Pneumonias
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Y'all should've come to my grand rounds, you would've been 2 steps ahead
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Acute bronchitis
A lower respiratory infection involving the large airways (bronchi) without evidence of pneumonia or COPD, does NOT involve the alveoli
Flu A/B, parainfluenza, coronaviruses, rhinoviruses, RSV
What viruses (94% of cases) can can cause acute bronchitis?
M. pneumonia, chlamydia pneumonia, Bordetella pertussis
What bacteria can can cause acute bronchitis?
H. influenza, strep. pneumonia
Secondary bacterial infections in acute bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis
Patient presents to the clinic with a cough that has been going on for 7 days. They report that the cough is dry and pleuritic chest pain. On a physical exam you note rhonchi that clear with cough. CXR is negative for pneumonia. What are we thinking?
Cough suppressnts (benzonatate, dextromethophan), NSAIDs for pain
How are we treating acute bronchitis since its self limited?
influenza in a high risk patient (DM, pulm issues, immunocompromised), pertussis
When are we giving antibiotics in an acute bronchitis case?
Pneumonia
An infection of the lung tissues with significant morbidity and mortality that can be community-acquired, hospital acquired, or ventilator associated?
Community acquired (CAP)
What type of pneumonia is characterized by an infection that occurs outside a hospital setting or within 48 hours of admission to a hospital?
Hospital acquired (HAP)
What type of pneumonia is characterized by an infection that occurs 48 hours after being admitted to the hospitals and you’ve excluded everything else?
Ventilator associated (VAP)
What type of pneumonia is characterized by an infection that occurs more than 48 hours after an endotracheal intubation and/or mechanical ventilation
cough reflex, mucocillary reflex, cellular immune response
Pneumonia occurs when which defense mechanism are down for the count or a large infectious load is present?
aspiration from the oropharynx, GI-content aspiration, hemtaogenous/spread from contigous areas
What are some things that can cause CAP?
Strep pneumoniae
What is the most common infectious agent of CAP and is characterized by rust colored sputum?
legionella
What infectious agent of CAP is associated with contaminated air conditioning/mist machines, recent travel, or low sodium due to SIADH?
old, smoking, viral respiratory infections, comorbidities (COPD, asthma, HF, stroke, DM, immunocompromise), impaired airway protection, crowded living conditions, environmental toxins
Risk factors for CAP
Augmentin + azithromycin or doxy, corticosteroids
67 y/o pt. presents to the ER with flu like symptoms. Patient reports pleuritic chest pain and a cough with sputum. They report they had a stroke 2 years ago and is diagnosed with COPD. Vitals are stable with an exception of a 103.4 temp, 134 bpm, O2 sat is 93% on RA, and 24 RR. While conducting a physical you find inspiratory crackles and bronchial breath sounds, as well as a dullness to percussion. CXR shows patchy airspace opacities and lobar consolidations. What medications do you want to use?
Cefpodxime + azithromycin or doxy, corticosteroids
67 y/o pt. presents to the ER with flu like symptoms. Patient reports pleuritic chest pain and a cough with sputum. They report they had a stroke 2 years ago and is diagnosed with COPD. They are allergic to penicillin. Vitals are stable with an exception of a 103.4 temp, 134 bpm, O2 sat is 93% on RA, and 24 RR. While conducting a physical you find inspiratory crackles and bronchial breath sounds, as well as a dullness to percussion. CXR shows patchy airspace opacities and lobar consolidations. What medications do you want to use?
Amoxicillin + azithromycin or doxy
67 y/o pt. presents to the ER with flu like symptoms. Patient reports pleuritic chest pain and a cough with sputum. Vitals are stable with an exception of a 103.4 temp, 134 bpm, O2 sat is 93% on RA, and 24 RR. While conducting a physical you find inspiratory crackles and bronchial breath sounds, as well as a dullness to percussion. CXR shows patchy airspace opacities and lobar consolidations. CBC shows leukocytosis at 17. What antibiotic do you want to use?
Levofloxacin or moxifloxacin, lefamulin
67 y/o pt. presents to the ER with flu like symptoms. Patient reports pleuritic chest pain and a cough with sputum. They report they had a stroke 2 years ago and is diagnosed with COPD. Vitals are stable with an exception of a 103.4 temp, 134 bpm, O2 sat is 93% on RA, and 24 RR. While conducting a physical you find inspiratory crackles and bronchial breath sounds, as well as a dullness to percussion. CXR shows patchy airspace opacities and lobar consolidations. Blood cultures are positive for pseudomonas. What antibiotic do you want to use?
urinary antigen testing, blood/sputum cultures
If you suspect a S. pneumonia or legionella CAP what test could you run?
PSI (pneumonia severity index), CURB-65
What can you use to justify your decision to admit the patient in the case of CAP?
Different agents, antibiotic susceptibility patterns, poorer underlying health
How can you tell HAP, VAP, and CAP apart?
MRSA, MSSA, P. aeurginosa, enteric gram negative, E.coli, klebsiella pnuemonia
What are some common infectious agents of HAP?
MRSA, MSSA, acinetobacters, Stenotrophomas meltophilia, P. aeurginosa
What are some common infectious agents of VAP?
new or progressive pulmonary opacity during inpatient stay, fever, leukocytosis, purulent sputum
What are some clinical findings of HAP and VAP?
ABG/VBG, CBC, CMP, blood cultures, CXR/CT, endotracheal aspiration and culture
What can you use to diagnoses VAP and HAP?
Vanc, piperacilllin-tazobactam, cefepime, meropenem, impenem
What antibiotics are you treating VAP and HAP with?
aspiration of gastric contents, oral/dental bacteria
What can cause anaerobic pneumonia and lung abscesses
Decreased levels of consciousness, impaired swallowing, tracheal/NG
What can create an increase risk of aspiration?
posterior segments with lying down, basilar segments with standing up
Anaerobic pneumonia tends to occur in
Antibiotics (ampilcillin-sulbactam, carbapenem, Fluroquinolone, metronidizole, clindamycin) and monitor
44 y/o patient presents to the ER with cough. While collecting a history the patient reports a recent weight loss (15 lbs) without trying and malaise. She reports that the cough is wet and when she coughs up the sputum it smells terrible. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 101.4. CXR shows thick walled solitary cavity surround by consolidation. What’s your treatment plan?
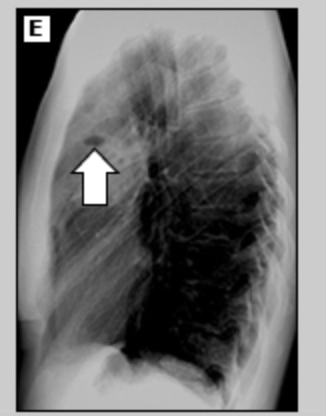
Necrotizing pneumonia
44 y/o patient presents to the ER with cough. While collecting a history the patient reports a recent weight loss (15 lbs) without trying and malaise. She reports that the cough is wet and when she coughs up the sputum it smells terrible. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 101.4. CXR shows multiple areas of cavitation within an area of consolidation. What are you thinking?
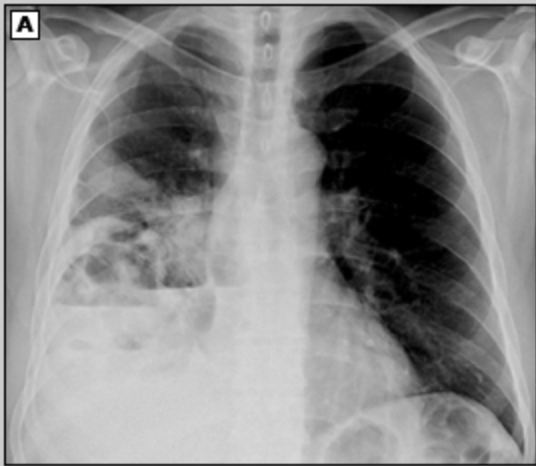
Viral pneumonial, antivirals/supportive care, monitor for secondary bacterial infections
Patient reports to the ER with flu like symptoms. Patient reports a non-productive cough and when something does come up its pink and frothy. On a physical exam you note the trachea is tender, and diffuse rales and wheezes in the lower lungs. Vitals are stable with the exception of an RR of 26. CT shows ground glass opacities and consolidations. What are you thinking and what is the treatment plan?
Penumocystis Jirovecii, Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (bactrim), corticosteroids
Patient reports to the ER for abrupt onset SOB. Patient reports that they are HIV positive. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 102.5 and 28 RR. On a physical exam you note bibasilar crackles. CXR shows ground glass appearance. ABG/VBG show hypocapnia and hypoxemia. What are you thinking and what is your treatment plan?
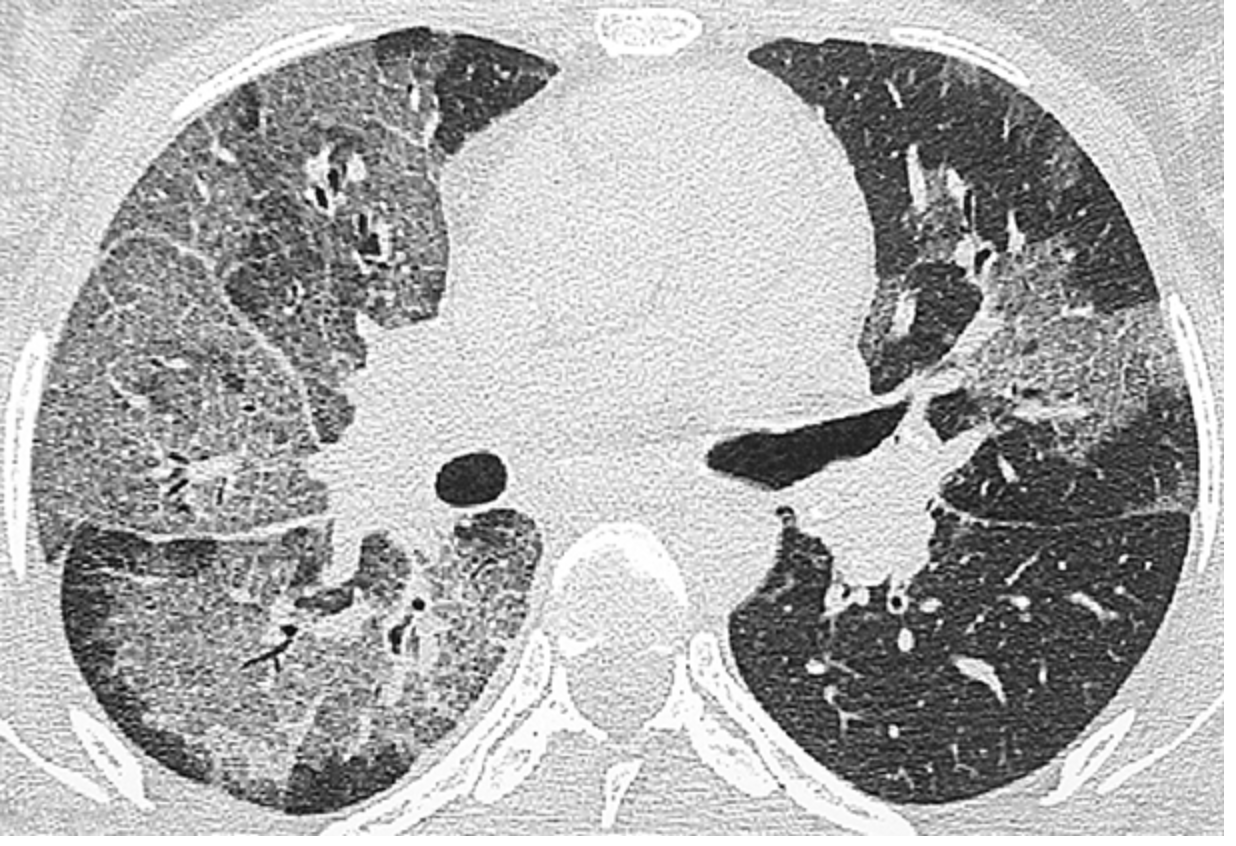
Histoplasmosis
What is endemic to Ohio and Mississippi river valleys, related to humid/acidic soil, and bird/bat dropppings?
intensity of exposure, underlying health and immune status
Extent and severity of histoplasmosis depends on
Amphotericin B and Itraconozole
Patient reports to the ER for chest pain and dyspnea. While collecting a history your patient reports that he just got back from a 2 week spelunking vacation. He also reports that he is a transplant patient and is on immunosuppression. He reports night sweats, cough, HA, chills, fever, and muscle pain. CXR shows prominent hilar adenopathy and pulmonary infiltrates. What is your treatment plan?
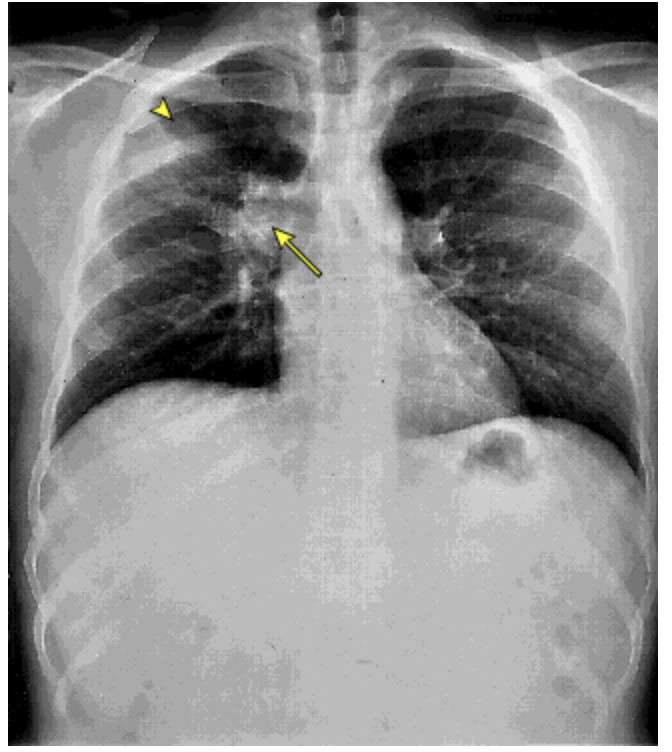
histoplasma antigen testing, cytopathology of bronchial lavage fluid
What labs do you order if you suspect histoplasmosis?
affected lymph nodes may coalesce and necrotize (bronchoesophageal fistulas), calcified mediastinal nodes may lead to broncholithiasis, fibrosis mediastinitis (superiod vena cava syndrome)
Complications of histoplasmosis?
Chronic cavitaty histoplasmosis
What type of histoplasmosis is seen with smokers who have COPD and looks like TB?