AP Macroeconomics Unit 1 Section 1 Vocabulary
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Last updated 9:25 PM on 8/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
absolute advantage
when a producer can provide a good or service in **greater** quantity for the **same** cost, or the **same** quantity at a **lower** cost, than its competitors
2
New cards
capital (goods)
physical assets a company uses to produce goods and services for consumers
3
New cards
ceteris paribus (other things equal)
a shorthand indication of the effect one economic variable has on another, provided all other variables remain the same
4
New cards
command economy
a type of economy in which governments own the factors of production such as land, capital, and resources, and officials determine when, where, and how much is produced
5
New cards
comparative advantage
an economy's ability to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partners
6
New cards
deflation
the general decline of the price level of goods and services
7
New cards
depression
a severe and prolonged downturn in economic activity; may be defined as an extreme recession lasting three+ years
8
New cards
economics
the study of scarcity and its implications for the use of resources, production of goods and services, growth of production and welfare over time
9
New cards
economy
the process or system by which goods and services are produced, sold, and bought in a country or region
10
New cards
efficient
achieving maximum productivity with minimum wasted effort or expense
11
New cards
entrepreneur
a person who organizes and operates a business or businesses, takes on greater than normal financial risks, conceives of the original idea, and makes decisions
12
New cards
incentive
generally, a motivator or form of encouragement; a payment or concession to stimulate greater output or investment
13
New cards
inflation
an economy-wide, sustained trend of increasing prices
14
New cards
labor
a force of production that refers to the work people do to produce goods and services, including all physical and mental efforts that go into production
15
New cards
labor force
the number of people who are either working or actively looking for work; all people capable of employment
16
New cards
land
a factor of production, similar to labor, as one of the crucial elements in creating goods and services; specifically a resource of raw materials
17
New cards
marginal analysis
an examination of the additional benefits of an activity compared to the additional costs incurred by that same activity
18
New cards
macroeconomics
the part of economics concerned with large-scale or general economic factors, such as interest rates and national productivity
19
New cards
market economy
a type of economy utilizing private ownership as the means of production and voluntary exchanges/contracts; prices are set by supply and demand
20
New cards
microeconomics
\
the part of economics concerned with single factors and the effects of individual decisions
the part of economics concerned with single factors and the effects of individual decisions
21
New cards
model
a simplified description of reality, designed to yield hypotheses about economic behavior that can be tested
22
New cards
normative economics
a perspective on economics that reflects normative, or ideological, judgments toward economic development, investment projects, statements, and scenarios; what the economy ‘should’ be
23
New cards
opportunity cost
\
the loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen
the loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen
24
New cards
output
quantity (or quality) of goods or services produced in a given time period, by an entity
25
New cards
positive economics
objective descriptions of economic phenomena; based on fact
26
New cards
production possibilities curve
measures the maximum output of two goods using a fixed amount of input
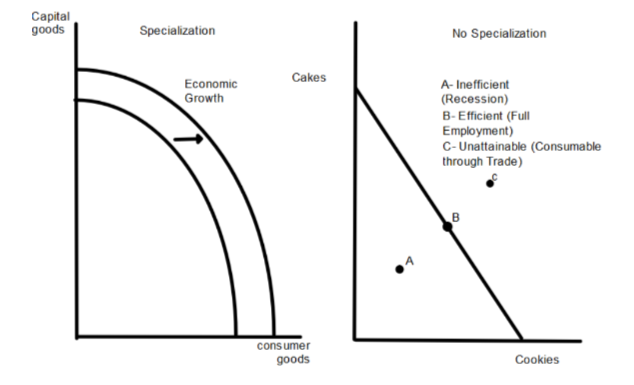
27
New cards
property rights
theoretical and legal ownership of resources, both tangible and otherwise, and how they can be used
28
New cards
resource
anything used to make something else, limited and desired to some degree
29
New cards
scarcity
the concept that all goods are to some degree limited, therefore scarce, requiring choices about how they are allocated
30
New cards
specialization
a method of production whereby an entity focuses on the production of a limited scope of goods to gain a greater degree of efficiency
31
New cards
terms of trade
the ratio between a country's export prices and its import prices, used as an indicator of a country’s economic health
32
New cards
trade-off
the option we give up when making a choice between two opportunities
33
New cards
unemployment
a state of actively looking for or being capable of work, but not currently being employed