Antihistamine Pharmacology ONLY
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
What is histamine?
Naturally developed chemical compound that helps initiate an immune response.
What are some immununologic rxns that histamine can mediate?
1. Inflammation
2. Allergic reactions
3. Gastric Acid Secretion
4.CNS Alertness, Attention
How is histamine created?
Decarboxylation of L-Histidine ( i.e removal of carboxylic acid on the alpha carbon from L-Histidine Compound )
T/F Histamine is rapidly degraded
F; Histamine is not degraded, it is inactivated and stored.
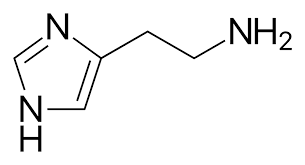
Describe the bonds expressed between histamine and H-receptors.
The nitrogens on the imidazole ring bind to the histamine receptor via Hydrogen Bond
The protonated amine (1*) bind with the histamine receptor via Ionic Bond
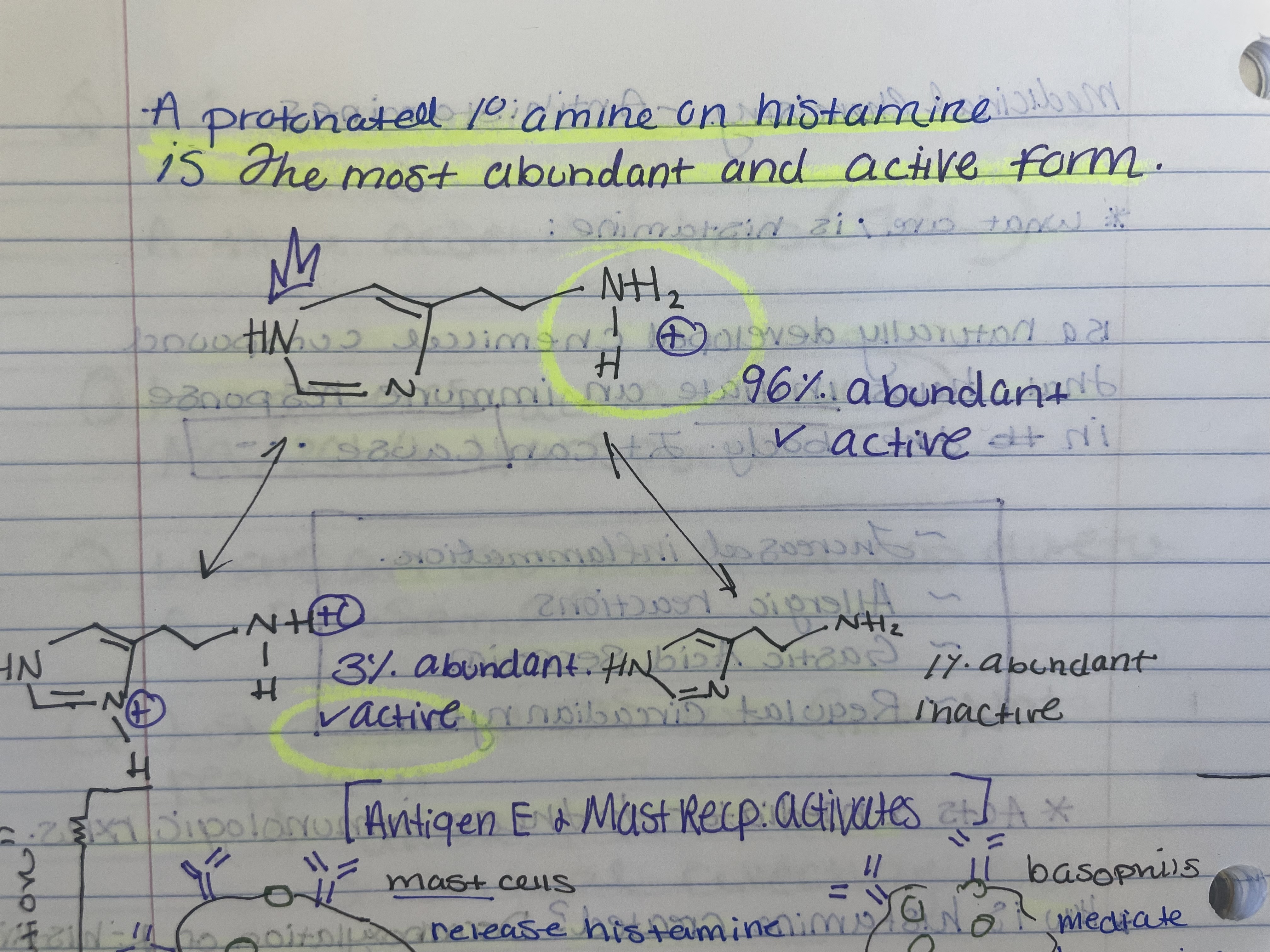
Which form(s) of histamine are active?
a. Protonated Amine
b. Protonated amine + imidazole ring
c. Neutral charged compound
A & B
Which form(s) of histamine are the most abundant?
a. Protonated Amine
b. Protonated amine + imidazole ring
c. Neutral charged compound
A only
Which form(s) of histamine are inactive?
a. Protonated Amine
b. Protonated amine + imidazole ring
c. Neutral charged compound
C only
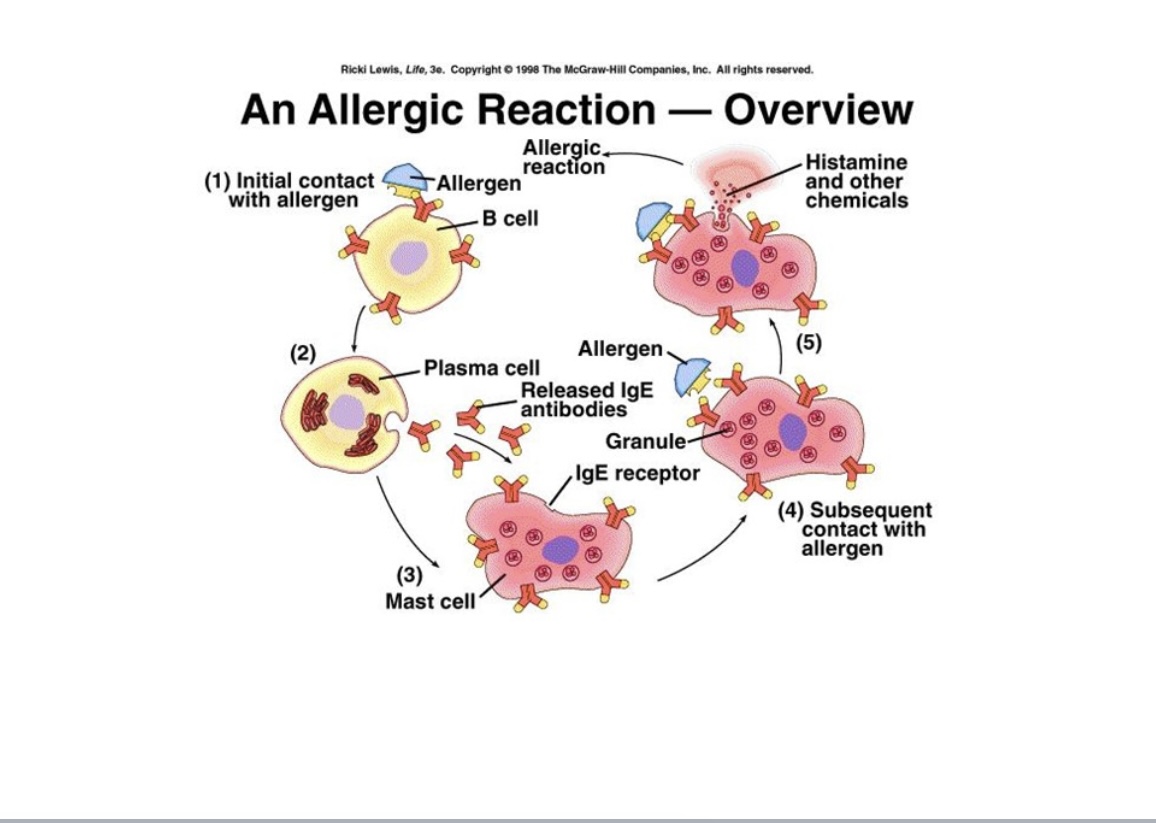
Describe the importance of degranulation, histamine, and allergic reactions.
On the initial contact of an allergen, the B-cells that recognize the the allergen and release IgE antibodies that will initiate mast cells and basophils.
The mast cells and Basophils once recognize the allergen independently will degranulate their content that will release the inflammatory mediator histamine as well as the other contents from the cell.
Where is histamine stored?
Mast Cells, Basophils, Enterochromaffin-like cells /“ECL” ( located in the stomach)
Where do mast cells mediate histamine release?
Mast cells focus on releasing histamine for local tissue injury
Where do basophils mediate histamine release?
Basophils mediate histamine release during systemic allergic reactions or inflammation.
T/F Not all Histamine is an Immune Response
T; (i.e CNS Awakeness and Alertness) & Gastric Secretion
List reasons why histamine is released.
Caused by an immunological response from Basophils
Exposure to Morphine, Tubocurarine, & certain dyes
Mechanical or Chemical Injury from Mast Cells
Describe the pathophysiology of Histamine release in blood/tissues
Seasonal Allergies
Anaphylactic Shock
Describe the pathophysiology of Histamine release in the stomach
Duodenal Ulcers
Zollinger Ellison Syndrome or Gastrinoma ( Stomach tumor)
Describe the pathway of GCPR’s ( that are histamine receptors )
G-Protein Couplesdreceptors are a transmembrane protein that regulate phosphorylation. The receptor is attached to an inactive heterotrimeric protien that has an alpha protien which directs the function; this function can be excitatory or inhibitory. Once a ligan binds the alpha protein triggers activation of a second messenger that will either trigger or hinder phosphorylation via adenyl cyclase and the PKA dimer or trigger phosphorylation via PLC-IP3-Ca2+ pathway.
Degranulation is involved in ____ allergic reactions. List some examples.
Type I hypersensitivity / Immediate
Examples: Food, Drugs, and Venoms
List and Describe Clinical Symptoms associated with MILD Histamine release.
Erythema - Reddening (of patches ) of the skin
Urticaria- Red, Itchy raised patches or wheals on the skin
List and Describe Clinical Symptoms associated with MILD to MODERATE Histamine release.
Skin Reactions
Tachycardia - fast heart rate
Dysrhythmias - abnormal rhythm
Moderate hyPOtension
Mild respiratory distress
“ This can be categorized as asthma attack”
List and Describe Clinical Symptoms associated with SEVERE Histamine release.
Severe HyPOtension- dramatic fall of BP
Ventricular Fibrillations- rapid, irregular heartbeats that can cause the heart to abruptly stop pumping blood into the body an lead into a a heart attack
Cardiac Arrest: Electrical issue; the heart stops beating effectively limiting blood flow to organs and brain
Bronchospasm: the muscle around the airways tighten making it harder to breath
Respiratory arrest: Can’t breath, loss of consciousness can result
Anaphylaxis - life-threatening allergic reaction causing multiple system involvement.
Clinical Presentation: Anaphylactic Shock and Asthma Attack
Where are H1 receptors distributed?
Smooth Muscle, Brain , & Endothelium
Where are H2 receptors distributed?
Gastric Mucosa, Cardiac Muscle, Mast Cells, and Brain
Where are H3 receptors distributed?
Presynaptic Auto-receptors and Heteroreceptors in the:
Brain
Myenteric Plexus
Other Neurons
Where are H4 receptors distributed?
Hematopoetic Cells via Bone Marrow and Blood Cells
Which downstream mechanism do H1 receptors go through?
Gq (activate maybe)
Increasing phosphylation (IP3) and DAG
Which downstream mechanism do H2 receptors go through?
Gs (activate adenylate cyclase), increasing cAMP levels.
Which downstream mechanism do H3 receptors go through?
Gi (inhibits adenylate cyclase), decreasing cAMP levels.
Which downstream mechanism do H4 receptors go through?
Gi (inhibits adenylate cyclase), decreasing cAMP levels.
List some Inverse Agonist( s) that are partially selective to H1 receptors
Cetirizine
Mepryamine
Triprolidine
List some Agonist(s) that are partially selective to H1 receptors
Histaprodifen
List some Inverse Agonist(s) that are partially selective to H2 receptors
Ranitidine
Famotidine
Tiotidine
List some Agonist(s) that are partially selective to H2 receptors
Amthamine
T/F all Histamine receptors are GPCR
T
What physiologies occur when H1 receptors are activated, describe the clinical presentation.
Which GPCR is relative to H1 receptors?
Smooth Muscle Contraction ( i.e Ca2+)
Vaso(blood vessels) dilation (i.e endothelial eNO)
Symptoms
Wakefulness
Alertness
Vasodilation
Separation of the endothelial cells
Vascular smooth muscles relaxation
GPCR: Gq/11
What physiologies occur when H2 receptors are activated, describe the clinical presentation.
Which GPCR is relative to H2 receptors?
Activation of Adenyl Cyclase - Cyclic AMP -PKA- cAMP
Presentation
Relaxation of Vascular smooth muscles
Vasodilation
Cardiac Stimulant
Gastric Acid Secretion
GPCR: Gs
What physiologies occur when H3 receptors are activated, describe the clinical presentation.
Which GPCR is relative to H3 receptors?
Inhibition of Adenyl Cyclase - decreased cAMP.
Presentation includes sedation, appetite stimulation, and modulation of neurotransmitter release.
GPCR: Gi/o.
What physiologies occur when H4 receptors are activated, describe the clinical presentation.
Which GPCR is relative to H4 receptors?
Stimulates Chemotaxis of mast cells and leukocytes towards sites of inflammation. ( local)
T/F H3 is a postsynaptic receptor
F
Describe the Feedback Regulation of Histamine Release
Stimulation of H2 receptors increase cyclic AMP and leads to feedback inhibition. Of histamine release from mast cells and basophils in the human skin.
T/F Histamine has no clinical relevance other than diagnostic
T
Where can we find histamine being used as a diagnostic?
Pulmonary Function
Allergy testing for histamine sensitivity
Gastric sensitivity testing
What are these two drugs examples of ? Betazole & impromidine
Histamine Agonist
T/F Vasodilation is the most important effect of histamine in humans and can result from activation of either H1 or H2 receptors
T
Infusion or Injection of histamine causes …
Decrease in Blood Pressure ( both systolic and diastolic)
Increase in Heart Rate
Why does histamine cause blood pressure changes?
The Vasodilation Action in the arterioles and pre capillary sphincters
Where does the histamine vasodilation action of histamine occur?
Arterioles and Pre-capillary Sphincters
Describe the ways histamine effects the heart ( direct and indirect effects)
Direct : Histamine increases heart rate and contractility, leading to increased cardiac output.
Indirect: Histamine caused vasodilation, which causes reflex tachycardia
Which histamine receptor is the major mediator for increase capillary permeability ?
H1
Describe Histamine effect on capillary permeability
Histamine causes an effluent of plasma protein and fluid in extra cellular spaces, causing am increase in blood flow, and increase in capillary permeability, and eventually edema.
Is this an H2 or H1 activity? Positive Chronotropism
H2
Is this an H2 or H1 activity? Negative Inotropism
H2
Is this an H2 or H1 activity? Slows AV conduction
H1
Is this an H2 or H1 activity? Increasing Heart automaticity
H1 & H2
Describe the “ Triple Response Phenomenon” and it’s relation to histamine
The Triple Response Phenomenon refers to the three-part reaction of the skin to injury, irritation, and Intradermal injections of Histamine
Development of a red spot (erythema),
Flushing (flare)
Swelling of a Wheal
Figure out the effects of histamine of the extravascular smooth muscles
I think just vasodilation,the slide cut off, check the video
List some adverse effects to Histamine ( ~6 listed on the slide)
Flushing ( feeling of warmness)
Hypotension
Tachycardia
Headache
Bronchoconstriction
GI Upset
What is Histamine Shock?
Occurring during a rapid release of histamine or large doses of histamine administered, histamine shock is systemic anaphylaxis causing profound and progressive drop in blood pressure
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Chlorpheniamine
Allergy, 1rst Generation
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Chloropheniramine
Allergy (1rst gen)
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Diphenhydramine
Allergy ( 1rst gen), Nausea, Insomnia Cough, Cold, and Pain relief
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Hydroxyzine
Allergy ( 1rst gen ) and Itching
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Cetirizine
Allergy (2nd gen)
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Fexofenadine
Allergy ( 2nd gen)
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Loratadine
Allergy (2nd gen)
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Desloratadine
Allergy ( 2nd Gen)
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Levocetirizine
Allergy (2nd gen)
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Cyproheptadine
Anti-migraine
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Ergotamine + diphenhydramine
Anti-Migraine
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Azelastine
Intranasal antihistamine
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Doxepin
Generalized Itching
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Dimenhydrinate
Nausea and Motion Sickness
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Cyclizine
Nausea and Motion Sickness
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Meclizine
Nausea and Motion Sickness
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Promethazine
Nausea, Motion Sickness, and Insomnia
Name the indication from this antihistamine: Pyrilamine
Insomnia only
A 45 year old truck driver complains of seasonal allergies. Which of the following would be indicated?
A. Cyclizine
B. Dozxepin
C. Doxylamine
D. Hydroxyzine
E. Fexofenadine
E
Name some sedating antihistamines
Doxylamine and Promethazine
List some causes to the “ Triple Response”
Skin injury
Skin irritation
Intradermal injections of Histamine