Blood Qs (Chap. 14)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What component of blood counts for the largest proportion of the blood volume?
Plasma
What is a result of reduced red blood cells count and/or reduce hemoglobin content of the blood?
Decrease oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood
Type of Anemia: Thalassemia
Condition: Deficiency of hemoglobin due to detective gene; short lifespan for RBCs
Type of Anemia: Sickle Cell Disease
Condition: Defective gene leads to abnormally shaped RBCs in conditions of low oxygen
Type of Anemia: Aplastic Anemia
Condition: Damage to bone marrow due to toxic chemicals, radiation, and other factors
Type of Anemia: Hemolytic anemia
Condition: Destruction of red blood cells; toxic chemicals are one possible cause
Type of Anemia: Pernicious anemia
Condition: Increase in RBC that are large and fragile; due to deficiency and vitamin B-12
What is the typical lifespan of a red blood cell?
120 days
What is a thrombocyte?
a platelet
Define hemostasis
Process that stops bleeding
The process that occur leading to hemostasis
The order:
Step1- Vasospasm
Step2- Platelet plug formation
Step3- Coagulation
What function do compounds heparin and coumadin have in common?
Prevention of coagulation
Indicate which situation would increase the risk of blood clot information
prolonged immobility
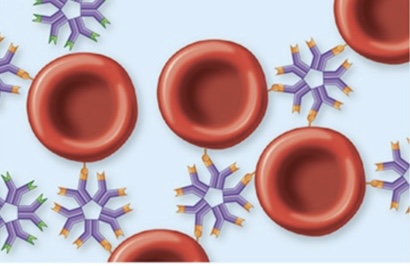
This figure shows the result of interaction of RBC antigens (A antigens) with the antibody against the RBC antigen (anti-A antibodies). What is this result called?
Agglutination
Which scenario involves the risk of erythroblastosis fetalis?
Rh- mom and Rh+ fetus
What is the name of the condition involving a deficiency in red blood cells or in the amount of hemoglobin?
Anemia
Type of WBC: Neutrophil
Phagocytizes small particles; first- responders at infection site
Type of WBC: Monocytes
Phagocytizes large particles in tissues
Type of WBC: Lymphocyte
Provides immunity
Type of WBC: Basophil
Releases histamine and heparin
Type of WBC: Eosinophil
moderate allergic reactions; defense against parasitic worm infections
Leukocytes can undergo diapedesis. What is diapedesis?
The ability of cells to squeeze between cells of capillary walls
Type of condition: Cyanosis
Low blood oxygen levels lead to bluish tint to the skin
Type of condition: Anemia
Reduced oxygen carrying capacity of the blood; leads to paleness of the skin
Type of condition: Sickle-cell disease
Abnormal hemoglobin; causes hemoglobin to crystallize and low oxygen conditions
Type of condition: Thrombocytopenia
Low platelet count; results in decreased blood clotting and bruising
Person with ______ blood have neither antigen A nor antigen B on their red blood cells but have antibody anti-A and antibody anti-B in their plasma
Type O
What characteristic of red blood cells allows oxygen to more easily reach hemoglobin molecules within the cytoplasm?
biconcave shape
Abnormal red blood cell counts have what consequences on health?
Altered oxygen-carrying compatibility of blood
In initiating hemostasis, what typically activates platelets?
exposed collagen