SA thorax and diaphragm
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:24 PM on 4/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
CASE
* 10 yr FS miniature poodle
* 4 week history of intermittent goose honking cough
* worse when active
* auscultation- slight wheeze, no crackles
* grade 2/6 systolic heart murmur
* 10 yr FS miniature poodle
* 4 week history of intermittent goose honking cough
* worse when active
* auscultation- slight wheeze, no crackles
* grade 2/6 systolic heart murmur
tracheal collapse
* c shaped tracheal cartilage weakens/ collapses progressively over
* c shaped tracheal cartilage weakens/ collapses progressively over
2
New cards
where to listen for the heart
left side:
* aortic valve- between 4th or 5th intercostal
* mitral valve- between 5th or 6th intercostal
right side:
* tricuspid in the 4th intercostal
* aortic valve- between 4th or 5th intercostal
* mitral valve- between 5th or 6th intercostal
right side:
* tricuspid in the 4th intercostal
3
New cards
how do you diagnosis a tracheal collapse
* diagnose by xrays
* but better by scoping
* but better by scoping
4
New cards
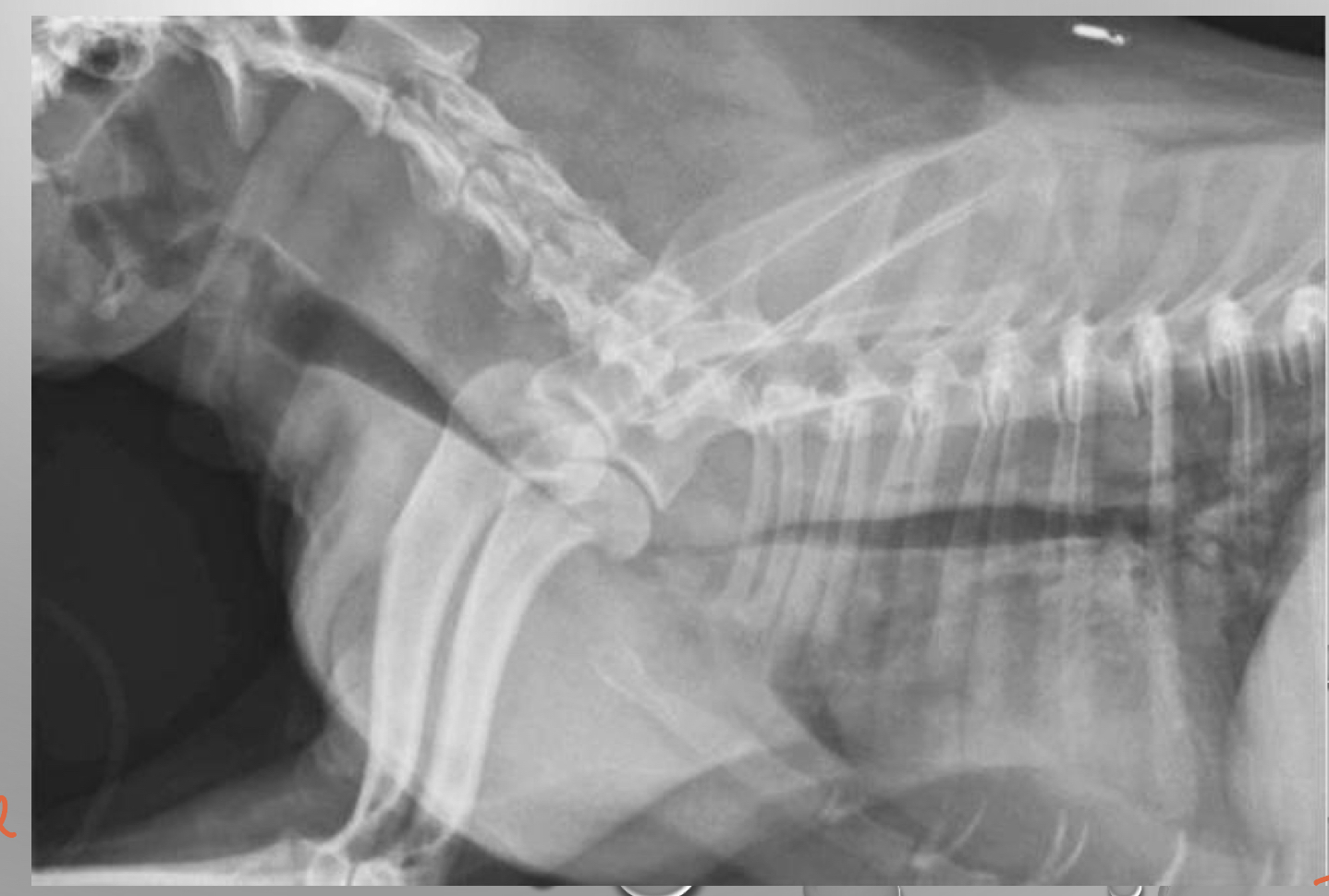
how to fix a tracheal collapse
* put a metal and stent it to widen and pushes airway out
* only have only shot of doing it
* only do it as a last resort
* cant breathe anymore and turn blue
* only have only shot of doing it
* only do it as a last resort
* cant breathe anymore and turn blue
5
New cards
what is significant about the great coronary vein
seperates the atrium with ventricle
6
New cards
whats significant about the paraconal interventricular groove
it is a landmark of the right and left ventricle
7
New cards
which ventricle is more muscular
left
8
New cards
which valve has common murmurs
* mitral valves
9
New cards
what do the papillary muscles prevent
inversion or prolapse of the valves
10
New cards
CASE
* 6 months Male australian shepherd
* continuous machinery heart murmur
* otherwise happy, normal puppy
* 6 months Male australian shepherd
* continuous machinery heart murmur
* otherwise happy, normal puppy
patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
\
\
11
New cards
describe PDA
* failure of the ductus arteriosus to close just after birth
* should immediately close right after birth
* classic machinery murmur
* cough, labored breathing, runt of the litter
* very common
* during a puppy exam the first thing you want to listen is this
* earlier diagnosis the better
* pulmonary arteries are getting overflowed
* should immediately close right after birth
* classic machinery murmur
* cough, labored breathing, runt of the litter
* very common
* during a puppy exam the first thing you want to listen is this
* earlier diagnosis the better
* pulmonary arteries are getting overflowed
12
New cards
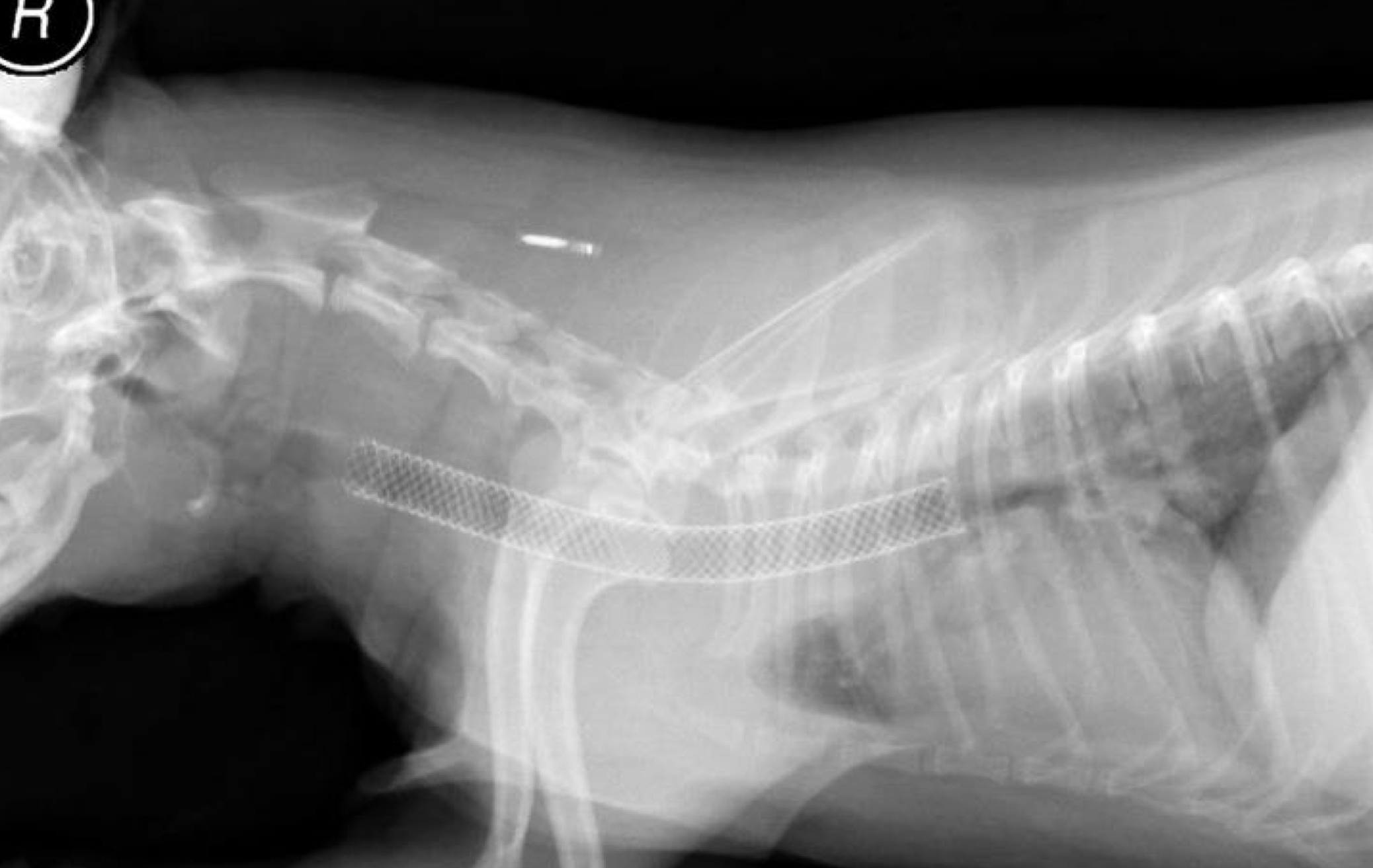
how to fix a PDA
* we can ligate it or put a ductal occuluder safer
13
New cards
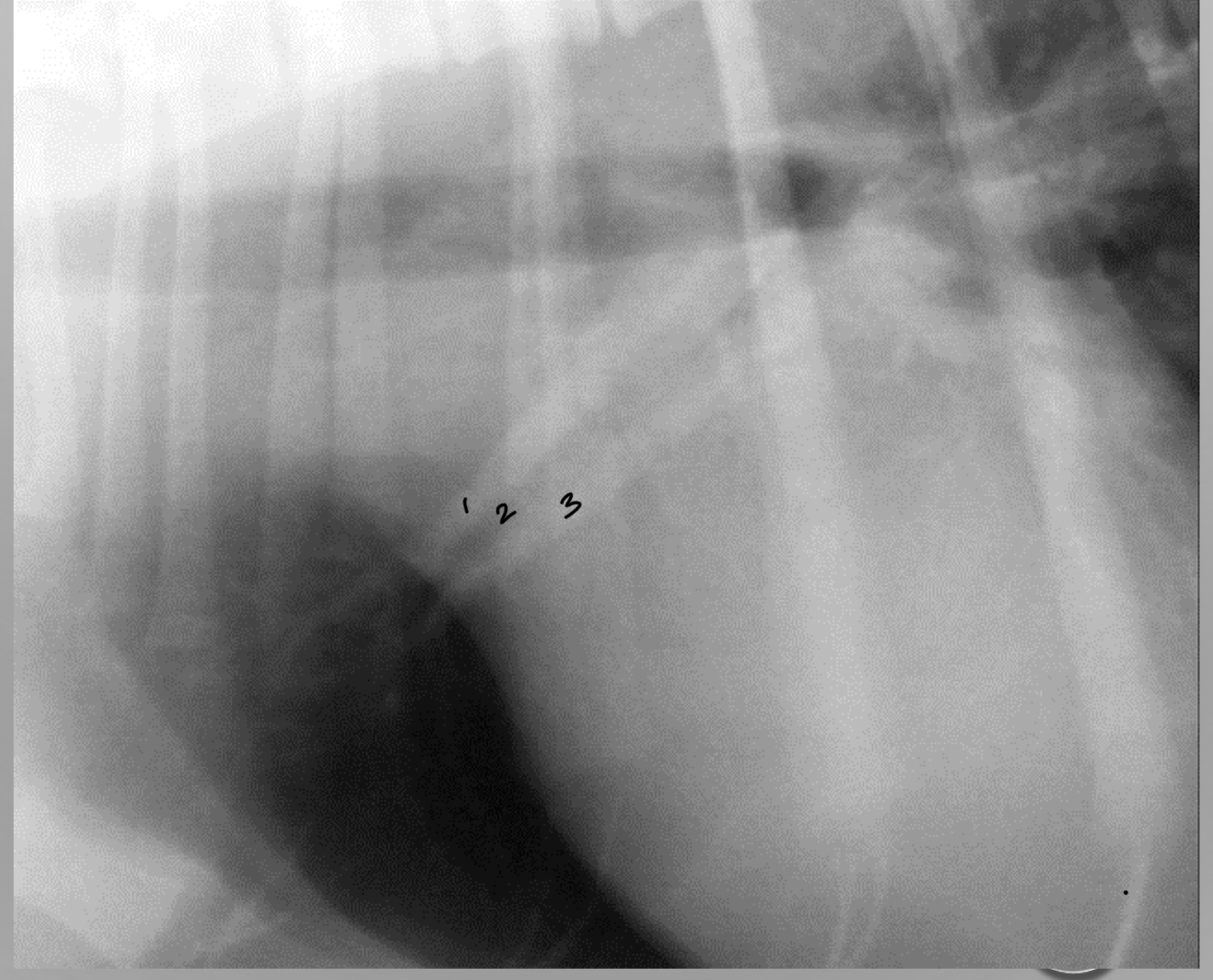
identify the artery vein and bronchus
1. artery
2. bronchus
3. vein
14
New cards
what does the size of the artery tell us in an xray
tells us if its in heart failure
* artery should not be bigger than a rib
* artery should not be bigger than a rib
15
New cards
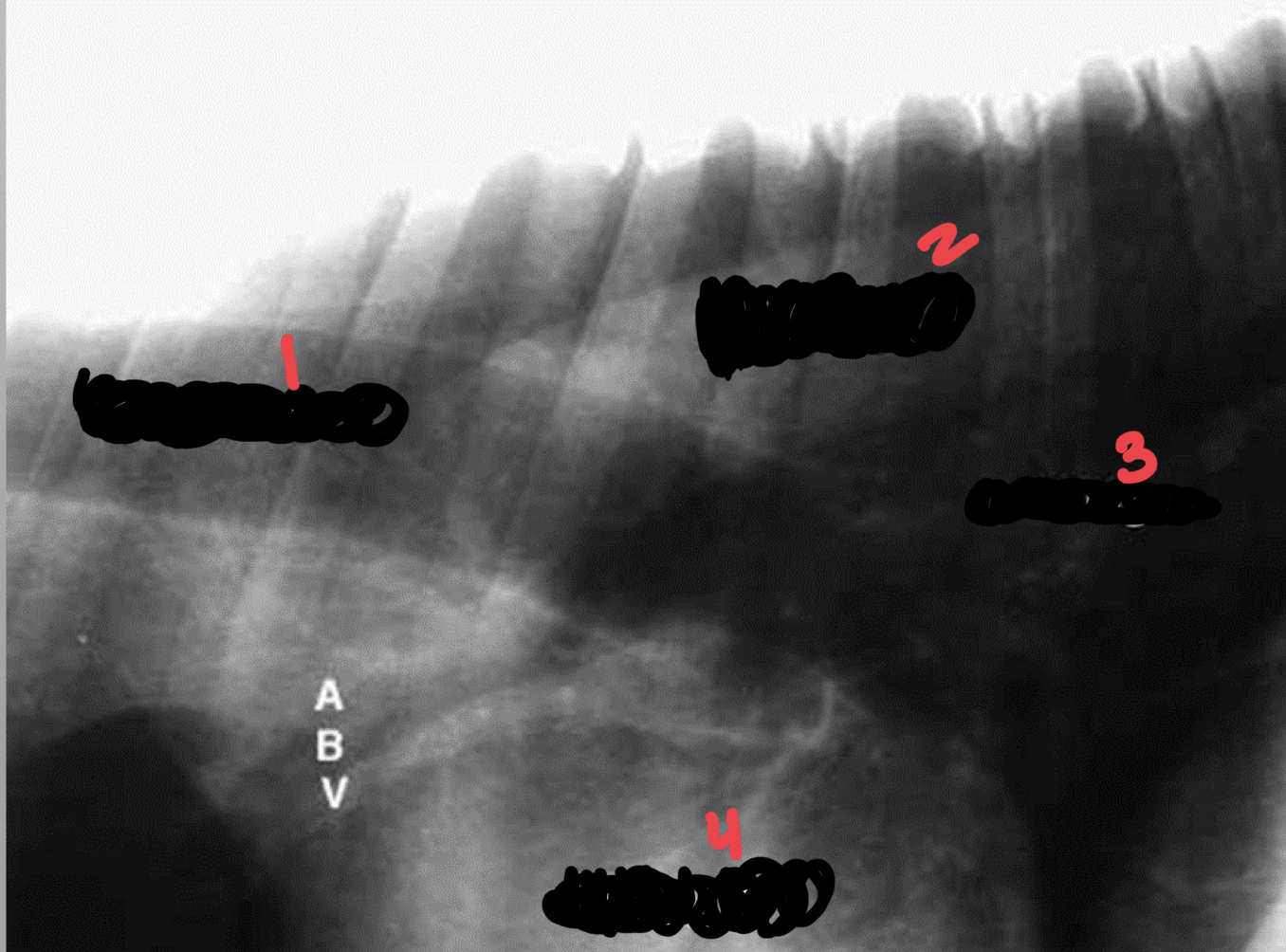
identify lung aorta trachea heart
1. trachea
2. aorta
3. lung
4. heart
16
New cards
what does each lung have
and artery
bronchus
and vein
bronchus
and vein
17
New cards
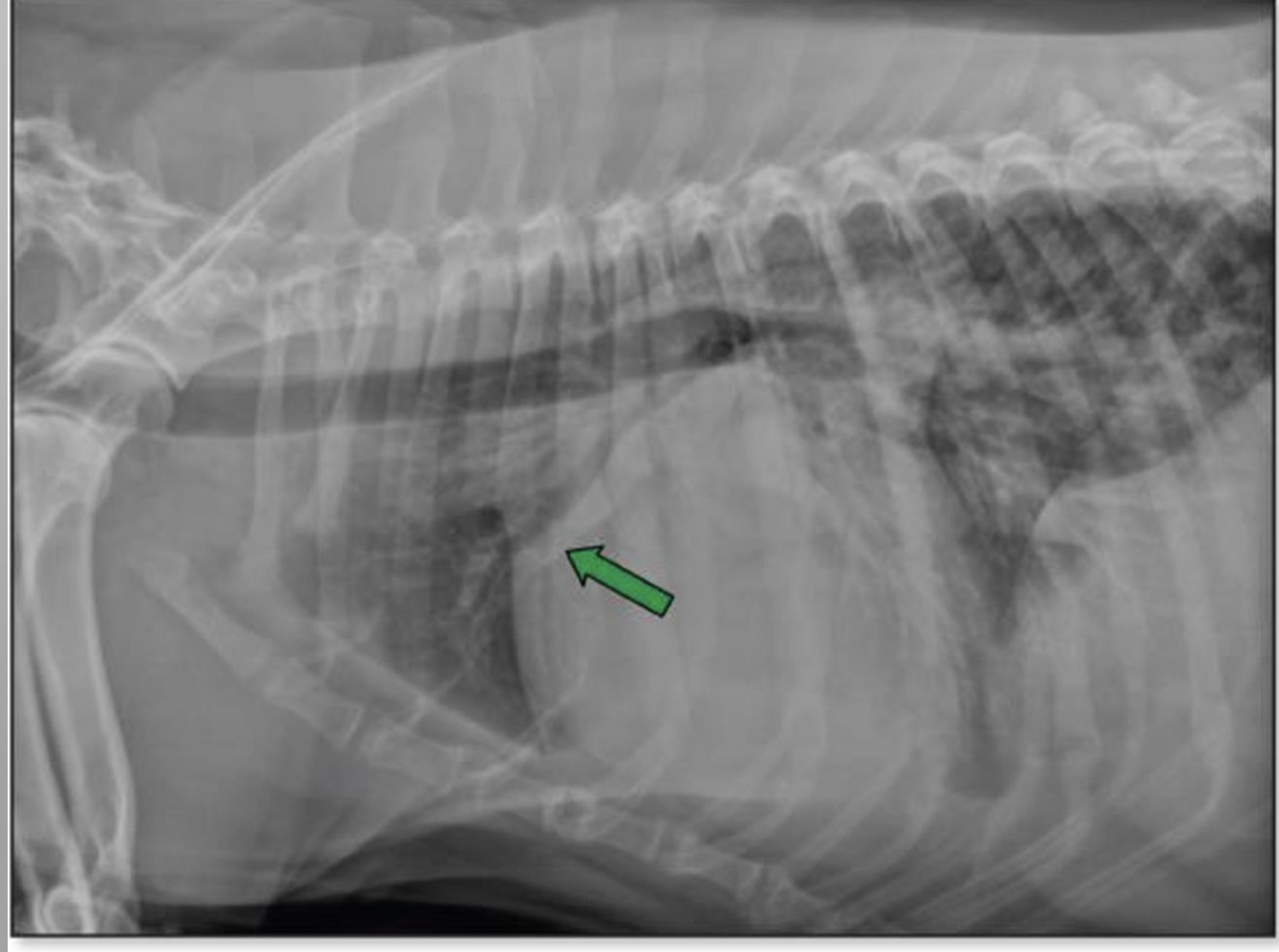
case
\-14 yr old chihuahua
progressive coughing
grade V/VI heart murmur
\-14 yr old chihuahua
progressive coughing
grade V/VI heart murmur
pulmonary congestion
* vein is huge
* used mostly to compare to the artery
* a lot of congestion in the lungs
* right sided heart failure
* vein is huge
* used mostly to compare to the artery
* a lot of congestion in the lungs
* right sided heart failure
18
New cards
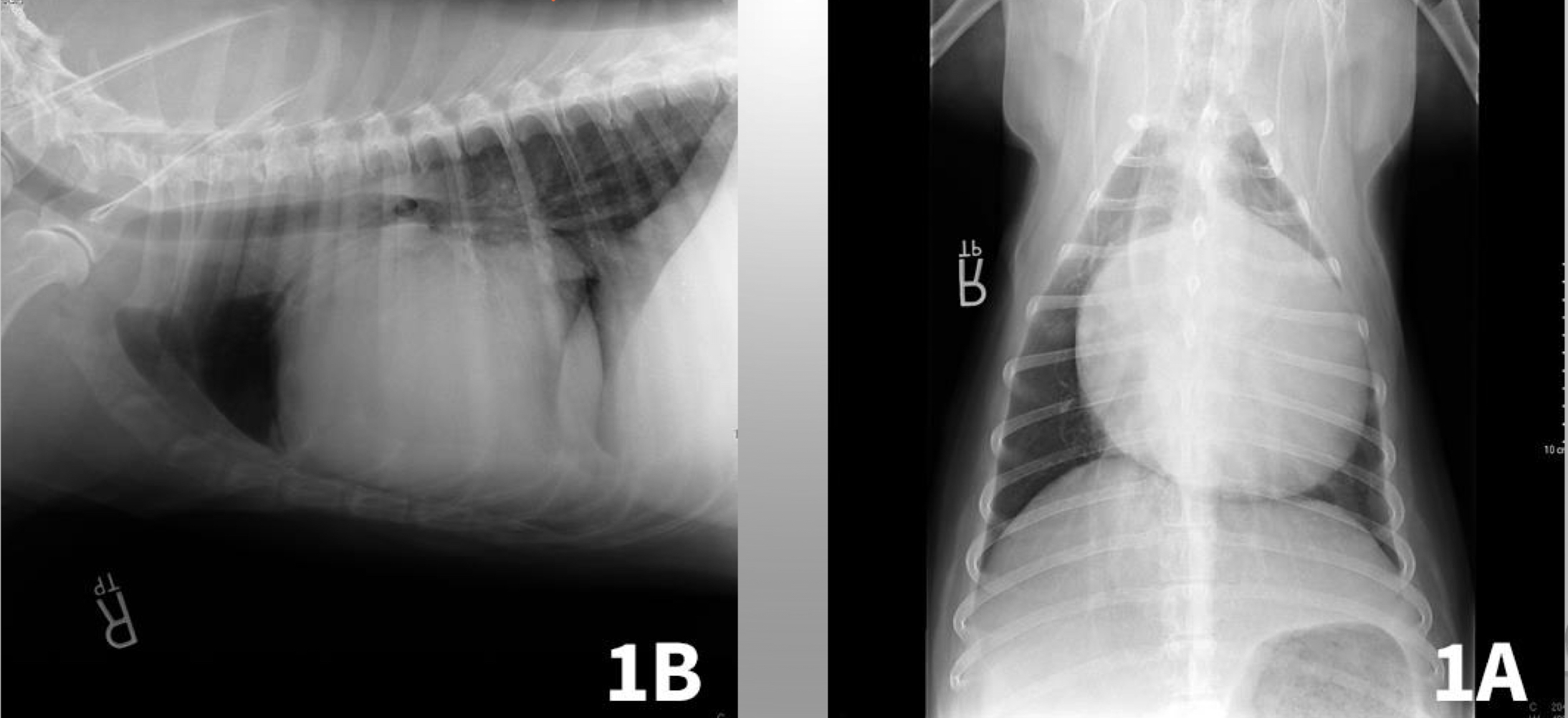
CASE
* 7 yr old MC golden retriever
* acute collapse in the backyard
* weak
* tachycardia
* increased heart rate
* tachypnea
* increased respiratory rate
* significant muffled heart sounds
* barley hear heart rate
* 7 yr old MC golden retriever
* acute collapse in the backyard
* weak
* tachycardia
* increased heart rate
* tachypnea
* increased respiratory rate
* significant muffled heart sounds
* barley hear heart rate
* pericardial effusion
* fluid in pericardium
* heart isn’t big its the fluid surrounding it
* heart cant pump with fluid around it
* most common cause is neoplasia
* rodenticide
* idiopathic
* cancer
* more common a tumor
* can cause cardiac tamponade
* decreased venous return
* ventricular filling
* cardiac output
* results in cardiogenic shock
* fluid in pericardium
* heart isn’t big its the fluid surrounding it
* heart cant pump with fluid around it
* most common cause is neoplasia
* rodenticide
* idiopathic
* cancer
* more common a tumor
* can cause cardiac tamponade
* decreased venous return
* ventricular filling
* cardiac output
* results in cardiogenic shock
19
New cards
where do you do a pericardiocentesis
* tapping pericardium
* most commonly performed right 4th and 6th intercostal space
* right side of the thorax
* cardiac notch
* Between right middle and right cranial of the lung
* heart sits away from the lungs
* most commonly performed right 4th and 6th intercostal space
* right side of the thorax
* cardiac notch
* Between right middle and right cranial of the lung
* heart sits away from the lungs
20
New cards
what the fix for pericardial effusion is
subtotal pericardectomy
* we dont take out the whole pericardium because of the phernic nerve
* if the phernic nerve is taken out then the diaphargm wont expand anymore
* we dont take out the whole pericardium because of the phernic nerve
* if the phernic nerve is taken out then the diaphargm wont expand anymore
21
New cards
what is the thymus and location
* its in puppies
* lymphatic grandular organ
* responsible for t cell production
* t cells migrate away from the thymus to lymph nodes and speel as pet matures
* located in the chest cavity cranial to the heart
\
* lymphatic grandular organ
* responsible for t cell production
* t cells migrate away from the thymus to lymph nodes and speel as pet matures
* located in the chest cavity cranial to the heart
\
22
New cards
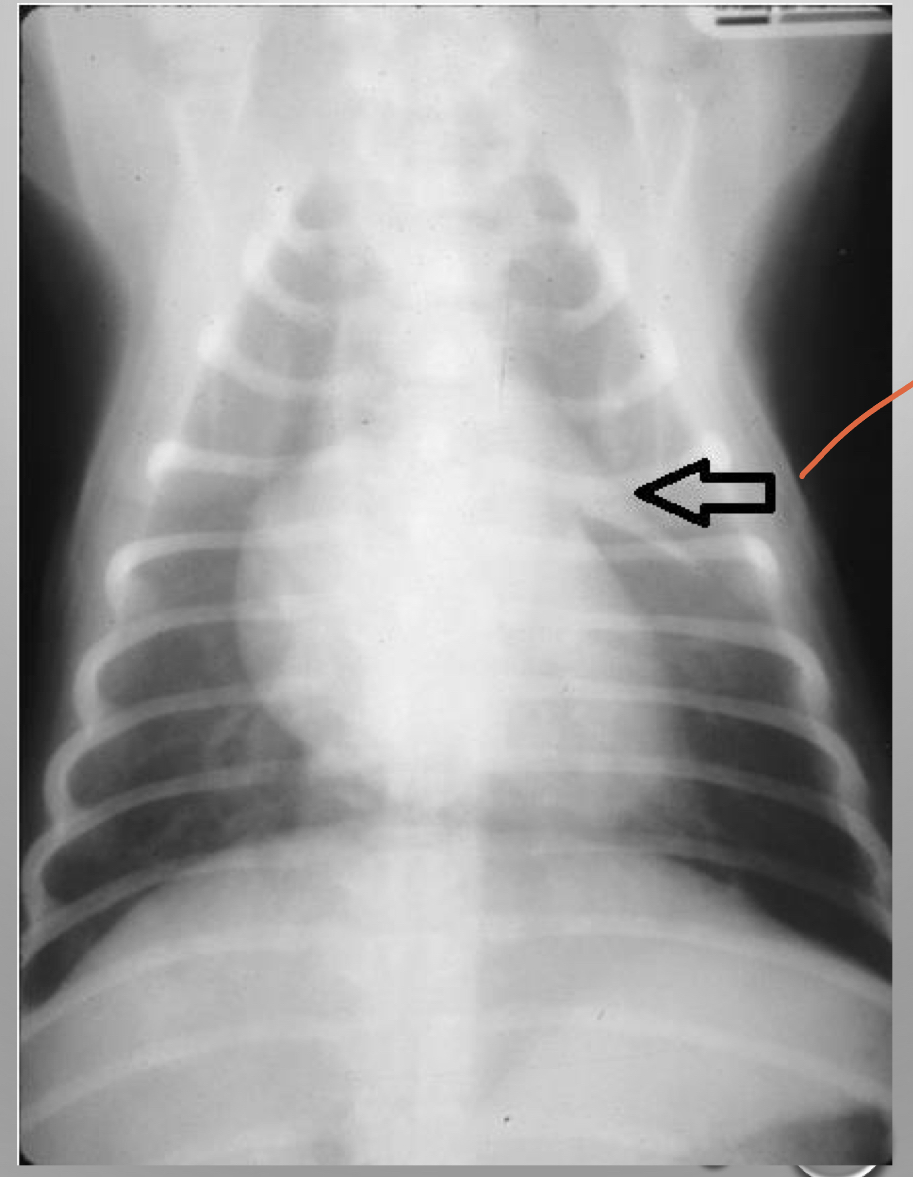
what is this
often referred to sail sign
often referred to sail sign
thymus
* cranial to the heart
* cranial to the heart
23
New cards
describe thoracocentesis
* removal of fluid or air from the pleural space for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes
* typically in the middle of the chest due to the expaxial muscles dorsally
* dont want to go through 4th and 6th intercostal bc thats where the heart is
* you want to go through 7-9 and you dont want to go high
* typically in the middle of the chest due to the expaxial muscles dorsally
* dont want to go through 4th and 6th intercostal bc thats where the heart is
* you want to go through 7-9 and you dont want to go high
24
New cards
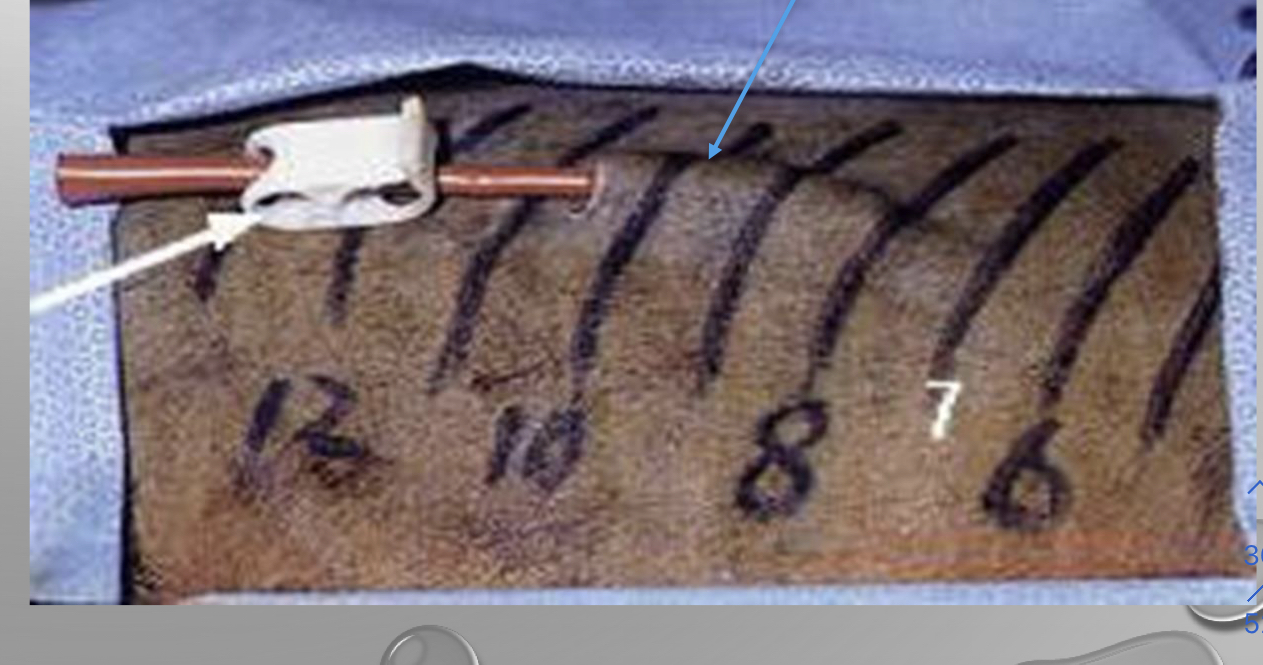

why do you need a thoracostomy tube
* management of pleural effusion or pneumothorax
* post op
* placed tunneled to prevent air from coming in and out
* post op
* placed tunneled to prevent air from coming in and out
25
New cards
what does -ostomy mean
making an incision
create an opening (stoma) in an organ or space
create an opening (stoma) in an organ or space
26
New cards
what are the three parts of the diaphragm
* lumbar
* forms the left and right crura
* tendinous attachments to bodies of L3 and L4
* costal
* from medial surface of 8th-13th ribs
* interdigitates with transversus abdominal muscle
* fans back
* sternal
* from the dorsal surface of sternum
* cupula is dome shaped- bulges into thorax
* v shaped tendinous center
* forms the left and right crura
* tendinous attachments to bodies of L3 and L4
* costal
* from medial surface of 8th-13th ribs
* interdigitates with transversus abdominal muscle
* fans back
* sternal
* from the dorsal surface of sternum
* cupula is dome shaped- bulges into thorax
* v shaped tendinous center
27
New cards
what are the left and right crus important
bc you can see in an xray
28
New cards
how many openings are in the diaphargm
3
29
New cards
what goes through the diaphragm
* caval foramen
* aortic hiatus
* aorta
* azygos vein
* thoracic duct
* lymphatic drains
* esophageal hiatus
* esophagus
* vagal trunk
* aortic hiatus
* aorta
* azygos vein
* thoracic duct
* lymphatic drains
* esophageal hiatus
* esophagus
* vagal trunk
30
New cards
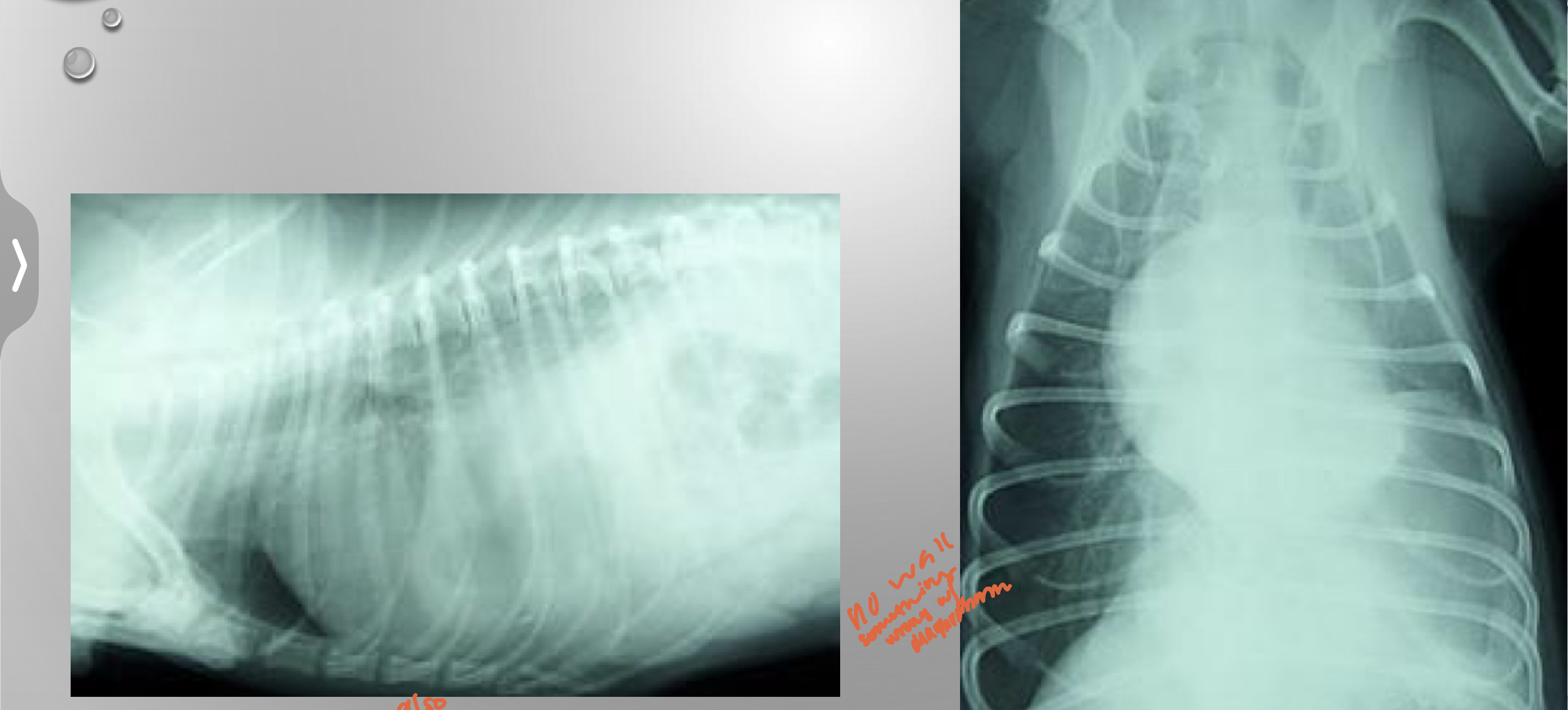
CASE
* 5yr MN Lab
* missing for 3 days
* came home and has been dyspenic
* muffled heart sounds
* muffled caudal ventral lung sounds
* painful abdomen
* 5yr MN Lab
* missing for 3 days
* came home and has been dyspenic
* muffled heart sounds
* muffled caudal ventral lung sounds
* painful abdomen
might be fluid in there
* no wall something is wrong with diaphargm
* you should be able to see the cupula and crus
diaphragmatic hernia
can be traumatic or congenital
* no wall something is wrong with diaphargm
* you should be able to see the cupula and crus
diaphragmatic hernia
can be traumatic or congenital
31
New cards
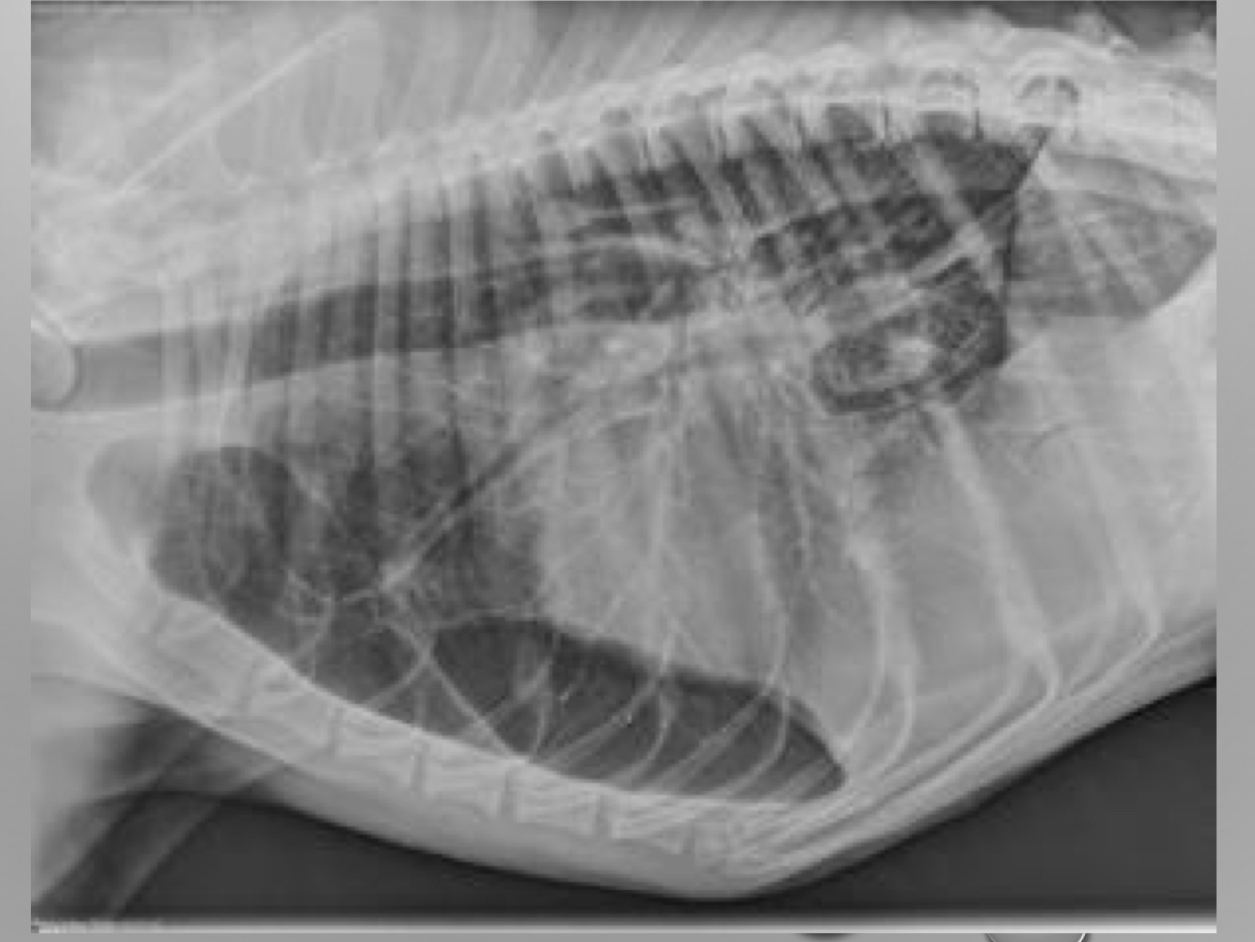
what is wrong with this xray
bowl stomach jejunum way up way front
32
New cards
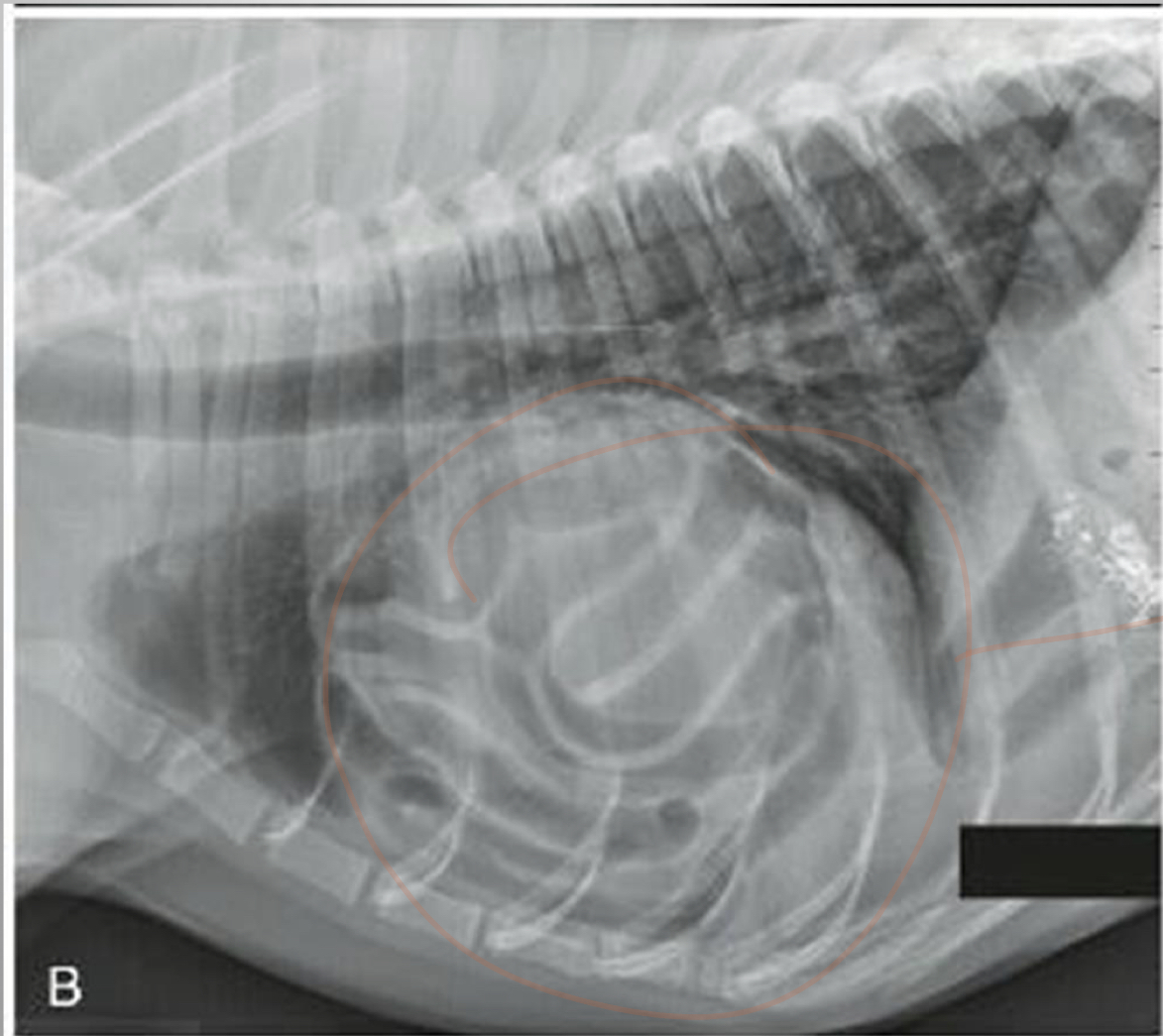
CASE
* 5 yr FS DLH
* chronically tachypneic (rapid breathing) when excited
* recently has gotten worse
* muffled heart sounds
* abdomen feels soft
* 5 yr FS DLH
* chronically tachypneic (rapid breathing) when excited
* recently has gotten worse
* muffled heart sounds
* abdomen feels soft
peritoneopericardial diaphgragmatic herina (PPDH)
* can be chronic
* congenital communication between the pericardial and peritoneal spaces
* abnormal development of the transverse septum of the diaphragm
* can be clinically silent depending on size of defect and what is herniated
* you may never know
* can be chronic
* congenital communication between the pericardial and peritoneal spaces
* abnormal development of the transverse septum of the diaphragm
* can be clinically silent depending on size of defect and what is herniated
* you may never know