geometry unit6 6.1-6.3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Concurrency
When 3-or more lines, rays or segments intersect at the same point
Circumcenter Theorem
The circumcenter of a triangle is equidistant from the vertices of the triangle.
Angle Bisector Theorem
If a point lies on the bisector of an angle. then it is equidistant from the two sides of the angle
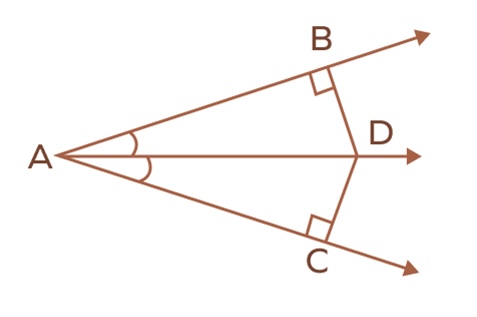
Converse of the Angle Bisector Theorem
If a point is in the interior of an angle and is equidistant from the two sides of the angle, then it lies on the bisector of the angle.
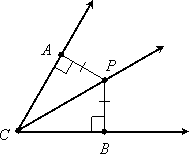
Perpendicular Bisector Theorem
In a plane. if a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then it is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment.
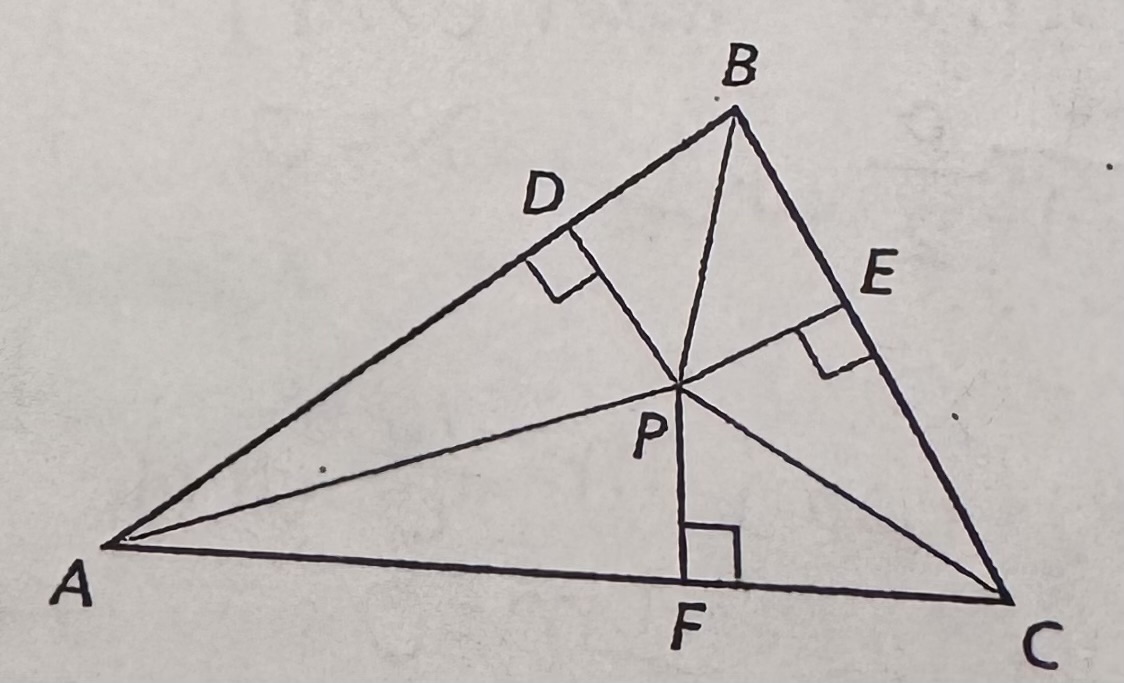
If CP is the angle bisector of AB, then CA = CB.
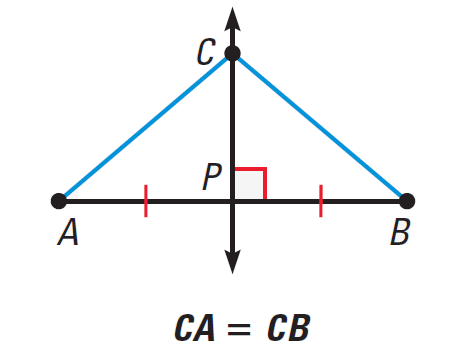
Converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem
In a plane, if a point is equidistant from the endpoints of a segment, then it lies on the perpendicular bisector of the segment.
Definition of incenter
The angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent. This point of concurrency is the incenter of the triangle.
Incenter Theorem
The incenter of a triangle is equidistant from the sides of the triangle.
If AP, BP, and CP are angle bisectors of
ABC, then PD = PE=PF.
Centroid Theorem
The centroid of a triangle is two-thirds of the distance from each vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
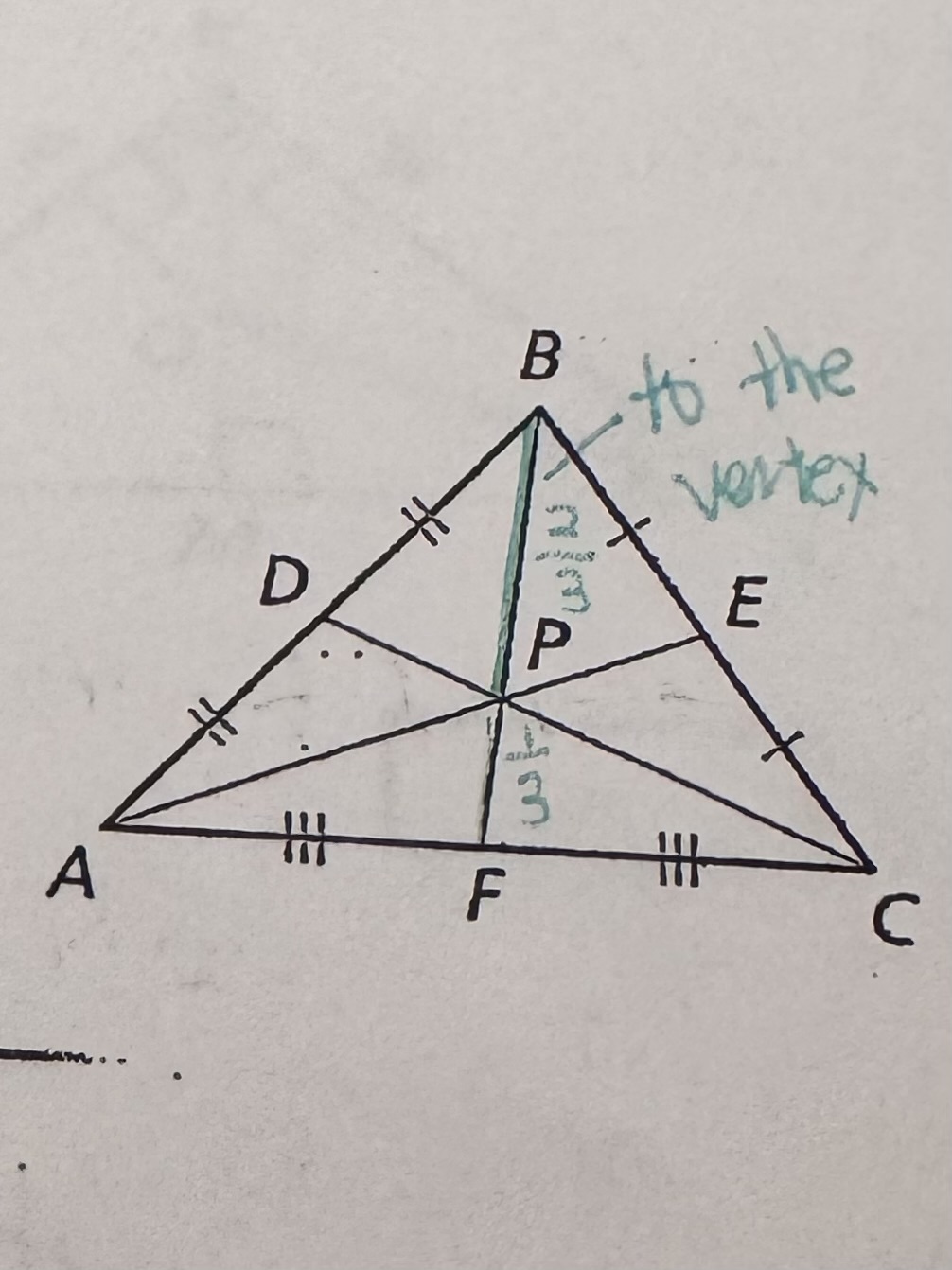
Median
segment from the vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
Orthocenter on the triangle
Right angle
Orthocenter inside the triangle
Acute triangle
Orthocenter outside the triangle
Obtuse triangle
Orthocenter
The lines containing the altitudes of a triangle are concurrent. This point of concurrency is the orthocenter of the triangle.
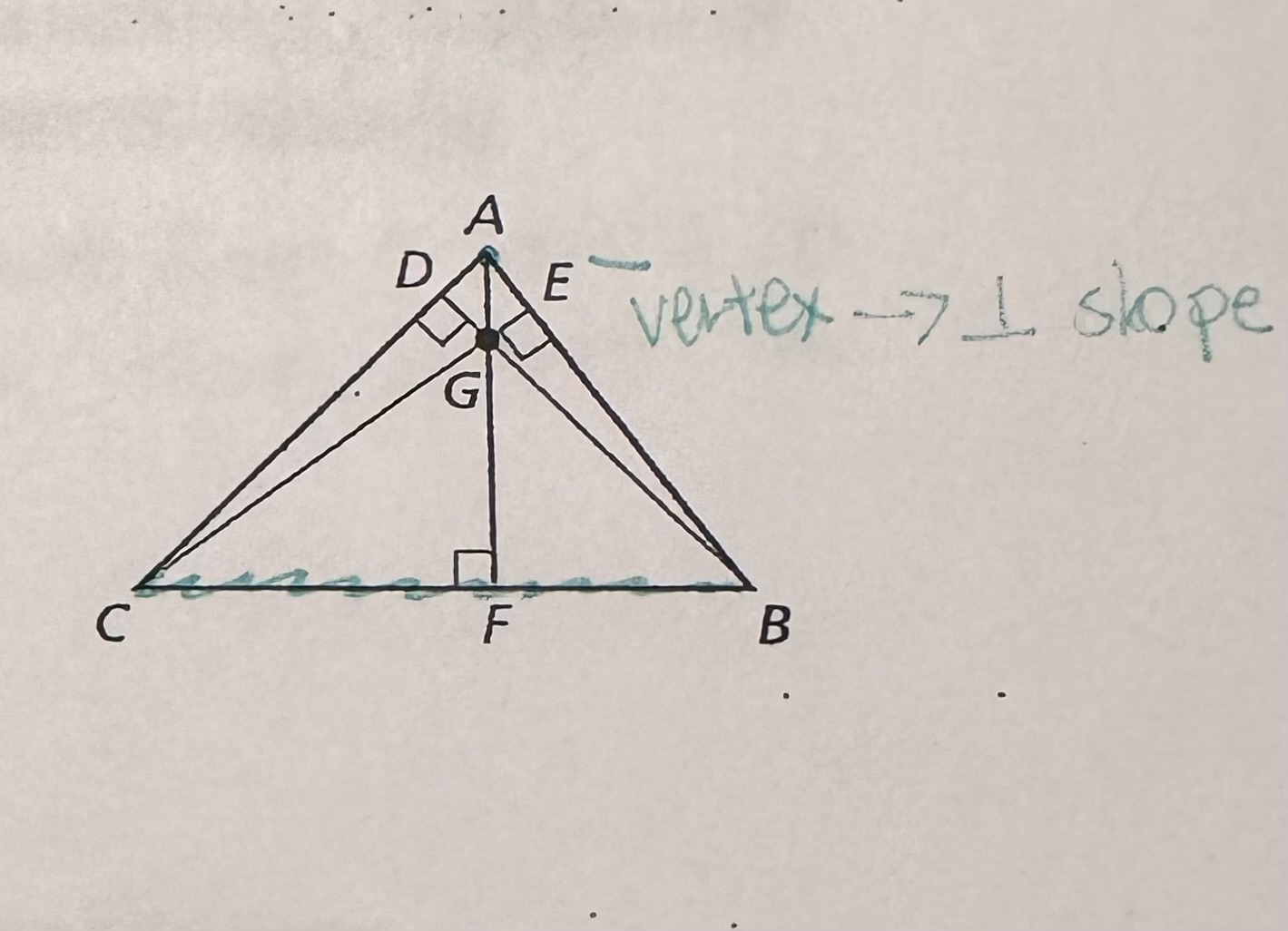
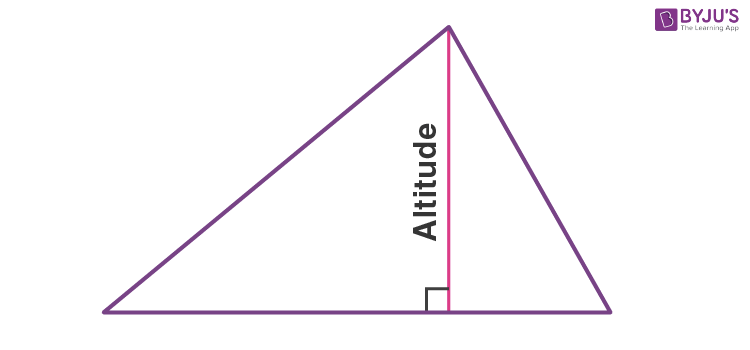
Altitude
a line segment from a vertex drawn perpendicular (at a 90° angle) to the opposite side