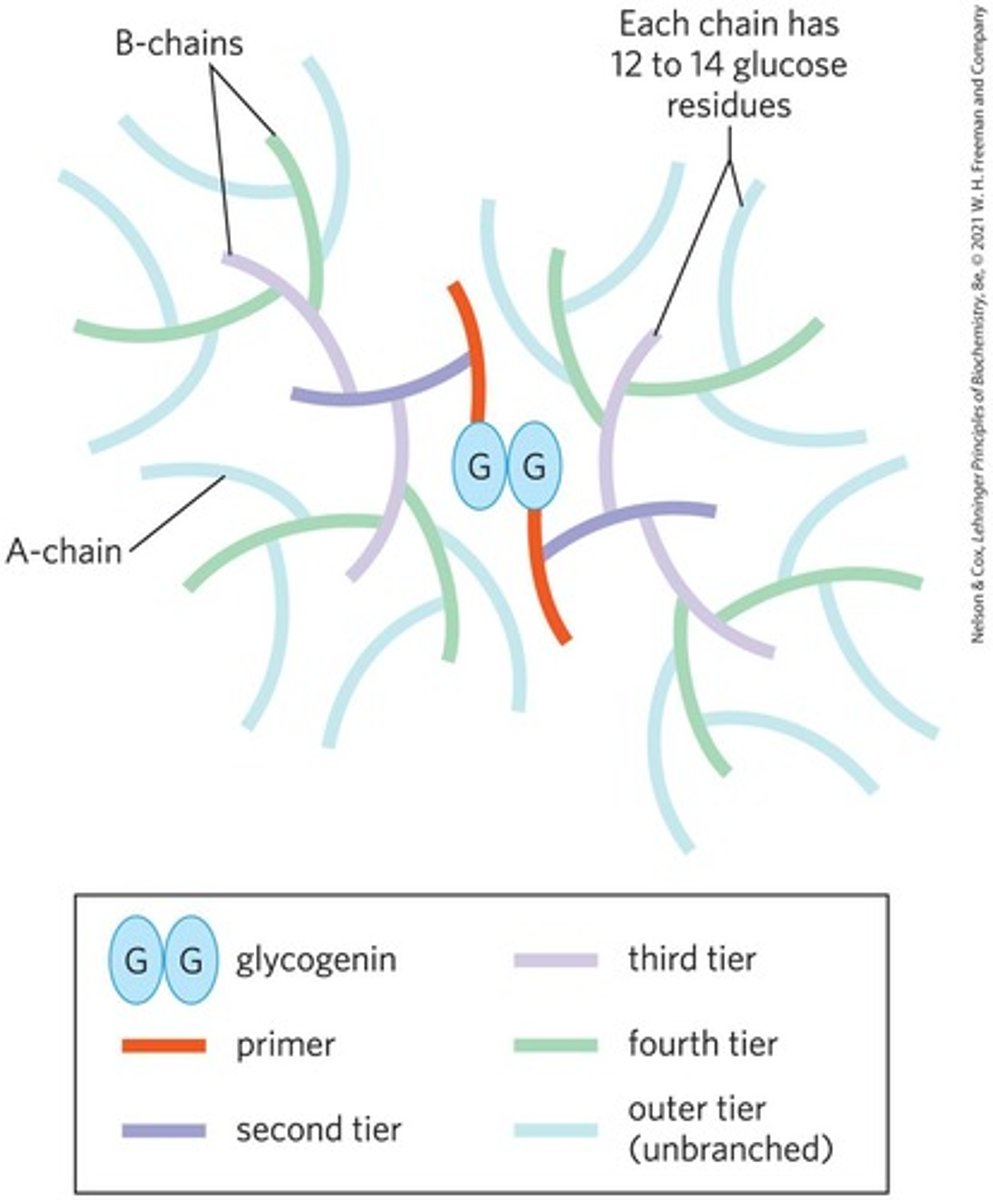
Glycogen is a homopolymer of α-D-glucose with α-1,4 linkages and branching at α-1,6 linkages approximately every 8-10 residues.
What are the two main biochemical pathways of glycogen metabolism?
Glycogen catabolism (glycogenolysis) and glycogen synthesis (glycogenesis).
What hormones regulate glycogen metabolism?
Insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine.
What is the physiological significance of glycogen?
Glycogen maintains blood glucose levels during fasting and physical activity.
What are glycogen storage diseases?
Genetic disorders that affect the metabolism of glycogen, leading to abnormal storage and clinical manifestations.
Why is glucose stored as glycogen?
To minimize osmotic stress and for storage efficiency and rapid release of glucose.
What is the role of liver glycogen?
Liver glycogen is degraded for distribution to other organs and to maintain blood glucose levels.
What is the role of muscle glycogen?
Muscle glycogen is degraded for energy production during physical activity.
What enzyme catalyzes the first step of glycogenolysis?
Glycogen phosphorylase, which catalyzes the formation of glucose-1-phosphate.

What is the function of the debranching enzyme in glycogenolysis?
It removes branches and cleaves α-1,6 glycosidic bonds.
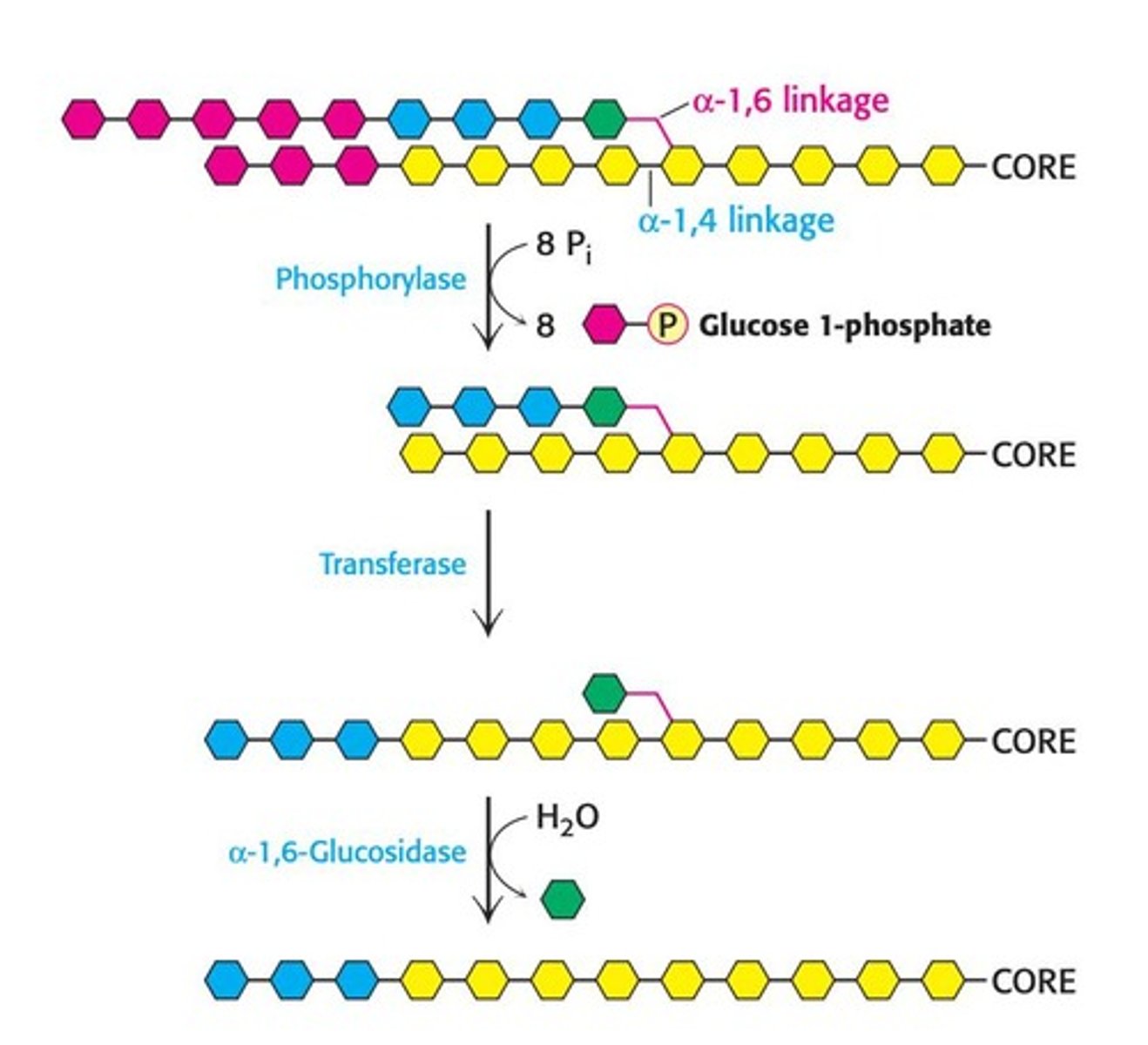
What does phosphoglucomutase do in glycogen metabolism?
It converts glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate.
What happens to glucose-1-phosphate in the liver?
It is dephosphorylated to free glucose, which can enter the bloodstream.
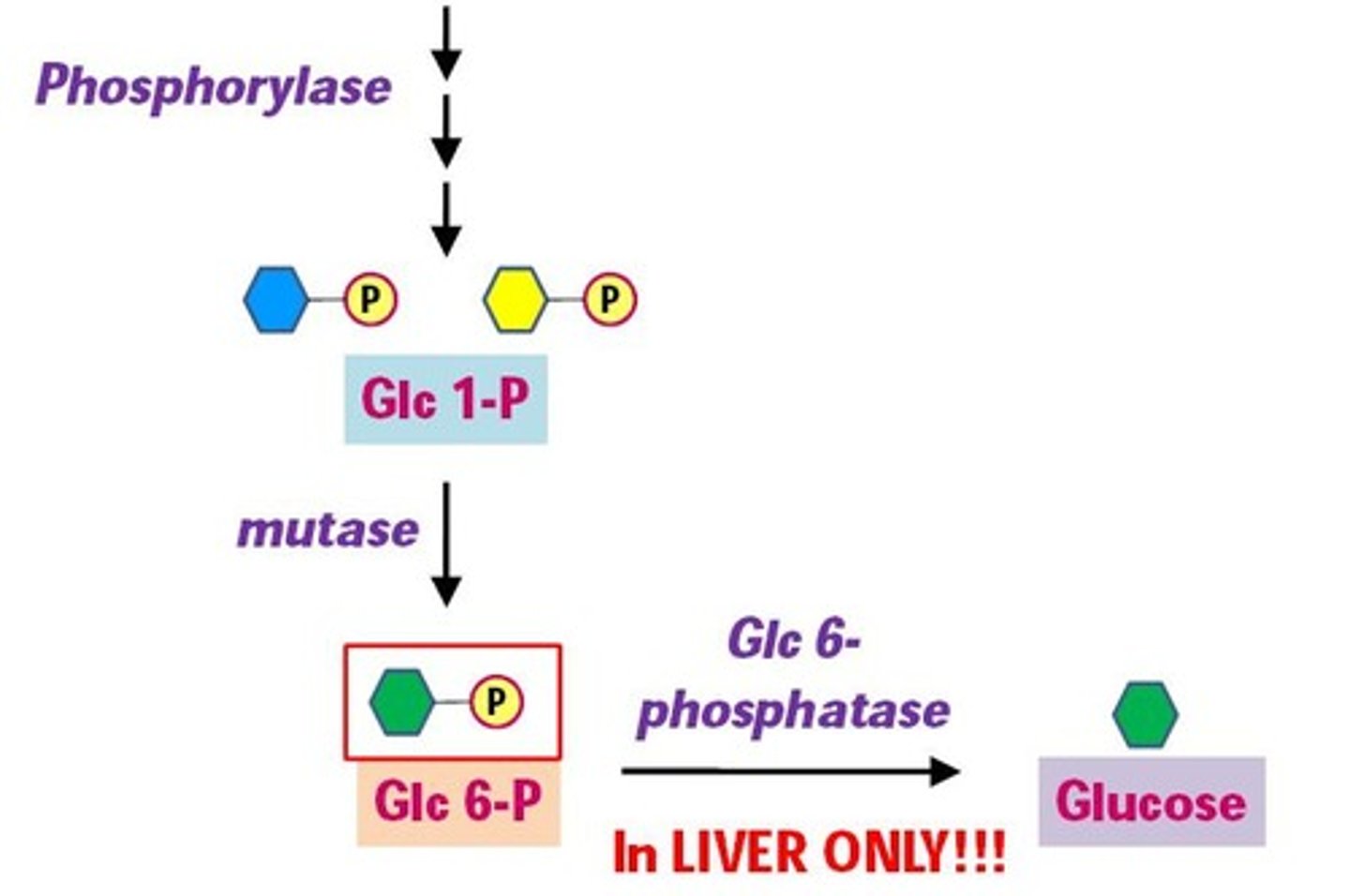
Why can't muscle cells release glucose into the bloodstream?
Muscle cells lack glucose-6-phosphatase, preventing them from converting glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose.
What is the Cori cycle?
A metabolic pathway that recycles lactate produced by muscles into glucose in the liver during hypoxia.
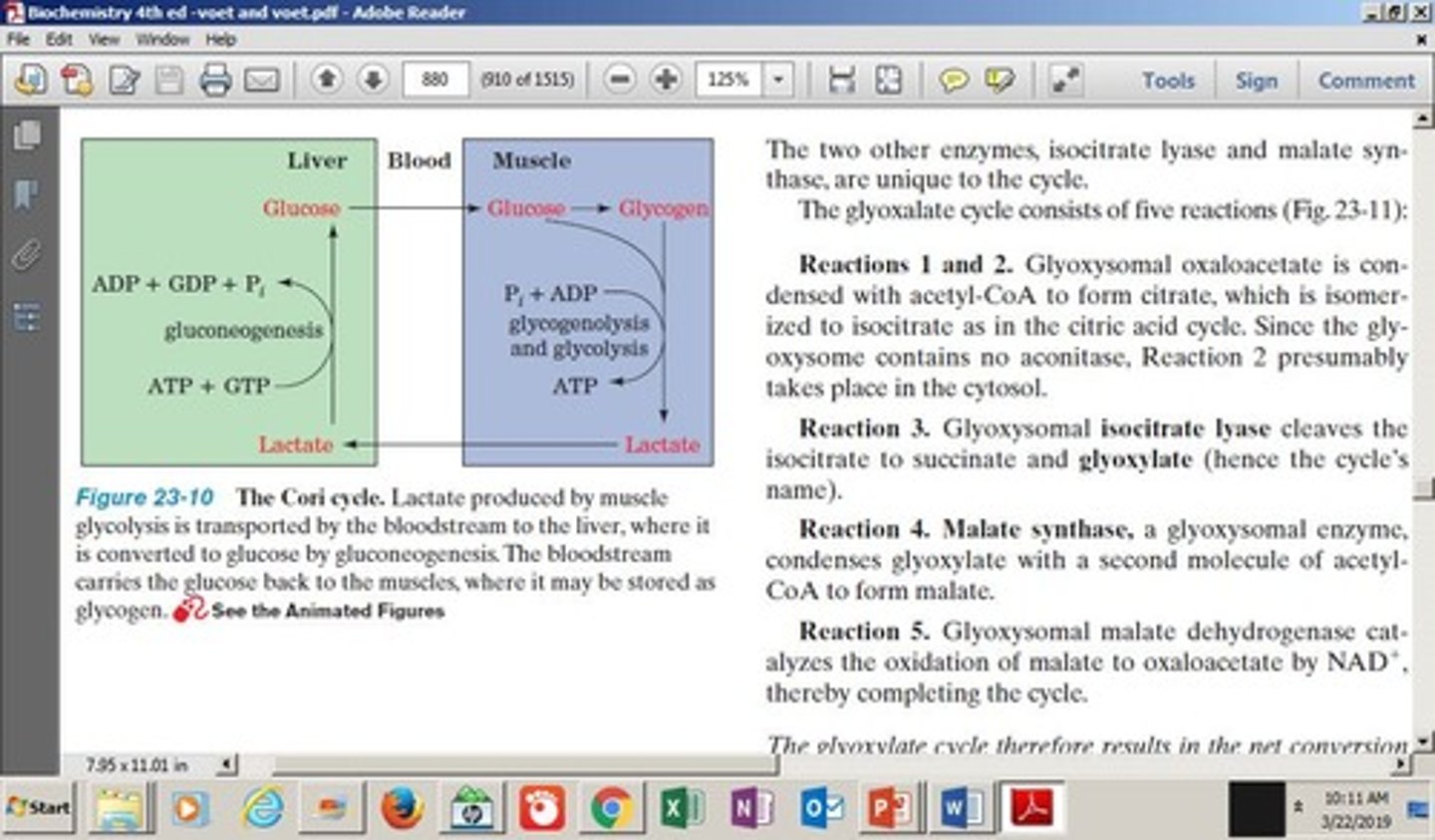
What is the energy cost of the Cori cycle?
Each iteration consumes a net total of 4 ATP.
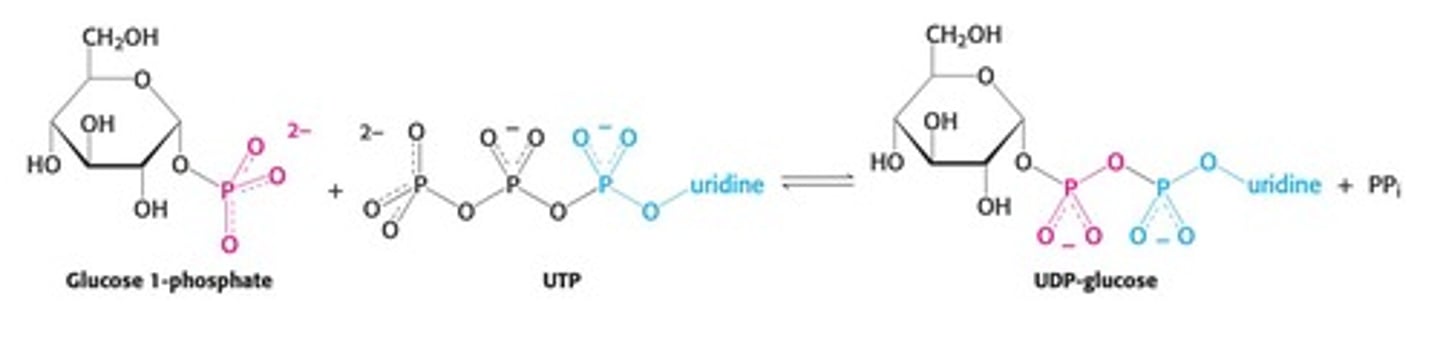
What is the role of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in glycogenesis?
It catalyzes the conversion of glucose-1-phosphate to UDP-glucose.
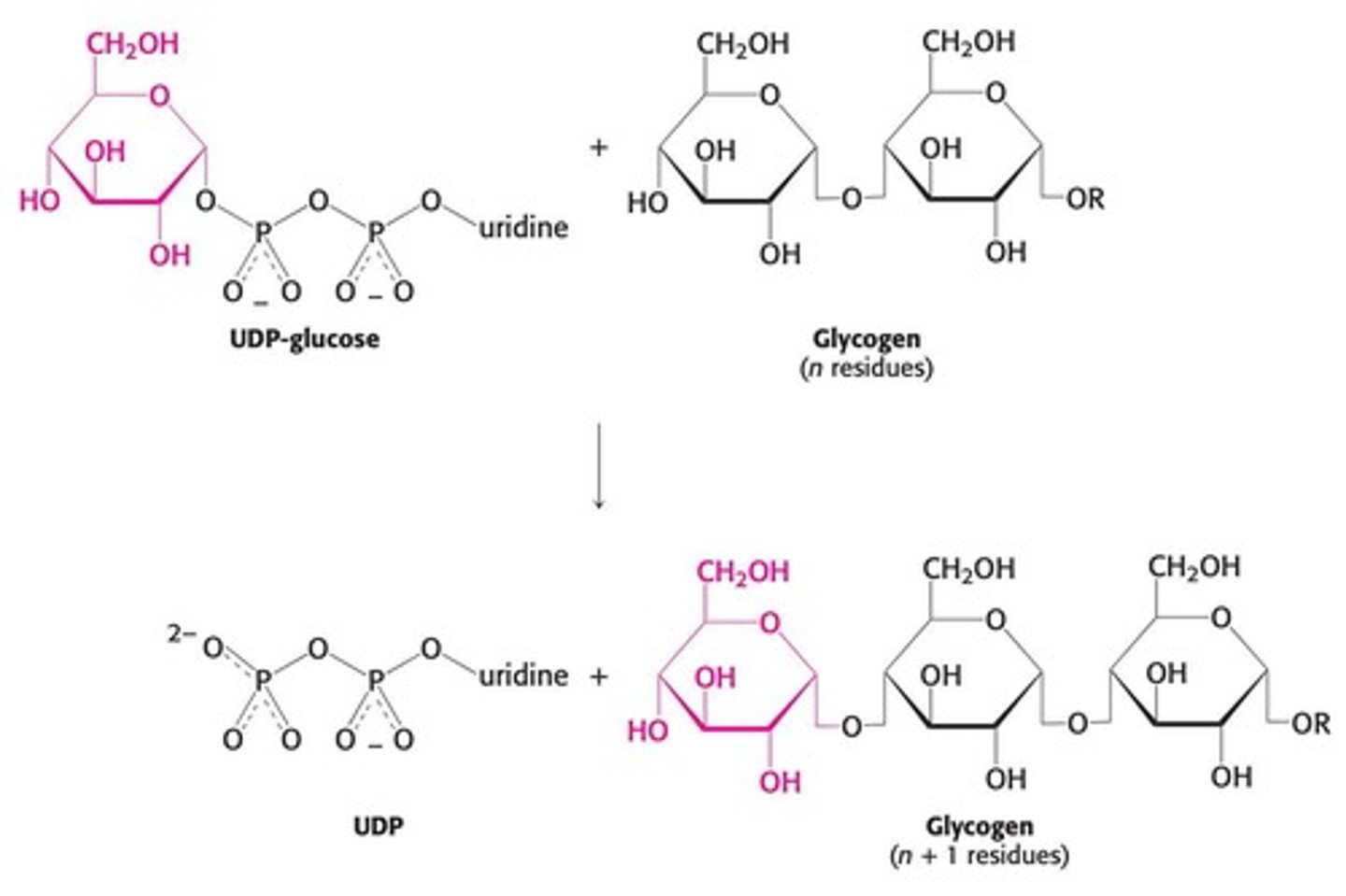
What is the main enzyme responsible for glycogen synthesis?
Glycogen synthase, which adds glucose units to the growing glycogen chain.
How does glycogenolysis differ from glycogenesis?
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen to release glucose, while glycogenesis is the synthesis of glycogen from glucose.
What is the significance of glycogen's branched structure?
It allows for compact storage and rapid enzymatic breakdown to glucose.
What is the effect of high phosphate concentration on glycogenolysis?
It makes glycogenolysis thermodynamically favorable.
What is the role of lactate in the Cori cycle?
Lactate produced by muscles is converted to glucose in the liver, which can then be used by muscles.
What is UDP-Glucose?
The activated form of glucose that serves as a glucose donor for glycogen synthesis.
What is the first step in glycogenesis?
Formation of Glucose-6-P.
What is the role of UTP in glycogenesis?
UTP is converted to UDP-Glucose, which is essential for glycogen synthesis.
What drives the formation of UDP-Glucose?
The rapid hydrolysis of PPi to 2 Pi makes the reaction proceed.
What enzyme is responsible for adding glucose to glycogen?
Glycogen synthase.
What is required for glycogen synthase to function?
A primer of 4 or more glucose molecules synthesized by glycogenin.
What is the function of the branching enzyme in glycogenesis?
It breaks the α-1,4 link and forms the α-1,6 branch, increasing the solubility of glycogen.
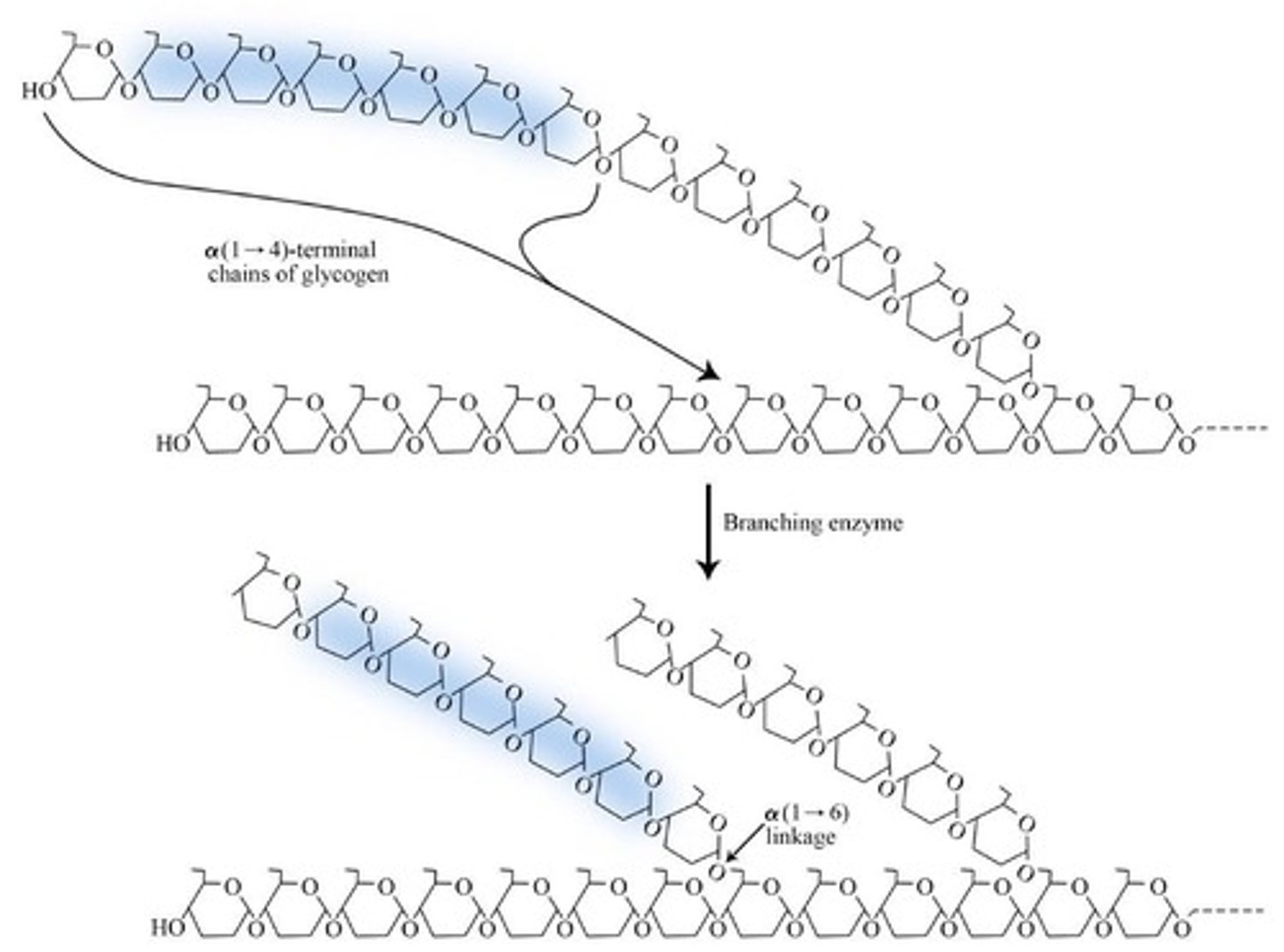
How many glucosyl residues are needed for a segment to be transferred by the branching enzyme?
At least 7 glucosyl residues must be transferred to form a branch.
What is reciprocal regulation in glycogen metabolism?
Glycogenolysis and glycogenesis are regulated such that conditions promoting one inhibit the other.
What hormone stimulates glycogenesis?
Insulin stimulates glycogenesis and promotes glucose uptake from the bloodstream.
What hormones stimulate glycogen breakdown?
Epinephrine (in muscle) and glucagon (in liver) stimulate glycogen breakdown to glucose.
What happens to blood glucose levels after a carbohydrate-rich meal?
Blood glucose levels elevate, leading to insulin secretion and promotion of glycogenesis.
What is the effect of glucagon when blood glucose levels decrease?
Glucagon promotes glycogenolysis to increase blood glucose levels.
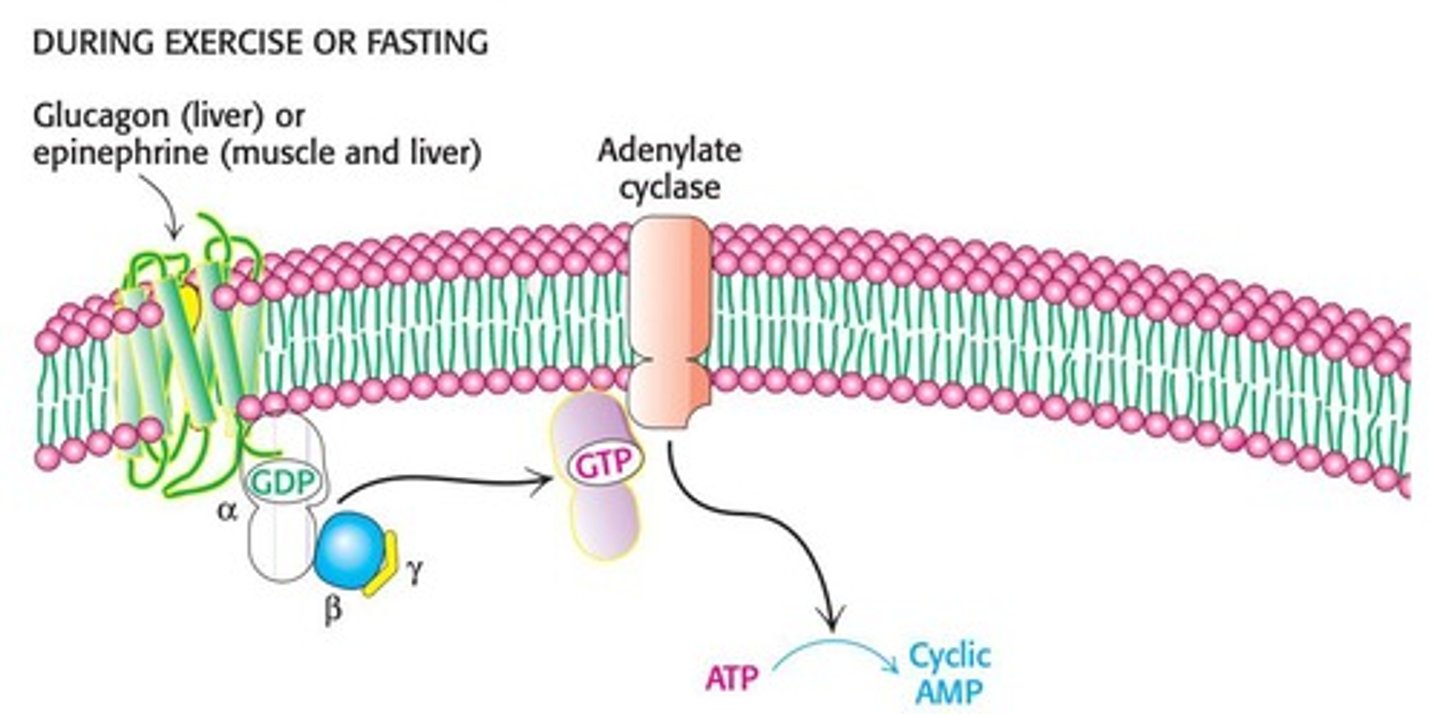
What triggers the release of epinephrine during stress?
Strenuous exercise, excitement, or stress triggers the adrenal glands to secrete epinephrine.
Why might a person feel lethargic after a carbohydrate-rich meal?
Increased insulin secretion activates glycogen synthesis, leaving less glucose available for immediate energy.
What is the role of adenylyl cyclase in the regulatory cascade?
Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cyclic AMP, which activates protein kinase A (PKA).
How does PKA affect glycogen phosphorylase?
PKA phosphorylates and activates glycogen phosphorylase, converting it from the inactive to the active form.
What is the effect of PKA phosphorylation on glycogen synthase?
PKA phosphorylation inactivates glycogen synthase, promoting glycogenolysis and inhibiting glycogenesis.
What is Diabetes Mellitus Type 1?
Insulin-dependent diabetes caused by autoimmune destruction of pancreatic insulin-secreting cells.
What characterizes Diabetes Mellitus Type 2?
Insulin-resistant diabetes where the patient is non-responsive to insulin due to receptor defects.