scrotum anatomy
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
In utero, where will the testicles arise?
What will it be near?
In the fetal upper abdomen
Kidneys
In the 4th gestational month, the testes will descend to the level of the…
Urinary bladder
After the 7th gestational month, what will the testes descend through?
The descent will be ________ controlled.
The inguinal canal and into the scrotum
Hormonally
The scrotum is a (1)____________ sac composed of several layers of (2)__________ and _________.
Fibromuscular
Fascia and muscle
The layers of the fibromuscular sac include… (4)
Tunica dartos
External, middle, and internal spermatic fascia
Cremasteric muscle
Tunica vaginalis
The scrotum is divided into two compartments by a (1)________ septum, called the (2)_____________.
Midline
Median raphe
The median raphe is created by the tunica…
Dartos
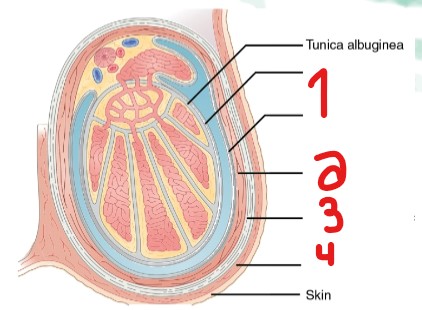
Label the layers of the scrotum that are crossed out.
Tunica vaginalis
Cremasteric muscle
External spermatic fascia
Dartos muscle (Tunica dartos)
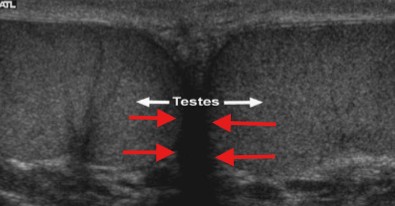
What is the name for the area pointed at by the red arrows?
Median raphe
What are the three major structures within the scrotum?
Spermatic cord
Epididymis
Testes
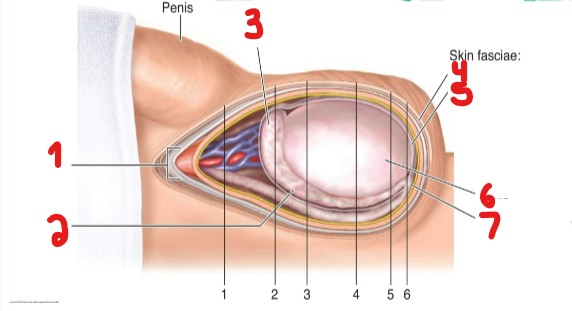
Label the layers/structures within the scrotum that are crossed out here.
Spermatic cord
Body of epididymis
Head of epididymis
Tunica dartos
Tunica vaginalis
Testis
Tail of epididymis
The spermatic cords are paired and extend from the pelvis through the (1)____________ and into the (2)________.
Inguinal canal
Scrotum
The spermatic cord (1)_______ the testicles into the (2)________.
Suspends
Scrotum
What 6 parts make up the spermatic cord? (AVLNVC)
Arteries
Veins of the pampiniform plexus
Lymphatics
Nerves
Vas deferens
Connective tissue
List the 3 arteries in the spermatic cord.
Testicular
Cremasteric
Deferential
Label the layers/structures of the spermatic cord that are crossed out here.
Vas deferens
Pampiniform plexus
Cremasteric muscle
A normal spermatic cord will appear as a (1)_____echoic, slightly (2)___________, linear structure.
Hypoechoic
Turtuous
A normal spermatic cord will measure up to __ mm in diameter.
2
An abnormal spermatic cord will measure over __ mm in diameter.
2
With color doppler, the normal spermatic cord will show how much flow?
Within what vessels?
At?
Minimal flow
Arteries and veins of the pampiniform plexus
Rest
For a normal patient, performing what maneuver will increase flow slightly on a color doppler scan?
Valsalva
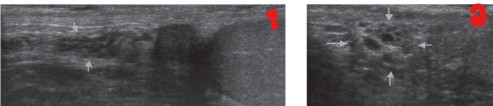
What is this an image of?
What plane was image one taken in?
What plane was image two taken in?
Greyscale spermatic cord
Sagittal view
Transverse view
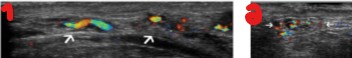
What is this an image of?
What plane was image one taken in?
What plane was image two taken in?
Colorscale spermatic cord
Sagittal view
Transverse view

What is this an image of?
What plane was image one taken in?
What plane was image two taken in?
Colorscale spermatic cord
Sagittal view
Transverse view
On an US scan, how will a spermatic cord appear after performing the Valsalva Maneuver?
• Significantly more color
• Dilated greater than 2mm in diameter
The epididymis is a (1)_________ structure that begins superiorly and then courses (2)_____________ to the testes.
Tubular
Posterolateral
What is the function of the epididymis?
To store, convey, and excrete sperm
What is the epididymis divided into anatomically?
Head
Body
Tail
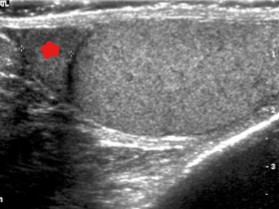
What structure is seen here, as indicated by the star?
Epididymal head
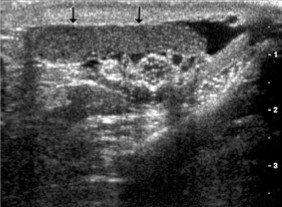
What structure is seen here, as indicated by the arrow?
Epididymal body and tail
What is another term for epididymis head?
Globus major
What part of the epididymis is seen most often, due to being the largest?
Epididymis head
The epididymis head is located __________ to the upper pole.
Superior
Compared to the testicle, how does the epididymis head appear?
Homogenous
Isoechoic to slightly more echogenic
The epididymis head is best seen in what plane?
How does it appear on US?
It will lie ________ to the testicle.
Sagittal
Triangle, crescent, or tear drop shaped structure
Superior
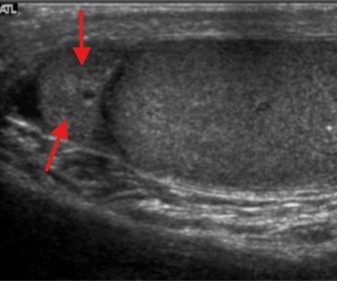
What structure is seen here?
Epididymis head
What is another term for the epididymis body?
Corpus
The body of the epididymis is much _________ than the head.
Smaller
The epididymis _____ is typically difficult to see with US.
Body
The epididymis body follows the (1)_____________ aspect of the testicle from the (2)______ to _______ pole.
Posterior/lateral
Upper, lower
What is another term for epididymis tail?
Globus minor
The epididymis tail is positioned to the _______ pole of the testicle.
Lower
A normal epididymal body and tail are (1)_______ and more (2)_________ in position.
Smaller
Variable
The epididymis tail is usually located (1)__________ and (2)_________ to the testicle.
Posterior
Inferior
The epididymis tail is best evaluated in what plane?
Sagittal
The epididymal head contains how many efferent ductules?
Where do they come from?
10-15
Rete testes
What do the converged rete testis form?
A single duct in the body and the tail
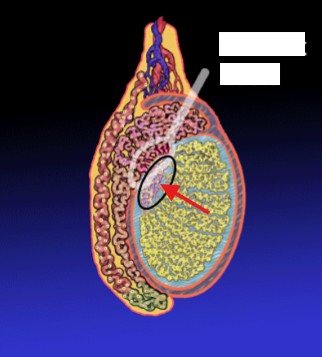
What does the white circle outline?
What does the red arrow point to?
Efferent ducts
Rete testes
In a longitudinal view, the mediastinum testes are seen as an (1)__________ band that run (2)_________ to _________ within the testes.
Echogenic
Superior, inferior
In a transverse view, the mediastinum testes may appear more ________ shaped.
Ovoid
The mediastinum testes function as a supporting system for what 4 structures?
Arteries
Veins
Lymphatics
Seminiferous tubules
The seminiferous tubules converge to form what?
Tubuli recti
The tubuli recti is formed from the convergence of what?
Seminiferous tubules
What does the tubuli recti help connect?
The seminiferous tubules to the rete testes
What is another term for tubuli recti?
Straight tubes
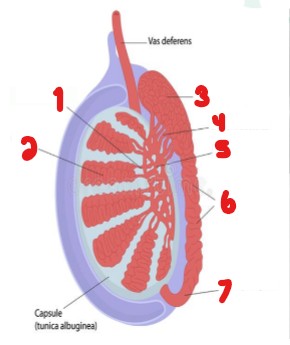
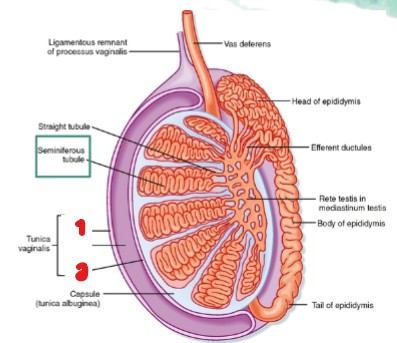
Label the parts of the testicle that are crossed out.
Tubuli recti
Seminiferous tubule
Head of epididymis
Efferent ductules
Rete testis
Body of epididymis
Tail of epididymis
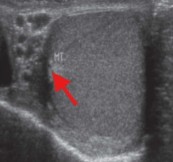
What part of the testicle is seen here?
Mediastinum testis
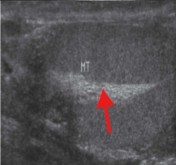
What part of the testicle is seen here?
Mediastinum testis
The rete testis are a network of (1)_________ lined channels within the (2)_________________.
Epithelial
Mediastinum testis
What does the rete testi drain into?
It drains through what structure?
Epididymis
Efferent ductules
Normal rete testis can be seen as (1)_________ areas with striations located adjacent to or within the (2)_________________.
Hypoechoic
Mediastinum testis
What does the rete testi play a major role in?
Carrying sperm to the epididymis
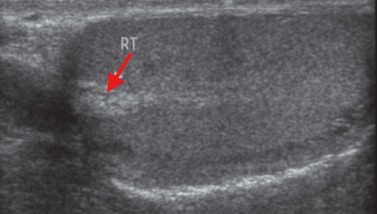
What is this hypoechoic striated structure seen within the mediastinum testi?
Rete testi
The creation of sperm occurs where?
Seminiferous tubules
Where does the seminiferous tubule empty sperm?
In the tubuli recti
Where does the tubuli recti converge?
At the rete testes
Between the seminiferous tubules are what cells?
Leydig cells
What are the leydig cells responsible for?
Producing testosterone and androgens
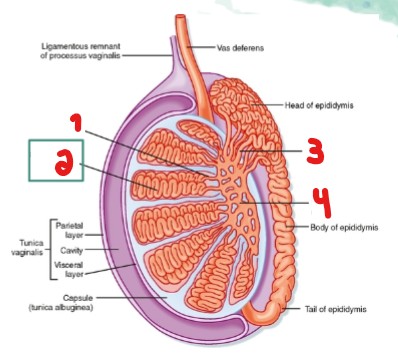
Label the parts crossed out on the image.
Straight tubule
Seminiferous tubule
Efferent ductules
Rete testi
The seminal vesicles are paired glands surrounded by __________ tissue.
Connective
The seminal vesicles lie anterior to the ________.
It lies posterior to the _________.
It lies medial to the _________.
And it lies lateral to the __________.
Prostate
Bladder
Ureters
Vas deferens
Each seminal vesicle joins with its corresponding…
Ductus deferens
What makes up a portion of semen and helps aid in sperm mobility?
Secretions
What forms the ejaculatory ducts?
Ductus deferens
The 2 ejaculatory ducts course through the (1)_______ and empty into the (2)________________.
Prostate
Prostatic urethra
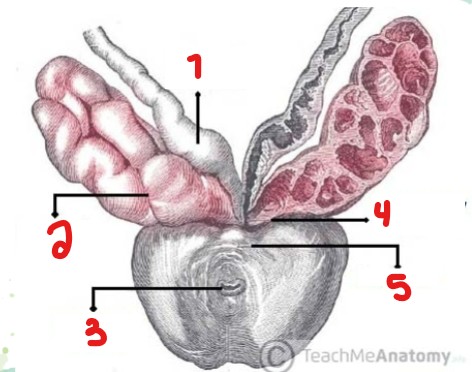
Label the parts crossed out on this image.
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicle
Prostatic urethra
Ejaculatory duct
Prostate
List the 10 step pathway of sperm from the testes to the urethra.
Seminiferous tubules
Tubuli recti
Rete testes
Efferent ductules
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicles
Ejaculatory duct
Prostate
Urethra
What are the testicles?
Bilateral, symmetrical ovoid structures within the scrotum
The testicles get to their max size around ______.
What is the measurement for length?
AP and width?
Puberty
3-5 cm
2-3 cm
What is the endocrine function of the testes?
Testosterone production
What is the exocrine function of the testes?
Sperm and semen production
What occurs to both testes and epididymis with age?
It will decrease in size
How does a normal teste appear on US?
Homogenous
Medium level echoes
Smooth contour
Similar to thyroid
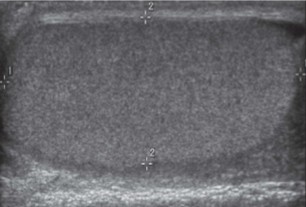
What is this image of?
What plane is this taken in?
What measurements are taken here?
Teste
Sagittal
Length and AP
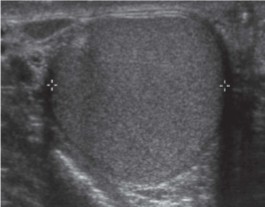
What is this image of?
What plane is this taken in?
What measurements are taken here?
Teste
Transverse
Width
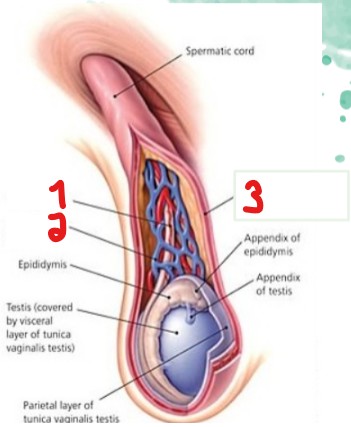
What are the names for the two layers crossed out?
Parietal layer
Visceral layer
The tunica vaginalis is a (1)_________ sac, composed of two layers that cover and surround the (2)_________ and (3)________.
Peritoneal
Testis
Epididymis
The visceral layer of the tunica vaginalis is a (1)________ membrane that produces secretions and covers the (2)__________ and (3)___________.
Serous
Testis
Epididymis
The parietal layer is the (1)______ lining of the scrotal wall containing (2)_________ for (3)_______ absorption.
Inner
Lymphatics
Fluid
There is a small bare area not covered by the tunica vaginalis, where is it located?
On the posterior aspect of the testicle
At the bare area site, not covered by the tunica vaginalis, what is occurring?
What can this area prevent?
The testicle is adhered to the scrotal wall
Torsion
What are the parietal and visceral layers of the tunica vaginalis separated by?
A potential space containing a few mL of fluid
In the normal scrotum, visualizing a small amount of fluid should not be mistaken for what pathology?
Hydrocele
Visualizing an excessive amount of fluid in the scrotum could indicate what pathology?
Hydrocele
What are three examples of pathology that can be seen in the potential space between the parietal and visceral layers?
Scrotal hernia
Hydrocele
Hematocele
A scrotal hernia will have what on the US between the parietal and visceral layer?
Bowel
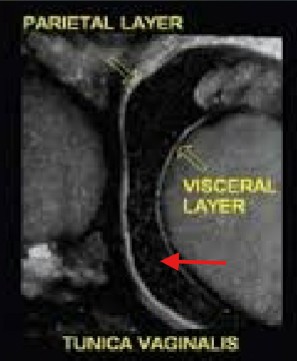
What is the name for this space indicated by the red arrow?
Potential space
The tunica dartos is a thin layer of (1)_________ fibers around the (2)_____ of the scrotum.
Muscular
Base
The tunica dartos will form what?
The median raphe
The median raphe will divide the (1)____________ into two (2)________ for the testes.
Scrotal pouch
Cavities