2.1.1 - Economic Growth
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the primary sector?
Extraction and use of natural resources and materials from the land and sea. Either consumed directly or are raw materials for the production of other goods.
Give some examples of the primary sector.
Coal miner
Farmer
Fisherman
Forestry
Quarrying
What is the secondary sector?
All the activities in an economy that are concerned with either manufacturing or construction (where raw materials are made into goods)
Give some examples of the secondary sector.
Refining oil to make petrol
Making components for cars
Constructing buildings / infrastructure
What is the tertiary sector?
All activities in the economy in which a service is provided. Includes sale of finished goods.
Give some examples of the tertiary sector.
Transport
Retailing
Entertainment
Finance
Tourism
What is economic growth?
Measures the rate of change in a country's output measured by changes in real GDP. It is the expansion of the productive potential of an economy.
What is short-run economic growth?
The actual annual percentage change in real national output (real GDP)
How is short run economic growth measured?
Measured by the annual change in real GDP (a.k.a Real National Output (RNO) or Real National Income (RNI))
What is GDP / Total National Income?
The measure of the total value of the quantity of finished goods and services produced in the economy (country) within a year
What is real GDP / Real National Income?
The value of all goods and services produced within an economy in a year adjusted for inflation.
What is nominal GDP?
The value of GDP without being adjusted for inflation - this is misleading because it can make GDP appear higher than it actually is
How can we work out an index number?
Index number in year Y =
(Data value in year Y / Base Year Value)*100
What is long-run economic growth?
An increase in the potential productive capacity of the economy.
How can we measure long-run economic growth?
Measured by the maximum potential output an economy could generate using the factors of production (CELL)
What can lead to an increase in productive potential of an economy?
Changes in the quantity or quality of the factors of production (resources) in an economy:
Capital
Enterprise
Land
Labour
What is GDP per capita?
GDP per capita measures the average economic output per person in a country
Why is GDP per capita useful?
It can help us understand the average standard of living or income level within a given nation.
It provides a way to compare the economic performances of different countries while considering their population sizes.
What is the formula for GDP per capita?
GDP per capita = Total GDP / Population
What is per capita income?
The total income divided by the population
What is gross national income (GNI)?
The value of goods and services produced by a country over a period of time, plus the income earned by citizens operating outside of the country
It calculates income instead of output and is an alternative measure to GDP as a measure of wealth
What are remittances?
When migrants earn in a country and send that money to family back home
What countries would have a GNI higher than their GDP?
Small island nations : due to a large inflow of income earned through finance, etc...
Countries with high remittances: e.g. India
Countries receiving foreign aid: money food or other resources given or lent by one country to another
What does the trade cycle diagram look like?
This is where there are variations in the level of productive capacity of an economy over time.
The level of economic activity also fluctuates over time, this pattern is referred to as the economic cycle.
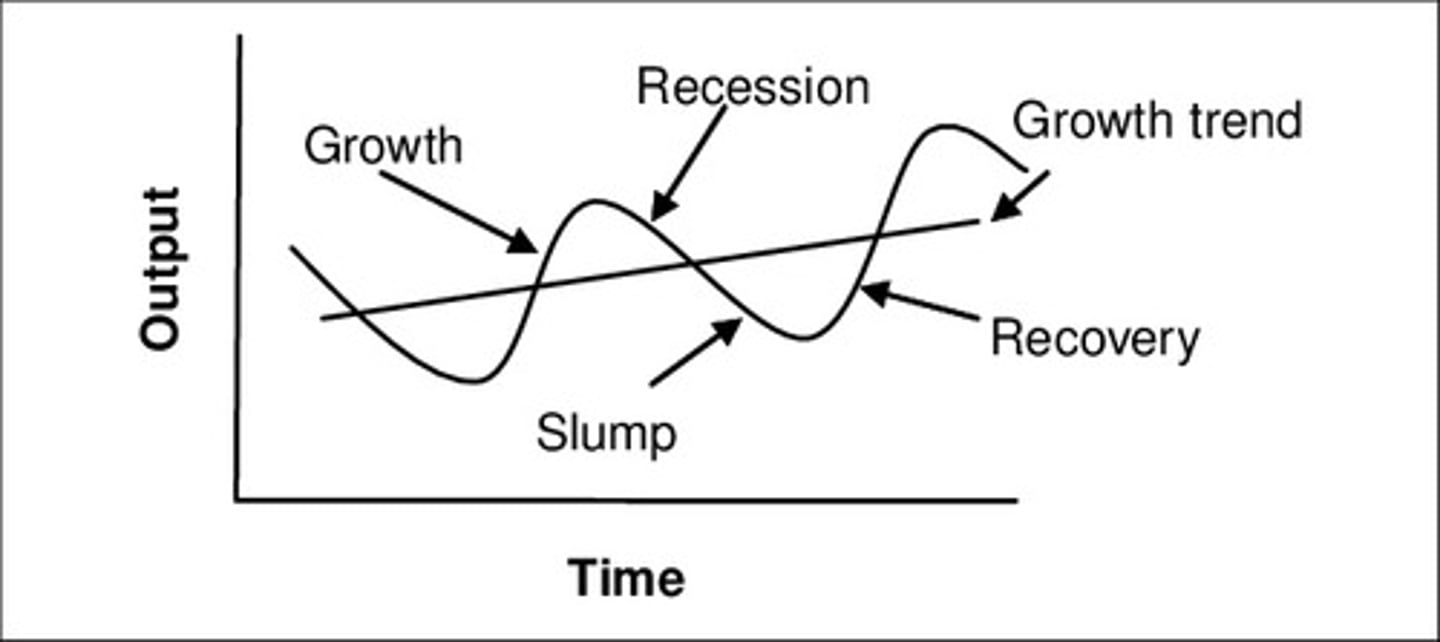
What is a boom?
A period of high levels of economic activity (high rate of real GDP)
What is a recession?
The rate of economic growth starts to fall in a downturn. If real GDP falls for 6 months then this is known as a recession.
What is a slump?
The bottom of the business cycle which represents a period of serious economic decline (very low / negative economic growth)
What is economic recovery?
When there are signs that economic growth is starting to rise
What is a purchasing power parity (PPP)?
A conversion from one currency into another to buy the same amount of goods.
E.g. when we look at living standards, any income (GDP per Capita) should be considered in relation to what you can buy in that country i.e. £30,000 will go further in Vietnam compared to the UK
What is an example of a PPP?
The Big Mac Index which compares the cost of the Big Mac throughout the world.