trace minerals
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
What are trace minerals?
Essential mineral nutrients required by the human body in small amounts (< 100 mg daily).
How much of trace minerals does the body require daily?
Less than 100 mg.
List the essential trace minerals.
Iron, Zinc, Iodine, Selenium, Copper, Manganese, Fluoride, Chromium, and Molybdenum.
Are there nonessential trace minerals?
Yes, other nonessential trace minerals also exist.
What is the significance of trace minerals?
They are vital for various biological processes despite being required in small amounts.
What affects the trace mineral content of food?
Processing, soil composition, and water composition.
What impacts the bioavailability of trace minerals in the body?
Dietary factors and the body's physiological state.
What are the general effects of trace mineral deficiencies?
They can affect many body systems and may lead to failure to grow in children.
What are potential dangers of trace mineral toxicities?
Toxicities can occur, especially from supplements or environmental exposure—buyer beware!
Are interactions between trace minerals common?
Yes, trace minerals frequently interact, which can lead to imbalances (e.g., lead interfering with iron).
What are the two ionic states of iron?
Ferrous iron (Fe²⁺): Reduced state
Ferric iron (Fe³⁺): Oxidized state
What is a cofactor?
A mineral that works with an enzyme to facilitate chemical reactions, such as oxidation-reduction reactions.
What processes require iron as a cofactor?
Amino acid synthesis
Collagen production
Hormone production
Neurotransmitter synthesis
What role does iron play in the electron transport chain?
It is part of the electron carriers that help make ATP for cellular energy.
Where is most of the body's iron located?
Hemoglobin (in red blood cells):
Oxygen-carrying protein that transports O₂ from the lungs to tissues
Contains 80% of the body’s iron
Myoglobin (in muscle cells):
Oxygen-holding protein in muscle cells
How is iron balance maintained in the body?
Through regulation of iron absorption.
What is ferritin?
Iron storage protein.
Receives iron from the GI tract and stores it in mucosal cells of the small intestine.
What is transferrin?
Iron transport protein.
Takes iron from ferritin and transports it to the rest of the body.
look over
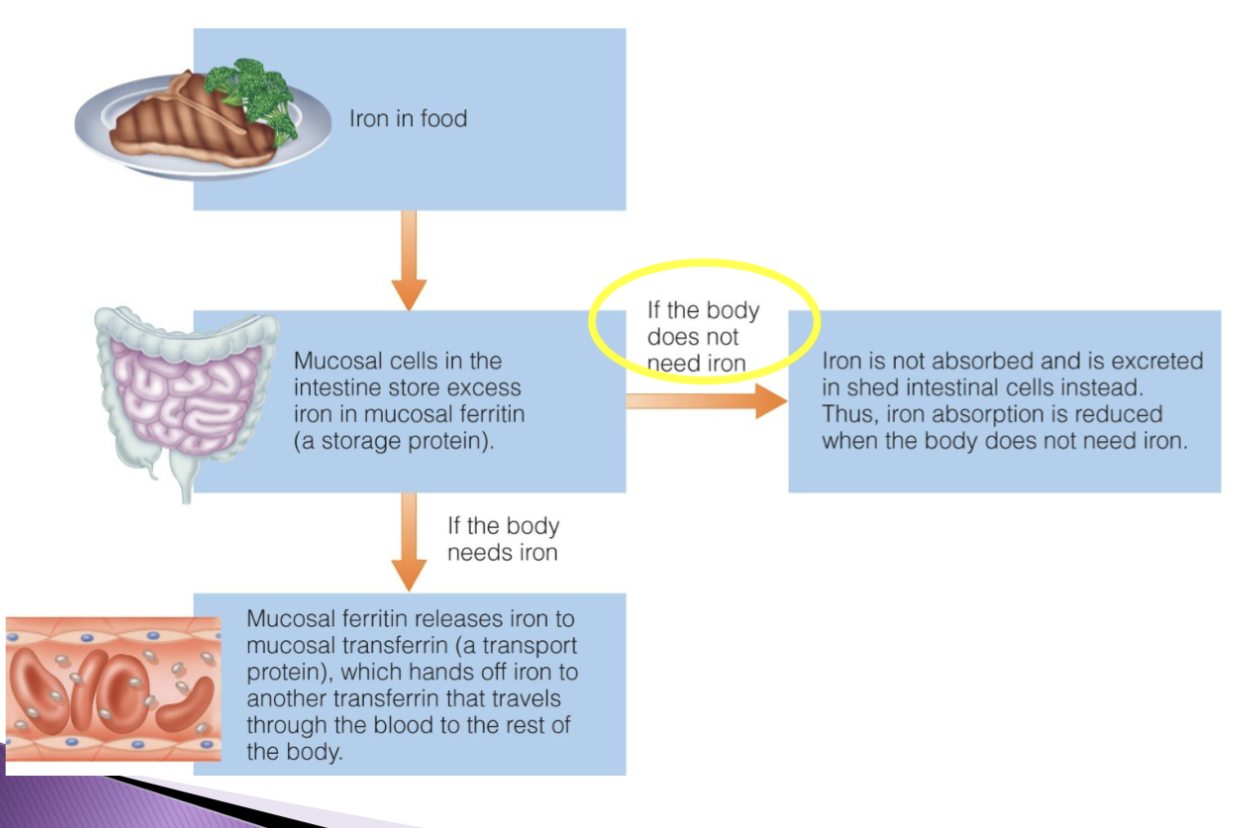
What influences iron absorption?
The source of the iron (heme vs. non-heme).
What is heme iron, and where is it found?
Found only in animal flesh (meat, poultry, fish).
Accounts for 10% of daily iron intake.
Better absorbed (25%) with higher bioavailability, unaffected by dietary factors.
What is non-heme iron, and where is it found?
Found in both plant and animal-derived foods.
Less well absorbed (17%) compared to heme iron.
What is the MFP factor?
A peptide released during the digestion of meat, fish, and poultry that enhances non-heme iron absorption.
How does Vitamin C enhance iron absorption?
It improves the absorption of non-heme iron but does not affect iron from supplements.
When is it recommended to take supplemental iron?
Between meals for better absorption.
What are phytates, and how do they affect iron absorption?
Phytates, found in legumes, whole grains, and rice, inhibit iron absorption.
What vegetable proteins inhibit iron absorption?
Proteins in soybeans, legumes, and nuts.
Which compound in spinach inhibits iron absorption?
Oxalates.
How does calcium affect iron absorption?
Calcium (e.g., from milk) inhibits iron absorption.
What is EDTA, and how does it affect iron?
EDTA, a food additive, inhibits iron absorption.
What are tannins, and where are they found?
Tannins are found in coffee, tea, grains, oregano, red wine, and some fruits and vegetables, and they inhibit iron absorption.
How does the body's need for iron affect absorption?
Iron absorption increases during stages of growth and life stages with higher needs, as more mucosal ferritin and blood transferrin are produced.
Where does the body lose iron?
Blood (e.g., through bleeding).
GI tract (feces).
Minute amounts in urine, sweat, and shed skin.
What is the most common nutrient deficiency worldwide?
Iron deficiency, affecting 1.6 billion people globally.
What is iron deficiency anemia?
A severe depletion of iron stores leading to low hemoglobin (Hgb) and small, pale red blood cells.
Known as hypochromic, microcytic anemia.
How does iron deficiency anemia vary?
It varies by life stage, with different groups being more susceptible (e.g., children, pregnant women).
What are the symptoms of iron deficiency anemia?
Apathy
Fatigue and weakness
Poor resistance to cold
Pale skin
chart
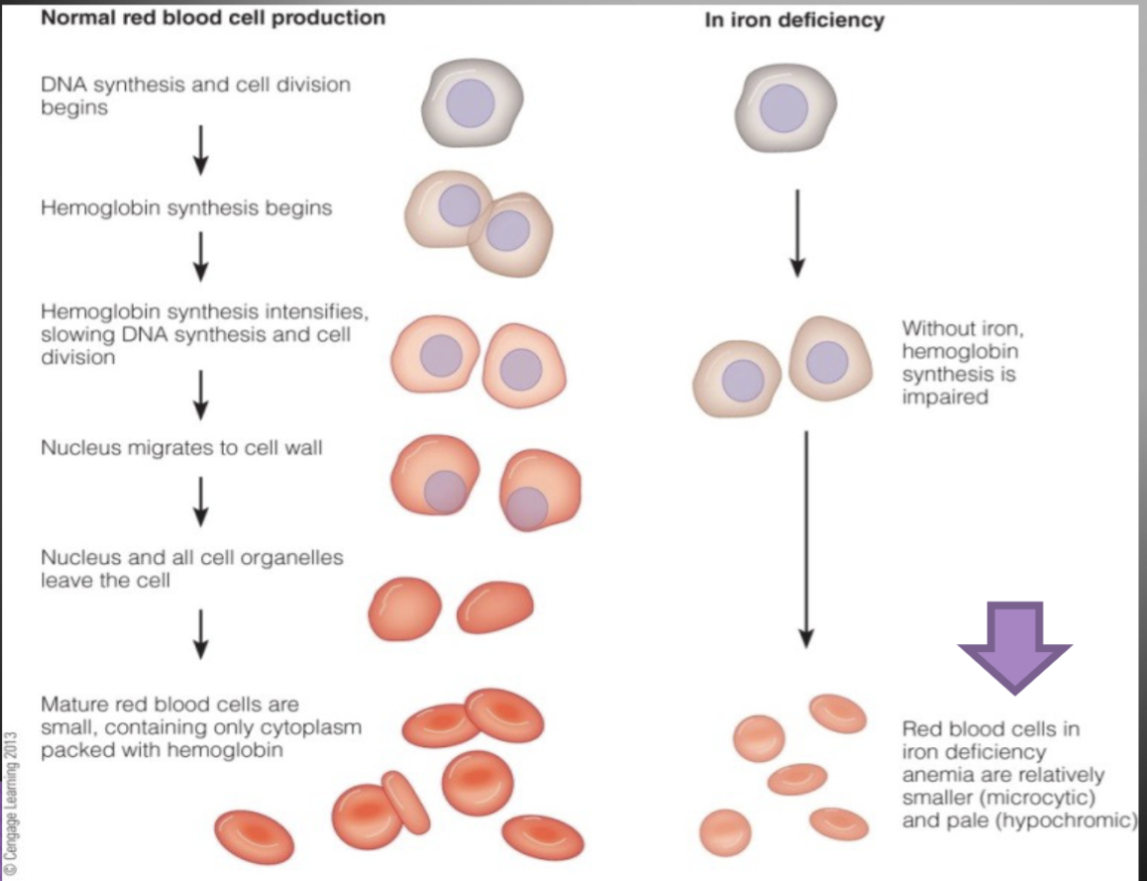
How does iron deficiency affect energy metabolism?
It impairs energy metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis.
What specific metabolic process is impaired by iron deficiency?
The complete oxidation of pyruvate.
How does iron deficiency affect physical work and cognitive functions?
It reduces physical work capacity, and the ability to plan, learn, think, and play.
What behavioral traits might iron deficiency mimic?
It may cause a person to appear lazy, apathetic, or contrary.
What is pica?
A symptom of iron deficiency characterized by the craving and consumption of nonfood substances.
How does pica affect iron deficiency?
Pica worsens anemia by interfering with proper nutrition and iron absorption.
What is geophagia?
A form of pica where individuals crave and consume nonfood substances like clay, baby powder, chalk, ash, ceramics, paper, paint chips, or charcoal.
What is amylophagia?
A form of pica where individuals crave and consume uncooked starches, such as flour, cornstarch, laundry starch, or raw rice.
What is pagophagia?
A form of pica where individuals crave and consume ice.
What is iron overload (toxicity)?
Toxicity caused by excess iron in the body.
What is hemochromatosis?
A hereditary defect in iron metabolism.
Characterized by iron-containing pigment deposits in tissues, leading to tissue damage.
The most common genetic disorder in the U.S.
What are the signs and symptoms of iron overload?
Apathy
Lethargy
Fatigue
Liver damage
What are common causes of iron overload?
Repeated blood transfusions.
Excessive supplemental iron intake.
How is iron overload diagnosed?
Through transferrin saturation and serum ferritin tests.
How is iron overload treated?
Chelating agents to remove excess iron.
Low iron intake.
Avoiding high doses of vitamin C (which can enhance iron absorption).
How does iron relate to heart disease?
Iron oxidizes LDL (low-density lipoprotein), which may contribute to heart disease.
How does iron potentially contribute to cancer?
Iron's free radical activity may damage DNA, potentially increasing cancer risk.
How does high fiber intake affect iron absorption?
High fiber, through phytates, can bind iron and reduce its absorption.
What is the tolerable upper intake level (UL) for iron in adults?
45 mg/day for adults.
Who is at the greatest risk of iron poisoning?
Young children.
What are the symptoms of iron poisoning?
Nausea/Vomiting
Diarrhea
Rapid heartbeat
Weak pulse
Dizziness
Shock
Confusion
Death (due to heart failure, respiratory distress, and internal bleeding).
How can iron poisoning be prevented in children?
Keep iron supplements out of reach of children.
What are some good sources of iron (Fe)?
MFP (Meat, Fish, Poultry)
Legumes
Eggs
Dark leafy greens
Dried fruits
How can iron absorption be improved from enriched foods?
Iron from enriched foods (e.g., bread and cereal) is not absorbed as well as naturally occurring iron. To improve absorption, eat these foods with vitamin C or MFP.
Why is milk a poor source of iron?
Milk is low in iron, making it a poor source for meeting iron needs.
How much more iron do vegetarians need compared to non-vegetarians?
Vegetarians need 1.8 times as much iron to compensate for the lower bioavailability of iron in plant-based foods.
Do women generally meet their iron needs?
On average, women do not meet their iron needs, with the average intake being 12-13 mg instead of the recommended 18 mg.
How can iron be found in foods due to contamination?
Iron can be found in foods through contamination by inorganic iron salts, iron cookware, or soil.
How can cooking in an iron skillet affect iron content in food?
The iron content in eggs can triple when cooked in an iron skillet.
How does the acidity of food and cooking time in iron cookware affect iron content?
More acidic foods and longer cooking times in iron cookware increase the amount of iron in the food.
How is supplemental iron absorbed compared to iron from food?
Supplemental iron is less well absorbed than iron from food.
What type of iron is found in supplements?
Ferrous iron.
When is supplemental iron best absorbed?
On an empty stomach for better absorption.
What is a common side effect of taking iron supplements?
Constipation.
Do you need to take vitamin C with iron supplements?
No, vitamin C is not needed because it converts ferric iron to ferrous iron, which is the form found in supplements.
iron RDA men
8 mg/day
iron RDA for women
18 mg/day (19-50 yrs)
8 mg/day (51+)
How many enzymes require zinc as a cofactor?
Zinc is required by more than 100 enzymes.
What types of enzymes are dependent on zinc?
Metalloenzymes, which are involved in metabolic processes, including the regulation of gene expression.
How does zinc affect cell membranes and DNA?
Zinc stabilizes cell membranes and DNA.
How does zinc protect the body?
Zinc helps protect cells from free radicals.
What role does zinc play in growth and development?
Zinc supports growth and development.
How does zinc impact immune function?
Zinc may help shorten the duration of the common cold.
How does zinc affect insulin?
Zinc is involved in the synthesis, storage, and release of insulin.
What is zinc’s role in blood clotting?
Zinc interacts with platelets in blood clotting.
How does zinc influence thyroid hormone function?
Zinc affects thyroid hormone function.
How does zinc impact behavior and learning?
Zinc influences behavior and learning performance.
What is zinc’s role in vision?
Zinc aids in producing retinal in visual pigments and retinol-binding protein (RBP).
How does zinc impact taste perception?
Zinc is involved in taste perception.
What role does zinc play in wound healing?
Zinc is essential for wound healing.
How does zinc affect sperm production?
Zinc is important for sperm production.
What role does zinc play in fetal development?
Zinc is critical for fetal development.
What is the absorption range of zinc?
Zinc absorption ranges from approximately 15-40%. As intake increases, absorption decreases, and vice versa.
What is the primary transport protein for zinc?
Albumin is the primary transport protein for zinc.
Which other protein does zinc bind to besides albumin?
Zinc also binds to transferrin.
How does zinc interact with other minerals?
Zinc interacts with copper (Cu) and iron (Fe).
Where are zinc losses primarily excreted from the body?
Zinc losses are primarily through feces.
Besides feces, where else can zinc be lost from the body?
Zinc can also be lost through urine, shed skin, hair, sweat, menstrual fluids, and semen.
In which regions is zinc deficiency most common?
Zinc deficiency is uncommon in developed countries but accounts for 1 in 20 childhood deaths in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
What are some symptoms of severe zinc deficiency?
Severe growth retardation, hypogonadism, hindered digestion and absorption leading to diarrhea, and impaired immune system resulting in infections.
How does chronic zinc deficiency affect the CNS and brain?
Chronic zinc deficiency can lead to damaged CNS, poor motor development, and cognitive performance.
What effect does zinc deficiency have on vitamin A?
Zinc deficiency impairs vitamin A metabolism, leading to symptoms of vitamin A deficiency.