Cognition
1/98
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
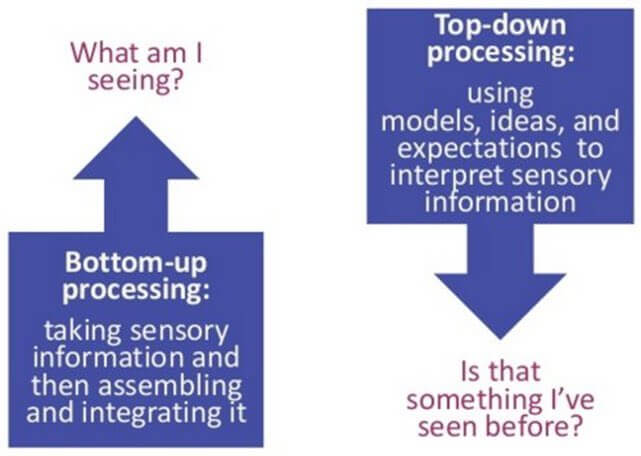
Top-Down Processing
Information processing is guided by higher-level mental processing. Our brain uses prior knowledge, expectations, and context to interpret sensory data
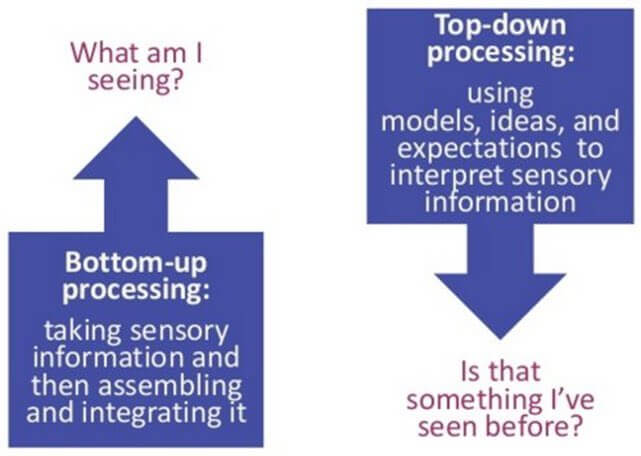
Bottom-up Processing
Learning based solely on the stimulus, without drawing on past experiences or contextual information
Signal Detection
It explains why we are able to pick up or focus on things we're expecting and ignoring or minimizing everything else
Selective Attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimuli, so because you are focused on one stimulus, you don't take notice of details or surrounding
Cocktail Party Effect
Ability to focus attention on a single talker among a mixture of conversation and background noises
Inattentional Blindness
Failure to notice an unexpected item
Change Blindness
Failure to detect change in a visual stimuli
Binocular Cues
Judging the distance of nearby objects with two eyes
Retinal Disparity
The slight difference in the images received by each eye due to their different positions
Convergence
The inward movement of both eyes to focus on a close object
Stroboscopic Effect
A visual illusion where a rapid series of slightly different images is perceived as a moving image
ex: flip book
Phi Phenomenon
A visual illusion of movement is created when 2 or more lights next to each other blink on and off
ex: christmas light shows, animated signs
Autokinetic Effect
A visual illusion where a stationary point of light appears to move in a dark environment due to small movements
ex: illusions
Perceptual Adaption
The brain’s ability to become accustomed to new or unusual sensation
Perceptual Set
To perceive one thing and not the other— how we perceive things in one perspective
context: external factors that can impact how we perceive info
motivation: we see what we want to see— desires or needs
emotions: they can alter what we experience
ex: if two people see a gathering of people in the street several hundred yards ahead, someone who is in a happy emotional state will likely see this is some form of party. Someone who is worried or anxious may instantly perceive it as some form of disturbance
expectations: we expect/predict certain results using prior beliefs
ex: last time I had grapes, they were sour, so this grape will be sour
Habituation
We stop responding to a stimulus because we’re uninterested or we’ve become used to it
Memory
Learning that persists over time
Encoding (get info)
Storage (retain info)
Retrieval/recall (get the info)
Information Processing Mode of Human Memory
Recall: retrieving past info that was stored away, not in our conscious awareness
Recognition: identifying/recognizing items previously learned
Relearning: going over information more than once to learn it easily
Working memory
A cognitive system that temporarily holds and manipulates information — you hold information AND work with it at the same time
Central Executive Functions
It decides what to focus on, what to ignore, and how to organize your thoughts.
It helps you switch tasks, plan, solve problems, and stay on track
tasks:
Focus attention
Divide attention between tasks
Switch attention from one thing to another
Connect working memory with long-term memory
Phonological Loop
Tendency to repeat over and over what you heard to help you remember
ex: phone number
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Mentally envisioning an image/event/scene
Explicit Memory
A type of long-term memory that involves conscious recollection of facts and events that requires intentional effort to recall
Episodic: memory of personal experiences and specific events
Semantic: memory of general knowledge and facts
Implicit Memory
Memory that enables you to perform tasks automatically after enough practice or exposure, without needing to actively recall how to do them — memory that influences behavior without conscious awareness
Automatic Processing
The subconscious encoding of information without active effort or conscious awareness. Allows for the absorption of information effortlessly, such as recognizing familiar faces or places
Auto processing leads to implicit memory formation
Effortful Processing
Active, conscious effort you put into encoding, storing, and retrieving information. It's essential for learning new, complex, or unfamiliar information — requires focused attention and concentration + often involves repetition and practice
Sensory Memory
A short-term memory system that holds information from what you see, hear, touch, smell, or taste for just a brief moment
Iconic: visual memory — flashbacks
Echoic: auditory memory that allows you to retain sounds for a short period even if you weren’t consciously paying attention
Short-term Memory
Helps store memory for up to 30 seconds and up to 5-9 items until we deem them as:
important —> transfers over to long-term memory
unimportant —> memory decays without active rehearsing or new information pushes out older information from short-term memory (displacement)
Long-term Memory
Can hold and retain memory over extended periods (from hours to decades)
due to its large and unlimited capacity
Chunking
A memory strategy that involves breaking down big pieces of information into smaller, easier-to-remember “chunks”
149217761812 —> 1492 - 1776 - 1812
Mnemonic Devices
Techniques that help you remember information more easily by using associations, patterns, or imagery. They work by making information more meaningful or easier to recall.
Method of Loci
A mnemonic device that uses spatial memory to aid in memorizing information
Hierarchies
A structure that organizes information from broad concepts to more specific details
animal —> mammal —> dog —> pug
Spacing Effect
Recalling memories by studying or practicing things in a distributed time — a learning strategy where you spread out your study sessions over time instead of cramming all at once.
Testing Effect
A phenomenon where testing yourself on previously learned material significantly improves long-term retention (the ability to remember information for extended periods) and learning compared to simply restudying the material — active recalling (actively trying to remember information from memory without looking at a reference)
Shallow Processing
A type of memory processing that involves focusing on surface-level features (appearance/sound) of information — leads to STM
Deep Processing
A type of memory processing that involves analyzing/focusing on the meaning of information and making connections to things — leads to LTM
Retrieval Cue
A hint or trigger that helps you access information stored in your memory
State Dependent Memory
We recall or learn better when we’re in a specific state
ex: If you study while feeling relaxed, you might remember better if you're also relaxed during the test
Mood Congruent Memory
Your mood can act as a cue to recall memories tied to that mood — helps us recall positive/negative memories
Context Dependent Memory
When you learn something in a particular place or situation—your surroundings or environment act as retrieval cues
Serial Position Effect
A psychological phenomenon where people tend to remember the first and last items in a list better than the items in the middle
Primary effect: able to remember the first items better because you’ve had more time to rehearse/repeat them
Recency effect: able to recall the most recent item because it’s still fresh in your STM — (higher than primary)
Retrograde Amnesia
Can not recall past (retro) memories
Anterograde Amnesia
Can’t form new long-term memories
Antero —> After
Encoding Failure
Failure to store information properly because the brain never processed the details deeply enough to store them because of:
distraction
lack of rehearsal
Storage Decay
Over time we forget things even if we encode it well due to lack of active recall
Forgetting Curve
A concept that shows how quickly we forget information over time if we don’t actively try to remember it
Proactive Interference
Prior information interferes with learning or remembering new information
Prior —> Pro
Retroactive Interference
New information interferes with recalling old information
Recent —> Retro
Motivated Forgetting (Repression)
A defense mechanism where the brain blocks out traumatic or distressing memories automatically
Constructive Memory
Memory distortion can replace some parts of your memory by filling in missing details to create a complete and coherent story. —> False, unreliable, and distorted memories
Misinformation Effect
Memories may not be accurate reproductions of events but can be altered by new information related to beliefs, attitudes, and perceptions to fill in gaps in the memory
Source Amnesia
The inability to remember where, when, or how previously learned information was acquired, while retaining the factual knowledge itself
Cognition
Your ability to think, know, remember, and communication with information
Schema
A mental framework where we categorize and store knowledge about objects, people, events, and ideas
Prototypes
Common or representative example of a category or concept
bird —> goose
Assimilation
Take in new information and incorporate it into our existing schema
Accommodation
Modifying your existing schema or creating a new schema to fit new information
Availability Heuristics
A mental shortcut where people judge the likelihood of an event based on how easily examples come to mind
Ex: If you recently saw news reports about plane crashes, you might overestimate the risk of flying, even though flying is statistically very safe. The plane crashes are more available in your memory, so they feel more common
Overconfidence
Overestimating the accuracy of our abilities, knowledge, or judgments
Belief Perseverance
Clinging onto our beliefs even though evidence argues otherwise—even after they’ve been proven wrong
Framing
The way information is presented or worded can significantly influence people's decisions and judgments
Gambler’s Fallacy
Where we believe something is less likely or more likely to happen based on the previous outcome
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
Reluctant to abandon strategy because they invested too much or heavily
Creativity
The ability to produce and express new ideas
expertise
imaginative thinking skills
adventurous personality
intrinsic motivation
creative environment
Concept
A mental categorization of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
Recall
Ability to remember without cues
Recognition
Ability to remember what you’ve been told — with cues
Function Fixedness
Can only see one common use for an item — no creativity
Divergent Thinking
Creative thinking that allows you to come up with many uses for an object or many solutions to a problem
Convergent Thinking
Logical thinking that focuses on finding the single best or correct solution to a clearly defined problem
Executive Thinking
Generating, organizing, planning, and carrying out goal-directed behaviors
Massed Practice
Cramming —> opposite of spacing
Tip of the Tongue Phenomenon
Unable to fully retrieve a word or name from memory, but feels like it’s about to come out any second
Prospective Memory
The ability to remember to perform an action in the future
Imagery
Attaching images to information to learn and remember better
Duel Encoding
We remember information better when it is processed in both verbal and visual forms
Representative Heuristics
Where people judge how likely something is based on its similarity to a stereotype
Ex: quiet person —> librarian
Mental Set
The tendency to approach problems with the same strategy — even when a new or better solution might be available
Metacognition
Being aware of your cognitive processes and adjusting those strategies when needed
Ex: “I remembered most things, but I still mixed up two terms. Next time, I’ll make flashcards for those.”
Semantic Networks
A semantic network is like a web in your brain where words and ideas are linked based on meaning.
Ex: Bird —> feather —> eggs —> nest —> fly —> goose
Multi-Store Model
How information flows through three separate memory stores:
Sensory memory
2. STM
3. LTM
Structural Encoding
A type of shallow processing that involves focusing on the physical appearance or structure of information — you notice how it looks, not what it means
Ex: “TABLE” —> remembering it because it was in caps
Phonetic Encoding
A type of shallow processing that focuses on the sound of information
Ex: “Cat” rhymes with “hat”
Semantic Encoding
A type of deep processing where you remember something because of its meaning
Elaborative Rehearsal
Strategies used to enhance encoding information
Autobiographical Memory
A memory system that helps you remember the story of your life — memory of personal life experiences
Episodic: specific event(s)
Semantic: facts about yourself
Baader-Meinhof Phenomenon
A cognitive bias, where something recently learned or noticed seems to appear more frequently than it actually does
Superior Autobiographical
The ability to recall personal life events with extreme accuracy — extremely rare case
Intelligence
The mental potential to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
General Intelligence/General Ability
One general ability that makes you good at many things — (g-factor)
Standardization
A uniform to test where an individual’s score is compared to the rest of the tested groups in order to see where you’re at compared to everyone else
Ex: SAT
IQ
Mental age/Chronological age x 100 = IQ score
**How you behave and think mentally
**How old you really are
Flynn Effect
A worldwide phenomenon where IQ scores showed an increase globally
Occurs decade to decade
Makes us question whether it’s the result of better nutritious meals or more access to education
Imagination Inflation
Imagining an event increases your confidence that it actually happened
**misinformation effect can influence your perspective:
“Peppa tripped Suzy” —> imagination manifests —> you now think Peppa did actually trip Suzy
Psychometrics
The field of psychology focused on the measurement of mental abilities, traits, and processes
Tests
Scales
Assessments
Multiple Intelligence
8 Types of Intelligence:
Linguistic Intelligence
Logical-Mathematical Intelligence
Spatial Intelligence
Musical Intelligence
Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence
Interpersonal Intelligence
Intrapersonal Intelligence
Naturalistic Intelligence
Crystallized Intelligence
Our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills increase with age
Fluid Intelligence
The ability to think, reason, and problem-solve quickly and abstractly without the influence of one’s prior knowledge or experience — decreases with age