SOC150 Midterm Flashcards
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Measurement
describe + ascribing meaning to facts, concepts or what is being investigated; defining ones terms in an as clear way as possible
Concept + Conceptualization
CONCEPT: image that we conjure up when we think of a cluster of related observations or ideas (eg: culture, class, masculinity, neoliberalism)
CONCEPTUALZATION: writing out clear definitions for key concepts (part of process of measurement)
eg: hegemonic masculinity (conceptualized by R.W Connell): dominant form of masculinity in society that legitimises male power + maintains gender inequalities)
represents idealized form of masculinity that most men are expected to aspire to (few achieve it); abt relationships of power over traits; compared to subordinated masculinity associated w/ queer men
Reification
treating abstract concept/ human made idea as if it were a concrete/real thing (e.g: saying “society expects us to behave a certain way”)
Operationalizing
taking an abstract concept + deciding how we will measure it
eg: often interviews will give choices: 1) Strongly agree, (2) Agree, (3) Disagree, and (4) Strongly disagree; higher score = higher of thing being studied
Indicators
characteristics that represent ideas that are being studied (used in operationalizing)
eg: indicators of masculinity = fatherhood, being the breadwinner of the family
eg: in a survey/interview a question abt work-family conflict would be “How often did you not have enough time for the important people in your life because of your job?”
question = indicator of the a work-life conflict
Process of Measurement

Reliability + Validity
RELIABILITY = consistency; if same measure applied to same person, result will be same every time = measure is reliable
VALIDITY = accuracy/social agreement; if same measure applied to diff ppl, all will understand it in same way = measure is valid
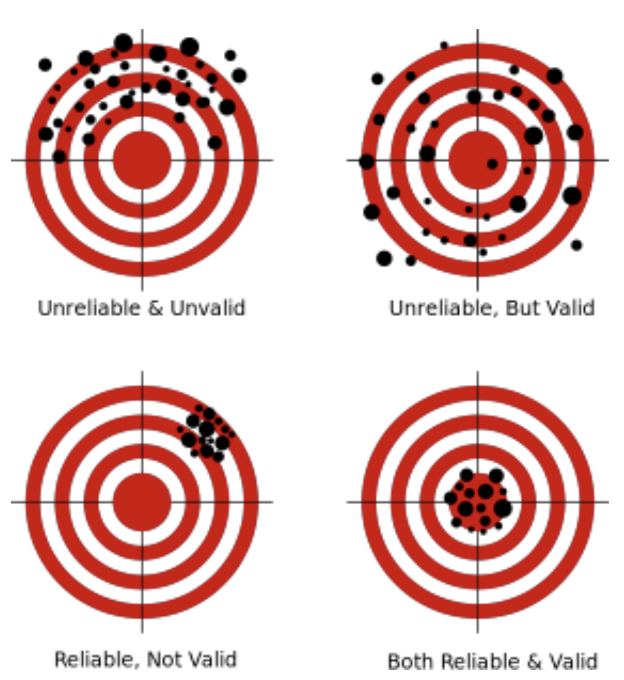
1991, 2016, 2021 Census (LEC 5 example of reliability + validity)
1991 census question: “To which ethnic or cultural group(s) did this person’s ancestors belong? Mark or specify as many as applicable” (4% responded that their ethnic origin is canadian)
2016 question: “What were the ethnic or cultural origins of this person’s ancestors?” (32% canadian)
2016 question: instead of giving list of potential ethnicities, a link was provided w over 500 ethnic origins (16% canadian)
no. of canadians fluctuated wildly over time; perhaps not reliable + valid?
Variable
grouping several characteristics called attributes
attributes determine its level of measurement (nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio)
Nominal Measurement (a level of measurement)
measures are qualitative, exhaustive (incl. all elements/aspects), mutually exclusive (2+ events that cannot happen simultaneously); attributes are all equally as important
eg: marital status measured as single, married, common-law, divorced, widowed
Ordinal Measures (a level of measurement)
can be rank ordered, but can’t determine mathematical difference between the attributes (often abstract concepts, like feelings)
eg: socioeconomic class could be measured as working class, middle class, upper class
Interval Measures (a level of measurement)
rank ordered + quantitative, can mathematically measure distance between them BUT no ‘true zero’ (can’t say ratio of one attribute compared to another)
eg: temperature- can’t say 100 deg = twice as hot as 50 deg.
Ratio Measures (a level of measurement)
quantifiable, mutually exclusive, exhaustive, rank ordered, equal distance and attributes hv true zero point
eg: income measured in dollars, you can make zero dollars, and we know $40k is twice as much as $20k
eg: age: you can be zero years old, and 12 years is twice as much as 6 years
What does it mean to say that Sociology is a Social Science?
uses quantitative methods (statistical analysis of survey data, etc) AND qualitative methods (interviews, etc) to answer research questions
Matching Claims to Evidence
use empirical evidence (rooted in scientific methods) to support/refute claims
must consider many diff. scientific studies before drawing conclusions → then inform public policy + promote better public understanding of complex social phenomena
eg:
Claim: Giving police more money creates safer neighbourhoods
Evidence: no consistent association betw. police funding + crime rates (using stat. analysis → found that majority of cities incr. police budget, but no relation to crime rates)
Ways sociologists use empirical methods to answer research questions
participant observation, interviews, sharing circles, statistical analysis
Who’s afraid of Sociology?
recent efforts to ban sociology in universities → instead, we should all be sociologists (equipped w sociological literacy in order to understand ourselves + the world around us better!)
Sociological Perspective (Sociological Literacy Framework)
(essential concepts)
sociological eye: understanding sociology a distinctive discipline
social structure: impact of social structures on human action
socialization: relationship betw. self + human action
stratification: patterns + effects of social inequality
social change + reproduction: show social phenomena replicate + change
Sociological Toolbox (Sociological Literacy Framework)
(essential competencies)
apply sociological theory → understand phenomena
evaluate explanations of human behaviours + social phenomena
apply scientific principles to understand social world
evaluate quality of social scientific methods + data
use sociological knowledge to inform policy debates + promote public understanding
Informal Observation (a way of knowing)
making observations without assessing accuracy of what we observed (eg: toronto is a very diverse city)
Selective Observation (a way of knowing)
only seeing what we want to see or assuming only patterns we experienced exist
Overgeneralisation (a way of knowing)
assuming broad patterns exist with limited observations
Authority (a way of knowing)
socially defined knowledge that may shape our beliefs about truth/untruth
Research Methods (a way of knowing)
organised, logical way of learning + know about social world
Ontology (+ interpretivist/social constructionist + positivist approaches)
beliefs abt nature of reality
interpretivist/social constructionist approach: think reality is in eye of the beholder (our job is to understand others’ view of reality)
positivist approach: only one true reality
Epistemology
study of origins of knowledge
diff methods to uncover knowledge (interviews, observations, surveys, reading public reactions)
How is the Canadian Census taken?
statistics canada conduct census of population every 5 years
census = way to gather data abt ethnic/racial diversity @ local/national scales (visible minority grp grew frm 2001-2021)
important source of quantitative data that sociologists use in their research, used to develop programs + services, analysed to make investment decisions (businesses), depended on to understand evolving needs of members of their community.
Basic + Applied Research, Public Sociology
Basic Research: research from personal interest
Applied Research: research frm beyond personal interest/for some purpose (eg: marketing firms conducting research on how to sell more product)
Public Sociology: application of sociological theories + research to matters of public interest

Qualitative Research
collecting data thru field research, interviews, enthography; results shown as words, pictures
gain in-depth understanding of small no. of cases
Quantitative Research
survey research, census analyses; results condensed into numbers
less depth but focused on large no. of cases
What role should sociologists play in society?
need more sociologists who are trained in research methods to provide factual information/ reduce the spread of false info
Examples:
Michael Burawoy advocates for more sociology in the public interest; argues that sociology has been divorced frm real world → sociologists talking to each other instead of informing policy + public
Patricia Hill Collins advocates for empowering everyday people as intellectuals; Black female musicians, artists, and writers should be considered intellectuals because they represent the interests of Black women as a group.
Craig Calhoun argues that academic sociologists are necessary to produce rigorous knowledge; they should not align too closely with political causes bc it makes public sociology lose objectivity
Intrinsic Cognitive Load
difficulty of material being learned (can’t be eliminated, only managed by breaking down material → presenting them in logical sequence)
Germane Cognitive Load
mental effort req. to learn + retain knowledge; can be incr. by actively engaging w material + engaging in higher order thinking
The Research Cycle
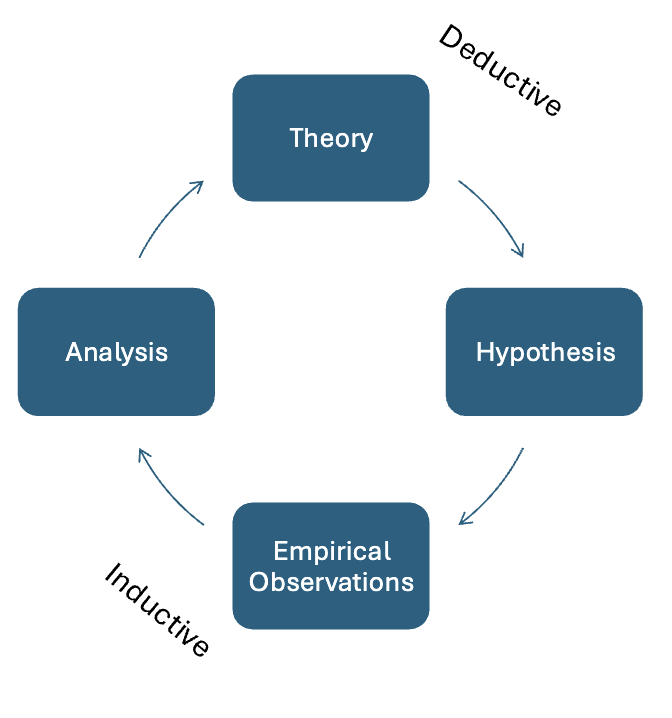
Inductive Reasoning
moving frm empirical observation (data collection) → general propositions (ie: moving frm specific (data) → general (theory))
Deductive Reasoning
test theory w/ empirical observation (general → specific)
Levels of Analysis (Micro, Meso, Macro Levels)
Micro: indiv. + 1-on-1 interractions
Meso: groups, communities, organisations
Macro: large systems + structures (nations, economies)
Paradigm
analytic way of viewing world + humanity (ie: ontological + epistomological approaches)
Positivism (a paradigm)
objective explanation + prediction; society can be studied empirically + scientifically w/o biases
Interpretism/Social Constructionism
focuses on ways ppl understand themselves, others + world around them
Critical Approaches
focus on roles of power, inequality, social change; assumes that social science should be conducted with social change in mind
Postmodernism
challenges existence of truth
Conflict Theory
questions of power (who wins/loses in society) + how ppl struggle over limited resources
Functionalism
how social structures work tgt to produce order
Symbolic Interactionism
how meaning is created + negotiated thru interactions
Relationship between Theory and Empirical Observation
theories explain why social patterns exist (can be used to examine research questions)
Exploratory Research
often @ early stages of research, done to test whether they should conduct a more extensive study
used to learn what method to use in collecting data, how to best approach research subjects, what questions to ask
Descriptive Research
to describe/ define a particular phenomenon (often quantitative research)
Explanatory Research
to explain why particular phenomena work in the way that they do (cause + effects of phenomenon studied)
Defining Research Questions
when formulating one, must ask yourself if the question is…
EMPIRICAL? sociologist best equipped to answer empirical questions (that can be answered w/ real experience in world, rather than ethical/moral philosophy)
SOCIOLOGICAL? sociology interested in human grps, patterns, deviations frm social patterns
A QUESTION? should hv more than one answer, unbiased, considering relationships among multiple concepts
Causality
idea that one event results in occurrence of another
to determine causality:
relationship must be plausible
cause must precede effect in time
relationship must be nonspurious
Idiographic Research
tries to explain/describe phenomenon
may hv to sacrifice breadth of understanding, BUT will gain much deeper understanding of phenomenon
Nomothetic Research
aims to provide general explanation of a topic
sacrifice depth of understanding for breadth of understanding
Plausability
causal claim has to make sense (2 variables may correlate, but doesn’t mean that causal relationship is plausible)
Temporality
cause must precede effect in time
Spuriousness
association between 2 variables appears to be causal but can actually be explained by 3rd variable.
eg: as ice cream sales go up, drowning rates also go up; this can be explained by the warmer weather, where ppl eat more ice cream + go swimming more
Correlation + Causation
CORRELATION: 2 things related
CAUSATION: one thing directly causes the other
Independent + Dependent Variable
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE: variable causing another
DEPENDENT VARIABLE: variable caused by another
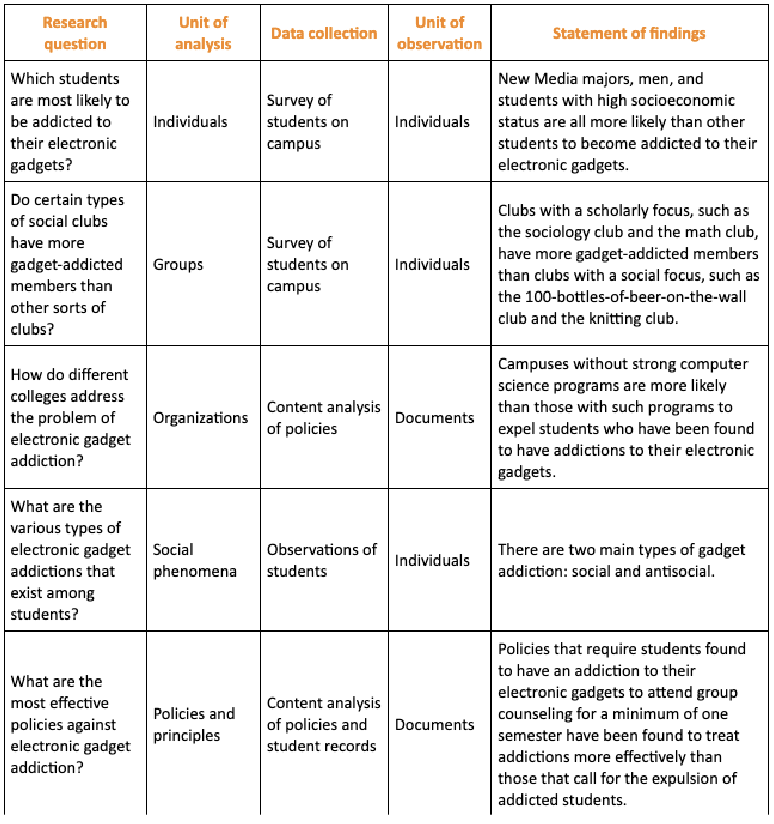
Units of Analysis
main focus of study + determined by research questions
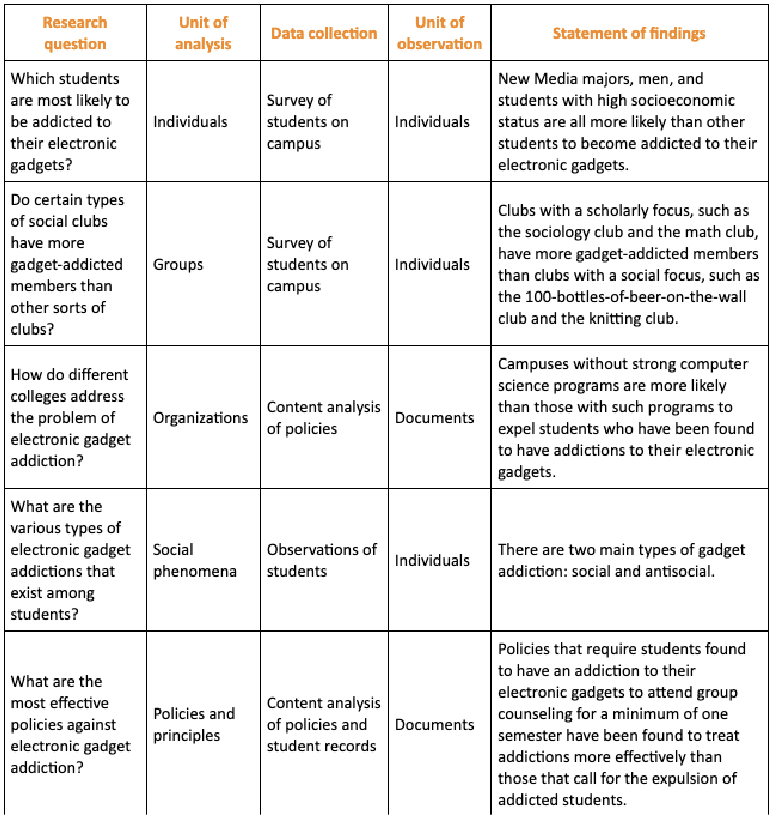
Units of Observation
item that you observe, measure, collect while trying to learn something abt unit of analysis (determined by data collection method)
Ecological Fallacy
when claims abt lower level unit of analysis made based on data frm higher level unit of analysis (e.g: claims made abt indiv., but only grp level data gathered)
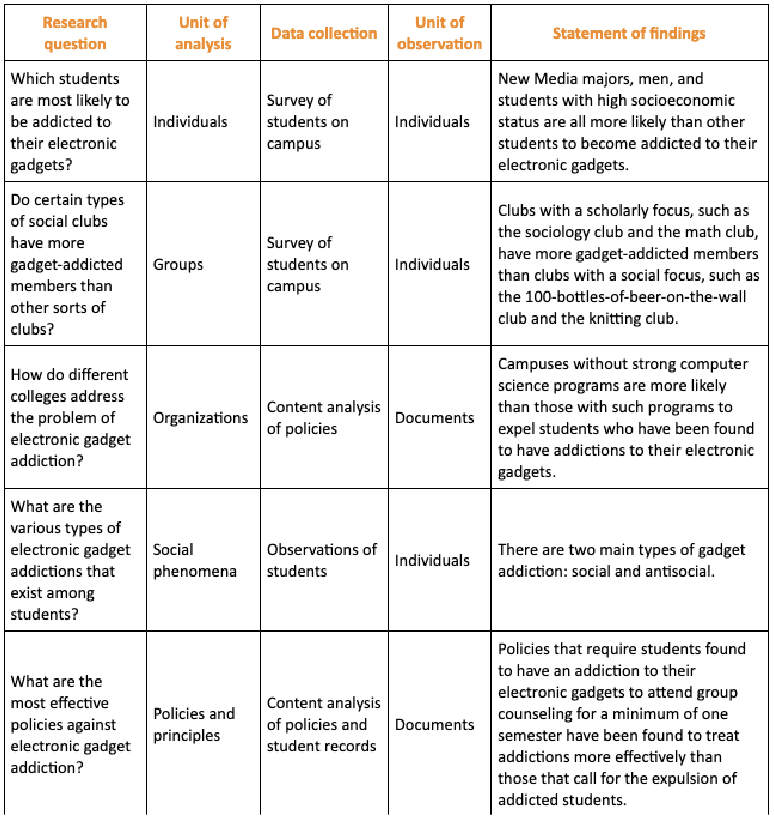
Reductionism
when claims abt higher level unit made based on data frm lower level unit (e.g: claims abt grps based on indiv)
Hypothesis + Null Hypothesis
HYPOTHESIS: statement (not always causal) describing researcher’s expectation regarding what he/she anticipates finding
- describe expected relationship betw 2 variables
- drawn frm theories
NULL HYPOTHESIS: predicts no relationship betw variables being studied
Informed Consent
voluntary agreement to participate in research based on full understanding of research
Anonymity
researcher unable to link participants’ data w their identities (eg: anonymous surveys)
Confidentiality
only researcher can link participant w data + not publicly
3 Father Types (Committed, Conflicted, Receptive) who take paternal leave
Committed Father: proactively + consciously contest gender boundaries
Receptive Father: have egalitarian views but not as proactive as committed fathers
Conflicted Father: hold flexible views abt men/women roles when taking leave, but rigid views about children gender socialisation (eg: boys should be masculine)
Researchers’ Conflicts w/ the Law (maybe not on test?)
researchers been subpoenaed (called to appear in court)
ex 1: Russel Ogden (1994) subpoenaed to appear before Vancouver Coroner’s Court; he conducted research into medically assisted suicide (eg: euthanasia) for HIV/AIDS patients + coroner believed Ogden knew identity of 2 ppl who assisted in a suicide
ex 2: UOttawa researchers Collete Parent + Christ Bruckert conducted research on sex workers. years later, one former interview subjects arrested+ charged w murder → police subpoenaed them to access interview transcript
Quebec denied police access to interview bc risk of jeopardising important research on sex work outweighed benefit to public safety
researcher-participant relationship = unique bc often hv little to offer participants besides interest + giving them opportunity for their voices to be heard
both researchers refused to hand over data!!
Qualitative vs Quantitative Approach
(both empirical + used @ diff points in research cycle to address same topics)

Triangulation
Using several/ a combination of different research strategies
Observational Terms
things we see just by looking at them (eg: height, race)
Indirect Observables
information obtained thru asking interview/survey questions (eg: income, birth place)
Scale
same as index BUT accounts for varying intensity
Index
type of measure that contains several indicators + used to summarise a general concept
Typology
Categorizes concepts into themes to simplify them.