AP Biology - Chapter 8: The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
asexual reproduction
process by which a single parent reproduces by itself
sexual reproduction
process by which a sperm and egg join to reproduce
budding
a type of asexual reproduction where a group of cells form a bud and break away from the original organism to form a clone
List the 3 parts of the cell theory
All living things are composed of at least one cell; The cell is the smallest unit of life; Cells arise only from the division of pre-existing cells
binary fission
a type of asexual reproduction done by prokaryotes where a cell first replicates its single chromosome, slowly separating as the cell membrane and wall expand, eventually splitting and dividing into two daughter cells
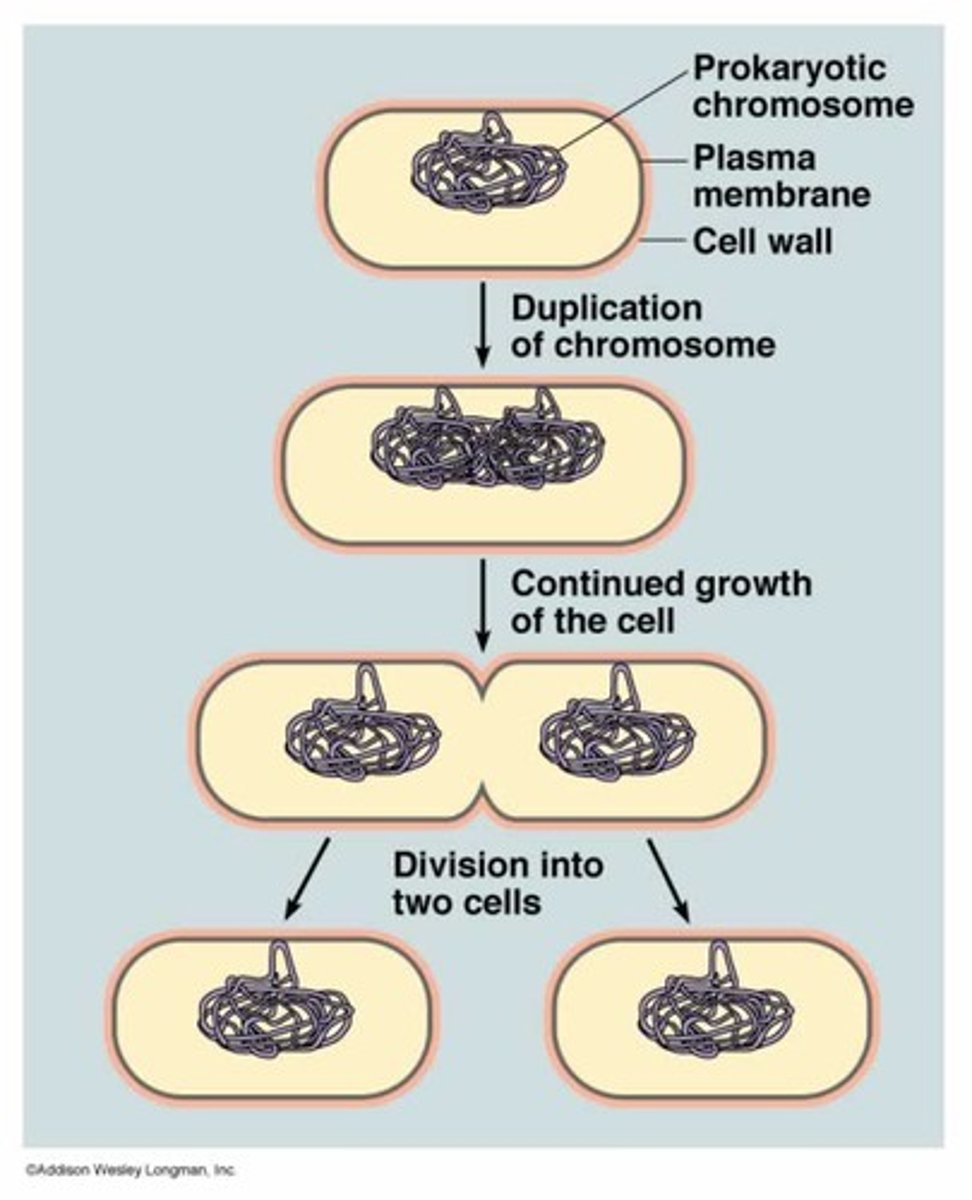
How many chromosomes do prokaryotes have, and what shape?
one circular chromosome
T/F: Genes are bigger than chromosomes
false; each chromosome has many genes
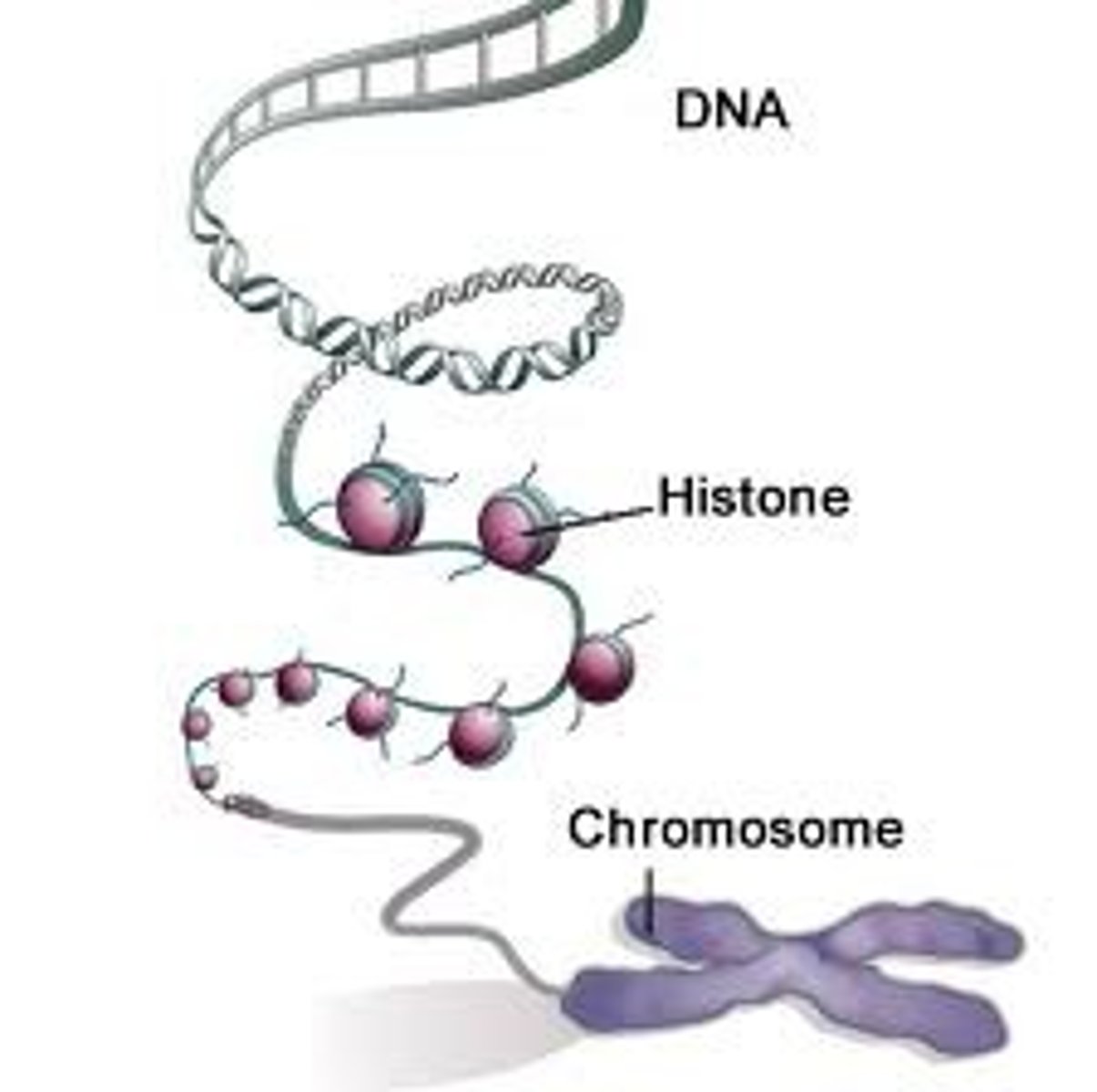
Which protein is attached with a DNA chain in chromosomes?
histone proteins
When is the only time chromosomes are visible?
during cell division, otherwise, they stay as chromatin
chromatin
loosely coiled DNA fibers (like spaghetti)
interphase
first stage of the cell cycle; DNA and organelles are duplicated; prepare for division
G1 (gap 1)
cell growth, protein production
S (synthesis)
all DNA is copied
G2 (gap 2)
organelles are replicated
What does DNA exist as during interphase?
chromatin
What are the 4 phases of mitosis?
prophase (and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, telophase/cytokinesis (PMAT)
What is the longest phase of mitosis?
prophase
prophase (mitosis)
chromatin condenses into chromatids, sister chromatids join at the centromere, nucleolus disappears, centrosomes (centrioles) start to produce spindle fibers and move towards poles
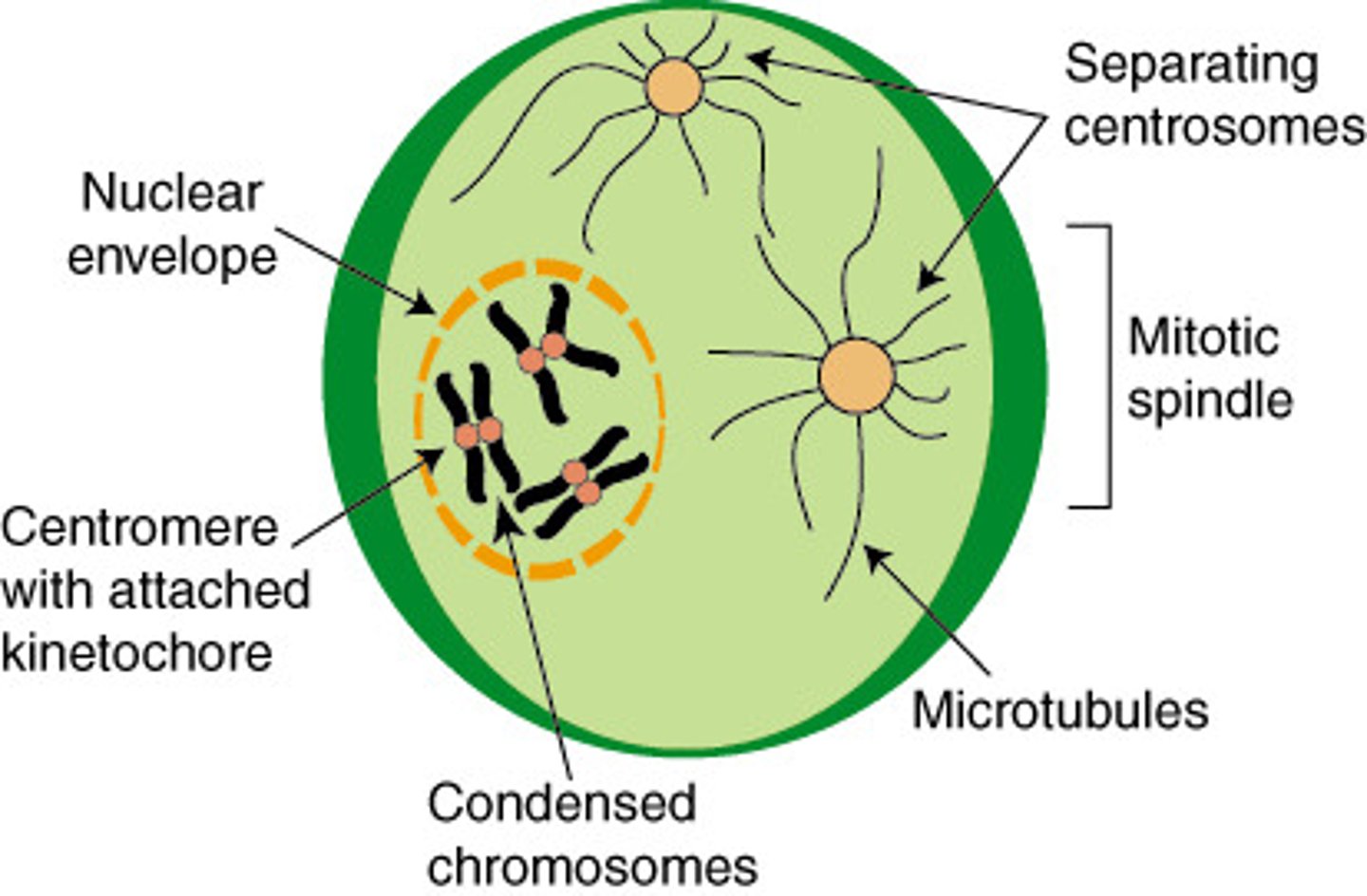
centrosomes
pair of centrioles; where spindles come from
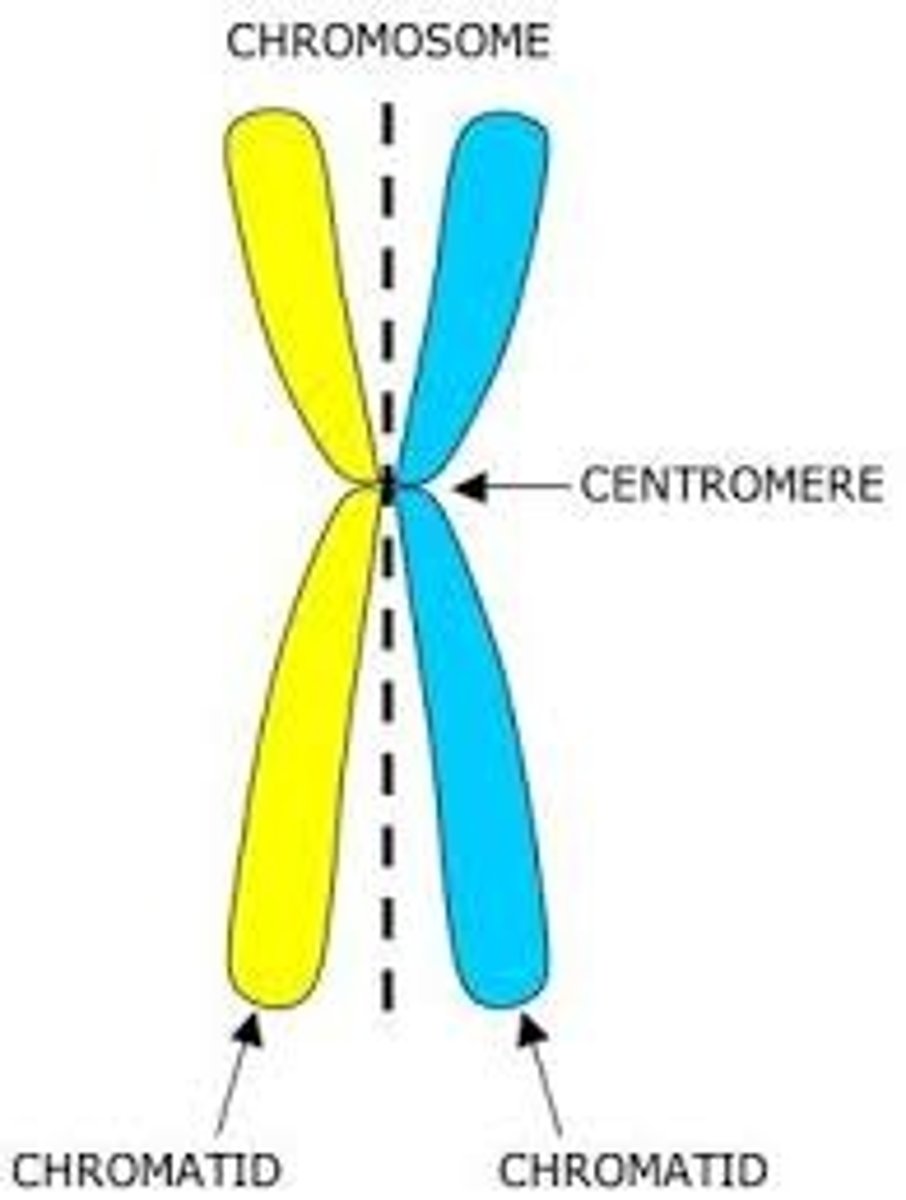
centromere
attachment site of sister chromatids
prometaphase (late prophase) (mitosis)
nuclear membrane breaks down, spindles attach at kinetochores, spindles move chromatid pairs to metaphase plate
kinetochore
where spindle fibers attach to the centromer
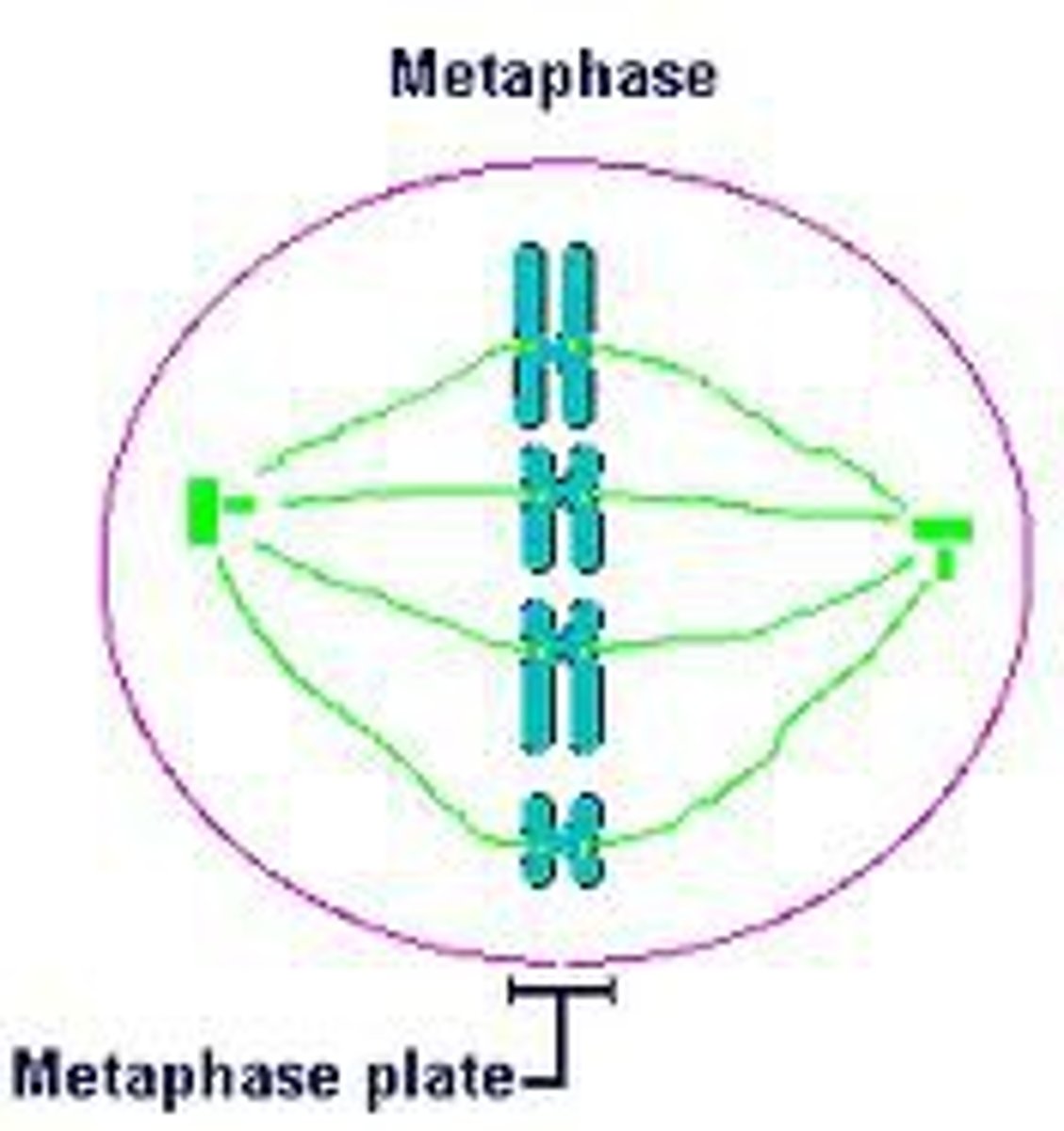
metaphase plate
an imaginary line in the middle of the cell where spindle fibers pull chromatid pairs to
metaphase (mitosis)
chromosome pairs and centromeres line up at metaphase plate
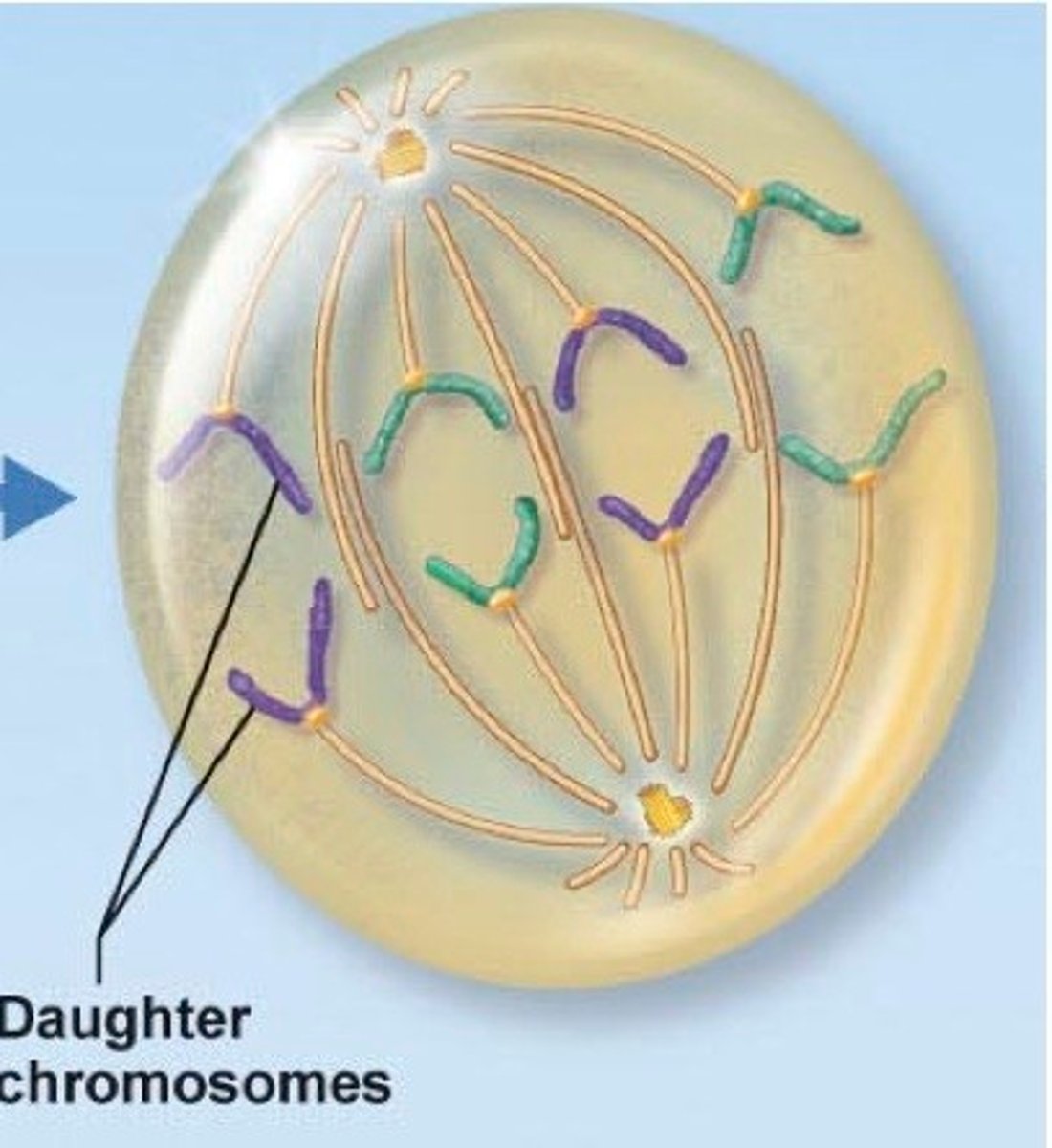
anaphase (mitosis)
centromeres split, spindles that are attached to chromosomes recoil and split sister chromatids apart, other spindles get longer and pull the poles apart (cell is stretched)
telophase (mitosis)
chromosomes unwind into chromatin , nuclear envelope and nucleolus form, spindles disappear, microfilaments pinch at center
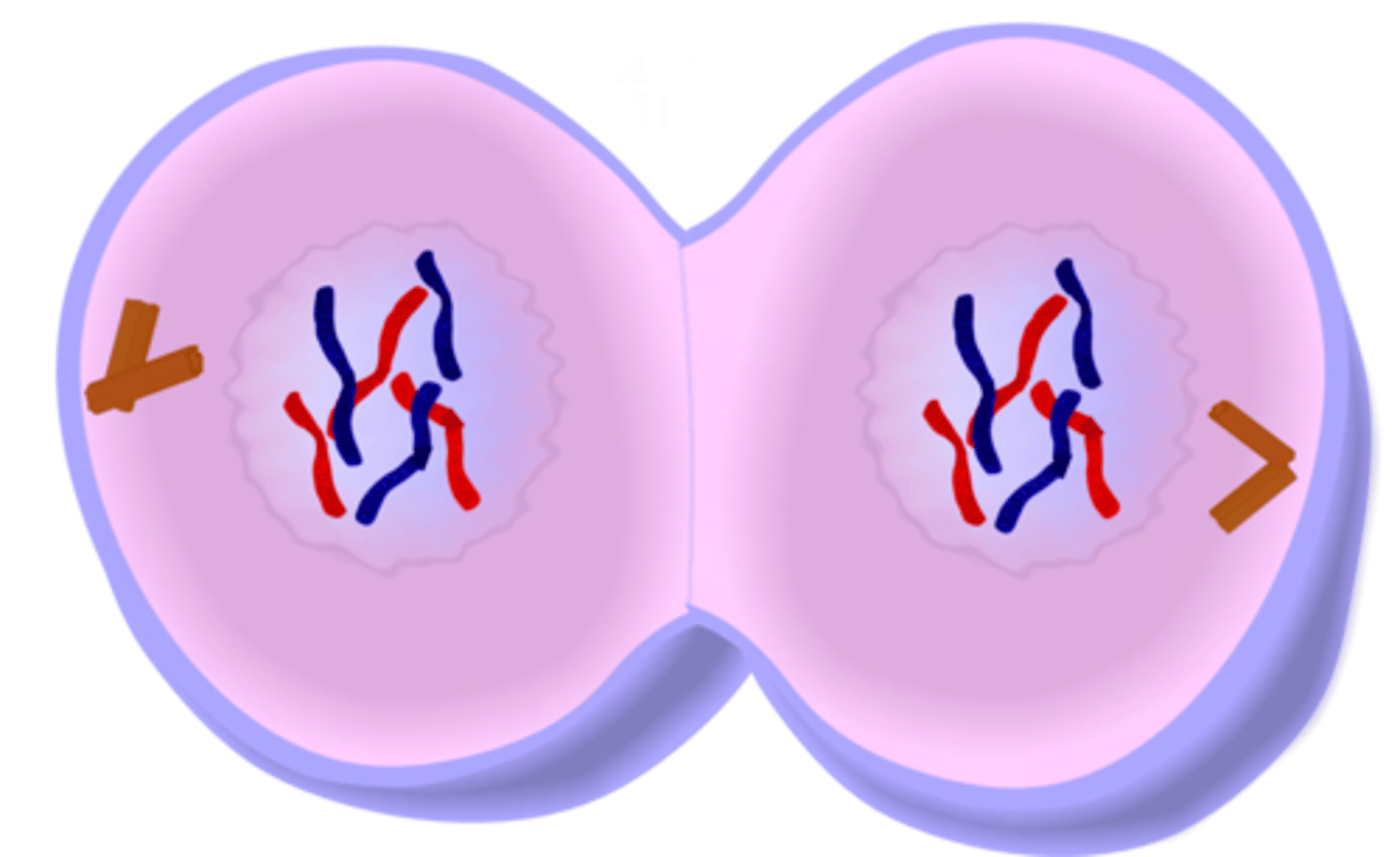
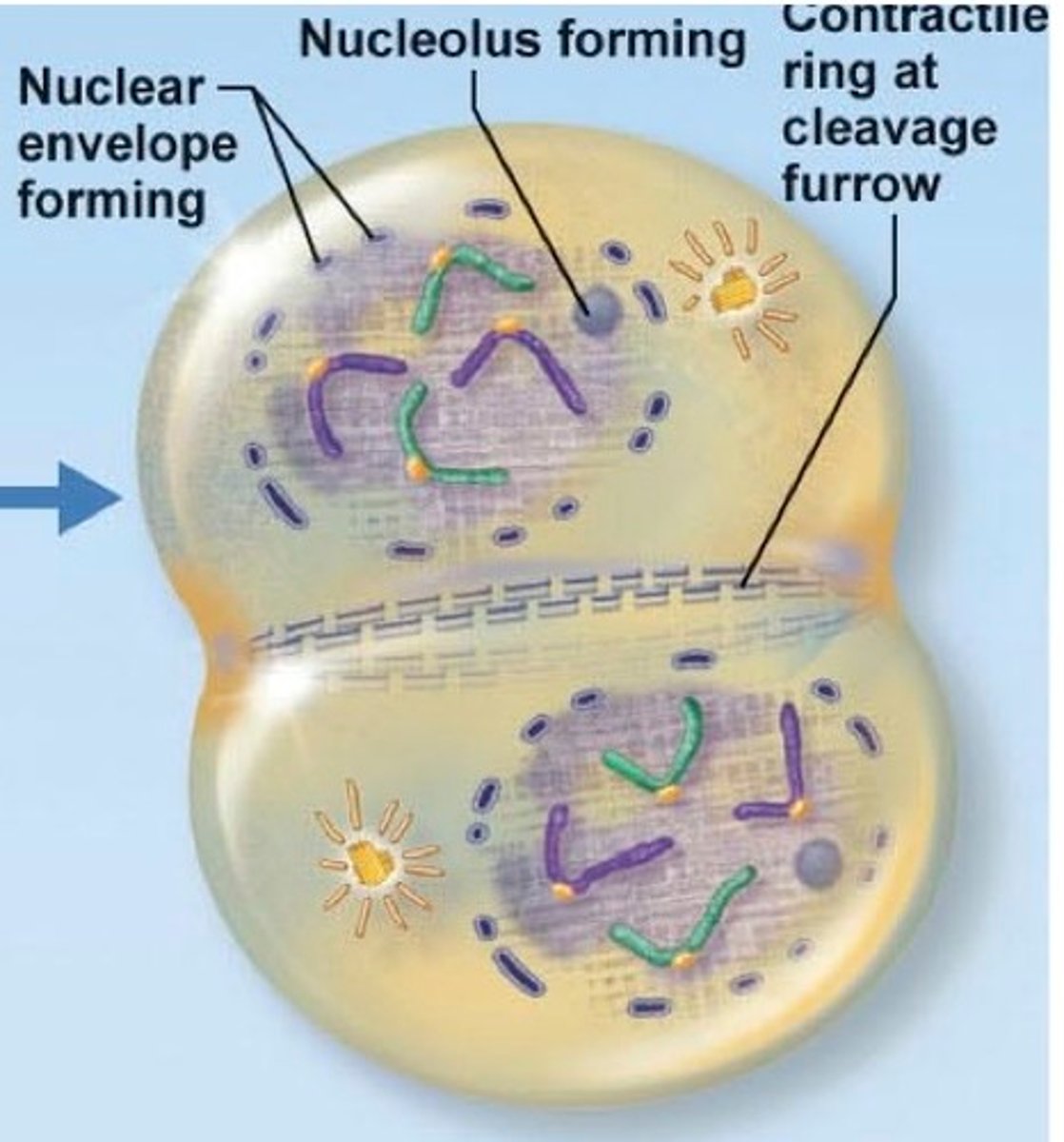
cytokinesis (mitosis)
cytoplasm division; cytoplasm completely divides along cleavage furrow (in plants, cell wall divides along cell plate made of vesicles), contractile ring of microfilaments pinches cytoplasm in half, forming 2 new cells
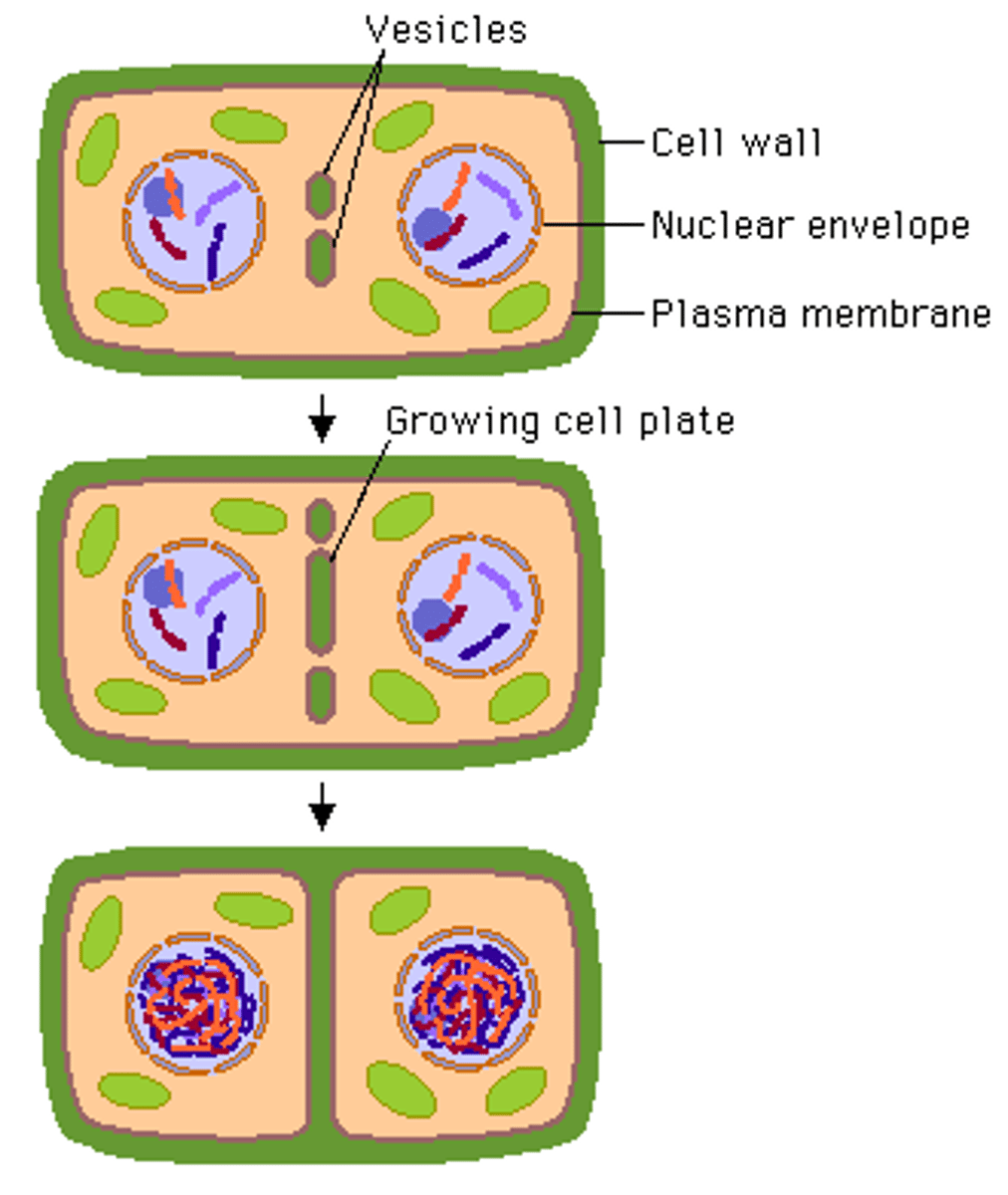
cytokinesis in plants
vesicles containing cell wall fibers line up on the cell plate, thickening and eventually forming a new cell wall
What type of reproduction do bacteria do?
binary fission
Name 3 categories of cells that do not divide
red blood cells, nerve cells, muscle cells
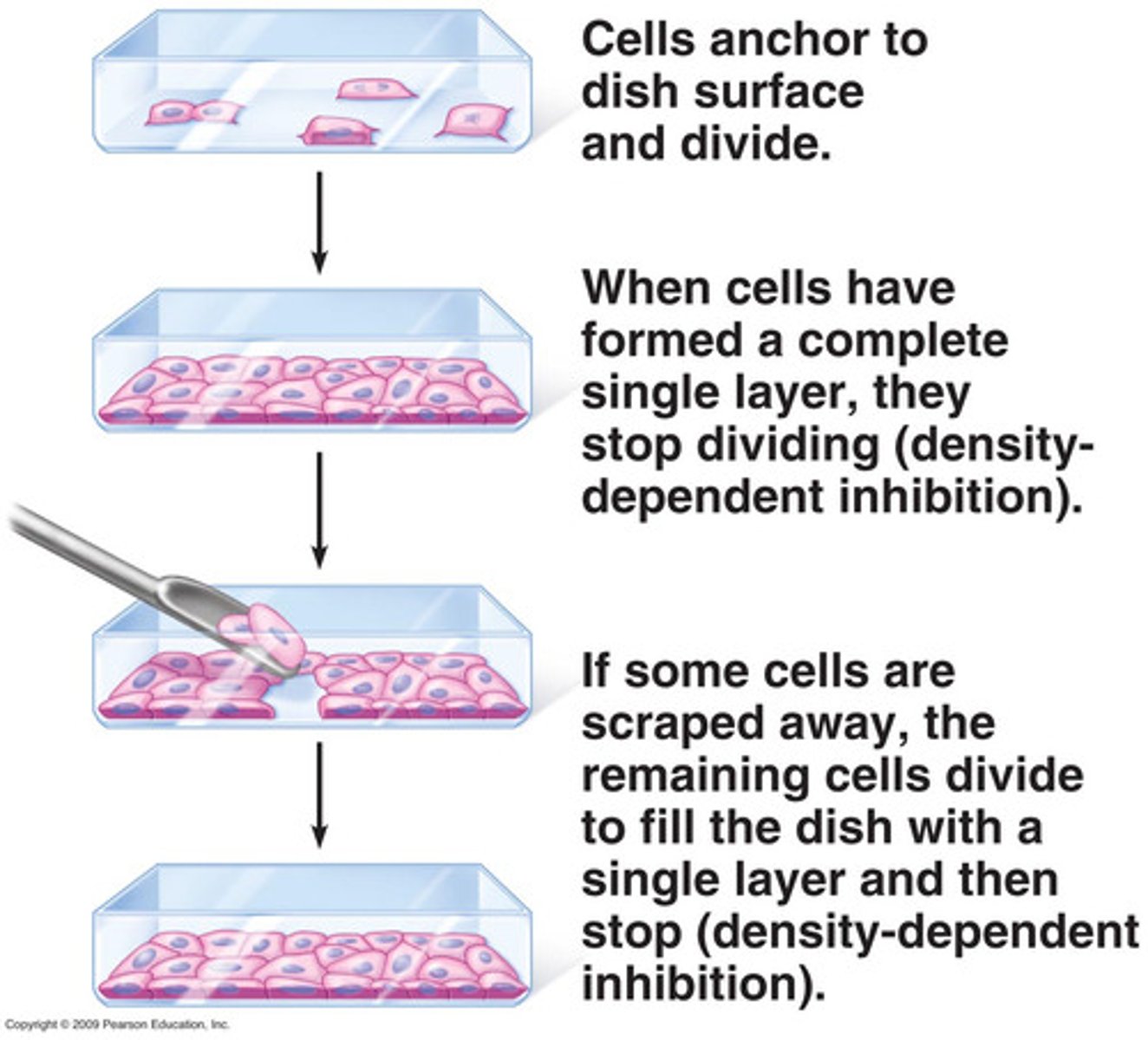
anchorage
an external physical factor that causes cells to divide only when attached to a surface
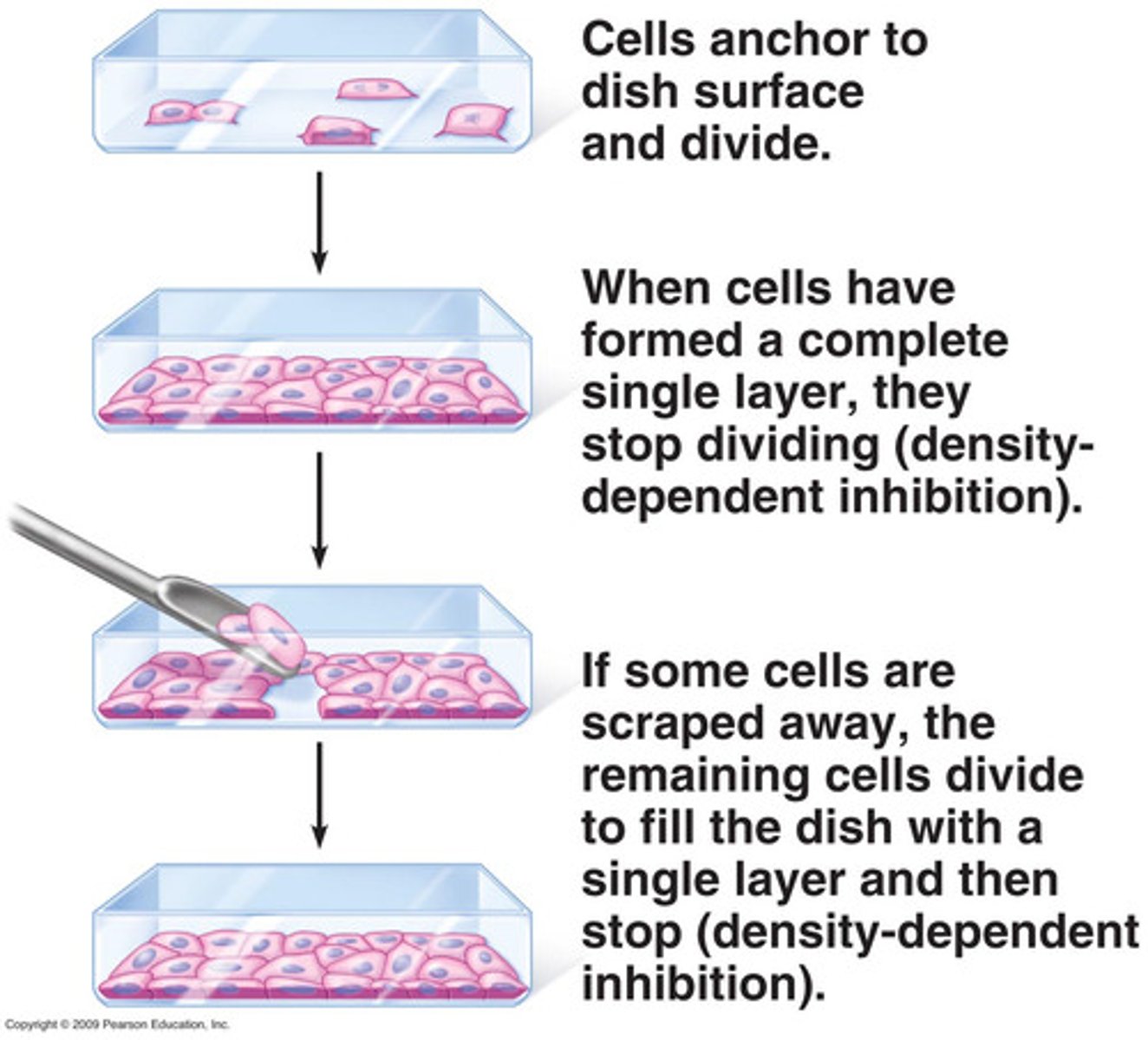
density-dependent inhibition
an external physical factor that causes cells to stop dividing once they are touching each other
growth factor
an external chemical hormone (so it's a protein) secreted by cells to stimulate other cells to divide
What structure of a cell receives growth factors? Where on the cell is this structure?
receptor protein, found on cell membrane
PDGF
platelet-derived growth factor, gives the 'green light' after G1 for progression into cell cycle
Where are check points found in the cell cycle?
After G1, G2, and metaphase
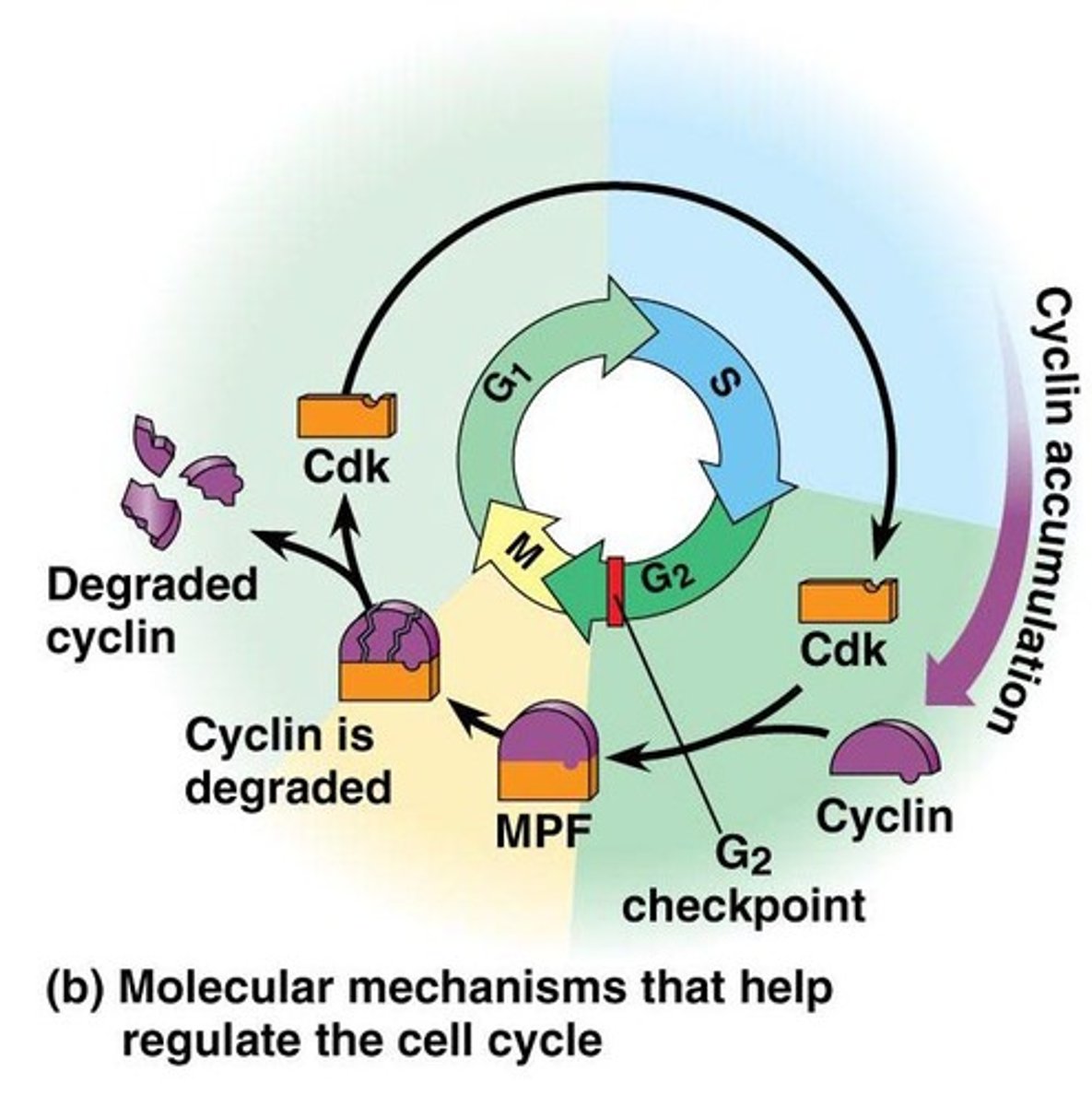
G2 checkpoint
makes sure the S phase properly replicated all DNA and the G2 phase properly duplicated all organelles
M checkpoint (METAPHASE, NOT MITOSIS)
triggers sister chromatid separation/starts anaphase
cyclin-dependent kinase (cdks)
enzymes that activate or deactivate other proteins by phosphorylating them; are only activated when bound to a cyclin; entirely dependent on cyclin concentration!
cyclins
proteins that bind to Cdks; concentrations peak during mitosis and fluctuate throughout the cell cycle
MPF
Maturation (M-phase) Promoting Factor; an ACTIVE type of Cdk; created from cyclins binding to Cdks; triggers mitosis; turned off during anaphase (after degradation of cyclin)
cancer cells
divide excessively, produce tumors and their own growth factor; divide and live longer than normal cells
Why do cancer cells keep dividing uncontrollably?
the growth factor they produce signals continuous cell division, no DDI or anchoring can stop them
benign tumor
a type of tumor that is pretty much harmless and stay put
malignant tumor
a type of tumor that spreads (metastasizes) to other organs, BAD
carcinomas
malignant tumors in the skin, intestines, and colon
sarcomas
malignant tumors in muscles and bone
leukemia/lymphoma
malignant CANCER in blood tissue; cancerous malignant tumors exist in liquid form
chemotherapy
treatment of cancer with drugs
Which cells are most impacted by chemotherapy?
fast dividing cells, including cancerous cells, hair follicles, intestinal lining, and immune cells
anti-cancer drugs
all botanical (plant) extracts that prevent cell division
taxol
an anti-cancer drug that freezes mitotic spindle in metaphase (no cell division)
vinblastin and colchicine (same thing)
an anti-cancer drug that prevents any spindle formation (no cell division)
somatic cells
normal body cells; needed for growth, repair, and replacement
gametes
sex cells (sperm and egg); needed for sexual reproduction only
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes with same size, shape, gene location, and centromere location
locus
specific location of a gene on a chromosome
haploid
a cell with one complete set of chromosomes (23 total in humans); sex cells
diploid
a cell with two complete sets of chromosomes (46 total in humans); body cells
autosomes
non gender-specific chromosomes (same for males and females)
Which cell determines the sex of the offspring?
sperm
What is the DIPLOID number of this cell?
>
< <
>
2n = 4
germ cell
a cell that undergoes meiosis to become a gamete
prophase I
chromatin condenses, sister chromatids join, homologous sister chromatids join into tetrads and cross over, spindles form from centrosomes and attach to kinetochore, moving tetrads to metaphase plate
Where do homologous chromosomes cross over in their tetrad?
chiasmata
synapsis
homologous chromosomes join into tetrads
metaphase I
tetrads line up at metaphase plate
anaphase I
chiasmata separate (centromeres don't), spindle recoils, pulling tetrad pairs apart, each pair of sister chromatids move to opposite sides of cell
T/F: The separated tetrads after anaphase 1 are homologous chromosomes
FALSE!!!!!!!!!! Because the crossed over during prophase 1, they are no longer identical pairs!!
telophase I & cytokinesis
cell pinches in the middle and cytoplasm divides, each cell (there are 2 at this stage) has 1 pair of non-identical sister chromatids from each OG tetrad
PMAT II
identical to PMAT in mitosis
After meiosis...
there are 4 haploid daughter cells NOT identical to each other
spermatogenesis
production of sperm
spermatogonia
male germ cells (diploid) that divide by MITOSIS, some undergo meiosis
What do spermatogonia become after mitosis?
spermatocytes (diploid & identical)
Why do most male germ cells divide by mitosis?
Allows for the production of identical diploid germ cells so there is always a supply
What results from spermatogenesis (after meiosis)?
spermatids
What process must spermatids undergo to become sperm?
maturation
Are spermatids haploid or diploid?
haploid
spermatozoa
fancy way of saying sperm
T/F: sperm have a nucleus, mitochondria, and flagella
true
oogenesis
production of ovum (egg)
T/F: Cytokinesis in oogenesis splits cells into equal sizes, all usable eggs
false, it splits cells into 1 large ovum, a usable egg, and 3 polar bodies, which are too small and unusable
oogonia
female germ cells (diploid) that divide by mitosis; some undergo meiosis
What do oogonia become after mitosis?
oocytes (diploid & identical)
How many usable eggs are formed from a female germ cell (diploid)?
1
primary oocyte/spermatocyte vs secondary oocyte/spermatocyte
primary oocyte/spermatocyte results from mitosis and goes into meiosis, secondary oocyte/spermatocyte is after meiosis I
alleles
different variations of a gene (black hair vs blonde hair)
T/F: All genes, no matter the variation, are found in the same spots on each chromosome (same locus)
true
karyotype
photograph of chromosomes grouped in order and paired; used to detect abnormal chromosomes
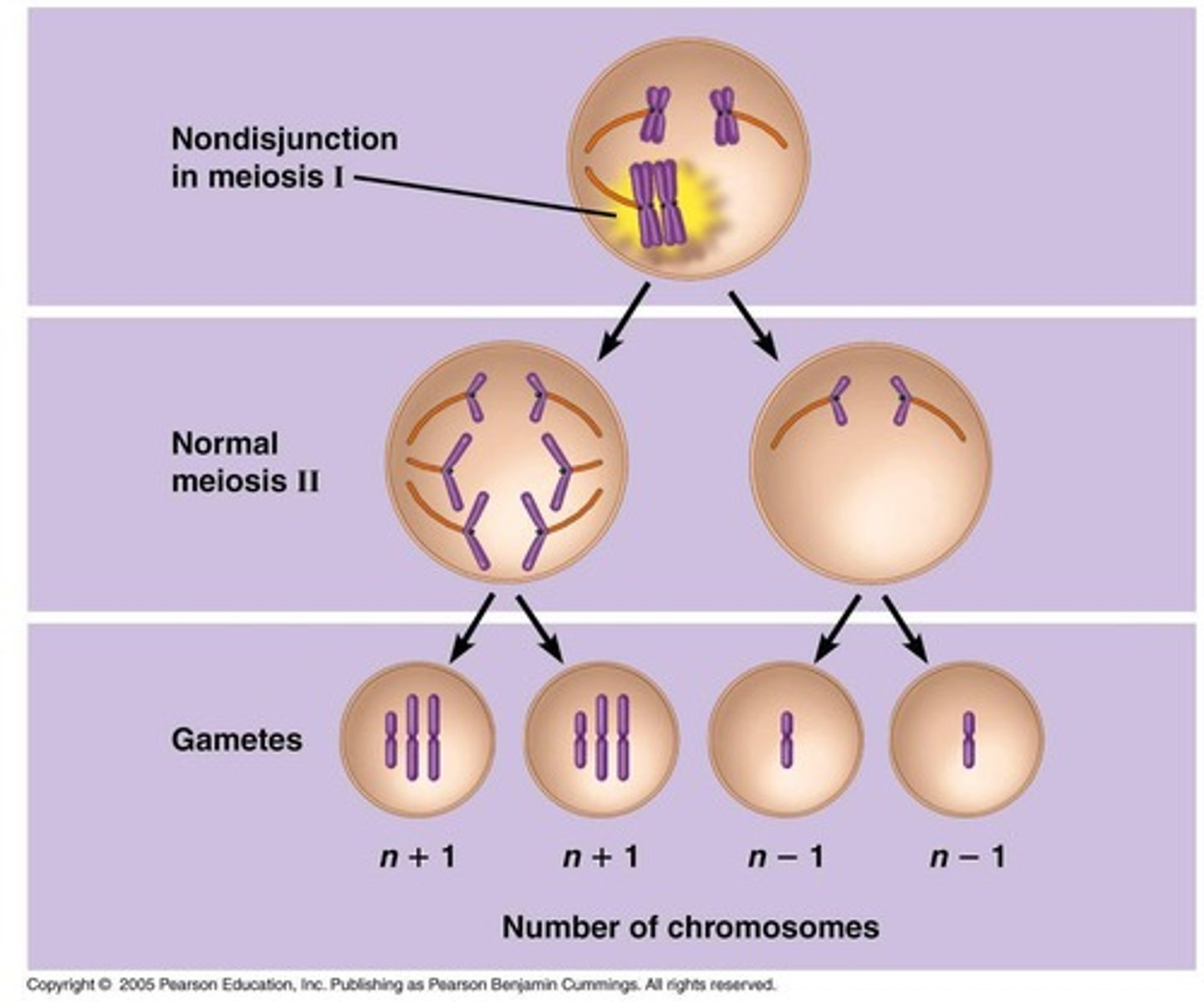
non-disjunction
failure of chromosomes to separate equally, can lead to trisomy
trisomy
an extra chromosome
trisomy 21
down syndrome, 3 chromosome 21s instead of 2
XYY
super male
XXX
super female
XXY
Klienfelter's syndrome
X0
Turner's syndrome (lack of Y or a second chromosome)
T/F: As long as there is a Y chromosome, it is a male
true
What does 47 XY + 21 mean?
the individual has a total of 47 chromosomes, is a male, and has an extra chromosome 21, hence he has down syndrome
nondisjunction in meiosis I
failure of homologous pairs to separate, so spindle drags an entire tetrad to a side of the cell