Tectonics Case Studies
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Volcano Case Study
Eyjafallajokull 2010
Volcano erupted under a glacier
Cause local flooding due to sudden ice melt
Local water supplies contaminated
100,00 commercial flights cancelled due to ash clouds
European economy lost $5billion
No deaths
Volcano Case Study
Montserrat 1995
Part of an island arc in the Caribbean sea (formed where the Atlantic plate sinks beneath the Caribbean plate)
Only 16km long and 10km wide, consisting almost entirely of volcanic rock
Volcano had been dormant for 350 years
Was a thriving tourist destination with a population of 11,000
July 1995 the Soufriere volcano in the south of the island began to erupt huge clouds of ash
Over the next 5 years, these eruptions continued, with pyroclastic flows also affecting a large part of the island
Effects
19 dead
7000 moved (population dropped 4000)
Plymouth (capital) destroyed
2/3 housing destroyed
3/4 infrastructure destroyed
Lots of farmland destroyed or abandoned
Acid rain damaged plants
Top heavy population pyramid - young people no longer saw a future on the island
Governance in a developed country
Japan 2011
Mega-disaster, unusually high impacts
Hazard
9.0 magnitude earthquake
4.5 magnitude aftershocks
Shallow focus - 20 miles
Tsunami reaching heights of 40m
Vulnerability
Landslides
High population density
Coastal
Strong infrastructure
Low level corruption
Capacity to cope
Sea walls
Strong healthcare
Rescue teams
Earthquake and tsunami drills
Strong economy
Strongly enforced building regulations - 75% built with earthquakes in mind
110,000 defense troops mobilised within 24 hours
Short term impacts
15,000 + deaths
6,000 + injured
130,000 displaced
Fukushima nuclear meltdown
Immediately after the earthquake, all radio and TV stations switched to official earthquake coverage, advising people
Long term impacts
Economic cost of $235billion
Nuclear meltdown
Roads and railways destroyed
1000 buildings destroyed from liquefaction
The Bank of Japan offered $183billion to Japanese banks to keep them operating (protecting the economy)
Governance in a developing country
Haiti 2010
Hazard
7.0 magnitude earthquake
Shallow focus - 8.1 miles
Epicentre 16 miles from Port-au-Prince (capital)
Capacity to cope
Corrupt governement - a lot of money donated was never seen
80% population live below povery line
Unregulated building codes
Heavily indebted to US, German and French banks
Small airport - struggled to recieve aid
Short term impacts
200,000 + dead
300,000 + injured
1.5million displaced
4000 schools destroyed
Long term impacts
Cholera outbreak killed 9000 by 2015
$1.1billion raised between major charities
World bank waived debt repayments for 5 years
Never fully recovered (Parks Hazard Response Curve)
Pressure and release model
Haiti 2010
Root causes
heavily indebted to US, German and French banks
Corrupt government
80% population live below poverty line
Dynamic pressures
Poor management systems
Poor education systems
Lack of urban planning and building regulations
Rapid urbanisation leading to slums
Significant deforestation and soil degredation
High population density
Unsafe conditions
Soft soil amplified seismic waves
Low GDP per capita $1300
Cheap / poorly built buildings
Hazard
7.0 magnitude earthquake
Triggered a small tsunami
Nepal 2015
Hazard
7.9 magnitude earthquake
Shallow focus - 9.3 miles
48 miles northwest of Kathmandu
Difficult resuce efforts due to topography
Capacity to cope
40% families live below poverty line
90% depend on subsistence farming (growing crops sufficient only for one's own use)
Short term impacts
8000 + dead
19000 + injured
3million displaced
Triggered avalanches and landslides - destroying Langtang village
19 dead from landslide on Everest
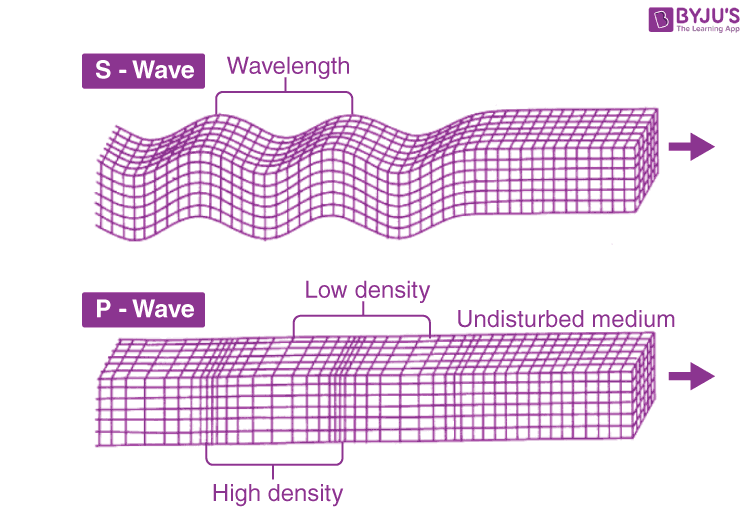
Seismic waves
P-waves (primary)
Fastest
Arrive first and cause least damage
S-waves (secondary)
Arrive next and shake the ground violently, causing damage
Love waves
Arrive last as they only travel across the surface
Large amplitude and cause significant damage, including fracturing the ground surface
Risk equation
Risk =
(Hazard x Vulnerability) / Capacity to cope
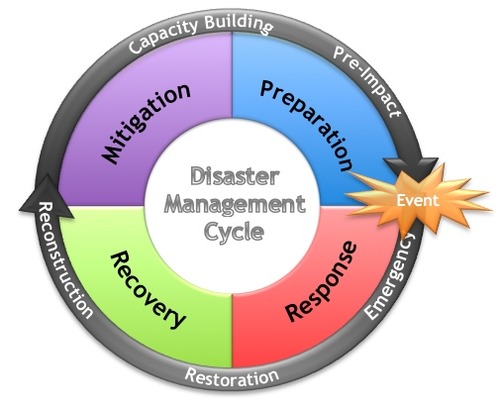
Hazard Management Cycle
Preparedness
Community education
Resillient building
Prediction
Warning
Evacuation technology
Response
Immediate help
Emergency shelter
Food and water
Recovery
Rebuilding infrastructure and services
Rehabilitating injured people and their lives
Mitigation
Acting to redue the scale of the next disaster
Land-use zoning
Hazard-resistant buildings and infrastructure