4.2 DNA and protein synthesis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Define ‘genome’ and ‘proteome’
Genome - the complete sets of genes in a cell (including those in mitochondria / chloroplasts)
Proteome - the full range of proteins that a cell is able to produce (coded for by the cell’s DNA / genome)
Describe the two stages of protein synthesis
Transcription - production of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA, in the nucleus
Translation - production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA, at ribosomes
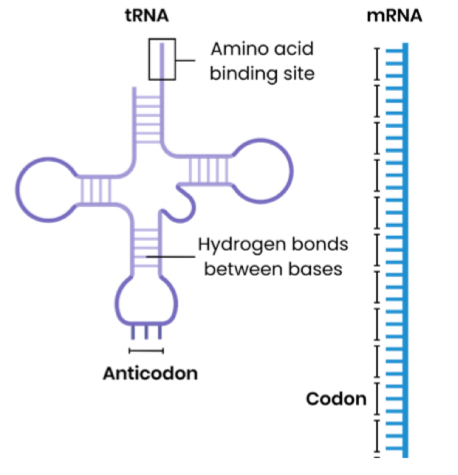
Compare and contrast the structure of tRNA and mRNA
Similarities:
both single polynucleotide strand
Differences:
tRNA is folded into a ‘clover-leaf shape’, whereas mRNA is linear / straight
tRNA has hydrogen bonds between paired bases, mRNA doesn’t
tRNA is a shorter, fixed length, whereas mRNA is a longer, variable length (more nucleotides)
tRNA has an anticodon, mRNA has codons
tRNA has an amino acid binding site, mRNA doesn’t
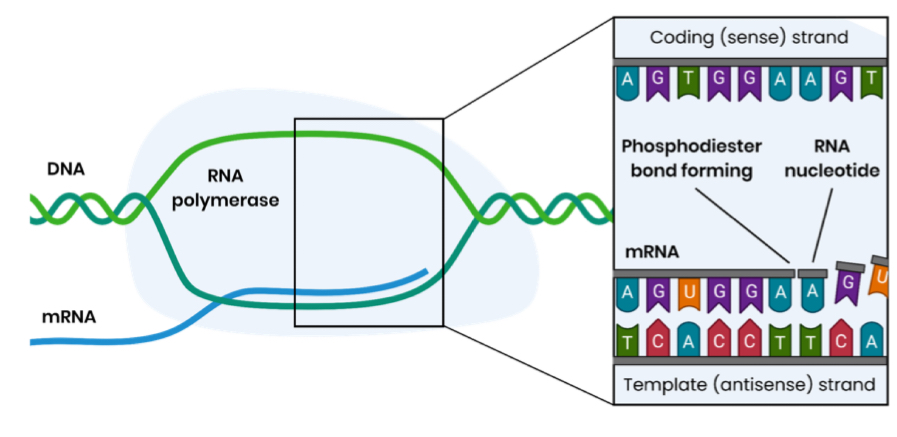
Describe how mRNA is formed by transcription in eukaryotic cells
Hydrogen bonds between DNA bases break
Only one DNA strand acts as a template
Free RNA nucleotides align next to their complementary bases on the template strand
- in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine (pairing with adenine in DNA
RNA polymerase joins adjacent RNA nucleotides
This forms phosphodiester bonds via condensation reactions
Pre-mRNA is formed and this is spliced to remove introns, forming (mature) mRNA
Describe how production of messenger RNA (mRNA) in a eukaryotic cell is different from the production of mRNA in a prokaryotic cell
pre-mRNA produced in eukaryotic cells whereas mRNA is produced directly in prokaryotic cells
Because genes in prokaryotic cells don’t contain introns so no splicing in prokaryotic cells
Describe how translation leads to the production of a polypeptide
mRNA attaches to a ribosome and the ribosome moves to a start codon
tRNA brings a specific amino acid
tRNA anticodon binds to a complementary mRNA codon
Ribosome moves along to next codon, and another tRNA binds so 2 amino acids can be joined by condensation reaction forming a peptide bond
using energy from hydrolysis of ATP
tRNA released after amino acid joined polypeptide
Ribosome moves along mRNA to form the polypeptide, until a stop codon is reached
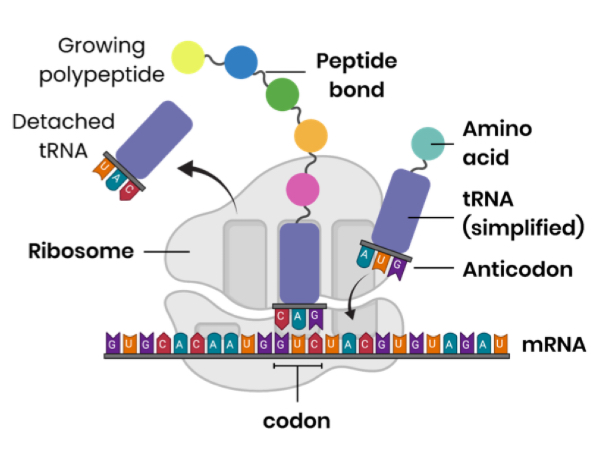
Describe the role of ATP, tRNA and ribosomes in translation
ATP:
hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi releases energy
So amino acids joins to tRNAs and peptide bonds form between amino acids
tRNA:
attaches to / transports a specific amino acid, in relation to its anticodon
tRNA anticodon complementary base pairs to mRNA codon, forming hydrogen bonds
2 tRNAs bring amino acids together so peptide bonds can form
Ribosomes:
mRNA binds to ribosomes, with space for 2 codons
Allows tRNA with anticodons to bind
Catalyses formation of peptide bond between amino acids (held by tRNA molecules)
Moves along (mRNA to the next codon) / translocation
Describe how the base sequence of nucleic acids can be related to the amino acid sequence of polypeptides when provided with suitable data
you may be provided with a genetic code to identify which triplets / codons produce which amino acids
tRNA anticodons are complementary to mRNA codons
- e.g. mRNA codon = ACG → tRNA anticodon = uGC
Sequence of codons on mRNA are complementary to sequence of triplets on DNA triplets on DNA template strand
- e.g. mRNA base sequence = ACG UAG AAC → DNA base sequence = TGC ATC TTG
In RNA, uracil replaces thymine