Physics - Circular Motion
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is centripetal force?
a center-directed force that causes an object to move in a curved path (net force that is directed toward the center of the circle) "center seeking"

What is centripetal acceleration?
acceleration directed toward the center of a circle
What is the rotational speed?
the number of revolutions per unit of time "angular speed"

What is tangential speed?
the speed of an object moving along a circular path "llinear speed"

What is static friction?
the friction that prevents an object from moving in a certain direction (i.e. between your tires and the road when you go around a curve)

units for mass
kilogram

units for speed or velocity
m/s
units for acceleration
m/s/s or m/s^2
units for Force or weight
Newton

Which of the following statements are true of an object moving in a circle at a constant speed? Select all that apply.
a. The object is accelerating.
b. The object is at equilibrium
c. The velocity of the object is changing
d. The direction of the object is changing
e. The net force experienced by the object is 0 newtons.
a, c, d
A centrifugal force is
a. An outward force that must be present to move in a circle
b. an inward force that causes objects to travel straight ahead
c. a false force that we make up to explain our feelings of going straight
c
What is the term for the net force directed toward the center of an object's circular path?
a. centrifugal force
b. centripetal force
c. circular force
d. orbital force
b
When calculating the gravitational force between two extended bodies, you should measure the distance
a. from the center of each body
b. from the closest points on each body
c. from the center of one body to the closest point on the other body
d. from the most distant points on each body
a
When an object is moving with uniform circle motion, the object's tangential speed
a. is circular
b. is directed toward the center of motion
c. is perpendicular to the radius of the circle
d. is perpendicular to the plane of motion
c
The centripetal force on a object in circular motion is
a. in the direction opposite the centripetal acceleration
b. in the same direction as the centripetal acceleration
c. in the direction opposite the tangential speed
d. in the same direction as the tangential speed
b
Why does an astronaut weigh less on the moon than on Earth?
a. The astronaut has less mass on the moon
b. The astronaut is continually in free fall because the moon orbits Earth
c. The astronaut is farther from Earth's center when he or she is on the moon
d. The gravitational field strength is less on the moon's surface than on the Earth's surface
d
When an object is moving with uniform circular motion, the centripetal acceleration of the object
a. is circular
b. is perpendicular to the plane of motion
c. is zero
d. is directed toward the center of motion
d
A ___ has both magnitude and direction. A _____ quantity has magnitude alone
vector, scalar
An object can move in a circle at constant speed and still have changing velocity.
True or False?
True
An object is moving in a circle at a constant speed of 30 m/s. It is known for sure that the object is accelerating because it is
changing the direction of its velocity
An object moves in a circle at a constant speed. The direction of the acceleration vector is best described as being
inwards, towards the center
An object is moving in a circle of a radius at a constant speed. The acceleration of the object will INCREASE if
- Speed were increased
- Its radius were decreased
A car makes a left-hand turn. The front seat passenger claims that she feels a sensation of being pulled outwards. This is best explained by the fact that
the passenger has a natural tendency to move tangent to and out of the circle
At the bottom of one of the circular loops, the normal force of the pilot is
- directed upwards
- of greater magnitude than the force of gravity
To make an object move in a circle with a constant speed, a force must act on it that is directed where?
-towards the center of the circle
In circular motion, does direction change frequently?
-yes, direction changes continuously
What is produced whenever the direction of a velocity changes?
-acceleration
In what direction does this acceleration act?
-towards the center of the circle
What is this center-directed acceleration called?
-centripetal acceleration
What is the magnitude of centripetal acceleration equal to? (in equation form)
acceleration centripetal = v^2/r
What must be applied to an object to give it a circular motion?
-centripetal force
For an object of mass m, what is the magnitude of the net force acting on it? (in equation form)
force centripetal = m(v^2/r)
How can centripetal force be produced?
-in any number of ways
What are some examples of how centripetal force may be produced?
-might be the tension in a string
-might be due to friction between tires and the road
-could be the force of gravity causing a satellite (or the Moon) to orbit the earth
If we are studying a system where the force of static friction provides the centripetal force required to move a car in a circular path, what is the effect of decreasing the radius the car's path?
-maximum speed that the car can have in a corner with out skidding decreases
In was direction does Fnet point when an object is in uniform circular motion?
-towards the center of the circle
What two forces can act on objects in circular motion?
-tangential force and centripetal force
In what direction does tangential force operate?
-parallel to velocity
If the tangential force is parallel to velocity, what effect does it have on an object?
-it causes the object to accelerate, thereby changing velocity
In what direction does centripetal force operate?
-perpendicularly to velocity
-radially inward
If the centripetal force is perpendicular to velocity, what effect does it have on an object?
-nudges an object to change direction
What is the size of acceleration due to centripetal force equal to?
Centripetal acceleration = v^2/r
If the energy required for circular motion is less than actual energy, what will be the path of an object?
-the object will move closer and closer towards the center of a circle
What will occur when the energy required for circular motion equals actual energy?
-the object will move in a circle
A popular carnival ride has passengers stand with their backs against the inside wall of a cylinder. As the cylinder begins to spin, the passengers feel as if they are being pushed against the wall. Explain.
-since the passengers are moving in a circular path, a centripetal force must be exerted on them
-->this force, which is radially inward, is supplied by the wall of the cylinder
The gas pedal and the brake pedal are capable of causing a car to accelerate. Can the steering wheel also produce an acceleration? Explain.
-yes, the steering wheel can accelerate the car by decreasing the radius of the turn
When rounding the corder on a bicycle or a motorcycle, the driver leans inward, toward the center of the circle. Why?
-when a bicycle rider leans inward on a turn, the force applied to the wheels of the bicycle by the ground is both upward and inward
-it is this inward force that produces the centripetal acceleration of the rider
What is Circular motion?
Motion of an object traveling in a circular path with a constant velocity and a constant radius
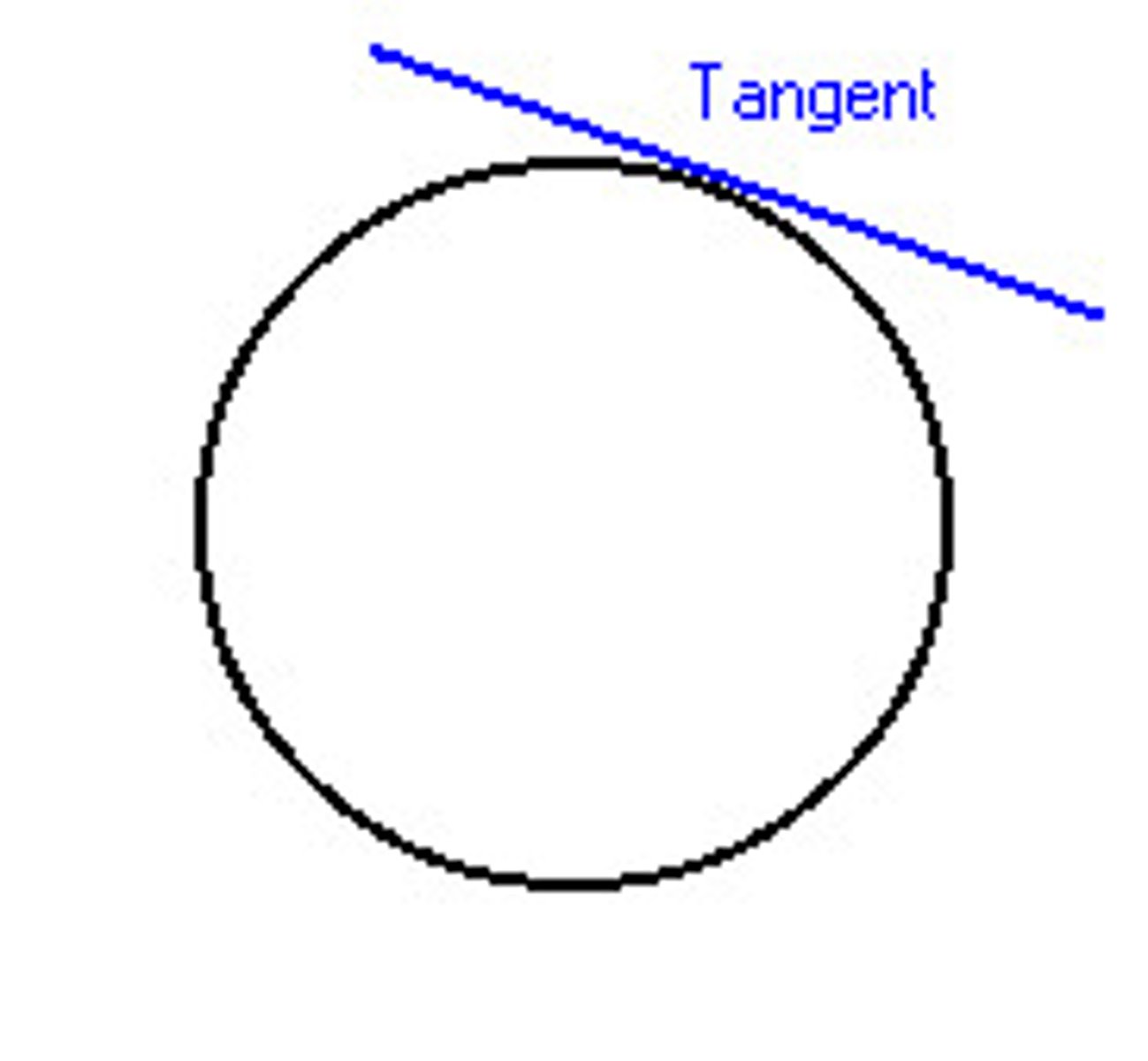
What is a Tangent?
A line in the plane of a circle that intersects the circle in exactly one point.
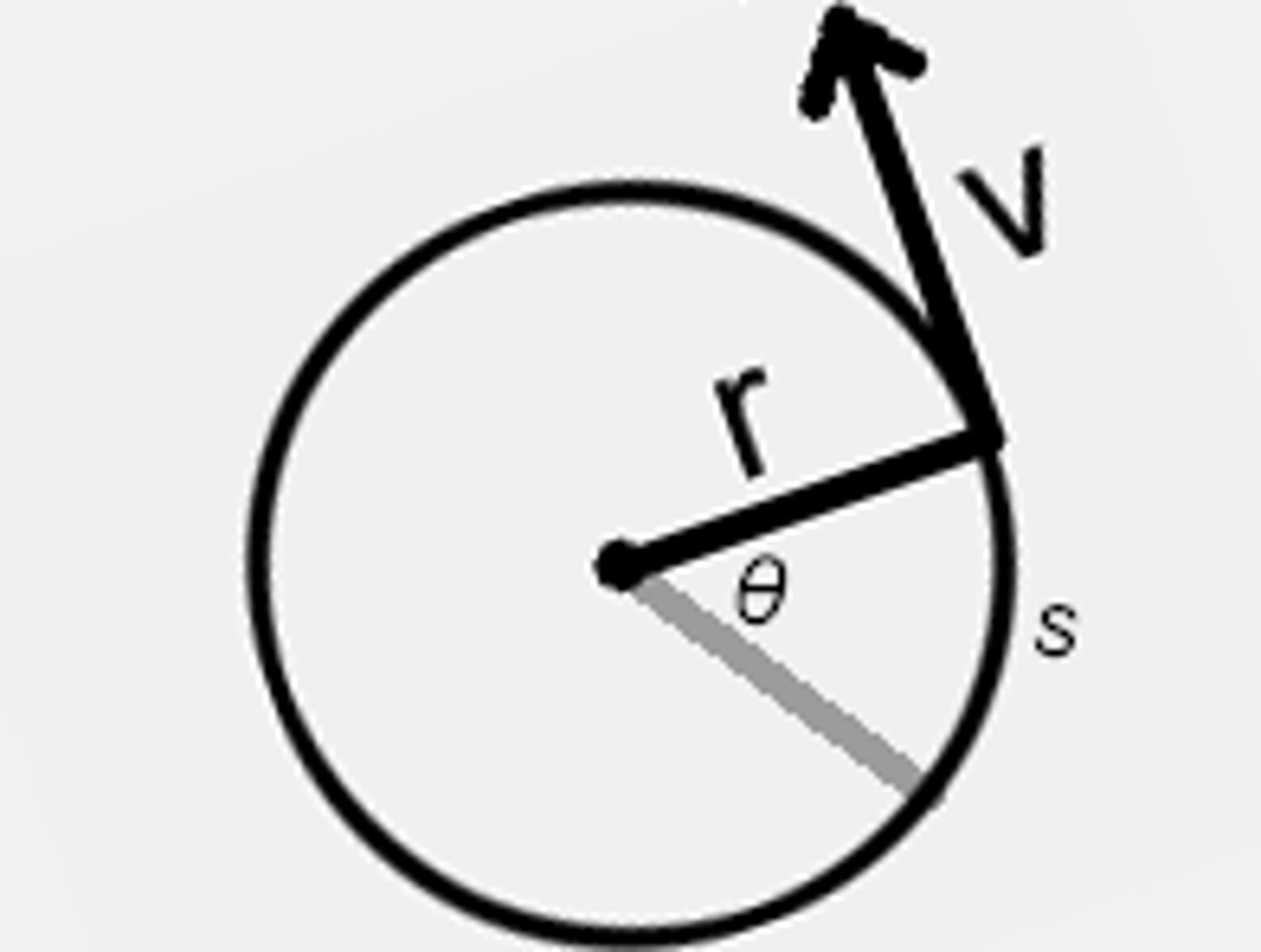
What is Tangential velocity?
The speed of an object at a point as it moves around the circumference of a circle.
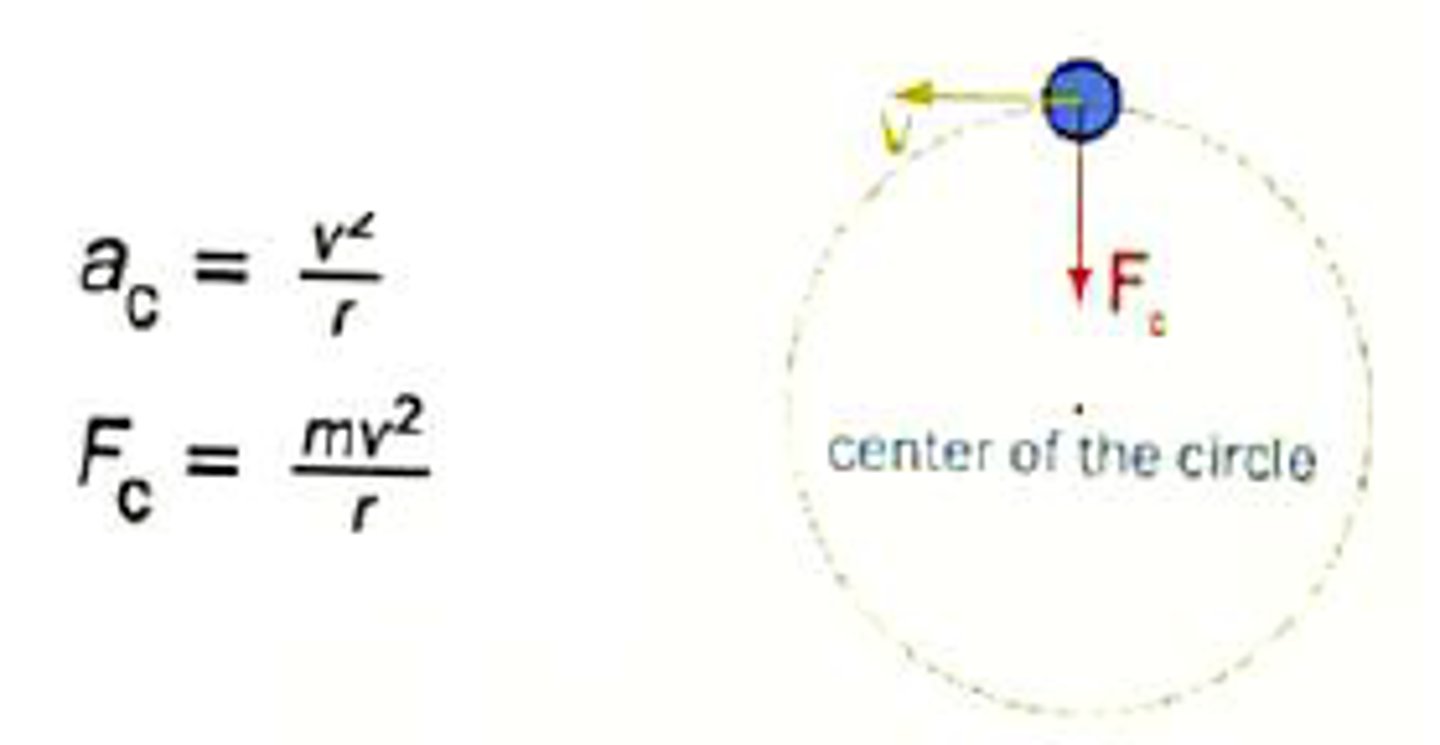
What is Centripetal acceleration?
Acceleration of an object toward the center of a curved or circular path.
What is Centripetal force?
A net force that is directed toward the center of a curved or circular path. It generates the Centripetal Acceleration.

What is the Formula for Centripetal Force?
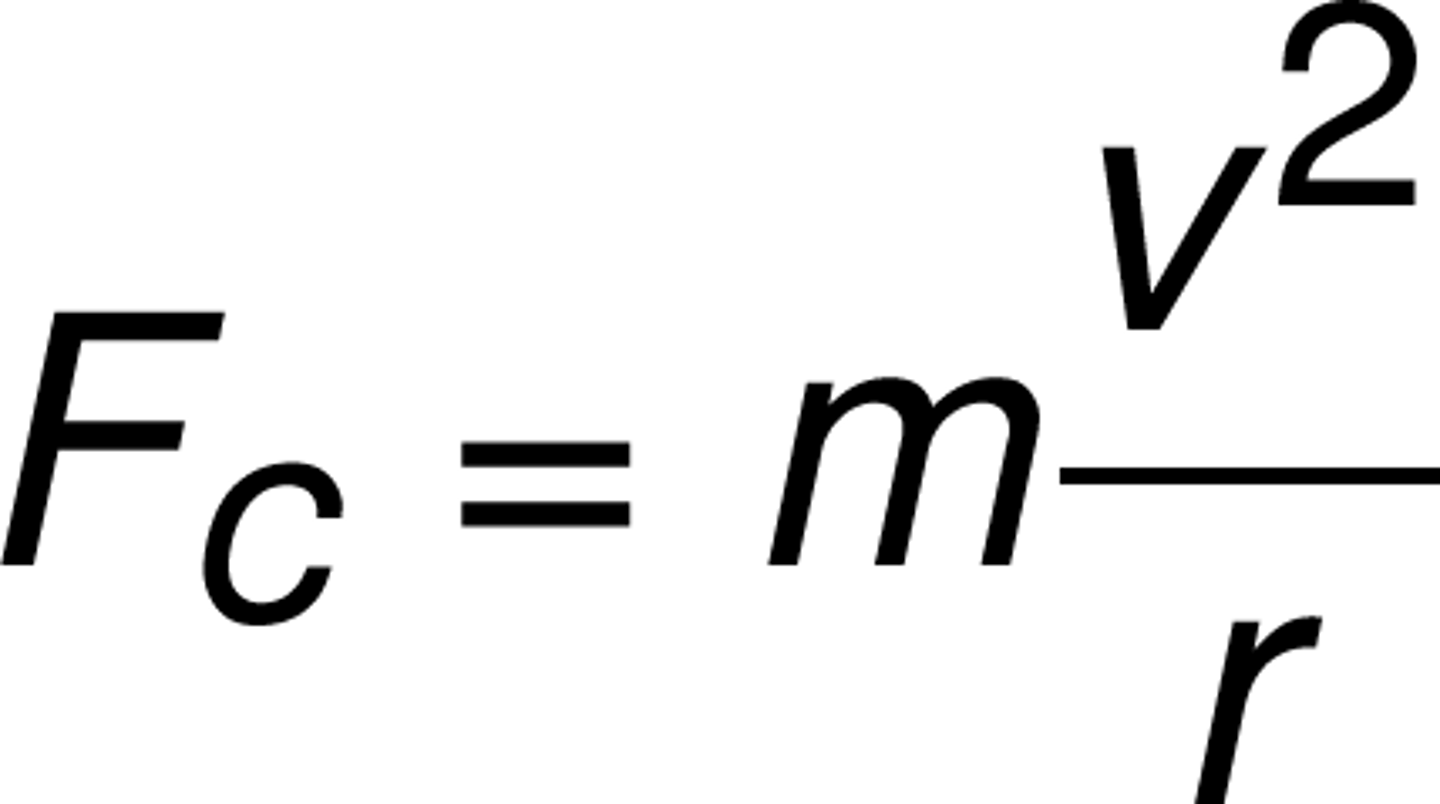
What is the Formula for Centripetal Acceleration?
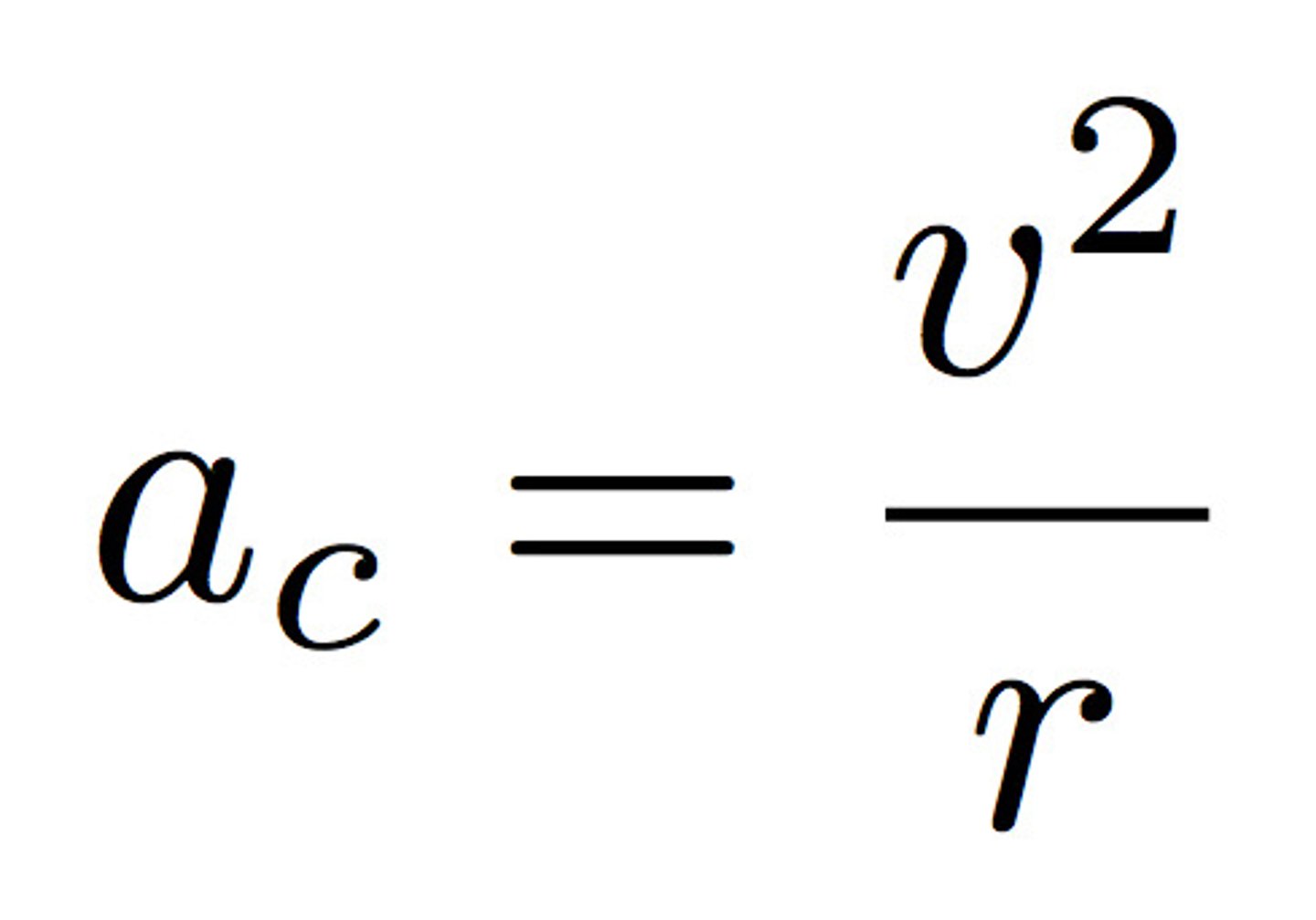
Which direction are Centripetal force & Centripetal acceleration directed to?
Directed towards the center of the circle
What does Centripetal actually mean?
This word means "center seeking"
What is the Radius?
The distance from the center of a circle to any point on the circle
When a force acts at an angle against a moving object, then the object will ________.
Change Direction
Type of force always acting in the direction opposite to the applied force. Opposite to sliding motion.
Frictional Force
Force holds the universe together, keeps orbits going, and keeps you grounded down on Earth so you don't float away.
Gravitational Force
A car moves around a circular path of a constant radius at a constant speed. Which statement is true?
The cars acceleration is directed toward the center
A car moves around a circular path of a constant radius at a constant speed. When the car is at the top of the circular path what is the direction of the velocity?
<-------
A car moves around a circular path of a constant radius at a constant speed. When the car is at the top of the circular path what is the direction of the acceleration?
I
I Downward
I
V
A boy stands at the edge of a rotating table. Which force prevents him from sliding off the table?
Static Friction
An object of mass m moves at a constant speed v around a circular path of radius r.The net force applied to the object F. What happens to the net force if the speed is doubled and the radius quadrupled?
Stays the same
A ball of mass m attached to a light string moves at a constant speed v in a vertical circle with a radius R. Which is true about the magnitude of the net force at point A compared to that at point B?
The net force at point A is equal to the net force at point B.
A rollercoaster car moves on a track with one section that is a vertical circular loop of radius R. When the car is at the top of the loop it just maintains contact with the track. What is the cars acceleration at this point?
g downward
What is Centripetal Force?
Any force that causes an object to follow a circular path is called a centripetal force.
What is Centrifugal Force?
Sometimes an outward force is also attributed to circular motion. This outward force is called centrifugal force. Meaning "away from the center."