Foundations Patient Care 4- Dentofacial Deformities
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
dental compensations; 12-18
.... are an integral part of skeletal malocclusions and can be treated with presugrical orthodontics taking typically ... months
growth
orthognathic surgery should be delayed until ... in complete
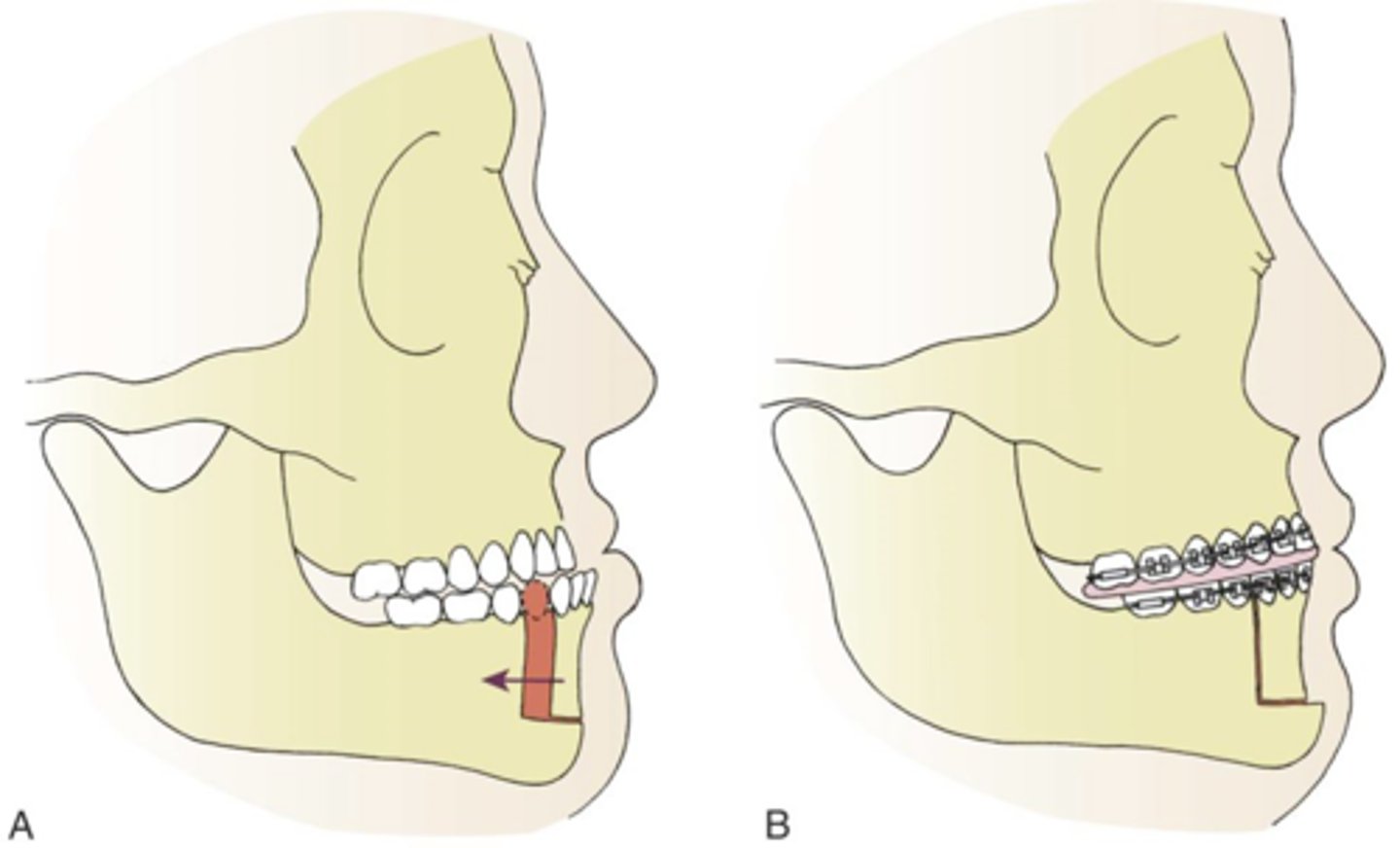
dingman body ostectomy
- involves a section of the lower jaw's body being surgically removed to correct deformities like a jaw that sticks out too far.
- often performed using a transoral (intraoral) approach, aims to preserve the inferior alveolar nerve, which is freed and mobilized before the bone is cut and the segments are repositioned and secured.
- done through a single-stage or two-stage approach, with the latter involving both intraoral and extraoral components.
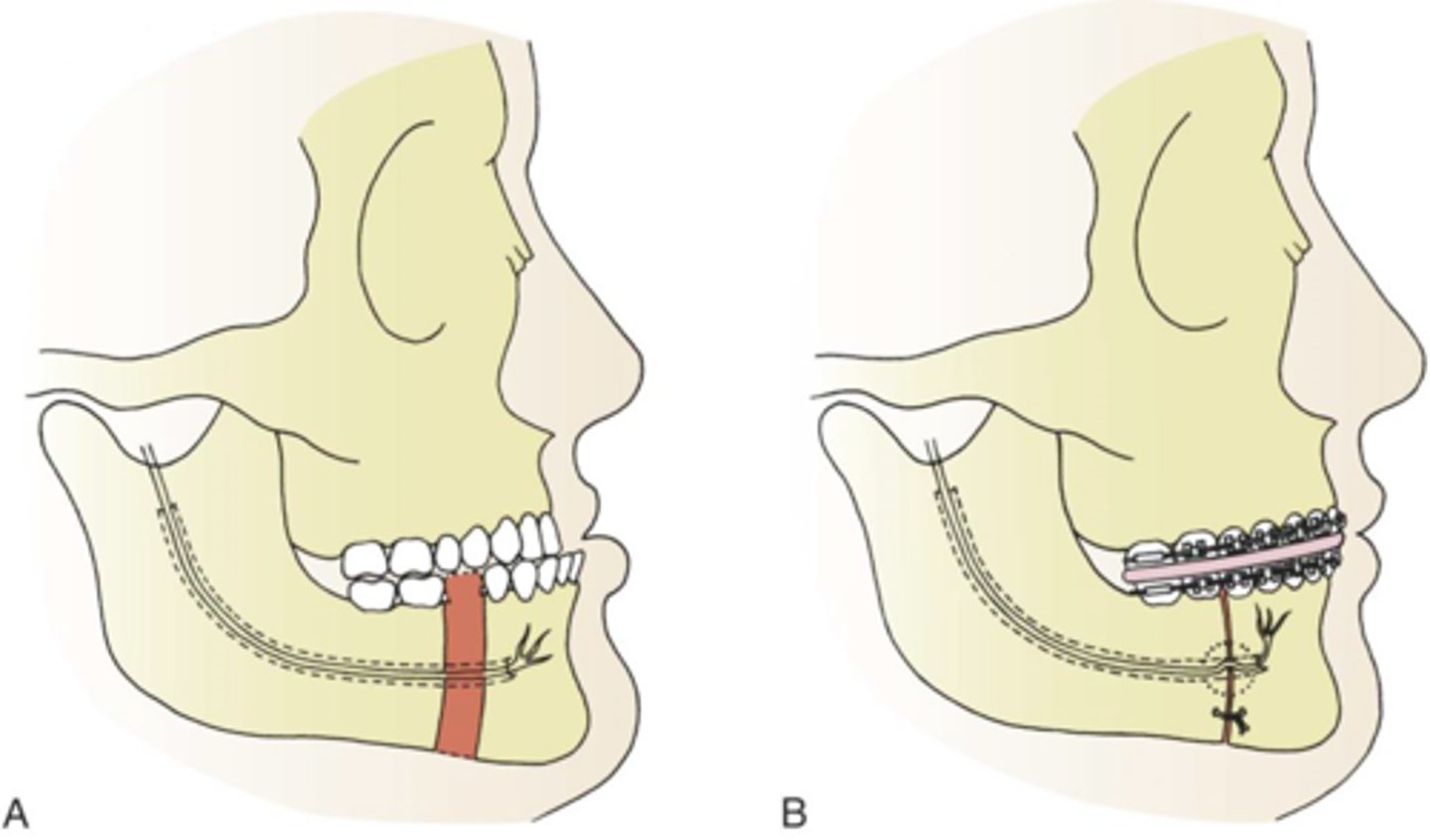
intraoral; IAN
Dingman body ostectomys are most often performed using an ... approach with the aim to preserve the ....
intraoral; extraoral
a 2 stage dingman body ostectomy involves both ... and .... components
subapical osteotomy
- cut and reposition the bone segment containing the anterior teeth (the anterior alveolar segment) of the upper or lower jaw.
- used to correct dental and jaw alignment issues, such as protruding or receding teeth,
- can be performed as an isolated surgery or as part of a larger orthognathic (jaw) surgery.
- involves cutting the bone both horizontally and vertically, repositioning the tooth-bearing segment, and securing it with plates and screws.
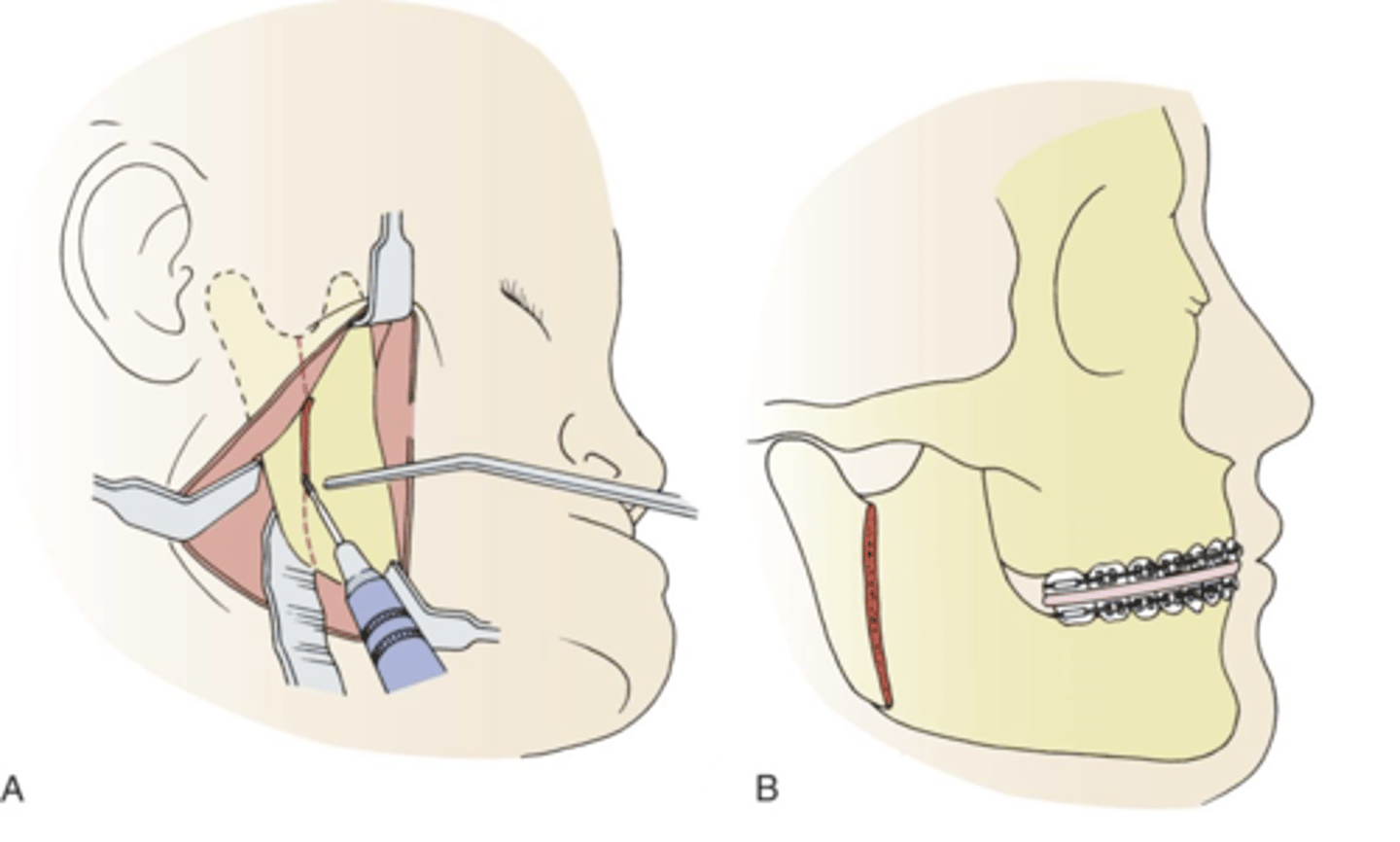
vertical ramus osteotomy
- cuts the mandibular (lower jaw) ramus vertically to allow for repositioning of the jaw for orthognathic surgery, which corrects facial deformities.
- used to treat conditions like mandibular prognathism and hemifacial microsomia, and is sometimes called intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy (IVRO) if performed inside the mouth
sagittal split ramus osteotomy
- used in orthognathic surgery to correct jaw deformities by splitting the lower jawbone (mandible) in a sagittal plane and repositioning the tooth-bearing segment.
- This is typically done to move the lower jaw forward or backward,
- often a part of a bilateral procedure (BSSO) used to treat conditions like mandibular prognathism.
- Post-surgery recovery often involves swelling, numbness, and a soft diet for several weeks
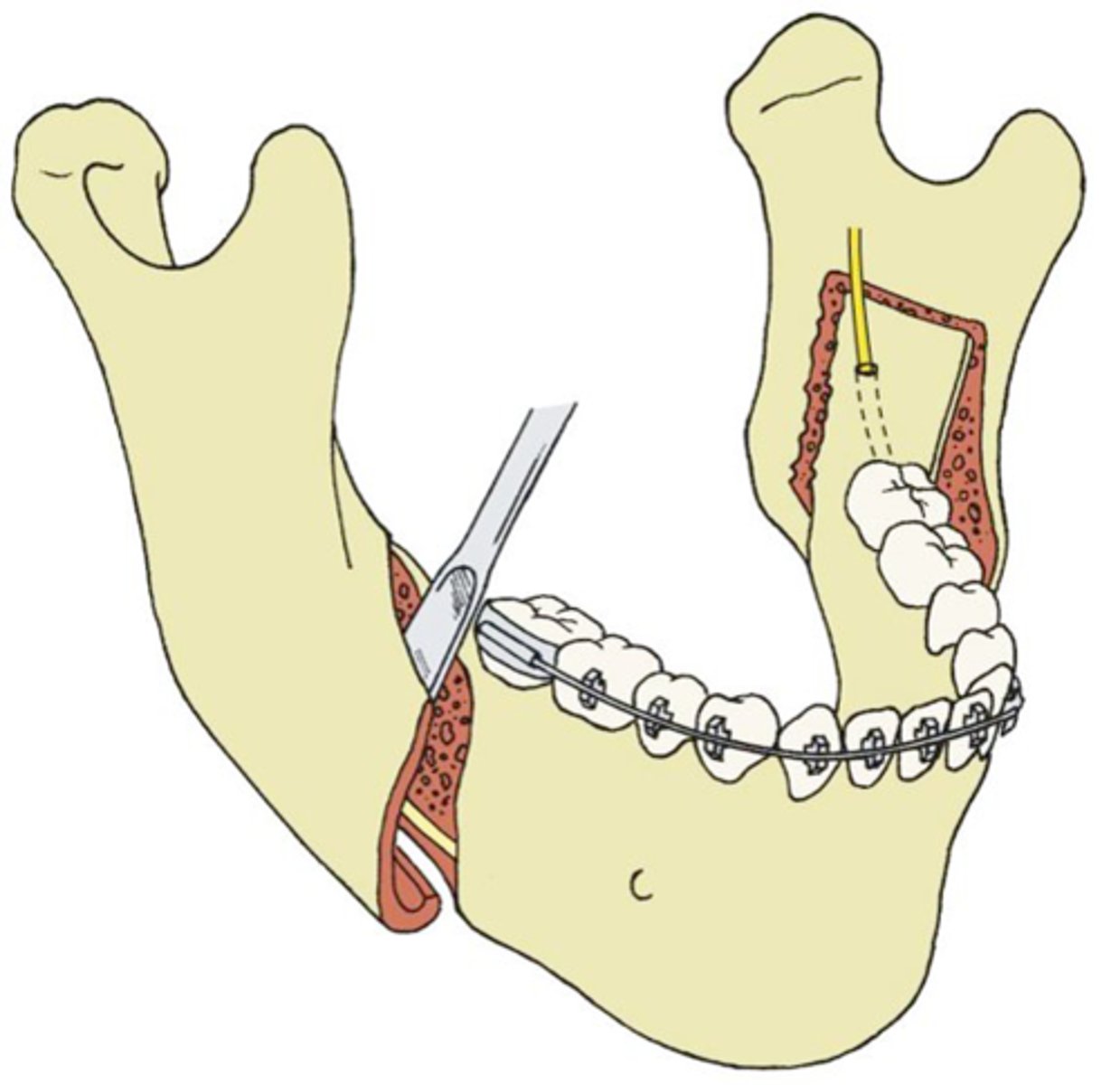
backward; forward
a sagittal split ramus osteotomy can be used to move the lower jaw either ... or ...
apertognathia
anterior open bites are also known as ... and occur when the upper and lower front teeth dont touch when the mouth in closed
uni; left
3/4 of clefts are ....lateral deformities more often on the ... side
males
are oral clefts more common in males or females
females
are isolated cleft palates more common in males or females
5-7
cleft lips occur between weeks ... IU
6-10
cleft palate occurs between weeks .... IU
pimary
... palate is failure of mesoderm to penetrate between the medial nasal and maxillary processes
secondary
..... palate is a failure of fusion of the palatine shelves
paternal
the incidence of clefts increases with ... age
1
what veau classification of cleft lip:
- vermillion
2
what veau classification of cleft lip:
- vermillion into lip
3
what veau classification of cleft lip:
- vermillion, total lip and into nose
4
what veau classification of cleft lip:
- any bilateral combination
1
What Veau classification of cleft palate:
- soft palate
2
What Veau classification of cleft palate:
- soft and hard palate
3
What Veau classification of cleft palate:
- unilateral soft and hard palate
4
What Veau classification of cleft palate:
- bilateral
3
clefts are often associated with class ... occlusion
soft palate
middle ear infection may occur with cleft of ....
laterals
a cleft that involves the alveolus will often have missing ...
10
cleft repair is guided by the rule of ...s referring to:
- weeks
- lbs
- g/dL of hemoglobin
8-18
a soft palate cleft is repaired at ... months
5
a hard palate cleft is repaired by .... years
2/3; canine root
an alveolar cleft is repaired at ... development of ...
cheilorrhapy
suture to repair cleft lip
palatorrapphy
suture to repair cleft palate
millard
.... closure is the most common type of cleft lip closure
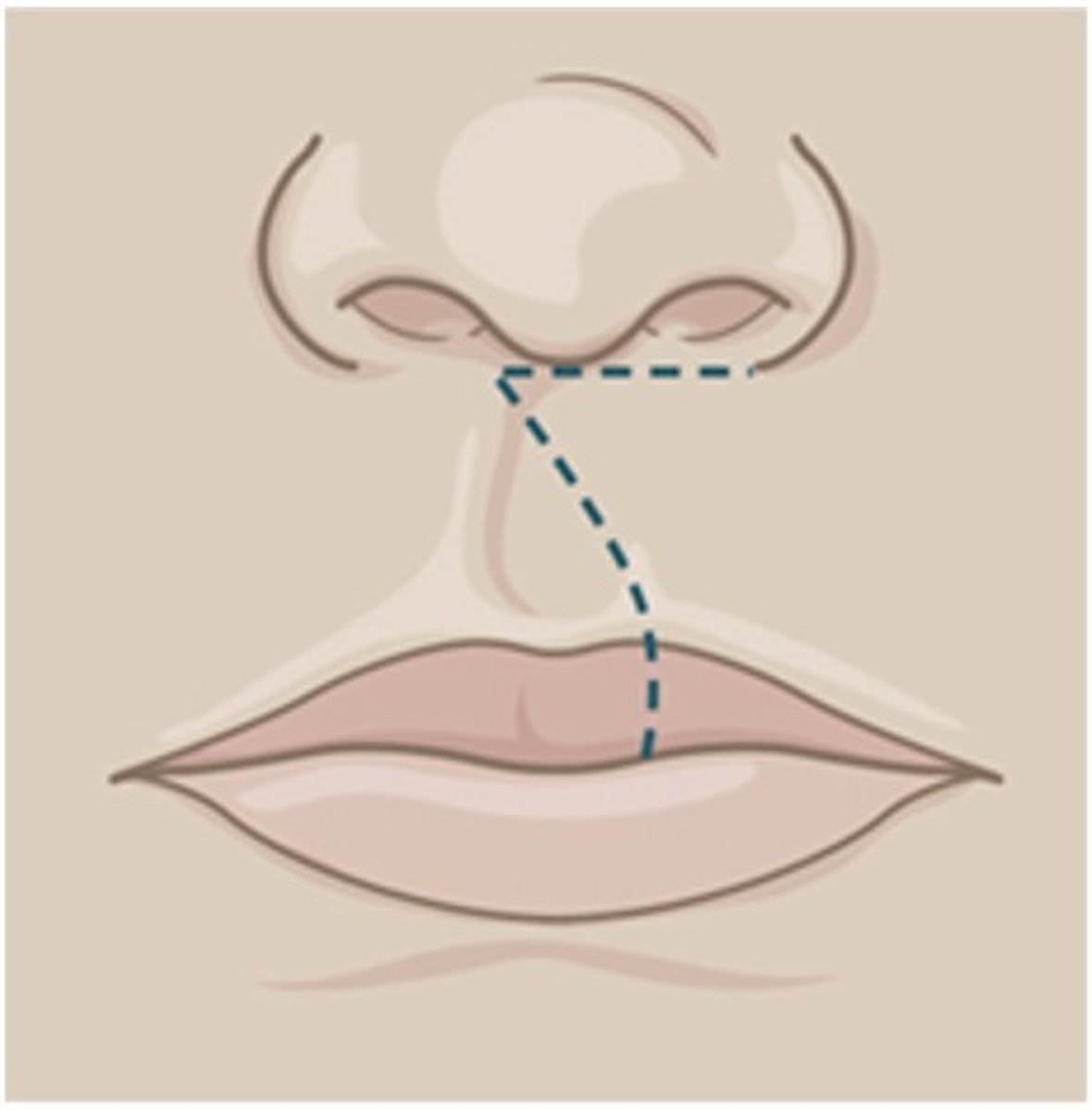
speech
the primary purpose of palatorrapphy is functional ...
von langenbeck
which palatorrapphy method:
- closure of the hard palate using lateral releasing incisions
- one-layer closure.
- Nasal (i.e., superior) aspect of palatal flaps will epithelialize, as will denuded areas of the palatal bone.
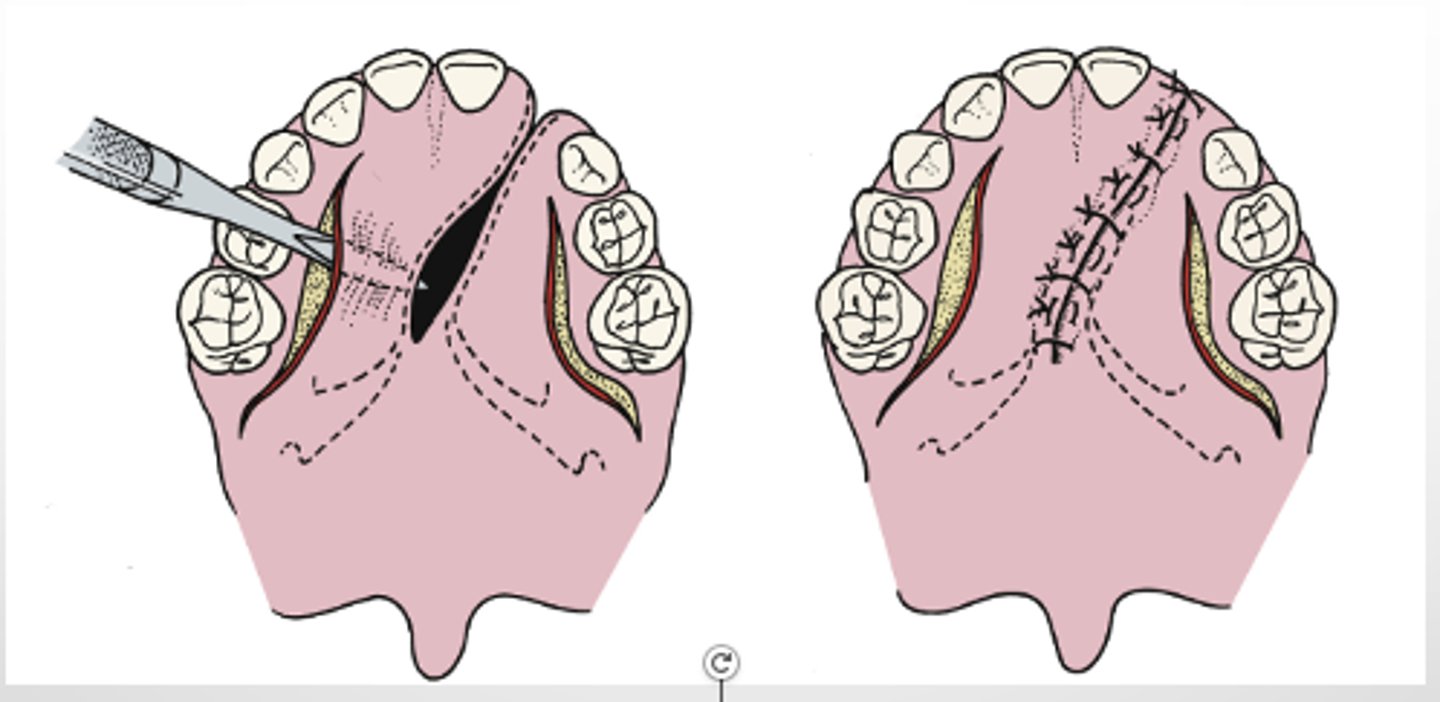
von langenbeck variation
which palatorrapphy method:
- operation for concomitant hard and soft palate closure.
- three-layer closure for the soft palate
- two-layer closure for the hard palate
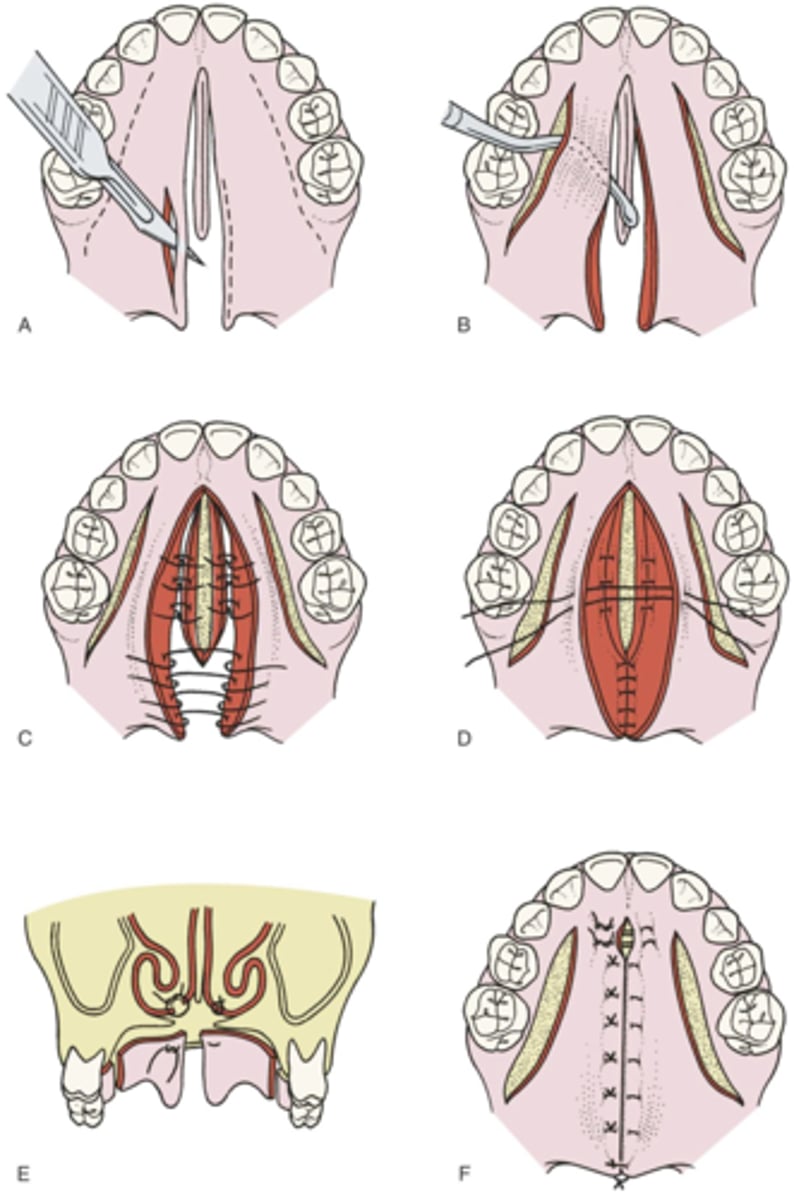
3
the soft palate is always closed in ... layers