Week 6 Group/Team Collaboration & Laboratory Errors
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Group or team
made up of individuals from the same or different organizations/departments within the same organization
Majority of groups have 4 -12 individuals
a group with more than 12 individuals is possible
but is usually a committee
determine safety and quality of patient care
with each having their own agendas
Members are connected through a common purpose
are working towards
a common goal
improvement
major change or project planning
Members are interdependent
so behaviors, communication and skills
have significant impact on the members
Healthcare Teams
is a small group, mandated with a specific task
committed to achieving the same clearly defined goal as stated by the patient
has clearly defined roles
is committed to achieving the same goal
patients circle of care
physican and allied health workers
Each member has a unique role and function
each member brings expertise and knowledge about the patient
in units
interdisciplinary teams are made up of
physician
nurse
physiotherapist
social worker
the specific goals are planning the
treatment
discharge/transfer of the patient from the Hospital
Team Work
Individuals working together for a common
purpose by collaborating with others
All individuals contribute knowledge and expertise
Characteristics of Effective Teams
1. Work together with specific objectives in mind
2. Members place the best interests of the team above
individual interests
3. Each team member has an important role and contributes
uniquely to the work
4. Use agreed-upon decision-making and communication
processes
5. Use problem-solving skills and trust each other
Tuckman’s (four) Stages for Group Development
Forming
Storming
Norming
Performing
Forming (Stages of Team Development)
Hesitant participation
need ice breakers as all strangers
need introductions
formal/informal leader to guide group through this step
Roles and responsibilities are unclear
Exchange of functional information
high dependence on leader for direction+
Practical Approaches
Get acquainted and orient members to the tasks
Clarify roles & goals
Establish group norms and agreements
Identify information resources
Storming (stages of Team Development)
Resistance to the task as members realize it is more difficult than imagined
Conflict among the members
because not everything is going smooth
Polarization of issues and lack of unity
Leader may be challenged by team members
Practical Approaches
Use active listening
Be flexible and open-minded
Clarify issues
Apply different approaches to conflict
Norming (Stages of Team Development)
Development of cohesive team
Engage in fun activities
Co-operation & commitment is high
making progress improves cooperation
Acceptance of others & respect for individual differences
Practical Approaches
Give and receive constructive feedback
Focus on the problem and not on the person
Seek opinions and perspectives from the team
Performing (Stages of Group/Team Development)
Shared vision & values
Strong interdependence of task & relationships
Team has a high degree of autonomy
everyone understands role
shared decison making, no formal leader
Practical Approaches
Use participative decision-making
Sense of achievement
Apply problem-solving approaches
Healthcare Problem Solving Group Stages – Four Stages
Opening Stage
Feedforward Stage
Feedback Stage
Closing Stage
Opening Stage: (first stage of Healthcare Problem Solving Group Stages)
Members in the group introduce themselves, their positions and roles
Feedforward Stage (second stage stage of Healthcare Problem Solving Group Stages)
The group identifies the mandate in terms of what
needs to be done
who will do what and the date the deliverables must be
submitted.
In hospitals.
Groups have an agenda which identifies the problems/issues that need resolution
any sharing of information and the tasks to be achieved
Feedback Stage (Third stage of Healthcare Problem Solving Group Stages)
The group reflects on what has been done and what else needs to be accomplished.
The group evaluates if the problem is solved
do we need more information
are we on track
do we need to re-group or change course
Closing Stage (fourth stage of Healthcare Problem Solving Group Stages)
The members reflect on the group’s accomplishments.
The focus of the group changes from tasks to interpersonal relationships
as the group terminates
Brainstorming
technique used in group for analyzing a problem by generating many ideas
is common process used in groups for problem solving as
it lessens group inhibitions
encourages participation by all the members
Each member contributes many ideas
no evaluation or criticism of the idea is permitted
examples
Each idea is written on a sticker “post-it” note
the members then group the ideas
in order of their
importance based on their individual perspective
resources required
The ideas are evaluated
the idea with the most “post-it” notes is considered as the priority.
Process Improvement
Define the problem and the root causes of the situation below
something a healthcare administration group would try to address
possible solution
add wait time to ticket to allow patient to comeback a later time
Patient arrives at Blood Collection Lab - 08:00
Patient asked to take a number - 08:05
Patient ‘s number is called by Receptionist - 08:30
Receptionist checks patient’s requisition and demographics and then asks the patient to take a seat - 08:40
Patient waits until called by Phlebotomist - 09:10
Phlebotomist calls patient and the blood is taken - 09:15
Complaint by Patient about waiting for over one hour
Decision by Authority (a type of decision making)
the group members provide recommendations with advantages and disadvantages.
The final decision is made by Management,
is considered an efficient process for decision making.
Management has a “big” picture view
understands the impact the decision may have on the organization.
ensure information flows to management
The disadvantage
is that the members may feel that they have very little influence
understandable feeling
Majority Rules (a type of decision making)
Where the group’s majority makes the decision and voting is the method used to decide on issues.
It is not an unanimous decision but a decision that the group can live with.
Disadvantage
The minority members of the group may feel
disenfranchised
not ideal for important/big decisions
Consensus (a type of decision making)
Each member has a say and the opinions are carefully considered.
not efficient, but more group satisfaction
The best ideas/opinions are synthesized and presented as a solution(s) that the group agrees to, and recommends be implemented.
Disadvantage
Consensus is time consuming
hard to do
timely meetings
however it facilitates participation and collaboration.
Focus Groups - in Healthcare
common means to elicit opinions on service delivery
but more importantly are used for
clinical trials and clinical studies
consists of people who use the service or the drug or have undergone a particular procedure.
Group is lead by a facilitator, who explains the process, the goals and time limit for each speaker on each question.
There is usually a scribe and the dialogue is taped
intent of focus groups is to
analyze the information generated by the groups,
implement changes to the service delivery model
modify the drug composition
Patient Partner Program (at the school level)
are community members including
patients
family members of patients
caregivers of patients
who with the hospital staff to enhance the care experience from the perspective of the patient, family and caregiver
Patients share their unique experiences and perspectives
while in hospital or about the service they receive in
hospital clinics.
How Will it Help Improve Patient Care?
By considering the patient care experience from
many different perspectives
hospitals adapts current and future practices to be more inclusive
create the best health experience for all
patients and their families
In practice
In 2023-2024 the MLAB program plans to include patient
who have had experience with phlebotomists
or the lab as partners with lived experience to support students in their
learning.
The plan includes having patient partners participate as guest lecturers in course MLAB 102
with students having an opportunity to ask questions and write a reflection
about their experience
will be recorded
Group Culture – Group Norms
These are rules and standards that identify appropriate behaviors among the group members
are explicit
Attending meetings
being on time
flexibility to learn
take on additional tasks
delivering what is required etc
In groups,
if you accept the norms
you are more likely to consider the group membership as important.
It is the group norms that
hold the members together
where every one knows
how to behave
to depend on each other
If you violate the norms, you are asked to leave the group
Groupthink
A phenomenon in groups and is marked by the consensus of opinion without critical reasoning or evaluation of consequences or alternatives.
evolves around a common desire to not upset
the leader
the balance of a group of people by creating conflict
Creativity and individuality are considered potentially harmful traits that should be avoided
causes employees and their bosses to overlook potential problems in the pursuit of consensus thinking.
Because the individual’s critical thinking is viewed negatively
employees may self-censor themselves and not bring up alternatives
at the risk of upsetting the status quo.
Strategies:
1) Ability to air objectives and to accept constructive criticism
2) Consider unpopular alternatives
3) After reaching a preliminary consensus on a decision
any alternatives should be reconsidered
Dysfunctional Groups
Conflict that obstructs the achievements or the goals of the group
Being Aggressive:
Criticizing and blaming others
showing hostility against the group or individuals
Blocking:
Unreasonably resistant
slowing the progress of the group
going off tangent and arguing too much
Recognition-seeking:
trying to call attention to self
boasting and reporting on personal achievements
Dominating:
Asserting authority by manipulating the group
interrupting others
Horsing Around:
Clowning
joking and disrupting the work of the group
It is Conflict
weakens the organization
valuable employees leave the organization
the distrust causes a negative impact on productivity
American System - Medical Errors & Financial Cost
Over 33.6 million admissions to U.S. hospitals in 1997
44,000 to 98,000 Americans die in hospitals each year as a result of medical errors
Attributable to the 8th-leading cause of death
Exceed the deaths attributable to
motor vehicle accidents (43,458)
breast cancer (42,297)
or AIDS (16,516)
Impact of medical errors is lost income, lost household production, personal disability, health care costs
$37.6 billion to $50 billion are accountable for adverse events
slightly higher than the direct and indirect costs of caring for people with HIV and AIDS.
A 2004 Canadian study estimated that in 2000 of the 2.5 million admissions to hospitals in Canada, about 185,000 patients were associated with an adverse event of which 70,000 were potentially preventable.
Error
the failure of a planned action or procedure to be completed as intended (i.e., error of execution)
Examples
the use of wrong
patient information
specimen
procedure
treatment
medical equipment
medication
Adverse event
injury caused by medical action or procedure or information resulting in a wrong diagnosis or treatment or injury/harm or even death to the patient
is not related to underlying health condition of the patient.
are preventable
SOME COMMON LAB ERRORS
Lab incident reports must be completed
Highlighted the most common
patient ID error
lost sample
sample delayed in transit
contaminated samples
wrong test performed
test performed inconsistent with the written procedure
proficiency testing error
no action on out of range controls
false negative result
late reports
missing reports
Complaints
laboratory accident “near miss”
Errors in Testing Process – Pre-Analytical
occurs before testing of sample occurs
test selection
Test collection
sample transport
errors in processing
Examples include:
Wrong sample collected
Sample mislabeled or unlabeled
Sample stored inappropriately before testing
Sample transported inappropriately
Reagents or test kits quality damaged by improper storage
Needle stick Injury
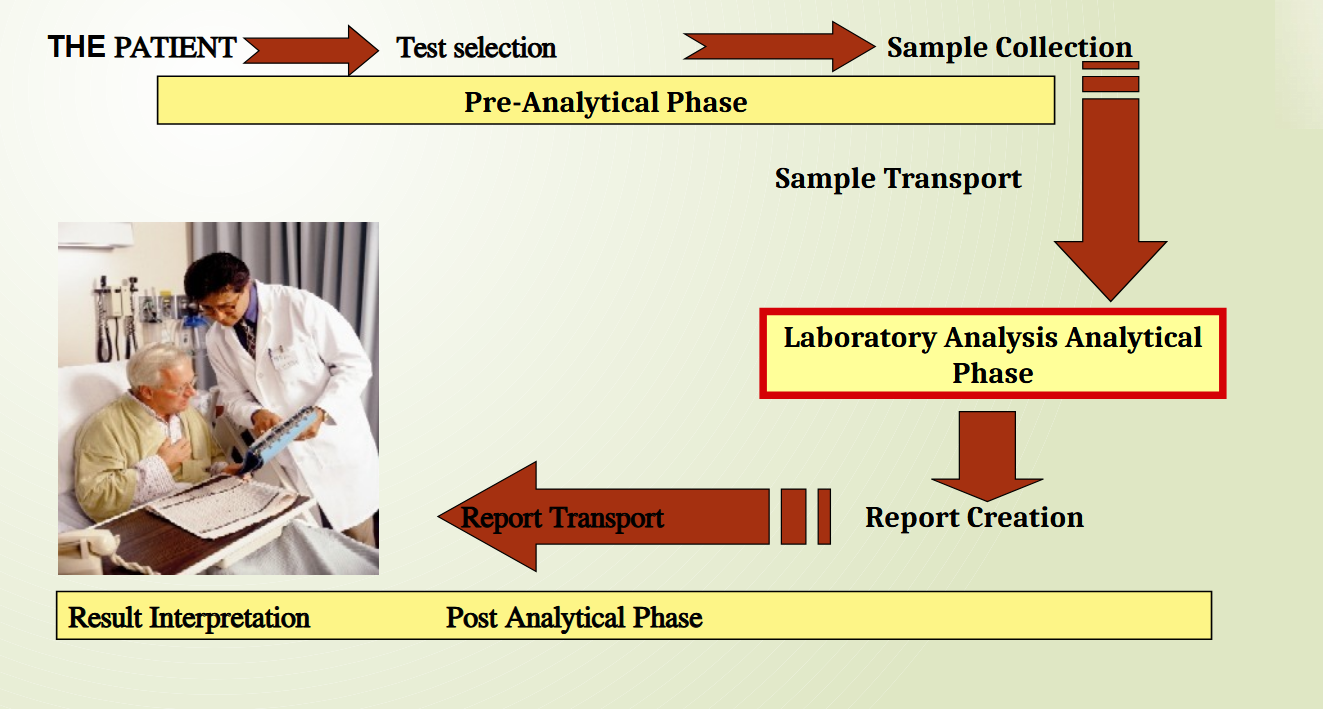
Post-Analytical Errors
Occurs when results are available till in physicians hands
does not include misinterpretation by doctors
unless if was done by lab tech
errors after sample testomg
report creation
report transport
System related errors
A quarter of incidents were related to data output problems, such
as retrieving the wrong patient record
because the system does not ask the user to validate the patient identity before proceeding.
This kind of problem has led to incorrect
lab requests
medication orders
unnecessary chest x-ray.
One system failed to issue an alert when a pregnancy test was ordered for a male patient or entering the health number (OHIP) of the patient
Health care providers errors
twenty-four percent of incidents were linked to data-input mistakes.
For example, the lab recorded blood glucose results for the wrong patient due to inputting the incorrect patient identification number to access the record.
This kind of mistake led to wrong diagnose and treatment.
Patient Safety and Risk Management Program
Continuously improve patient safety
minimize and/or prevent the occurrence of errors
Minimize adverse effects of
errors
events
system breakdowns when they do occur.
Enhance the safety of
patients
visitors
employees
minimize the financial loss to the hospital
through
risk detection, evaluation and prevention
Protect human and intangible resources
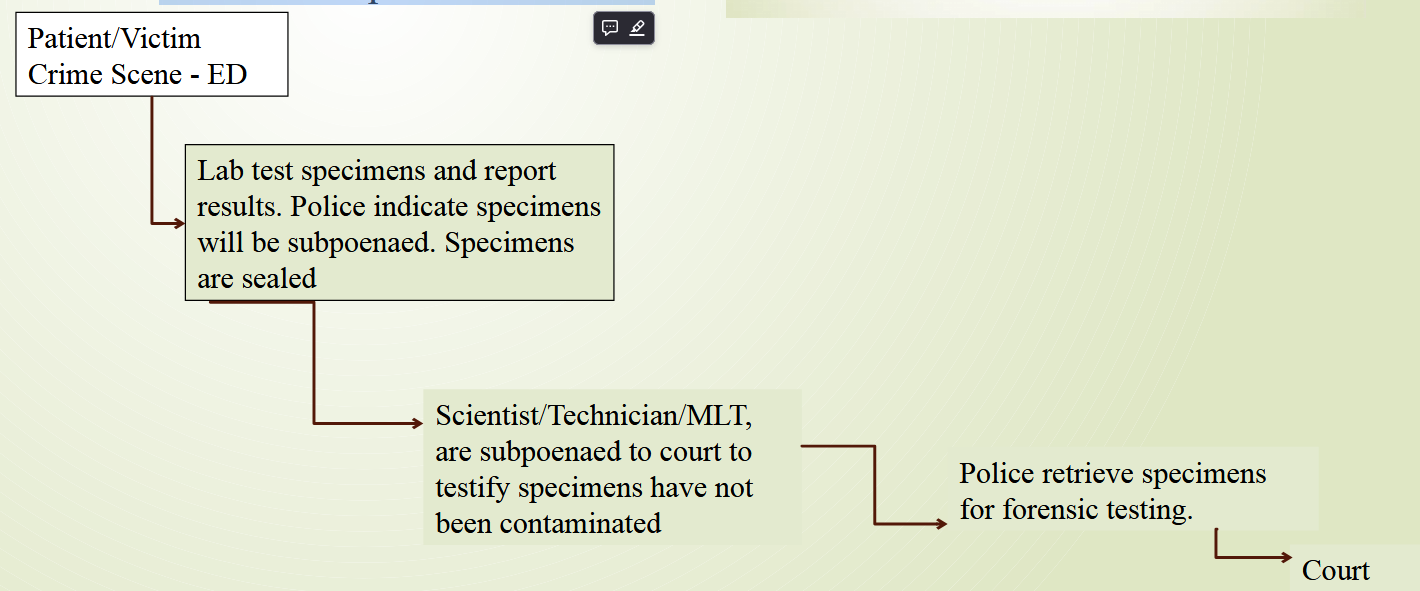
Principles Regarding Chain of Custody
States that chain of custody is a set of procedures to ensure physical evidence is not subject to tampering, misconduct or anything that raises questions about whether the evidence is what the government or court says it is
Occurs when patient/s are considered criminal responsible for a crime
or for investigations, or coroner reports
The number of persons handling evidence from the time it is secured should be limited
Individuals who handle the evidence should affix their names and signature on the seals to the package containing the evidence and the chain of custody sign in and out form/log
Statutes and ordinances very often dictate the methods and procedures for handling, storage and disposal of property
proper documenting and copies have to be made, but also ensure patient information is protected
Chain of Custody Process
The movement and location of physical evidence from the time it is obtained until the time it is presented in court