Chapter 6 Skeletal System
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What are the general characteristics of cartilage?
avascular, no innervated, perichondrium, produced by chondrocytes
What are the 3 types of cartilage?
Hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
What is the most abundant cartilage?
Hyaline
What does red marrow produce?
RBC, WBC, platelets
In what part of bone and in what type of bones does blood cell formation occur?
red bone marrow, flat and ends of long
What does yellow marrow produce?
fat storage
What are the functions of bone?
support, protection, movement, mineral storage, fat storage, blood cell formation
What mineral and growth factors are stored in bone?
calcium and phosphate
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
nose tip, respiratory tract, costal cartilage, where joints form
Where is elastic cartilage found?
ear pinnae, epiglottis
Where is fibrocartilage found?
spine discs, pubic symphysis, knee meniscus
Organic components make up ____% of mass and contribute to bone ____ and ____. Inorganic components make up ____% and are responsible for ____.
35, structure, flexibility, 65, hardness
What are the organic cells of bone tissue?
osteogenic, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
What are the inorganic components of bone tissue?
calcium phosphates
Where are osteogenic cells found? What do they give rise to?
periosteum and endosteum, osteoblasts
Osteoblasts are young and secrete ____.
matrix
Osteoblasts become completely surrounded by and turn into ____.
Osteocytes
Osteocytes maintain what?
matrix
Osteoclasts ____ ____ bone by secreting _____ that release ____ and ____ ____ into blood.
break down, enzymes, calcium, amino acids
What two bone tissue work together for growth and remodeling?
osteoblasts, osteoclasts
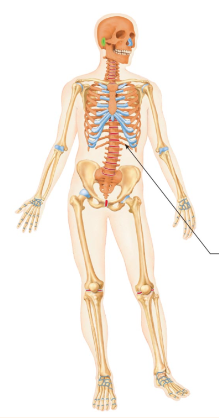
What are the orange and tan parts of the skeleton?
axial, appendicular
What is the external layer of bone?
compact
What is the internal layer with honeycomb appearance?
spongy
Long bones
length>width
Short bones
cube
Flat bones
thin, flat
According to location, to what part of the
skeleton do the ribs belong?
Axial
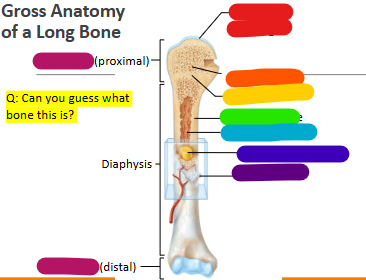
Label red
Articular cartilage
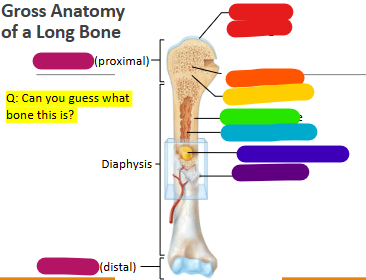
Label orange
Spongy bone
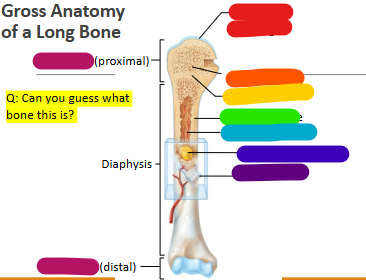
Label yellow
Epiphyseal line
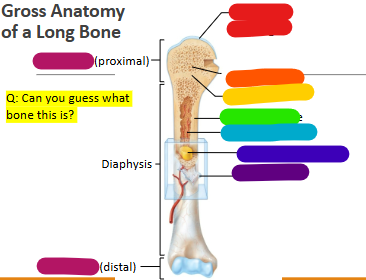
Label green
Compact bone
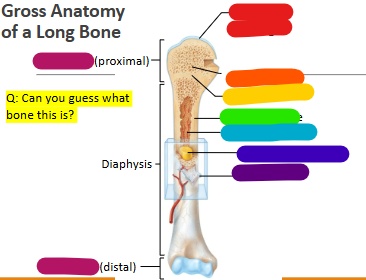
Label light blue
Medullary cavity
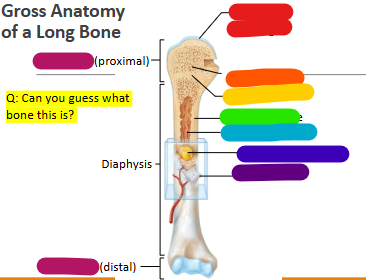
Label dark blue
Yellow marrow
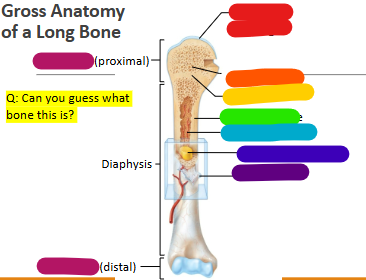
Label purple
Periosteum
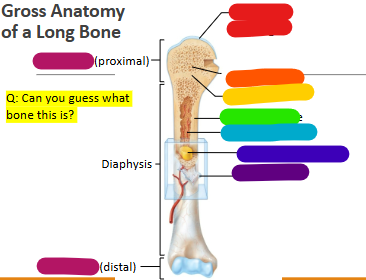
Label magenta
proximal and distal epiphysis
What does the endosteum line?
internal surfaces
Periosteum surrounds the entire bone except where there is:
articular cartilage
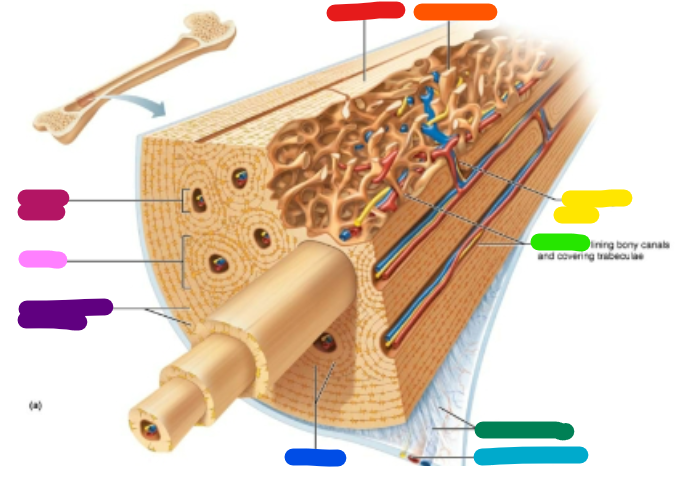
Label red
Compact bone
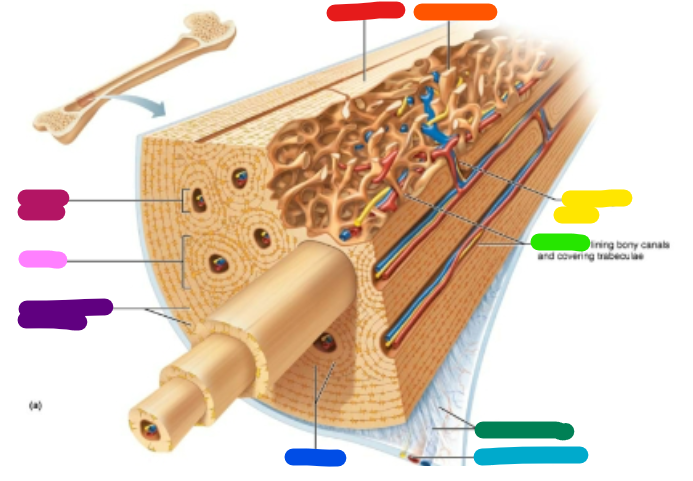
Label orange
Spongy bone
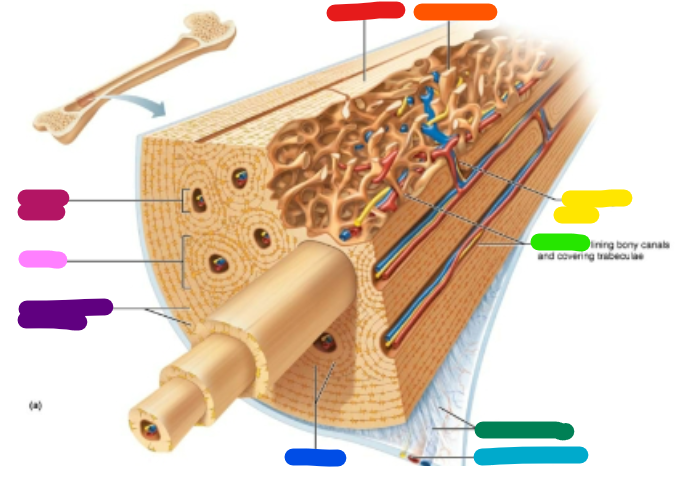
Label yellow
Perforating canal
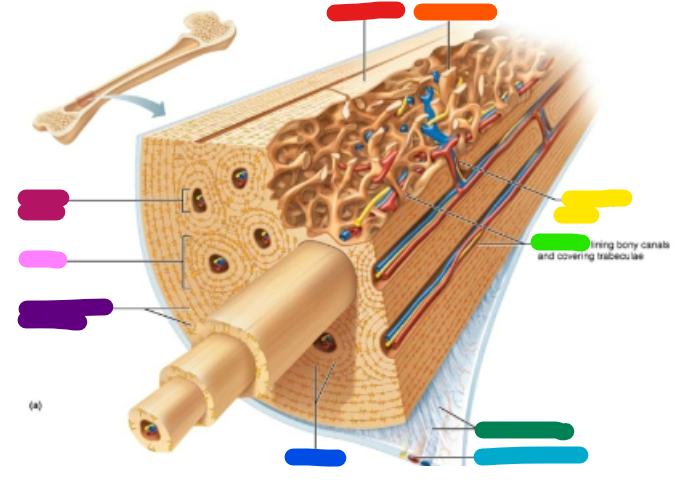
Label green
Endosteum
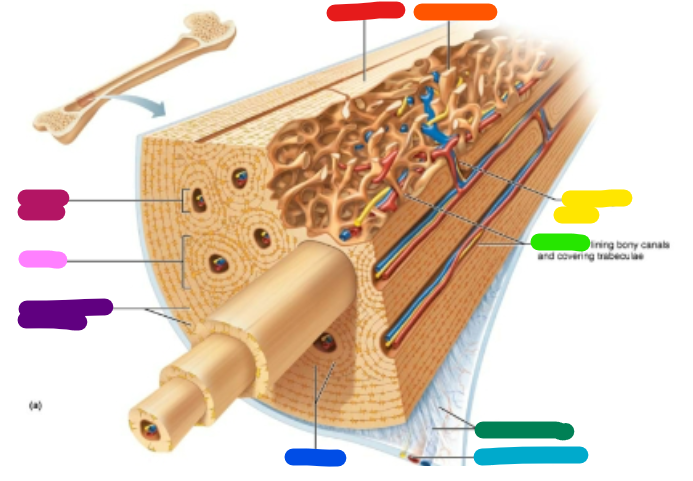
Label dark green
Perforating fibers
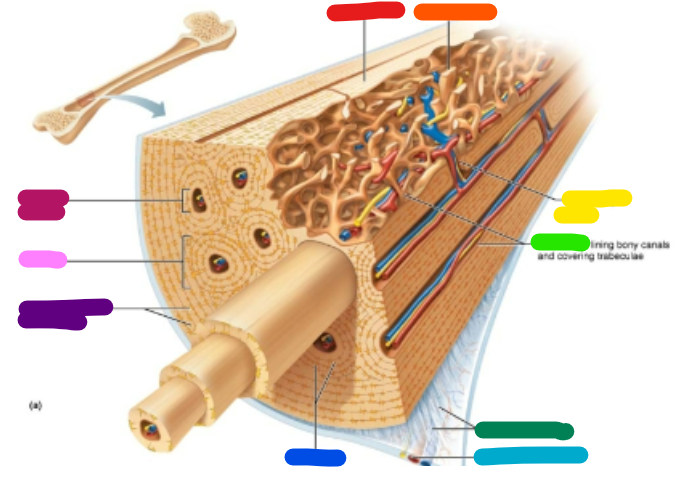
Label teal
Periosteal blood vessel
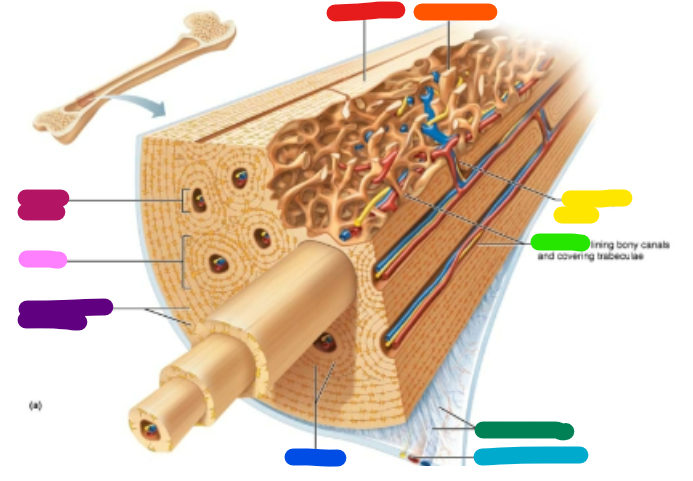
Label dark blue
Lamellae
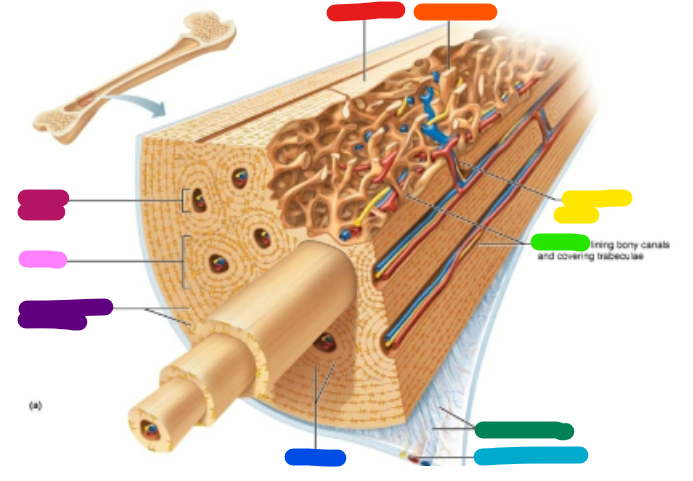
Label purple
Circumferential lamellae
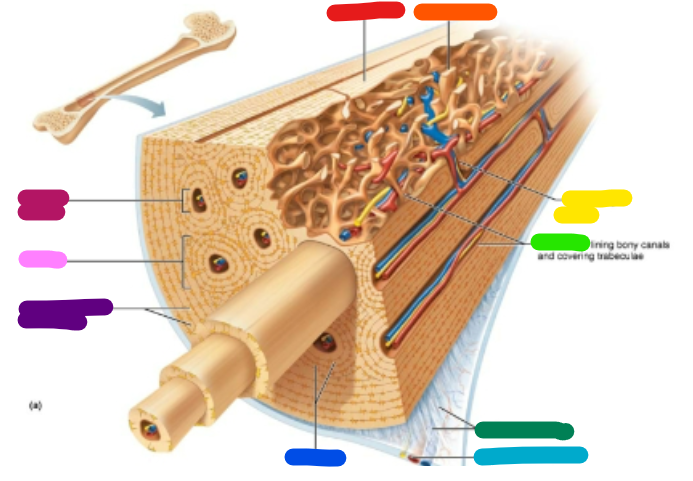
Label pink
Osteon
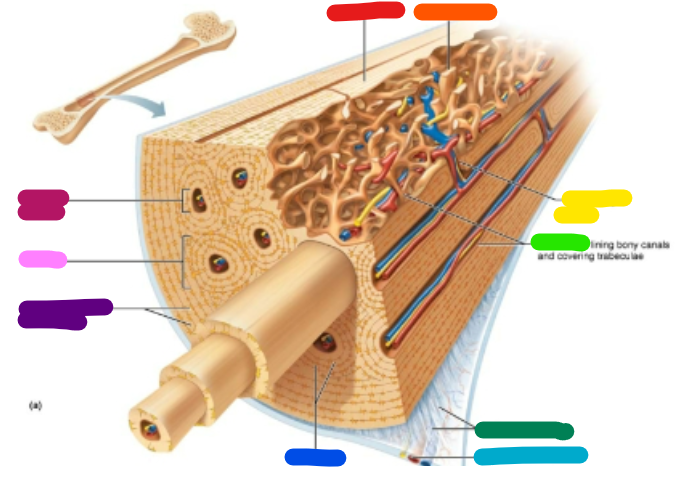
Label magenta
Central canal
Before 8 weeks, embryo’s skeleton is made of
______ cartilage and membranes; bone tissue
will eventually _____ most of these existing
structures
hyaline, replace
______ occurs differently in cartilage than
in membrane
Ossification
What are the 2 types of ossification?
Intramembranous, endochondral
How does intramembranous ossification occur and where?
fibrous membrane, skull and clavicles
How does endochondral ossification occur and where?
replaces hyaline cartilage, all bones below skull
In fetal development, what type of ossification occurs in the skull and clavicles?
Intramembranous ossification
Osteoblasts _____ matrix and osteoclasts ____ matrix.
deposit, resorb
Wolff’s Law
bone growth depends on demand
What are the three fracture classifications?
position, completeness, position

How would you
classify this fracture?
Transverse
How would you
classify this fracture?
Linear
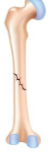
How would you
classify this fracture?
Oblique, nondisplaced

How would you
classify this fracture?
Oblique, displaced
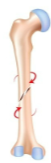
How would you
classify this fracture?
Spiral
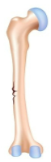
How would you
classify this fracture?
Greenstick

How would you
classify this fracture?
Comminuted
Hematoma
blood collection at fracture
Osteoporosis underlying problem
osteoclast>osteoblast, resorption>deposition
Osteoporosis main risk
postmenopausal women
Rickets and Osteomalacia underlying problem
insufficient calcium/vitamin D
Rickets occurs in _____, osteomalacia occurs in _____
children, adults
Put the steps
of endochondral ossification into the correct
sequence.
A. Epiphyseal ossification; hyaline cartilage remains at
epiphyseal plates and articular cartilages
B. Cartilage calcifies and cavitates
C. Bone collar forms around diaphysis of hyaline cartilage
model
D. Periosteal bud invasion and spongy bone formation
E. Elongation of diaphysis and formation of medullary cavity;
secondary ossification of epiphyses
C B D E A
The organic component of bone is
made up of what?
Collagen
What is the main hormone
responsible for bone growth in
childhood?
growth hormone
Bone development during childhood occurs where?
Epiphyseal plate
What hormones beside growth are required in childhood?
thyroid
At puberty, low levels of ______ are responsible for initial growth spurt
estrogen
Certain structures are influenced by different levels of ___ and ____
estrogen testosterone
Describe the stages of fracture repair
hematoma forms, fibrocartilaginous callus forms, bony callus forms, bone remodels