General Terminology
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
regional neurobiology
study of the structure and function of anatomical parts of the nervous system (e.g. study of the brainstem)
systems neurobiology
study of the functional systems that involve the interaction of multiple regions of the nervous system (e.g. study of the motor system)
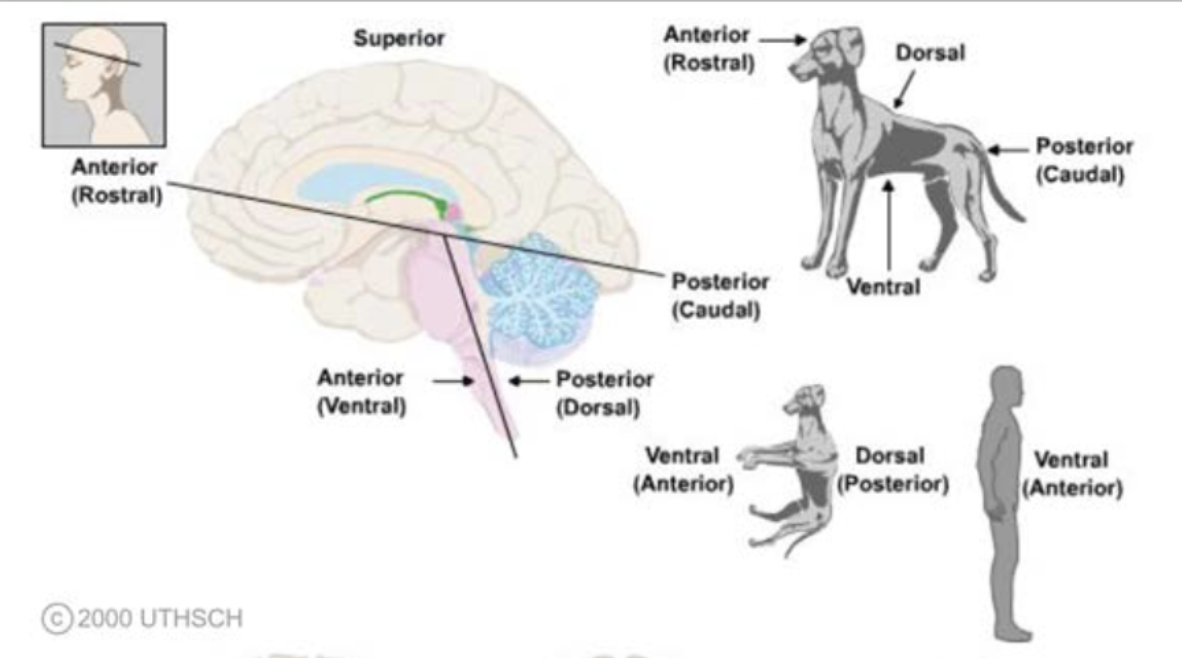
terms of relationship and comparison: rostral
head of the organism; towards the face/nose (exclusing brainstem)
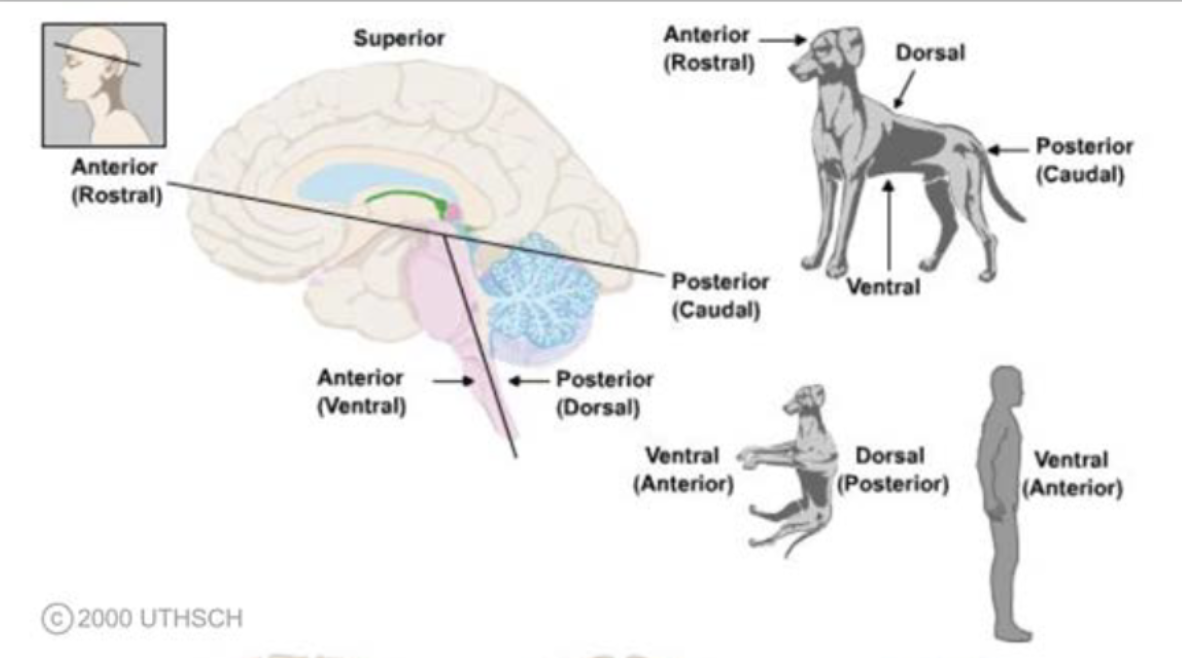
terms of relationship and comparison: caudal
tail of the organism; towards the buttocks/tail (exclusing brainstem)
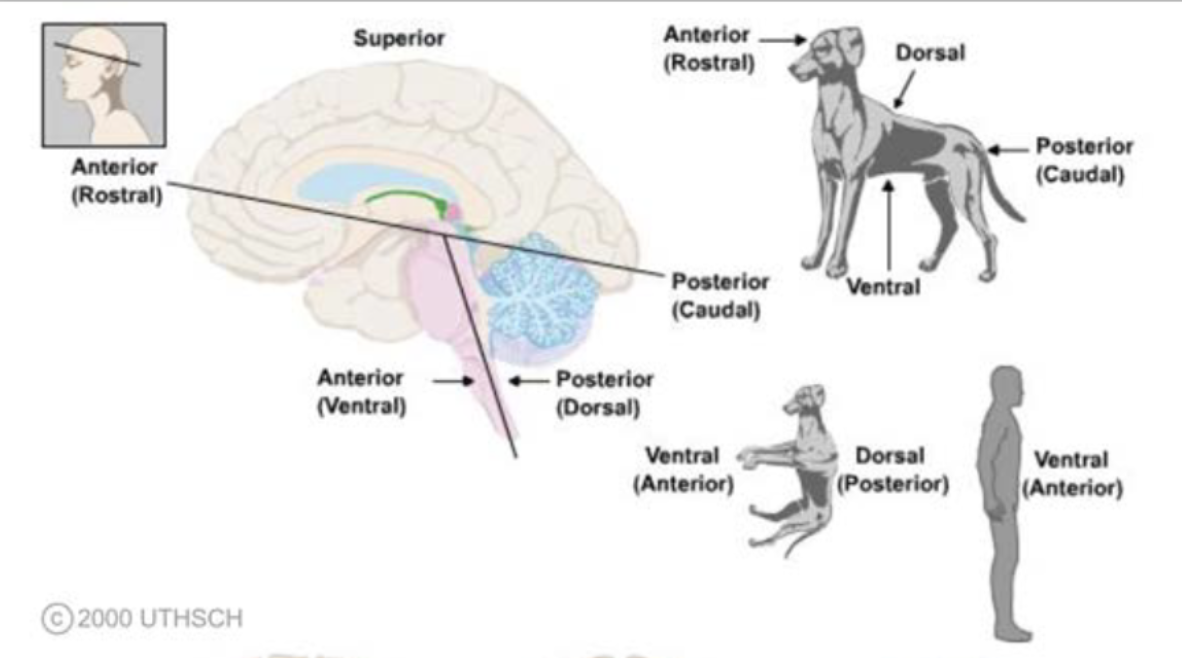
terms of relationship and comparison: ventral/anterior
front of the organism; towards the front or “belly”
terms of relationship and comparison: dorsal/posterior
back of an organism; towards the back
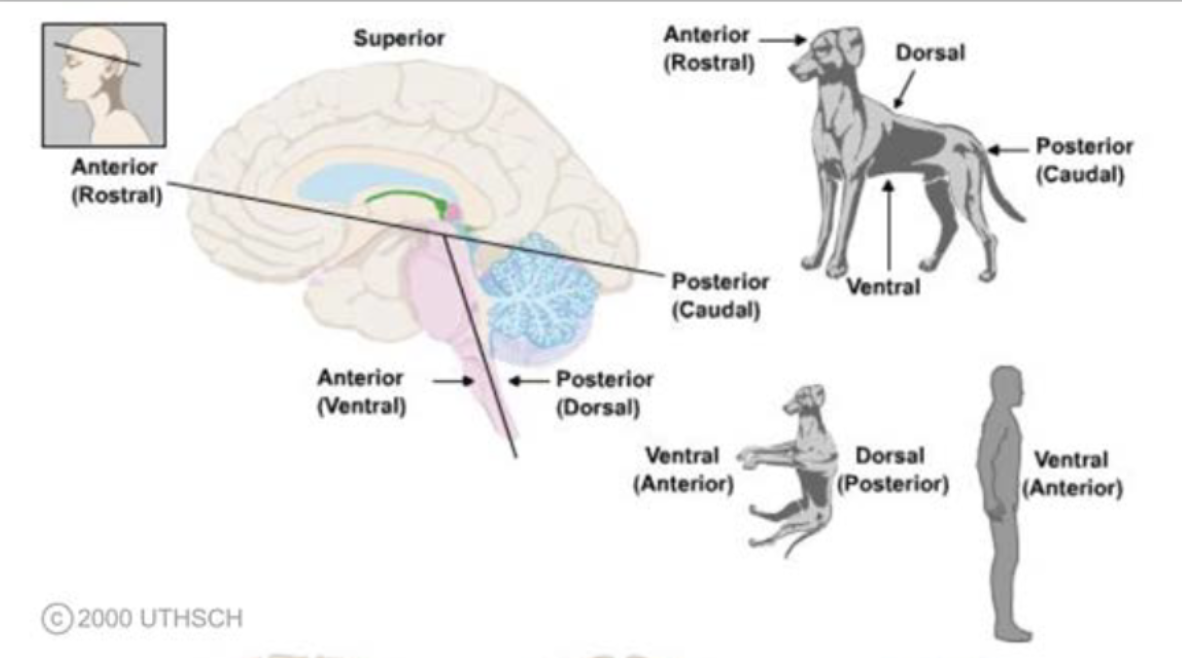
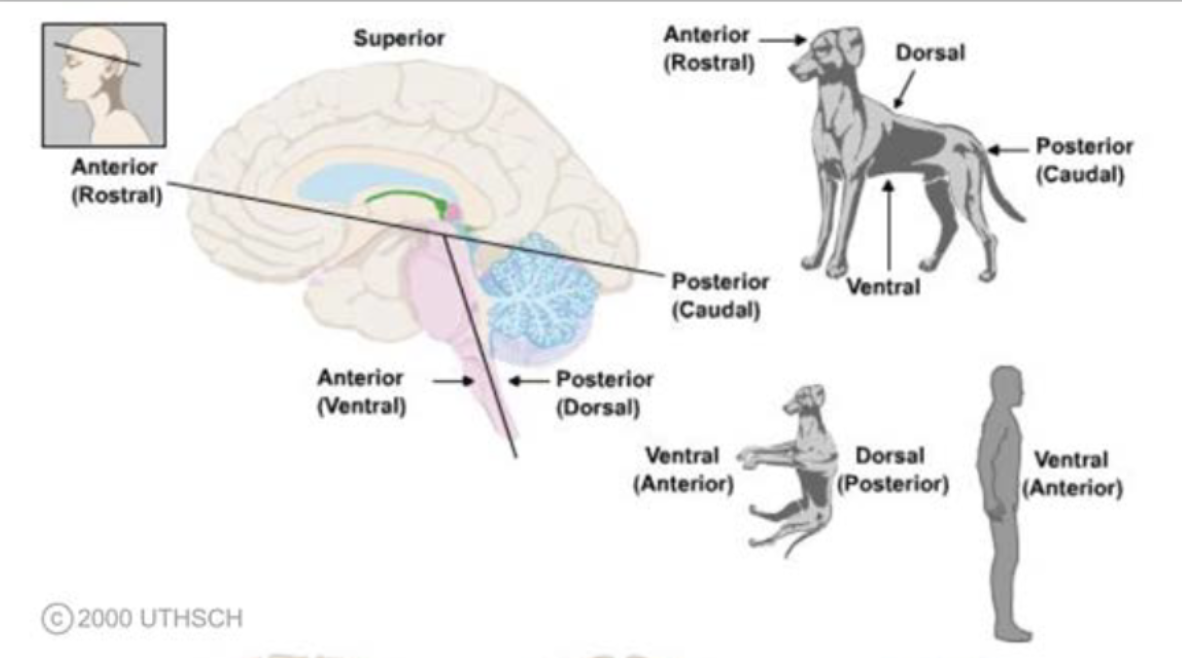
terms of relationship and comparison: superior
toward the top; with reference to the cortex of the brain, dorsal is frequently used
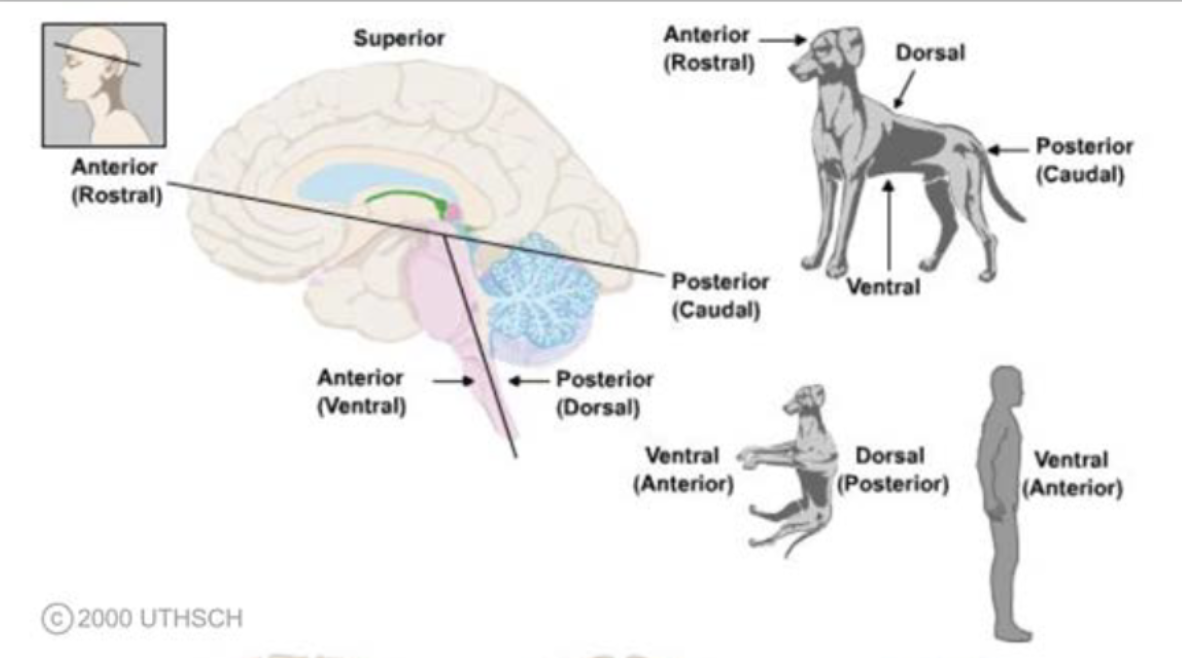
terms of relationship and comparison: inferior
toward the bottom; with reference to the cortex of the brain, ventral is frequently used
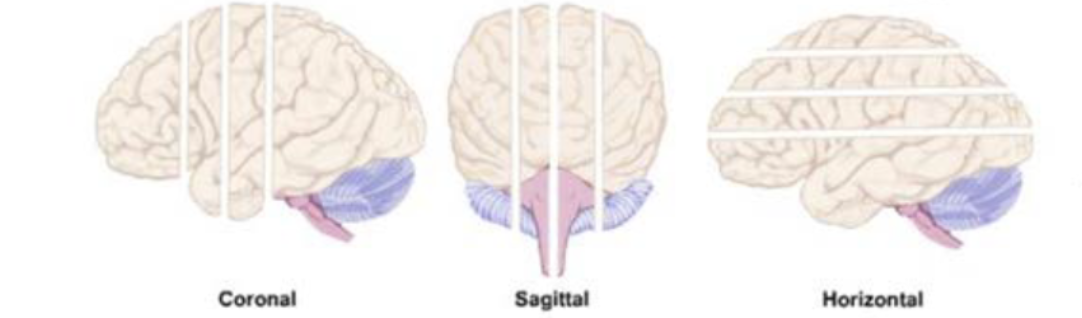
planes of the brain sections/brain slices: horizontal slice
cut made in the horizontal plane: mid-horizontal section divides the brain into superior and inferior halves
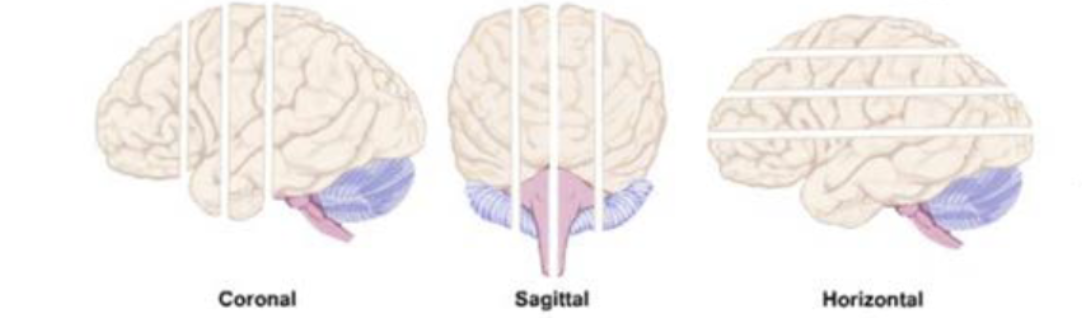
planes of the brain sections/brain slices: coronal slice
cut made in the coronal plane: mid-coronal section divides the brain into anterior and posterior halves
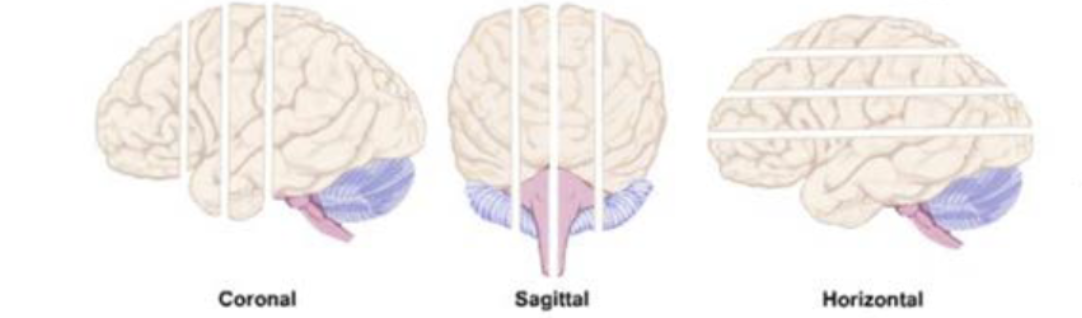
planes of the brain sections/brain slices: sagittal slice
cut made in the sagittal place: mid-sagittal section divides the brain into right and left halves
structural divisions of the nervous system: central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord
structural divisions of the nervous system: peripheral nervous system
consists of the spinal nerves, the cranial nerves, and the ganglia (collection of cell bodies located outside the CNS) associated with them
functional divisions of the nervous system: somatic nervous system
parts of the CNS and PNS that regulate skeletal muscle and that convey somatic sensory information coming from the periphery
functional divisions of the nervous system: autonomic nervous system
parts of the CNS and PNS that regulate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glandular secretion, and that convey sensory information coming from the viscera
parasympathetic division: rest/digest
sympathetic division: fight/flight
neuron
(aka nerve cell)- basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system; responsible for receiving, integrating, and transmitting electrical impulses that impact other neurons or target tissue (e.g. skeletal muscle)
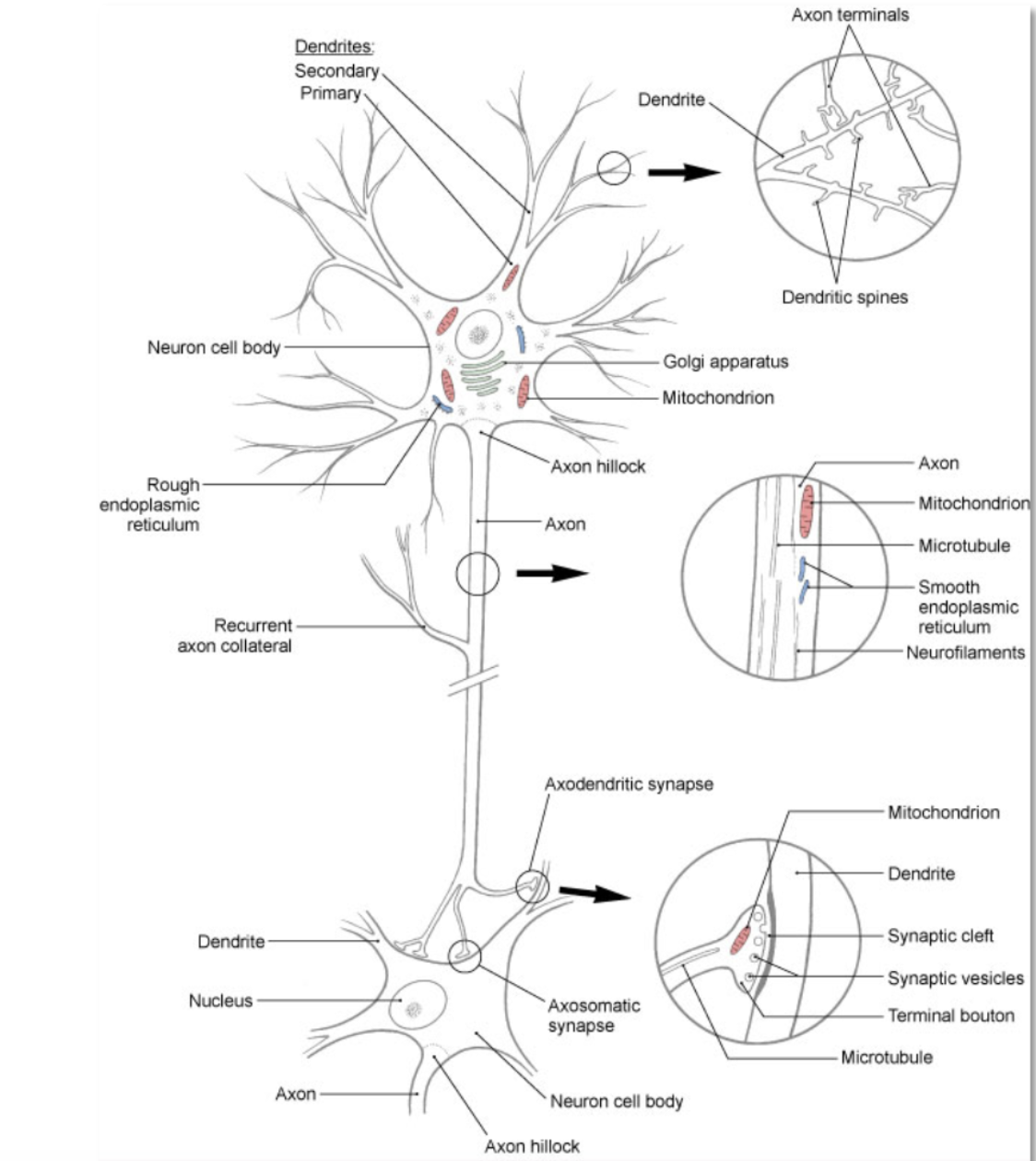
neuron: dendrite
branching processes that conduct impulses toward the body of a neuron (receiving end of the neuron)
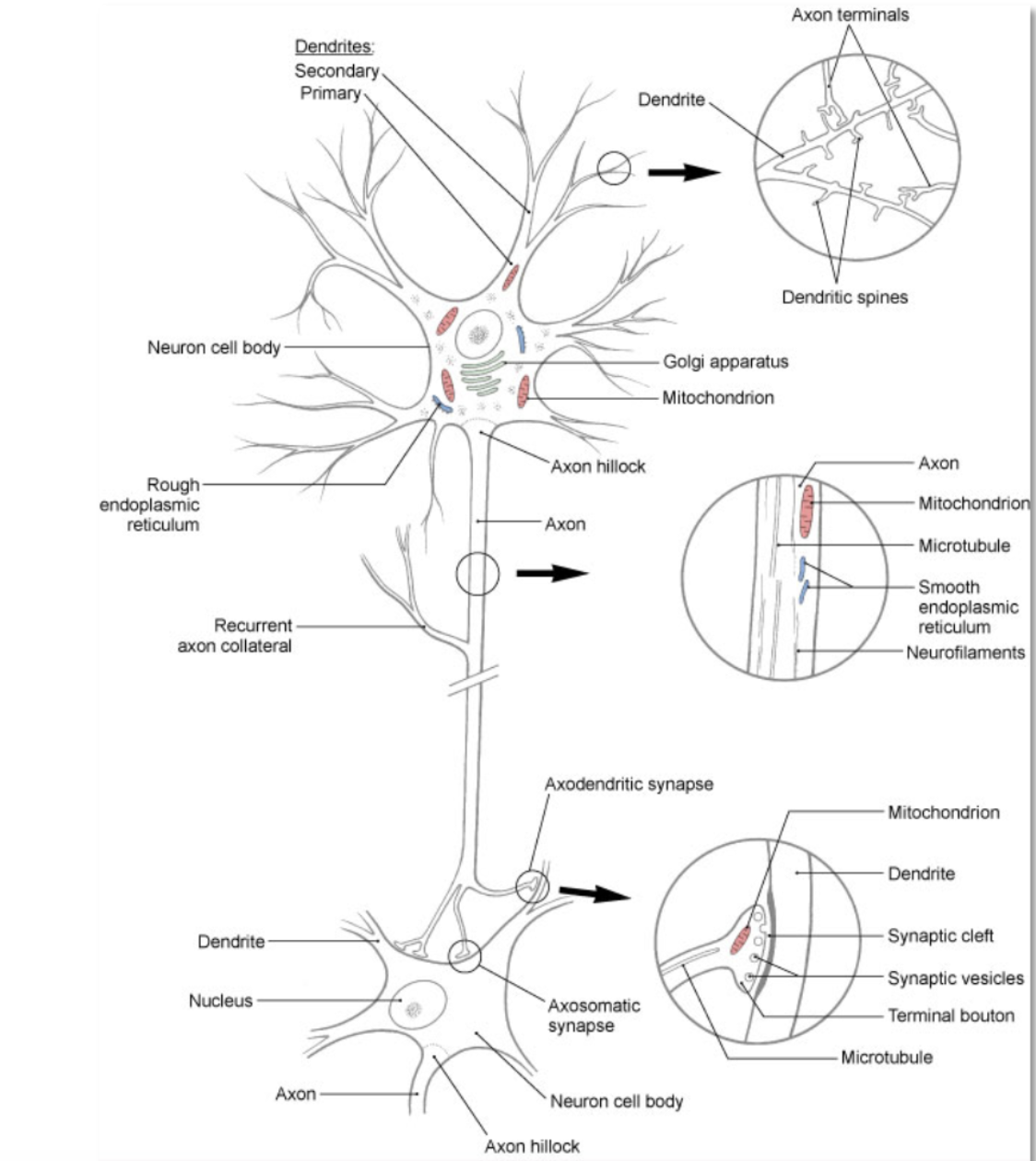
neuron: soma
cell body- contains all of the organelles that are required to keep the cell functioning
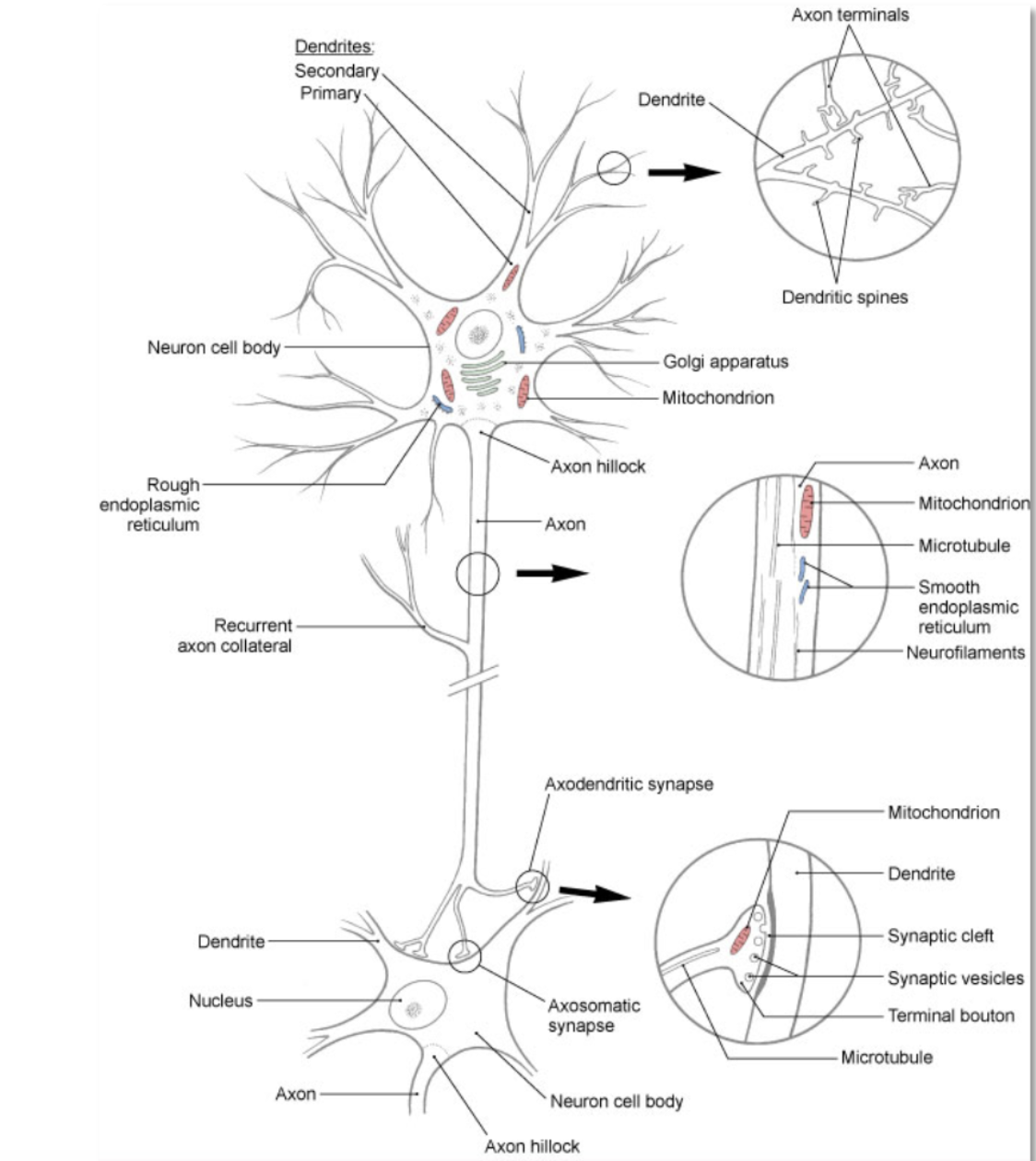
neuron: axon
branching processes that conduct impulses away from the body of the neuron (sending end of the neuron)
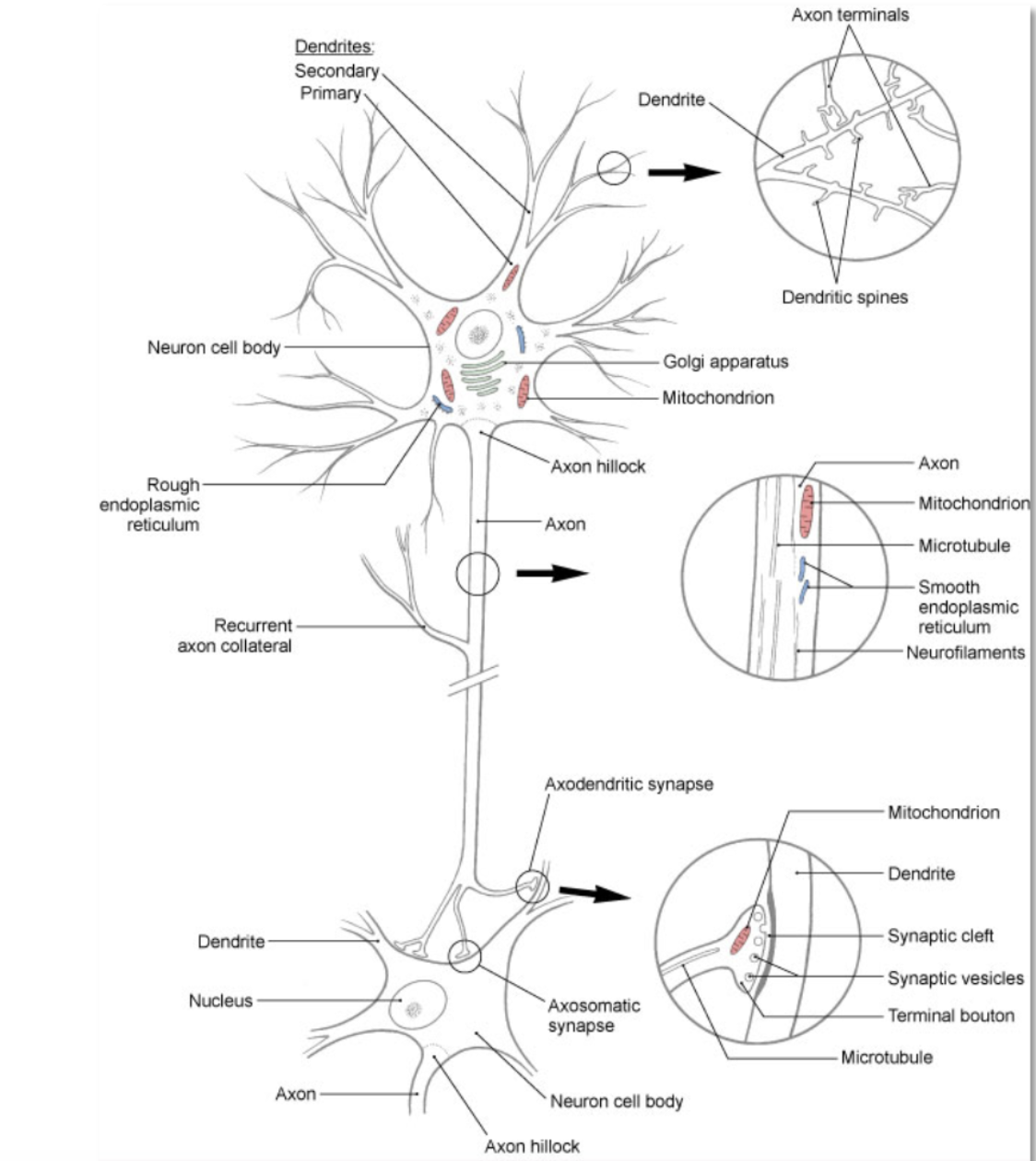
neuron: myelin
insulating lipoprotein that surround some axons
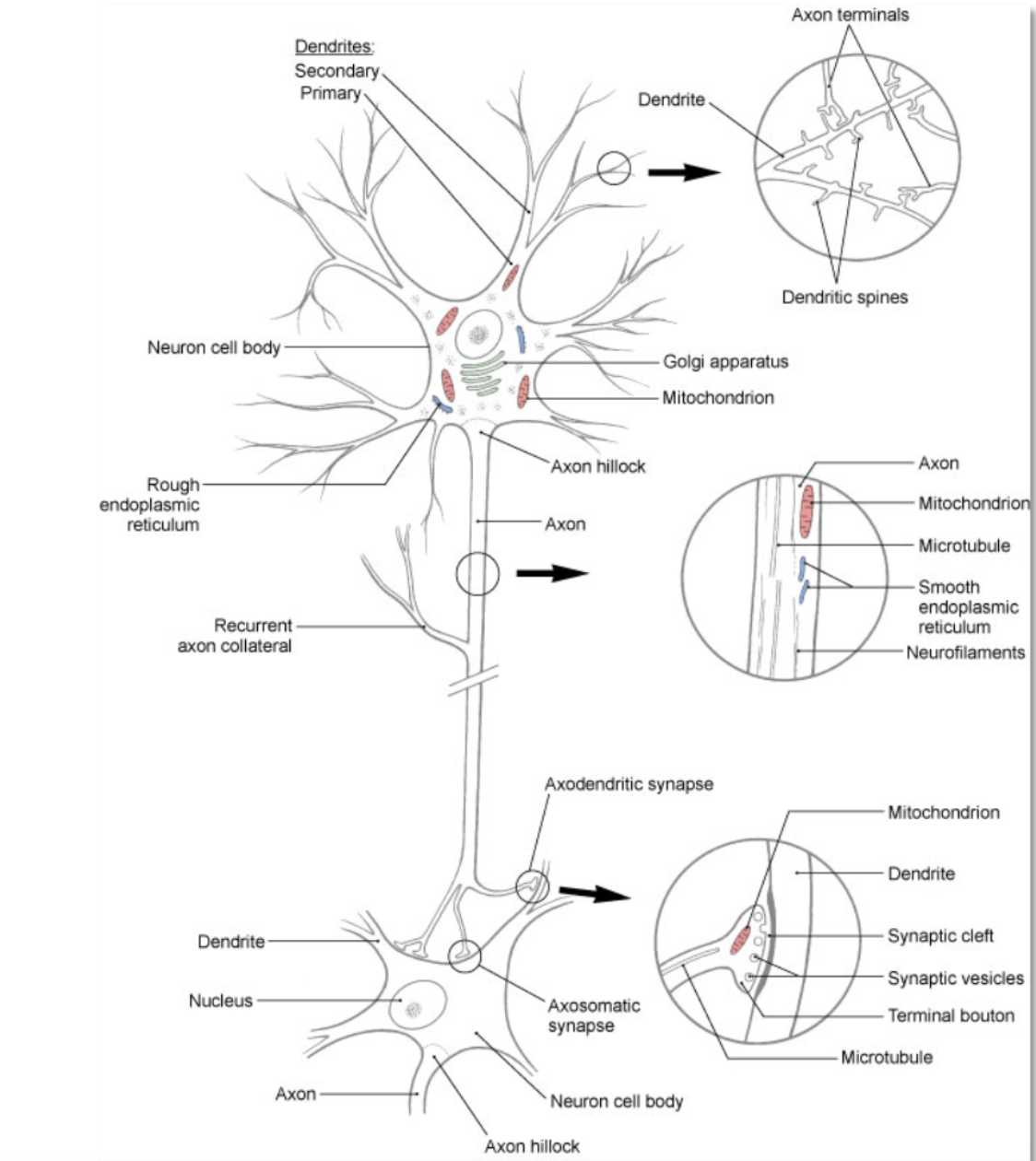
neuron: afferent
conduction toward a structure or incoming information (posterior or dorsal root of a spinal nerve)
neuron: efferent
conduction away from a structure of outgoing information (e.g. anterior or ventral root of a spinal nerve)
neuron: synapse
location where information from 1 neuron is transmitted to another neuron or to an effector target (e.g. muscle or gland)
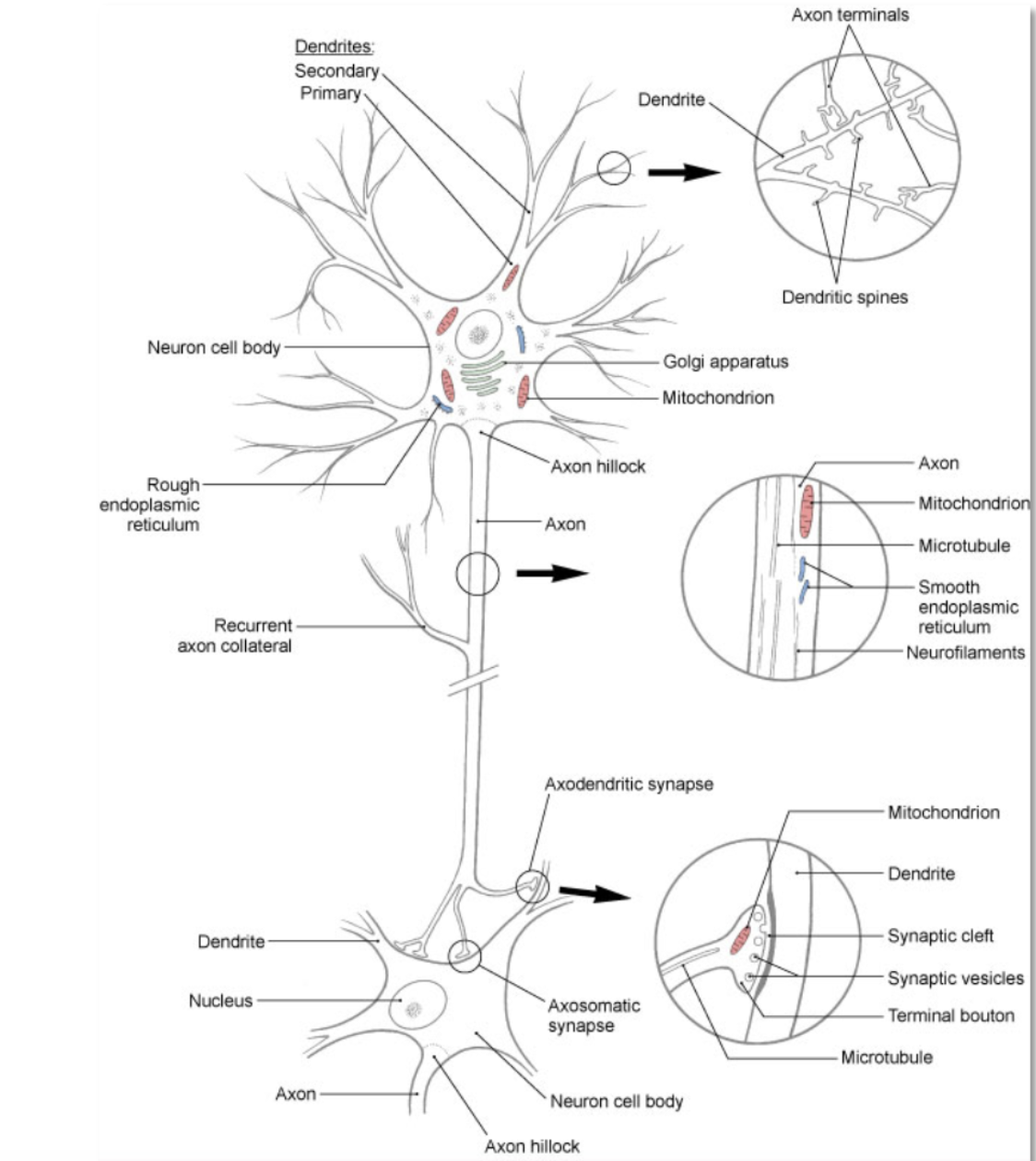
neuron: neurotransmitter
chemical messenger
glia
“glue” supporting cells in the CNS
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglial cells
gray matter
collection of neural cell bodies
gray matter: cortex
(pl. cortices) outer layer of gray matter that covers the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum
gray matter: nucleus
(pl. nuclei) a distinguishable mass of neuronal cell bodies in the CNS
gray matter: lamina
(pl. laminae) a distinguishable layer of neuronal cell bodies in the CNS
gray matter: posterior or dorsal horn
gray matter in the spinal cord that contains second order sensory neurons
gray matter: anterior or ventral horn
gray matter in the spinal cord that contains somatic motor neurons
gray matter: lateral horn
gray matter in the spinal cord that contains visceromotor neurons
gray matter: ganglion
(pl. ganglia) a distinguishable mass of neuronal cell bodies in the PNS
white matter
collection of axons in the CNS
white matter: nerve
bundle of axons in the PNS
white matter: tract
collection of axons in the CNS that originate from a similar location and go to a similar destination
white matter: commissure
collection of axons that connect both hemispheres or both sides of the spinal cord
white matter: column
axonal tracts that carry information to and from the spinal cord
white matter: lemniscus
(pl. lemnisci) tract that travels through the brain resembling a ribbon
white matter: fasciculus
(pl. fasciculi) bundle or packet of nerve fibers traveling in the CNS (e.g. cuneate fasciculus)
white matter: funiculus
(pl. funiculi) cord- area of white matter that may consist of several functionally different fasciculi (e.g. lateral funiculus of the spinal cord) or tracts
white matter: decussation
point of crossing of paired tracts (e.g. left tract crosses to the right side and vis versa; decussations of the pyramids, the medial lemnisci, and superior cerebellar peduncles are examples)
regions of the brain: telencephalon
consists of the cerebral hemispheres and related deep structures (e.g. insula, limbic structures (e.g. hippocampus and amygdala) and basal nuclei)
cerebral structures:
cerebrum: is divided by a fissure (deep groove) called the median longitudinal fissure into right and left hemispheres, and it has a folded appearance:
the ridge or elevated area of the fold is called a gyrus (pl. gyri) and the groove or crease between folds is known as a sulcus (pl. sulci)
Gyri and sulci have specific names and are associated with specific functions (e.g. the precentral gyrus is considered the primary motor cortex (M1) and it contributes to the control of voluntary movements
regions of the brain: cerebrum- frontal lobes
mediates motor planning and execution, expressive language, and mental functions (e.g. executive functions, social cognition, and emotional regulation)
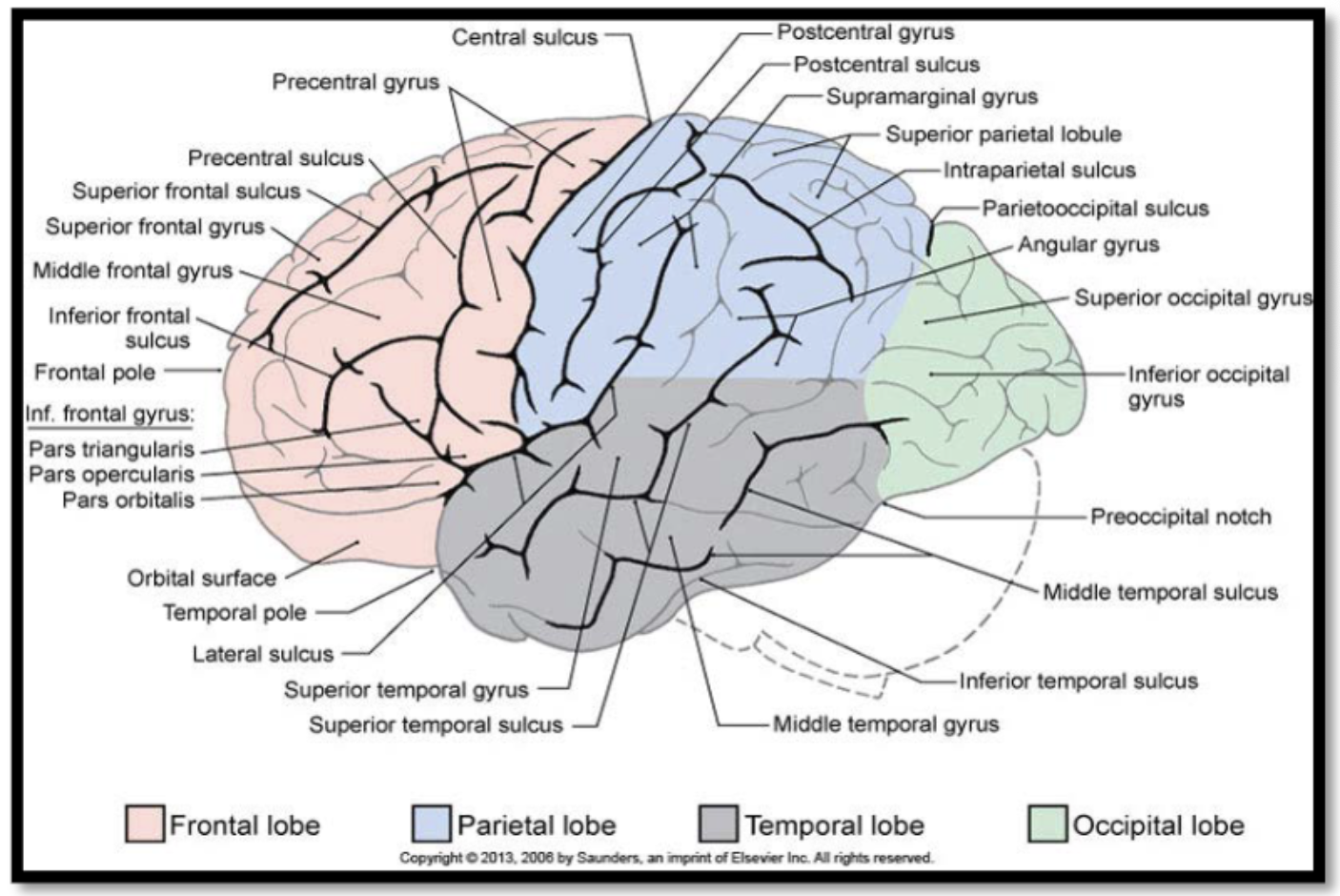
regions of the brain: cerebrum- parietal lobes
detection of somatosensory information, and the integration, perception, and interpretation of sensory information (e.g. visuospatial processing, language comprehension, and self-processing operations)
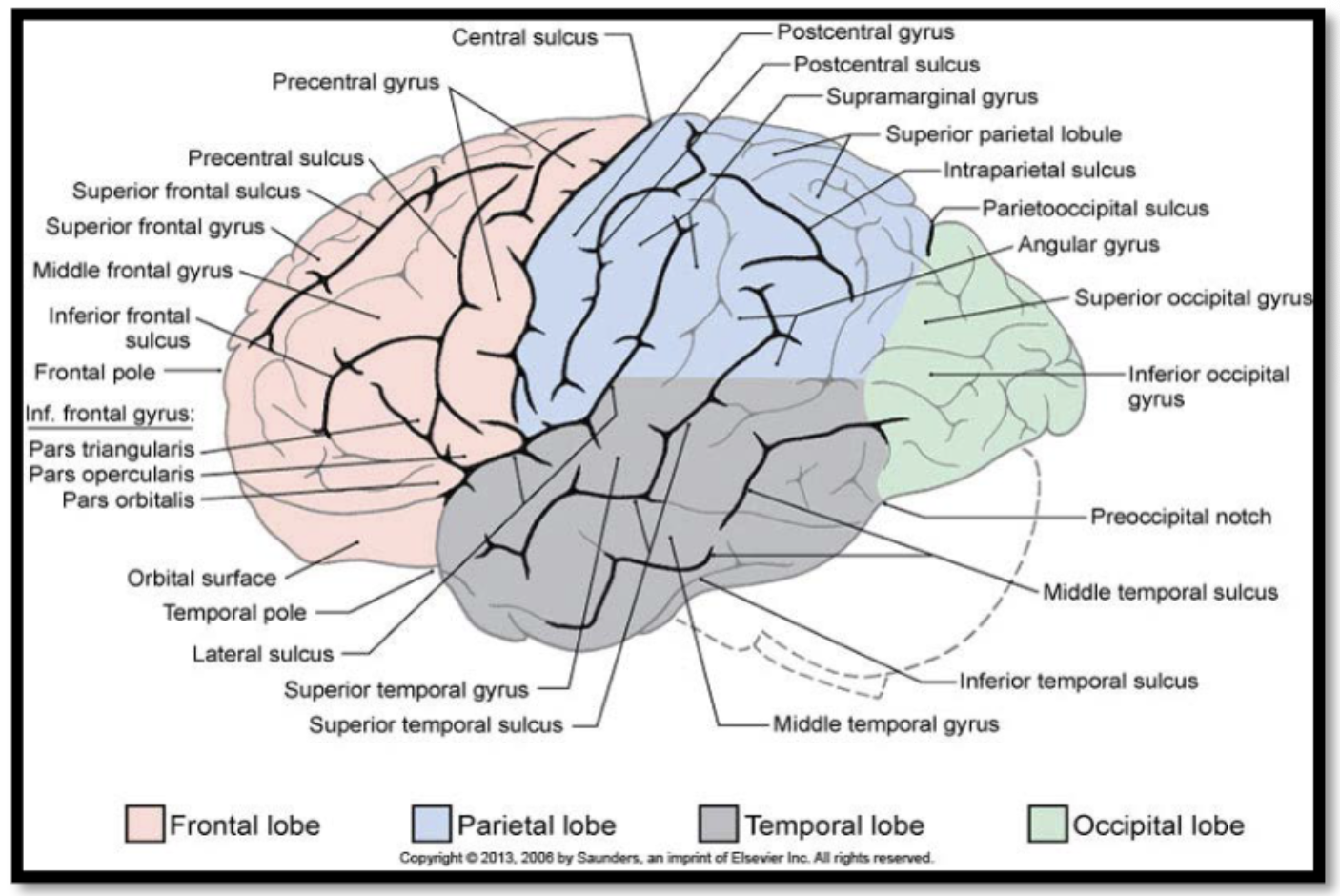
regions of the brain: cerebrum- temporal lobes
detection of auditory information and basic auditory processing, language comprehension, object identification, long-term memory formation, and social cognition
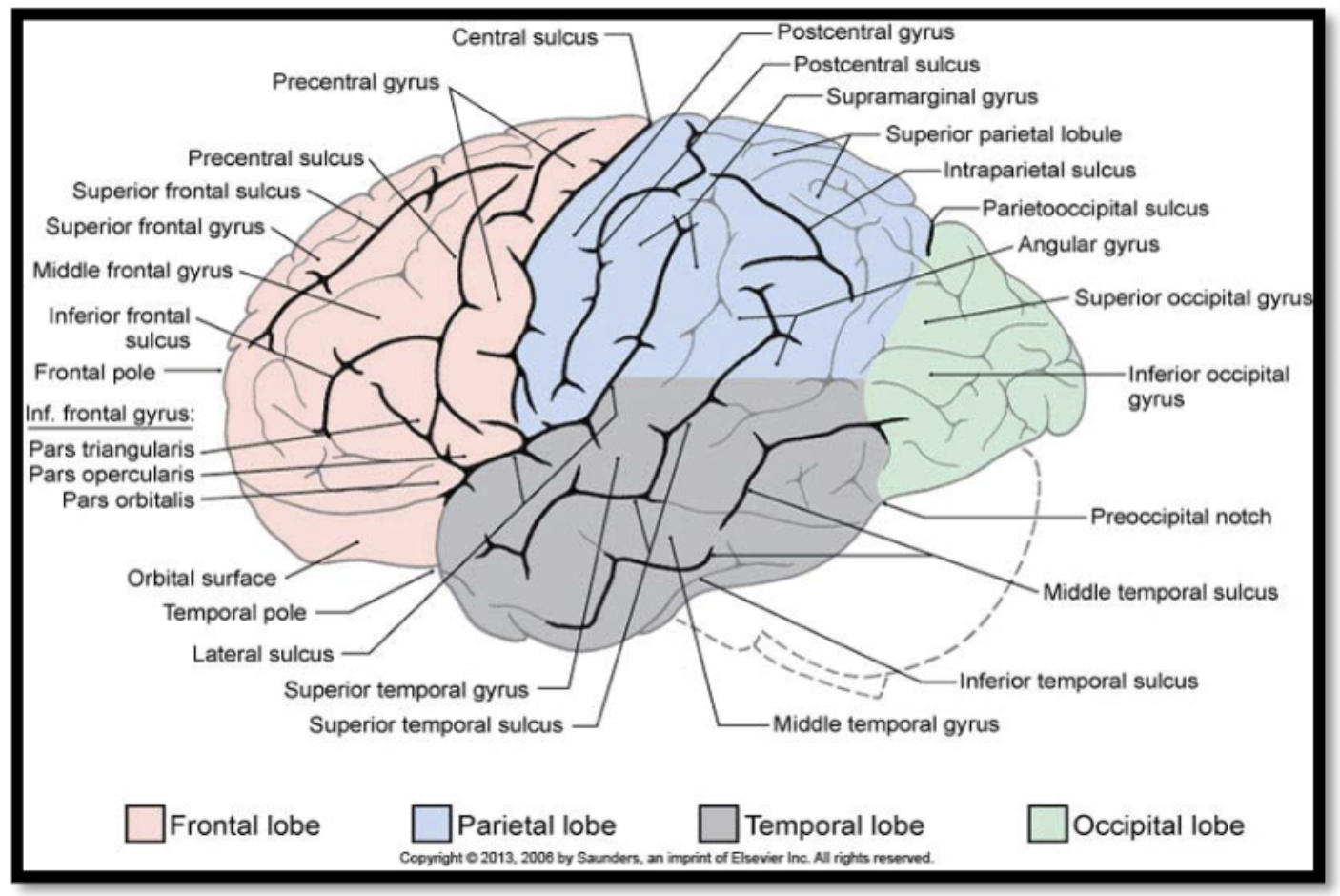
regions of the brain: cerebrum- occipital lobes
detection of visual stimuli and basic visual processing
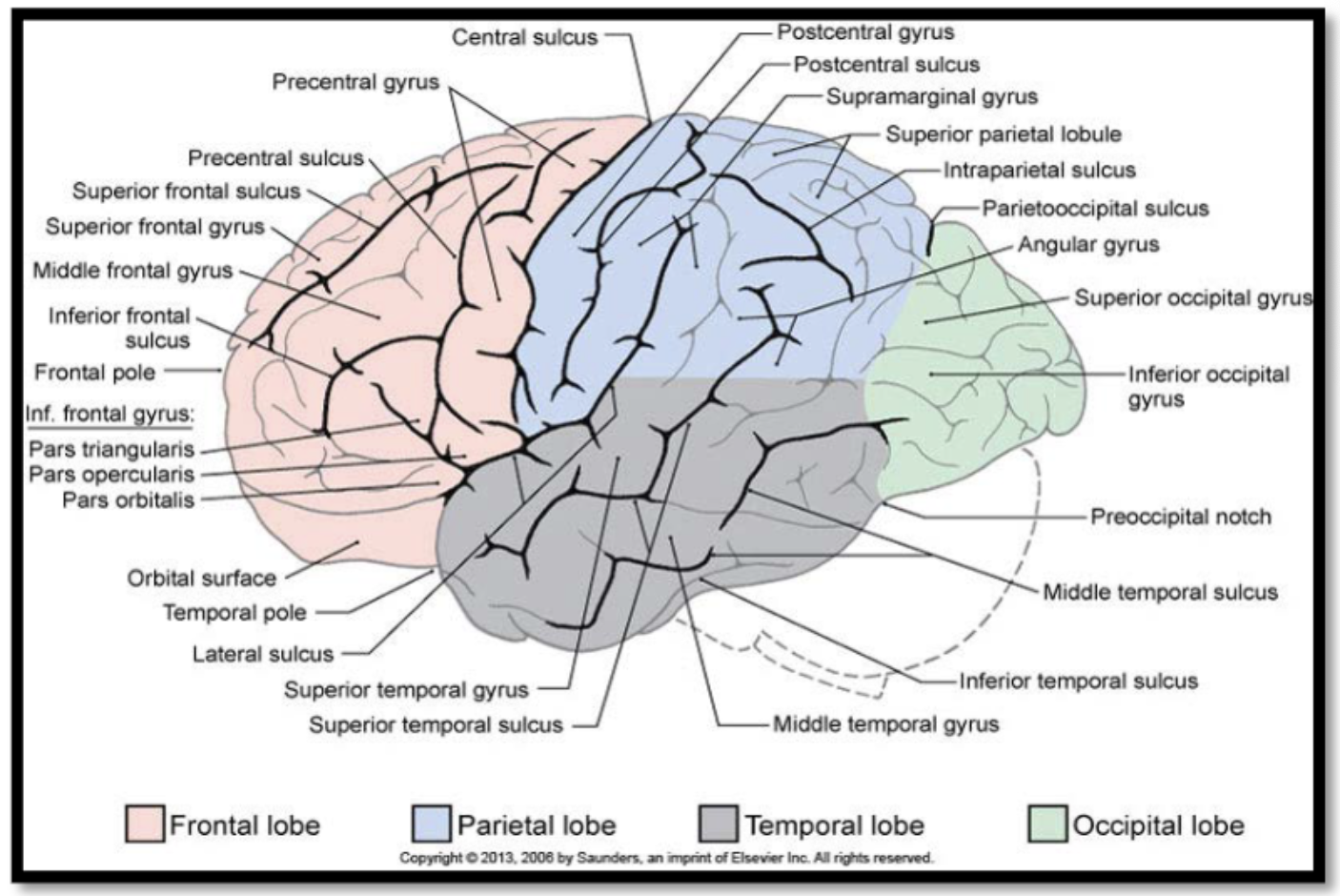
regions of the brain: cerebrum- insula
considered a 5th lobe in some sources: related to basic survival mechanisms such as taste perception and the processing of visceral sensations; also though to play a role in emotional processing
regions of the brain: cerebrum- deep structures
basal nuclei: caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus- involved with motor, cognitive, and emotional functions
limbic structures: hippocampus and amygdala- involved with memory formation and emotional functions
internal capsule: large fiber bundle that connects the cerebral cortex with the diencephalon
diencephalon
consists of the following structures
thalamus: contains multiple nuclei and seves as a gateway for information traveling to/from the cortex, as such it is involved with multiple functions
hypothalamus: contains multiple nuclei and is instrumental in regulating visceromotor, viscerosensory, and endocrine functions
sub-thalamus: contains the subthalamic nucleus, which plays a role in motor control
epithalamus: contains the pineal gland which plays a role in regulating circadian rhythms
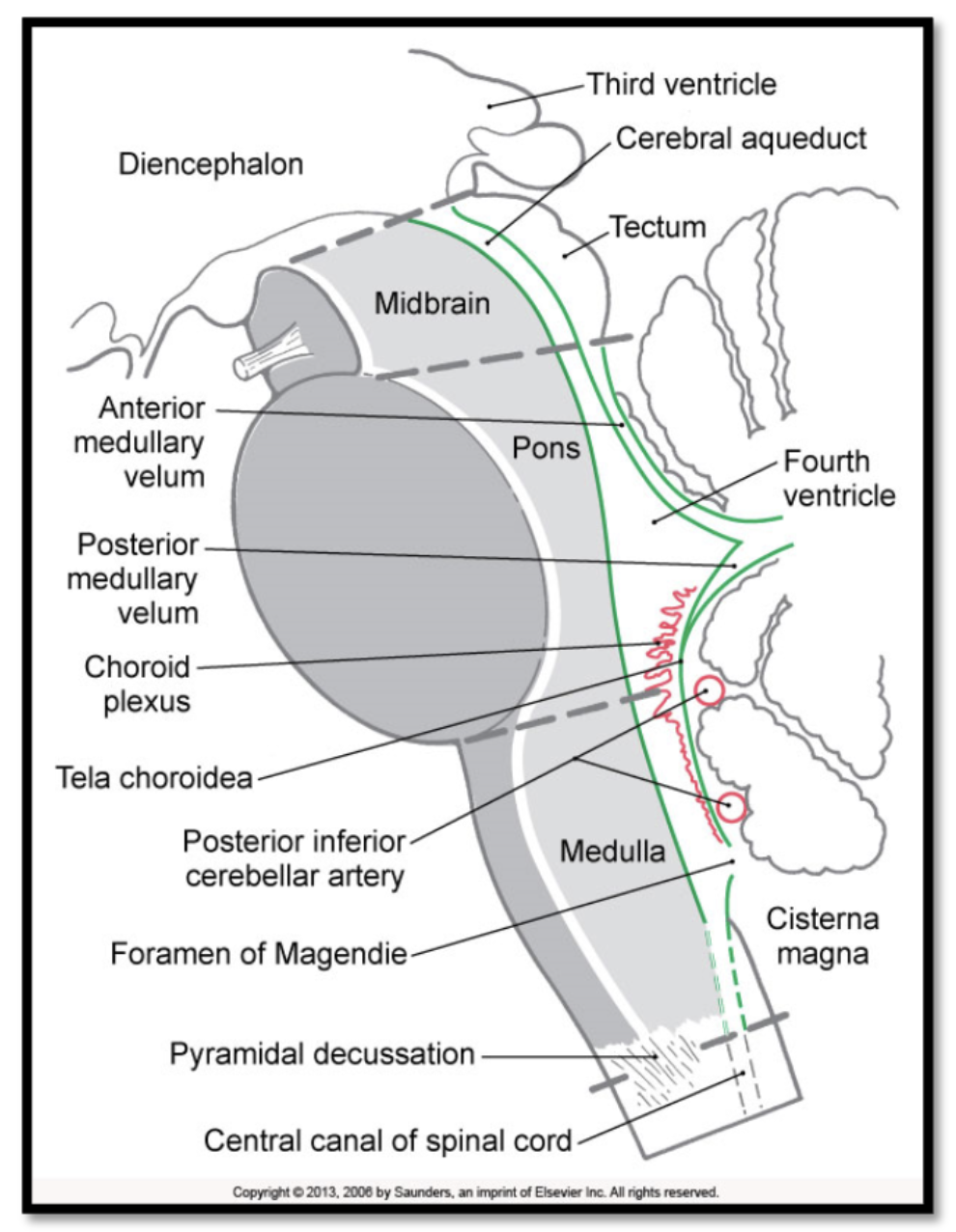
cerebellum
means “little brain”- plays a prominent role in motor control and motor learning
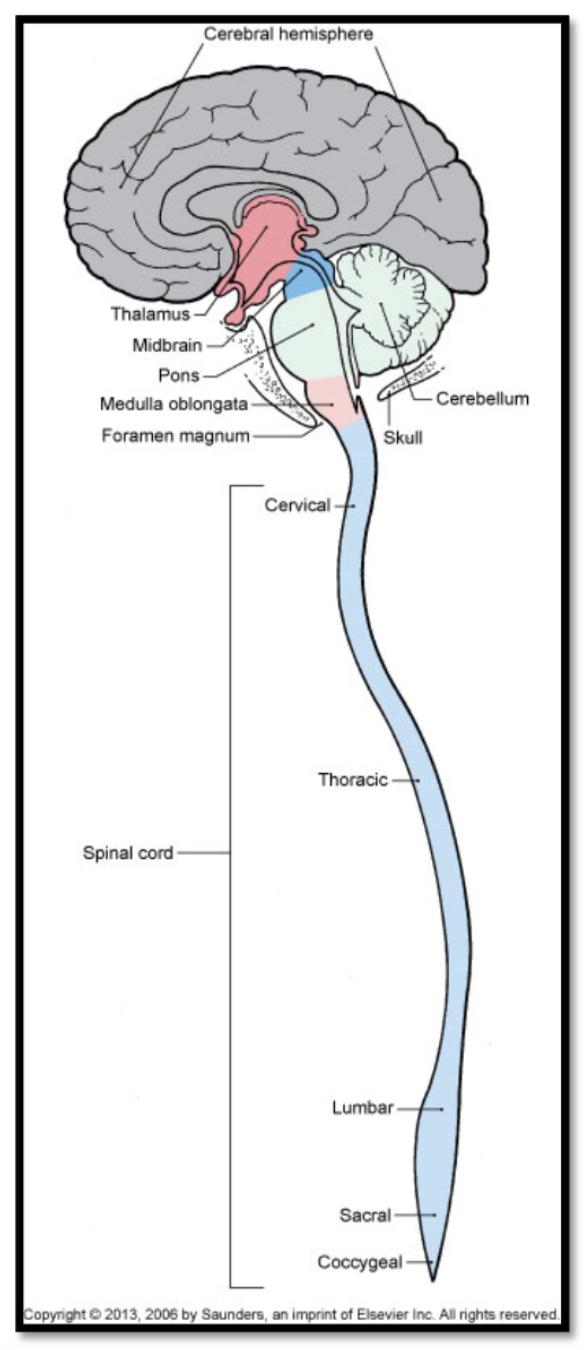
brainstem
mediates vegetative functions (e.g. control of respiration, blood pressure regulation), auditory and visual reflexes, arousal, sleep/wake patterns, modulation of pain signals, and it plays a role in motor control
consists of 3 structures from rostral to caudal:
midbrain
pons
medulla
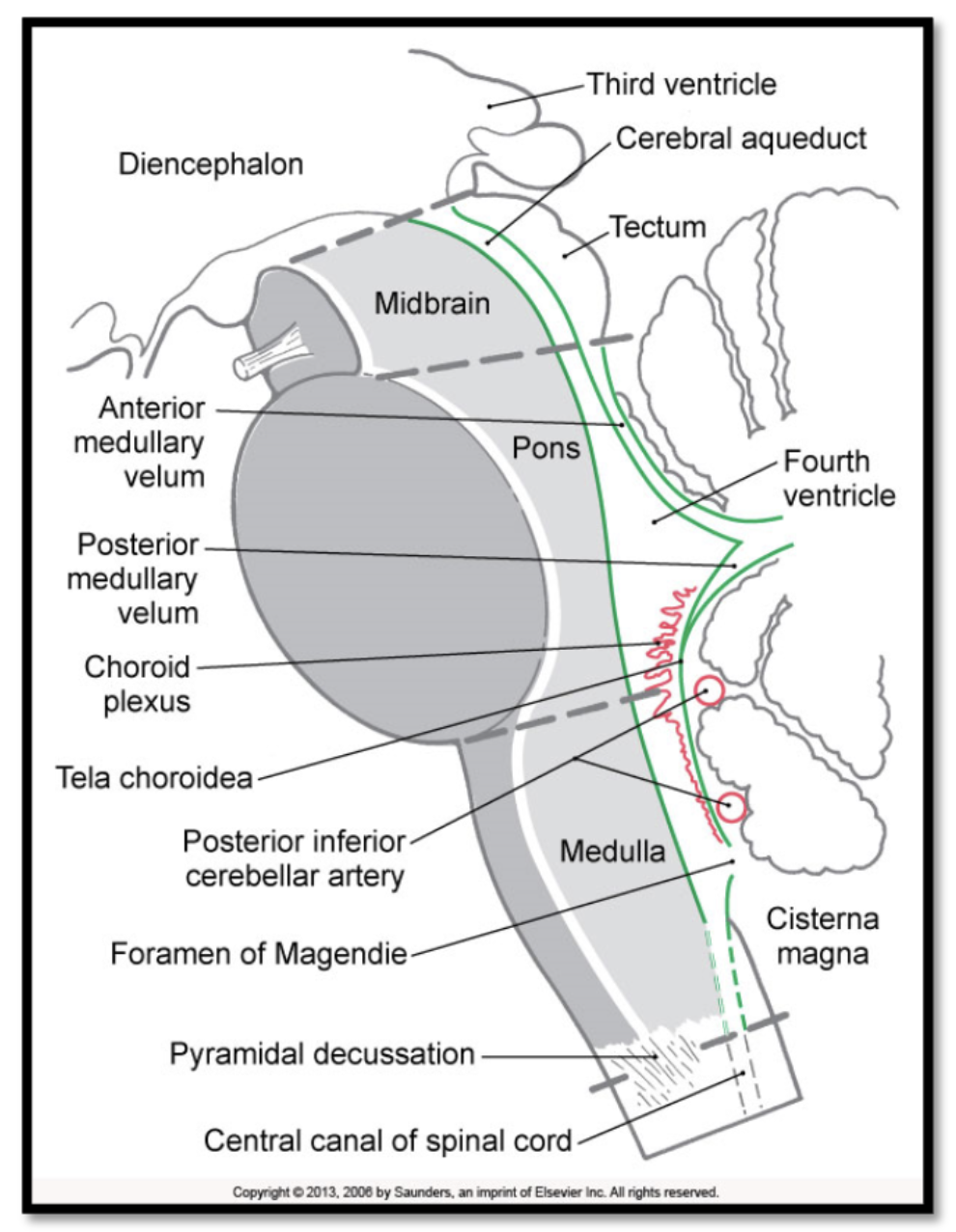
mesencephalon
corresponds to the midbrain during development
metencephalon
corresponds to the pons and cerebellum during development
myelencephalon
corresponds to the medulla during development
prosencephalon
forebrain during development
rhombencephalon
hindbrain during development