Bio112 exam 2 part 3
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Kinesins
Moelcular motors that walk along microtuboles. Works through ATP hydrolysis
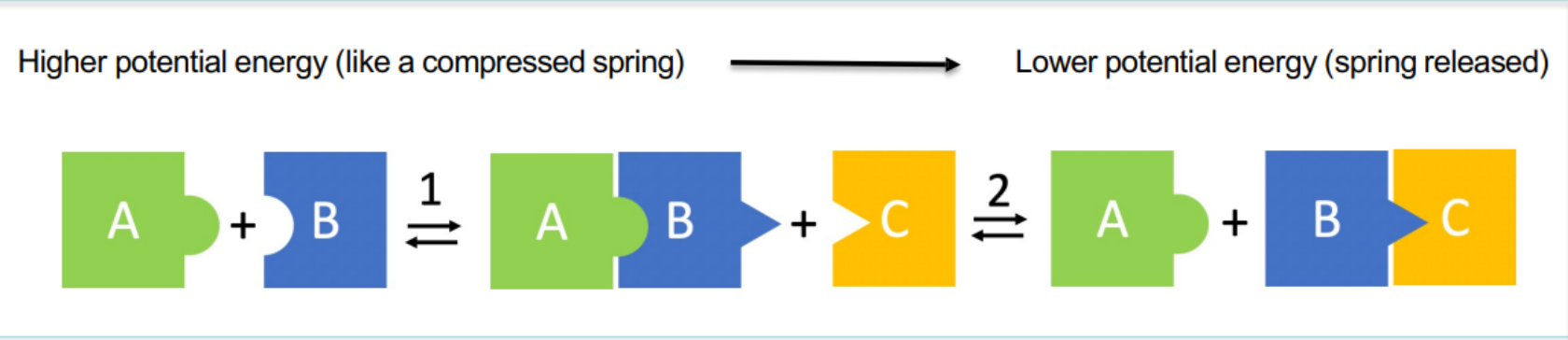
Sequential binding-induced conformational changes provide…
The thermodynamic impetus to drive processes in the forward direction
SRP is a _________ process
Unviersally conserved
Secreted proteins
Proteins meant for secretion and direction outside of the cell
Integral protein
Proteins that have intermembrane domains (span cross memebrane)
Peripheral protein
Intracellular or secreted proteins that bind to the inner or outer membrane, usually via association with integral membrane proteins
Gram positive vs Gram Negative bacteria
Gram- →double membrane with peptidoglycan wall in between
Gram+ →single membrane, thicker peptidoglycan wall.
Just a side note bacteria have no ER
Targeting (secretory pathway)
When ribosomes that are translating the secretion cargo are delivered to the ER membrane. Typically driven by energy use and targeting proteins such as SRP.
Vesicular Trafficking (Sorting)
"downstream of targeting”. These events involve the budding of membrane vesicles from compartments like the Golgi and their fusion to downstream compartments.
(Bus vs Uber example)
Peptide Signal sequence
A short amino acid sequence that is recognized by a signal sequence receptor.
Signal sequence receptor
The receptor that recognizes the peptide signal sequence this is the source of the selectivity.
Docking SRP receptor
The cognate membrane (the membrane to which the protein is being targeted) contains an SRP docking receptor that binds the [signal sequence-signal sequence receptor] complex
Translocon
function is to facilitate the translocation of the cargo into or across the lipid membrane. A channel protein
Co-translational secretion
For example, in SRP-mediated secretion, the protein is targeted to the membrane for secretion while it is being synthesized.
The most notable feature of secretion signals is a core of…
hydrophobic amino acids
Differences between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic SRP
Eukaryotes: 7S RNA and 6 different polypeptides
Prokaryotes 6S RNA and ffh (SRP54 ortholog)
Domain strucute of SRP54
M domain: Binds the signal sequences as it emerges from the ribosome exit tunnel. The M domain also contains sequences that are responsible for its binding to SRP RNA.
N: Stabilizes interactions between binding partners, mainly the ribosome.
G: A GTPase enzyme, catalyzes the hydrolyzes GTP to GDP. The G domain also forms a complex with SRP receptor during docking.
SRP step 1: Binding
SRP54’s M domain recognizes and binds to the nascent signal sequence, causing SRP9/14 to pause translation and other parts to bind SRP to the ribsome
SRP step 2: Docking
SRP 54’s NG domains bind to SRP Receptor (SRalpha and beta, which is homologus) on the membrane of ER
in prokaryotes its fFh and ftsy
SRP step 3: Handoff
SRP54 slides down srRNA adjusting position for handoff, exposing the translocon tunnel
GTP on both SRP54 and SRa are converted into GDP, forming a seal between the ribosome and translocon, and also dissociated SRP.
This also means translation is resumed since SRP9 and 14, and dissociated as well
After SRP has dissociated, it induces a change in the structure of the translocon, forming a water-tight seal, and secretion continues.
SRP step 4: translocation
Translocon opens laterally allowing the signal sequence peptide and integral membrane spanning domains to pass into the hydrophobic interior of the membrane
Signal peptidase only cuts the signal sequence after translocation has finished
(the thermodynamic impetus that drives the elongating polypeptide in the forward direction across the membrane is a Brownian ratchet. This type of probabilistic mechanism plays roles in other cell processes, including protein synthesis itself.)
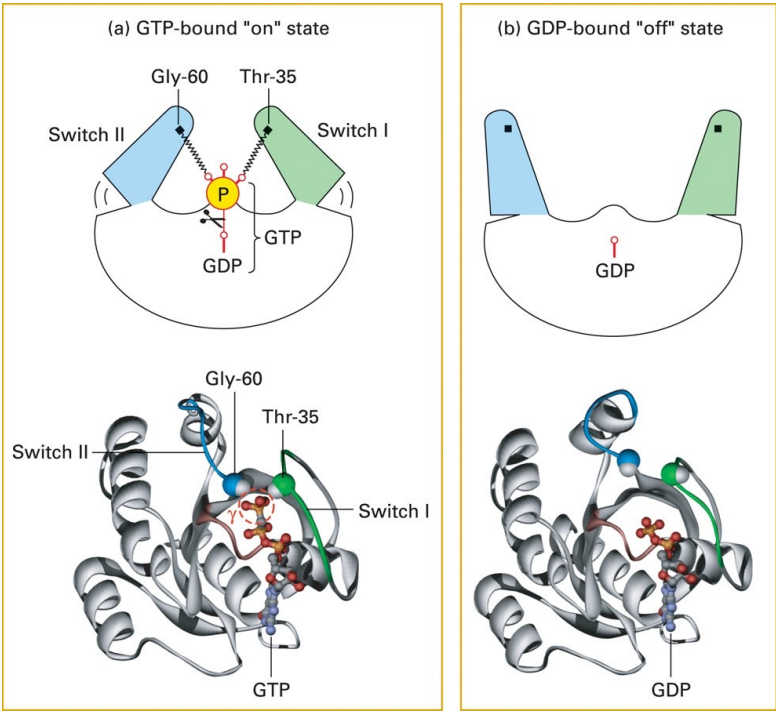
GTPase switches
Can either be turned on by GAP (which aids in GTP hydrolysis) or GEF(which alone for conversion into GTP from GDP)
Phosphate is bound when the GTPase is active
unbound when it is inactive
Signal peptide opens…
opens the lateral gate of the translocon through insertion
Biogenesis of integral membrane proteins
Depends on stop-transfer sequences(hydrophobic regions thus why it becomes integral) , which trigger the lateral release of the co-translating protein.
Signal peptidase cleaves the signal sequence before it dissociates.
Vesicular Trafficking in Eukaryotes
Integral membrane and secreted proteins are sorted to different membranes, including the plasma membrane
-This process is unnecessary in bacteria because secretion occurs directly across the plasma membrane.