Endocrinology (9.1-9.20)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Hormone
regulatory substance to stimulate specific cells or tissues
Endocrine
Enzyme or hormone that acts inside the body
Exocrine
enzyme or hormone that acts outside the body
Tropic Hormone
causes cell to secrete another hormone
trophic hormone
causes a direct effect on the cell
glucocorticoid
affects glucose level in blood
mineralocorticoid
affects the sodium and potassium levels in blood
diurnal variation
concentration varies throughout the day
steroid hormones
hydrophobic, derived from cholesterol, bound to carrier and bind to receptors in nucleus of cells
polypeptide hormones
formed by amino acids and have a short life, bind to membrane bound receptor and uses a second messenger for effect
positive feedback loop
signal tells the body to accentuate the process, blood clotting and birth
negative feedback loop
common pattern, signal changes in response to opposite direction, maintaining homeostasis, body temp
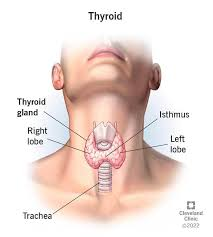
thyroid gland
butterfly shaped gland in the neck for hormone production
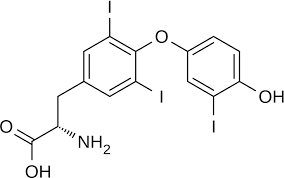
triiodothyronine T3
active tissue type, binds to receptors at a greater rate
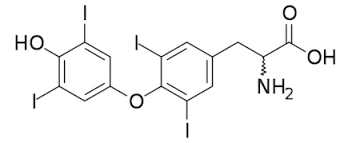
thyroxine T4
inactive type to get secreted and convert to the other TH
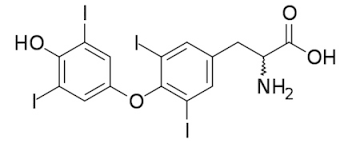
TH metabolism
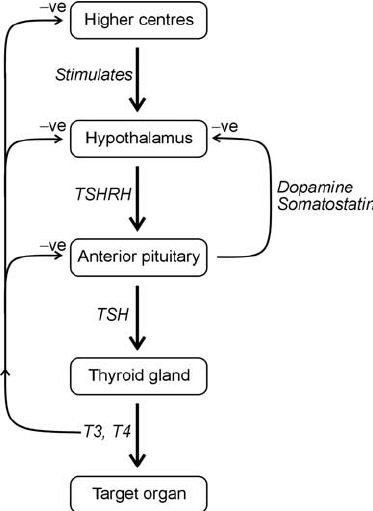
Hashimoto thyroiditis
primary hypothyroidism, TSH high, T4 and T3 low, anterior pituitary telling thyroid to produce more but thyroid isnt listening
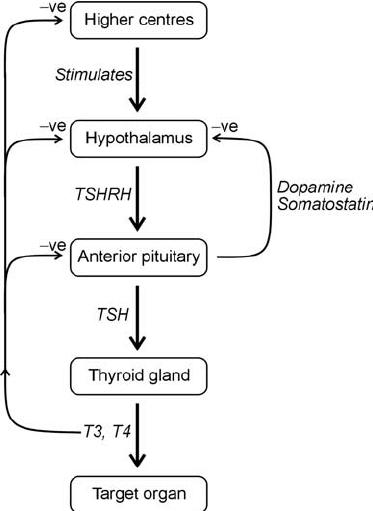
pituitary adenoma
secondary hypothyroidism, everything low, pituitary problem
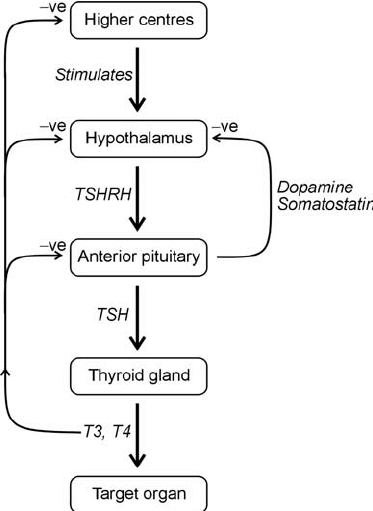
Graves’ disease
primary hyperthyroidism, TSH low T3 and T4 high, the problem is the gland and not anything upstream
non-thyroid illness THI
abnormally low T3 and T4 without an apparent problem in thyroid, generally other diseases present causes body to not secrete thyronine
Addison disease
adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, adequate ACTH, but the adrenal glands dont secrete enough cortisol
cushing syndrome
primary hypercortisolism, adrenal glands autonomously hypersecrete cortisol and ACTH is low, pink/purple stretch marks
hypercortisolism
excess exposure to cortisol in tissues, muscle weakness, stretch marks, difficult memory
hypocortisolism
adrenal insufficiency, unintentional weight loss, poor appetite
conn disease
adrenal gland produces too much aldosterone, salt and fluid in kidneys lead to hypertension
pheocromocytoma
overproduces catecholamines, low rate of malignancy, found in adrenal medulla
neuroblastoma
malignant neuroplasm in neural crest tissue anywhere in body, half found in children less than 3 years old.
hypopituitarism
panhypopituitarism
ancillary factors
9.15 differentiate the tests for hypo/hyperthyroidism
9.16 differentiate the tests for adrenal testing
hormones used in testing for carcinoid tumor
hormones used in testing for infertility testing
parathyroid hormone anomalies
principles of immunoassays for hormone testing