U of U PA School Intro to Viral Diseases and Human Herpes Viruses
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
How are viruses grouped?
STRUCTURE:
- DNA vs RNA
- Enveloped vs non-enveloped
- Single stranded vs double stranded
Life cycle of a virus
Virus enters cell
Begins replication
Buds off of cell
Spreads through blood/lymph
Clinical symptoms develop (based on area of infection)
Recovery
Viral shedding
Immune response to virus
Interferons released to inhibit viral replication
Antigen presenting cells activate immune T/B cells
General diagnosis practice for viruses
Clinical history and exam
Antigen testing
ELISA
Serology - antibodies IgM, IgG
PCR
Cultures
Treatment for viruses
Largely supportive care
Some antivirals
Vaccines
What are the clinically important HHVs?
Herpes simplex viruse (HSV) - 1 and 2
Varicella-Zoster (VZV)
Epstein Barr - EBV
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Human Herpes 6 (HHV6 aka Roseola)
HSV 1/2 diseases
Very similar
Orofacial infections
Genital
Gingivostomatitis
Conjunctivitis
Neonatal diseases
Corneal ulcers
Encephalitis
HSV 1/2 properties
DNA
Spread by skin to skin contact
Infect nerve cells into ganglia where latency occurs
Reactivate due to stimulus
Epidemiology of HSV 1/2
Both can spread without lesions
HSV1 - acquired earlier in life (6months - 3 years), 80-90% of adults have antibodies for HSV1
HSV2 - 40-60 million infected individuals in the USA
HSV1/2 clinical disease in adults
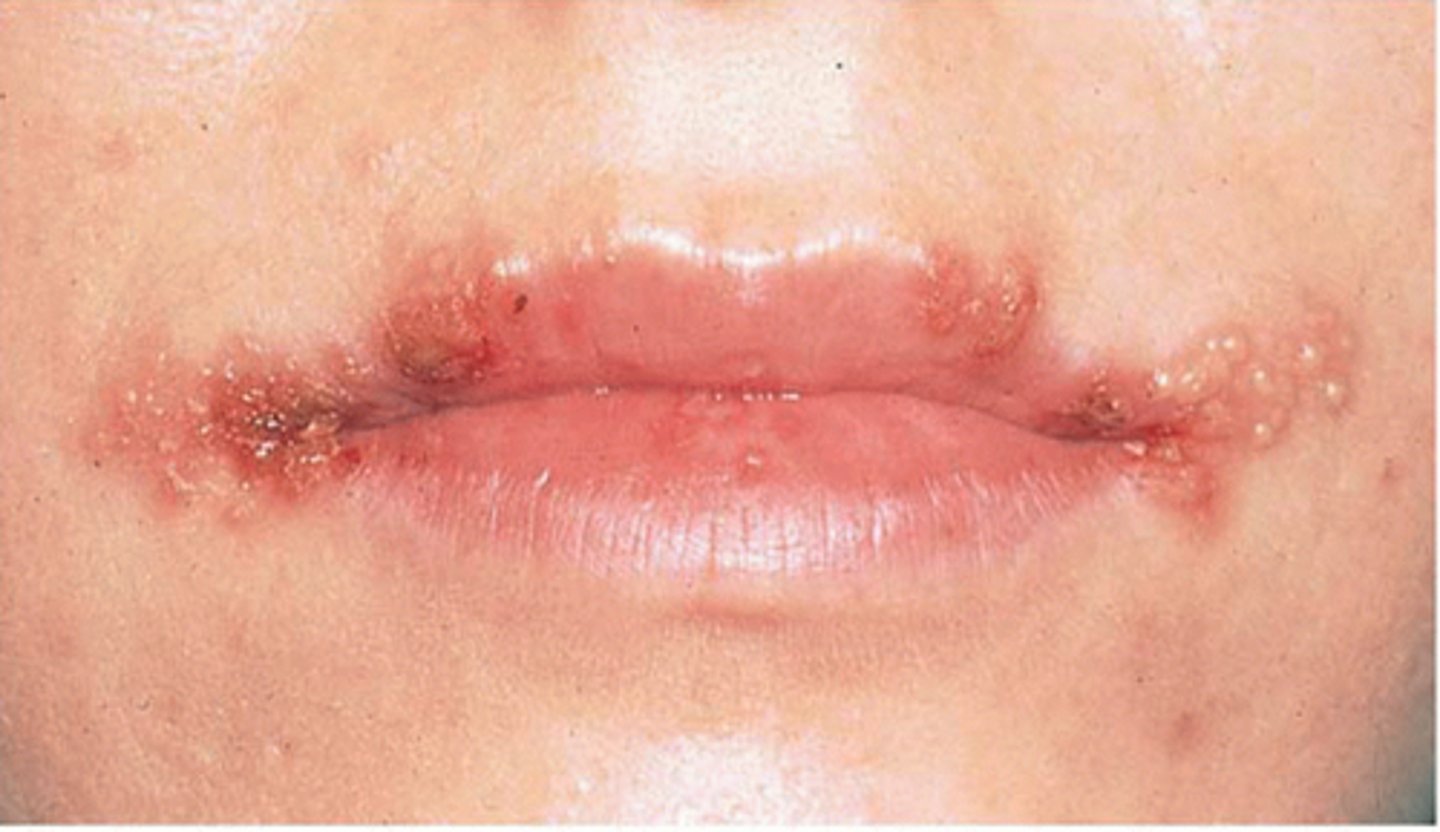
Orofacial infections - cluster of vesicular lesions on lip
-Herpes labialis, pharyngitis, tonsilitis
Prodrome of numbness, tingling, burning before eruption
First episode is worst, recurrence varies
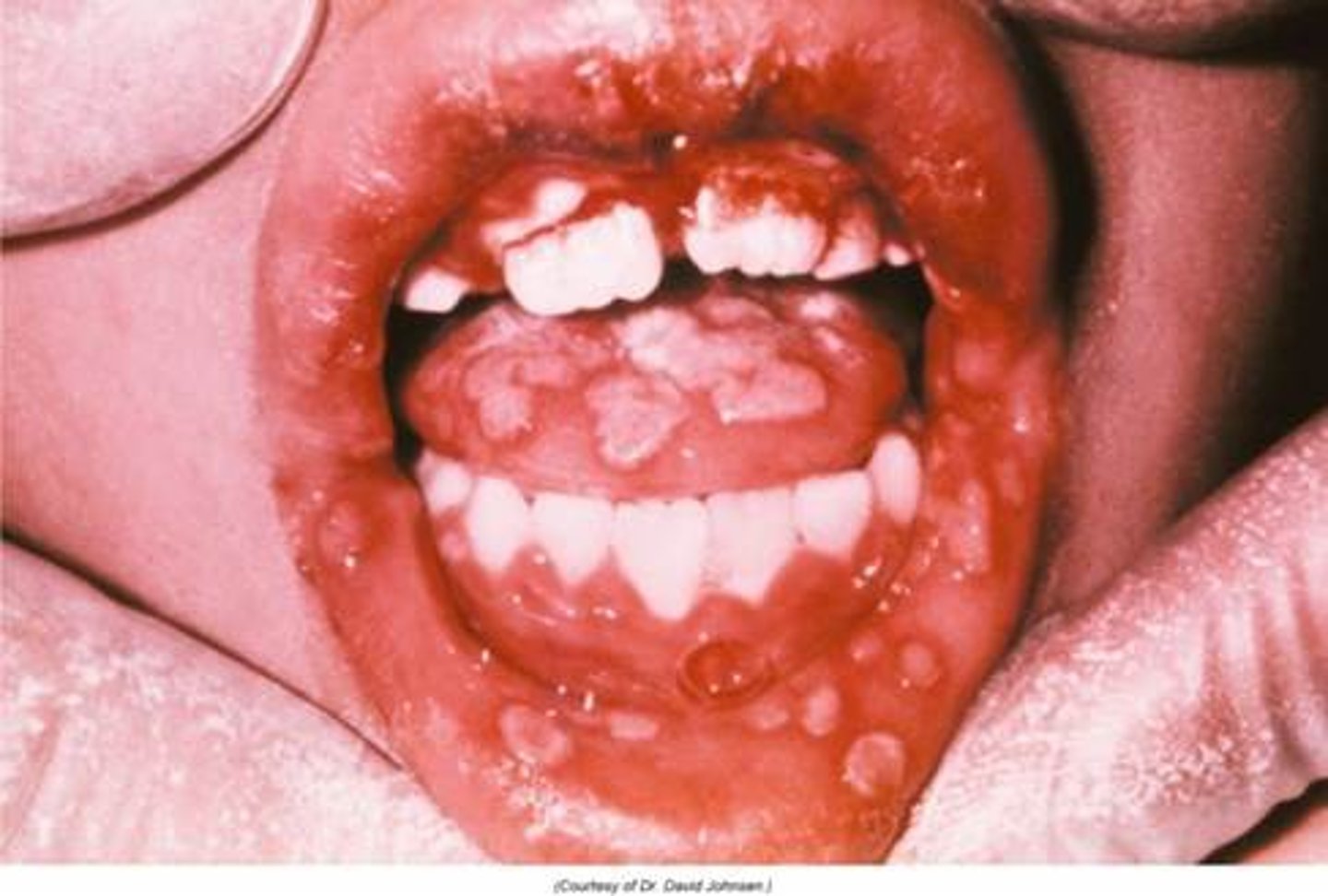
HSV1/2 clinical disease in peds
Orofacial infections - vesicular lesions on lips and mucosa
-pharyngitis, gingivostomatitis, fever, sore throat
Lasts for 2 weeks
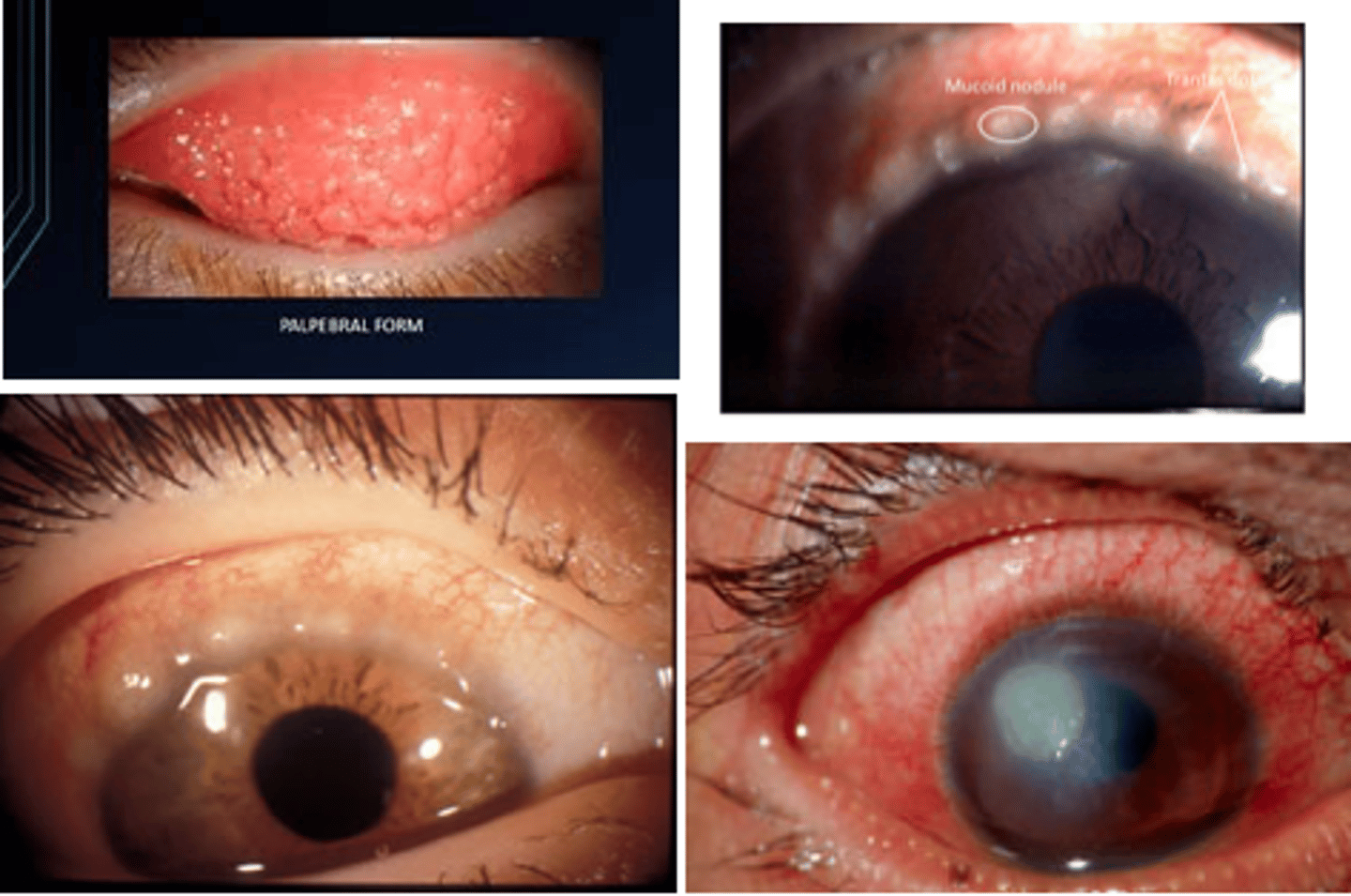
HSV1/2 clinical disease keratoconjunctivitis
Keratoconjunctivitis - infection of iris, conjunctive that can cause blindness
-Dendritic lesions on corneal stain
HSV1/2 clinical disease encephalitis
Infection of brain - RAPID fever, headache, AMS, seizure/neurologic symptions
High morbidity and mortality
Can be due to primary or recurrent flare ups
Most commonly caused by HSV1
Genital herpes
Usually HSV2
Vesicular, ulcerative lesions of genitalia
Prodrome of fever, malaise
Transmissible without lesions
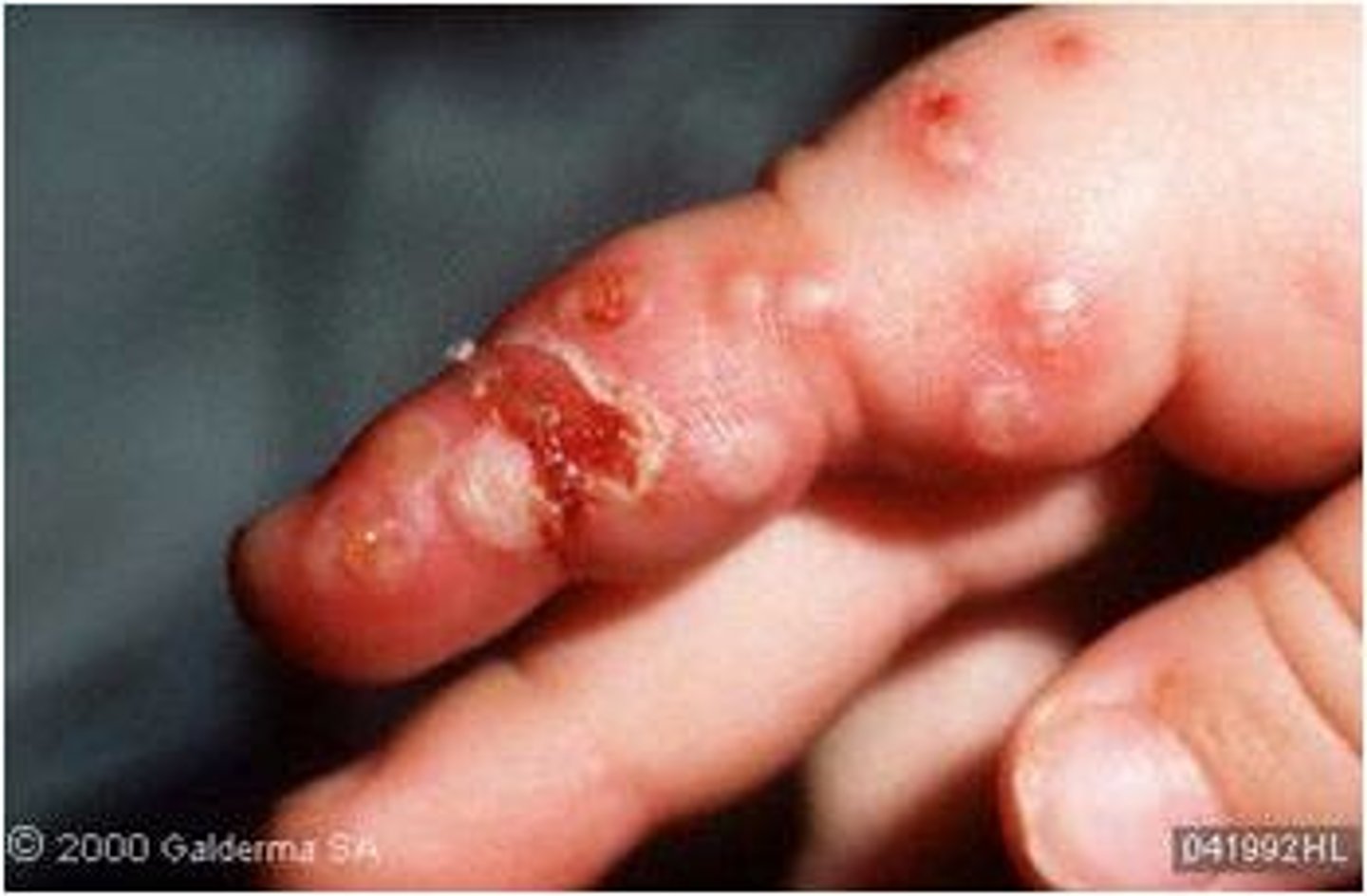
Herpetic whitlow
HSV1/2 skin infection
Enters via skin abrasion
Causes vesicular lesions of hands/fingers
Herpes gladiatorum
HSV1 common in wrestlers
Lesions on head and neck
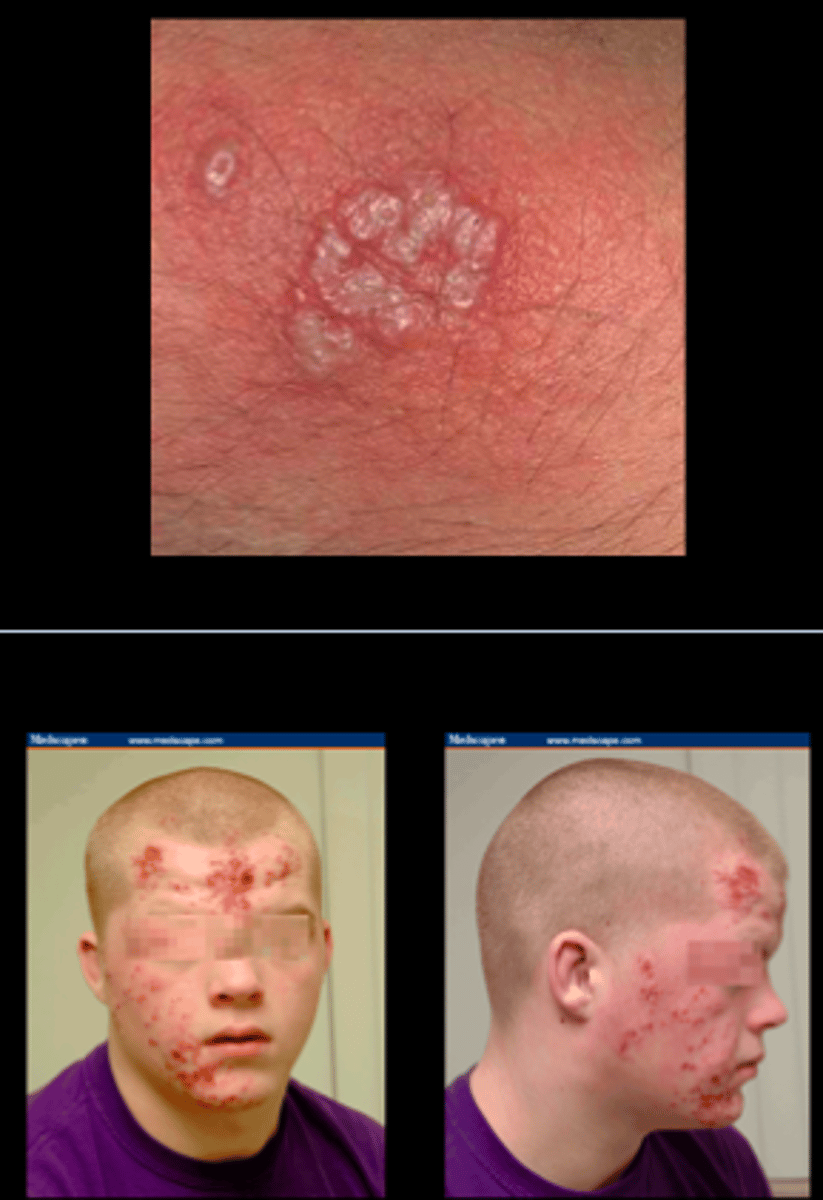
HSV1/2 diagnosis
Clinical history
Lesions
PCR/NAAT swab of blood, CSF, tissue
HSV1/2 treatment/prevention
Antivirals acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir
PO for cold sores or genital herpes
IV for encephalitis
Ophthalmic drops for eyes
No screenings/vaccines
VZV
Chicken pox and herpes zoster (shingles)
VSV properties
DNA
Replication in upper respiratory and spreads via lymph node
VSV epidimiology
Worldwide
Respiratory spread human - human
Chickenpox is primarily a childhood disease, decreased incidence with vaccine
VZV clinical disease - chicken pox
2 week incubation
Prodrome of fever, rash, malaise
3-5 days later maculopapular rash with vesicles and erythema
-last 1-2 weeks
Can cause encephalitis in immunocompromised
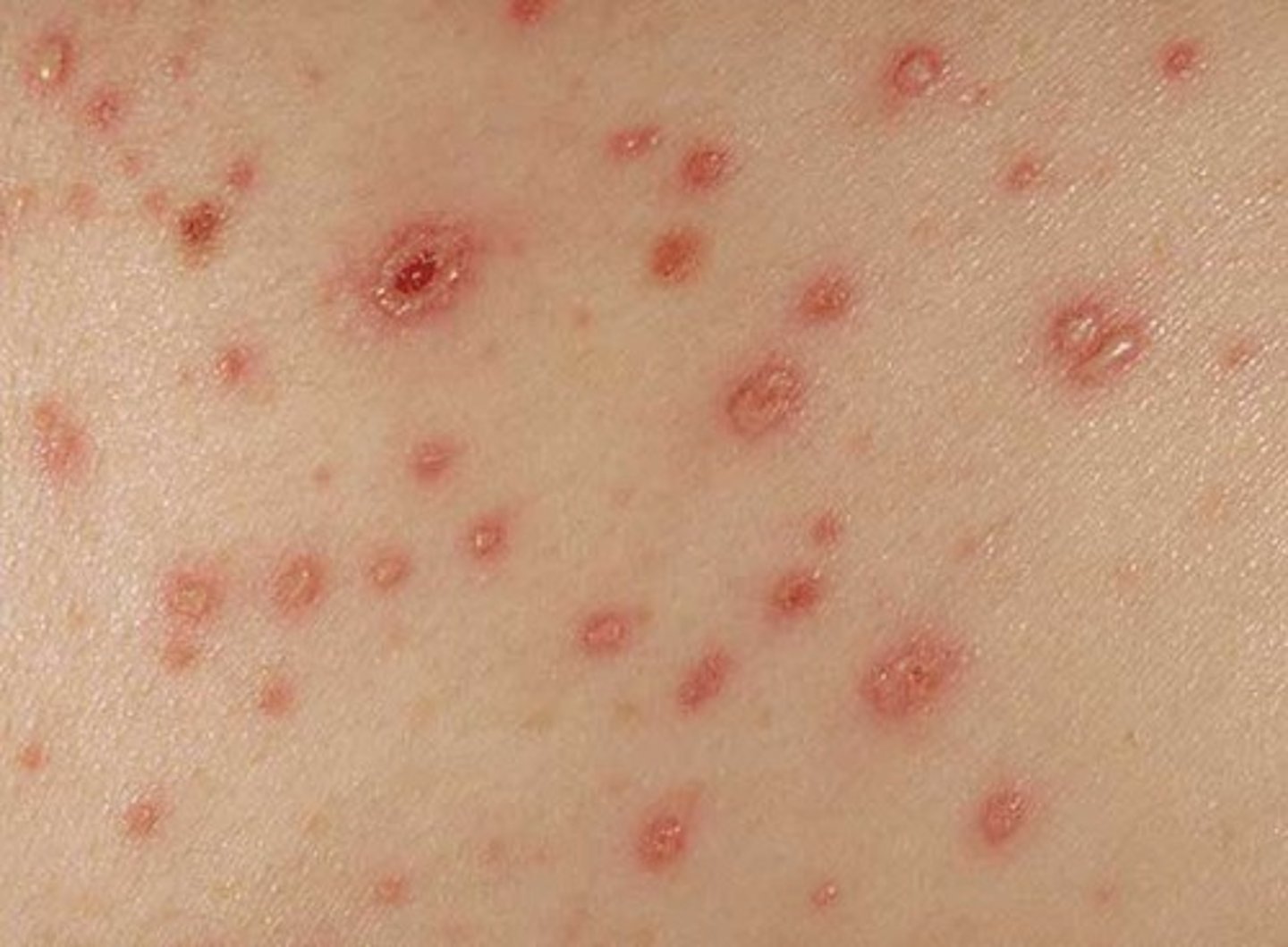
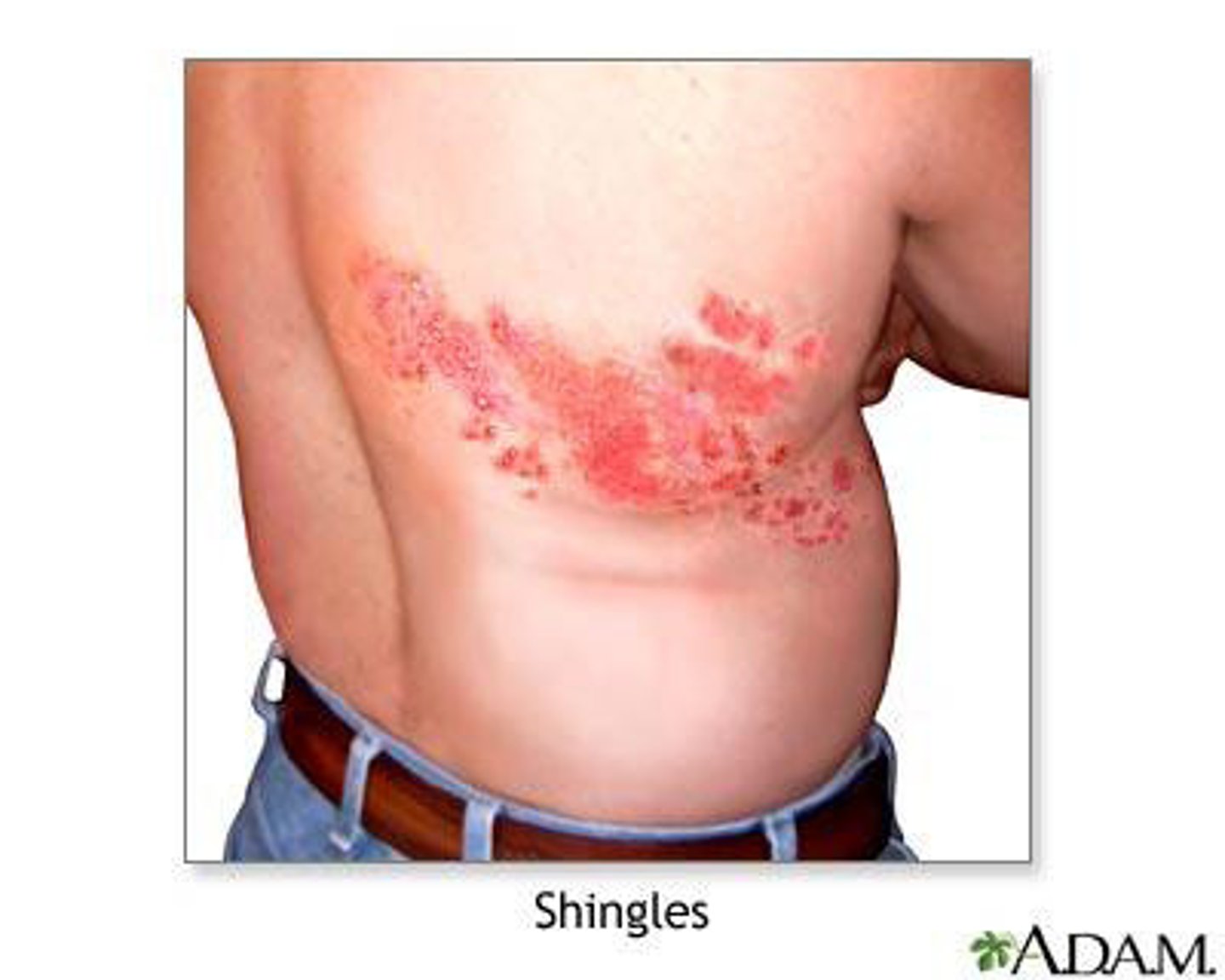
VZV clinical disease - herpes zoster/shingles
Disease of adults
Latent infection of chicken pox
Prodrome of burning skin 3-5 days prior to outbreak
Vesicular rash that does not cross midline, dermatomal distribution. Very painful
VZV diagnosis
Clinical diagnosis from history and exam
Rash examination
Swab with PCR/NAAT to confirm
VZV treatment/prevention
Chicken pox -
Self limiting
Supportive care, limit itching
Vaccine @12 months old, booster @4-6 years, may repeat as adult if needed
Singles -
Antivirals - Acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir
NSAIDs, opiates, gabapentin
Shringrix vaccine >50 years, 2 shot series
CMV properties
DNA
Wide array of diseases, more severe in immunocompromised
Latency in multiple cell trypes
Seen in most body fluid
CMV epidimiology
Most infections asymptomatic
40-100% seroprevalence in adults
CMV disease
Congenital CMV
Mononucleosis
Pneumonia
Retinitis
Congenital CMV
Mom to fetus
If at birth - mainly asymptomatic
Intrauterine - growth retardation, hearing loss, 20% mortality rate
CMV mononucleosis
Milder than EBV
Fever, lymphadenopathy, pharyngitis, profound fatigue
CMV pneumonia
Mild for healthy, severe for immunocompromised
Cough, fever, malaise
CMV retinitis
Retinal inflammation causing vision disturbances
CMV diagnosis
Clinical
Noted infection in mother via PCR/Antibodies
Mononucleosis - clinical diagnosis
Pneumonia/retinitis - PCR/history
CMV treatment
Recognition
Supportive care
Ganciclovir
EBV properties
DNA
Latent infection
Can cause lymphoma
EBV epidemiology
95% of the world's population is exposed to the virus
Transmitted primarily by close contact with saliva or blood
EBV diagnosis
Clinical presentation
Serology -
-acute= + IgM, IgG
-past= -IgM, +IgG
PCR
EBV treatment
Supportive care
Mono - no sports with splenomegaly
No antivirals, vaccine
HHV-6 properties
Roseola or Sixth disease
DNA
Grows in T-lymphocytes
Lifelong persistence
HHV-6 epidimiology
90% worldwide have had virus and have antibodies
Primary spread via saliva
Most common in young children, reactivation in immunocompromised
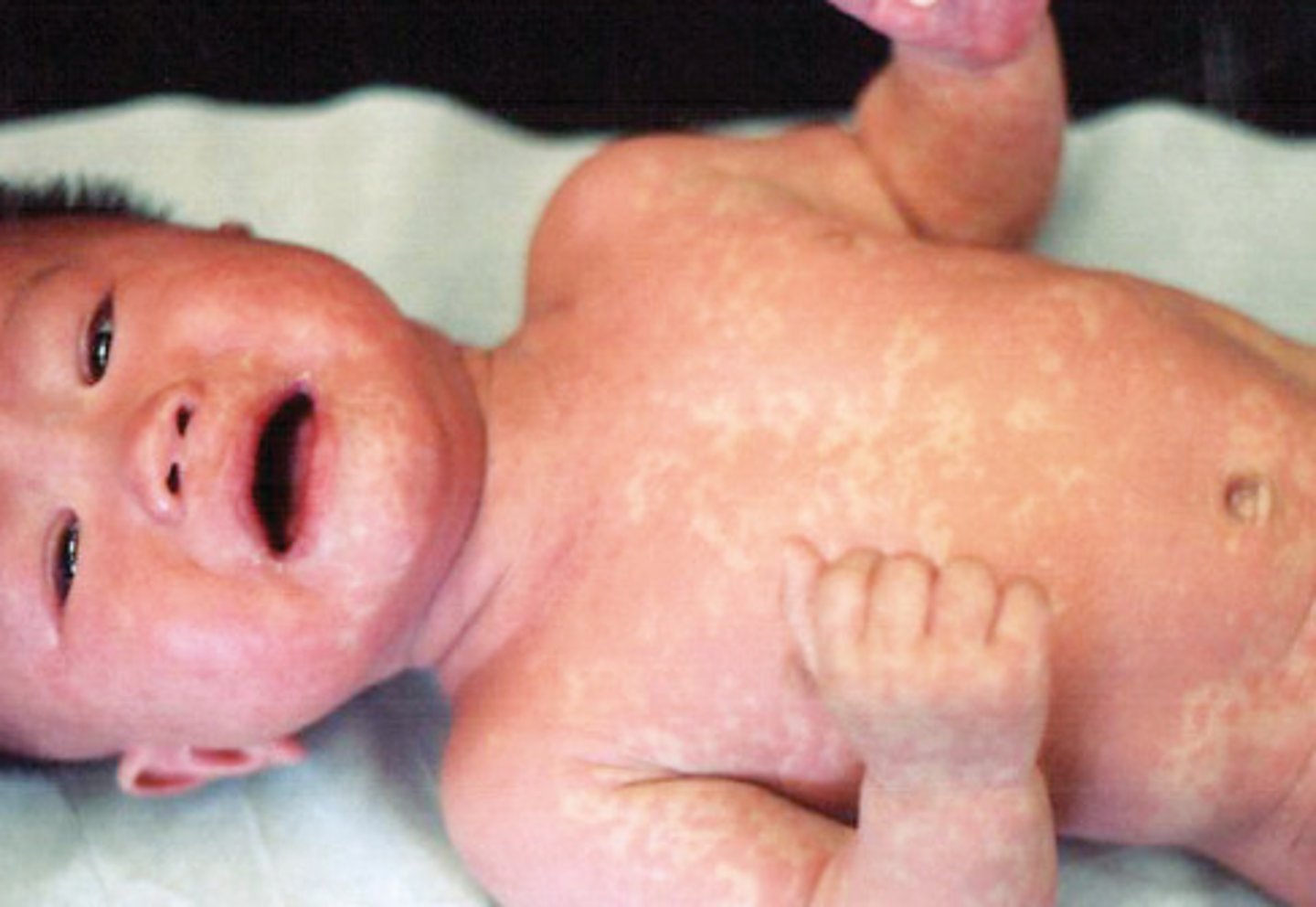
HHV-6 disease
3 day fever
Exanthem subitem (roseola) - rash after fever - 1-5mm papules that blanche with pressure, start on trunk then legs/arms
HHV-6 diagnosis
Clinical
History of fever than exanthem subitem
HHV-6 treatment
Self limiting, benign rash
Supportive care
Immunocompromised - gancicylovir if severe