Sketchy Microbiology: Salmonella (Salmonella Enteritis, Salmonella Typhi)
1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
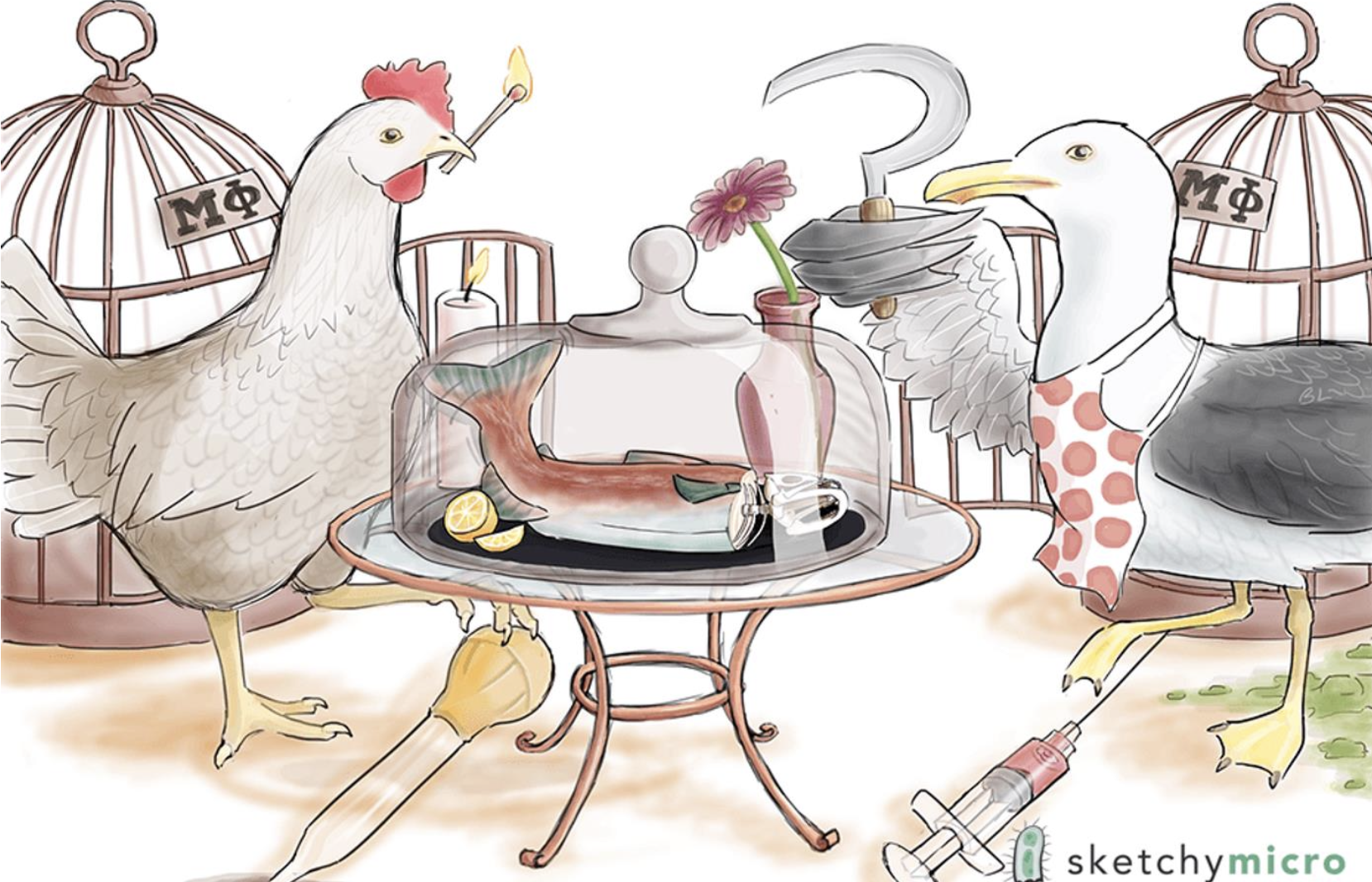

The salmon dinner — Salmonella
According to lecture there is a NEW classification. What is it?
There are 2 species;
Salmonella Enterica
Salmonella Bongori
However, most pathogens are from Salmonella Enterica species. Including S. Enterica, S. Serovar, S. Typhi.
What is common about all Salmonella?
Gram Negative Rod
Motile
Non-lactose Fermenting
Resistant to bile salts
H2S Producing
According to lecture a single change in antigen (H1) causes different diseases. What is the 2 groups?
Group B — found in S. Paratyphi → enteric fever
Group i — found in S. Typhi → gastroenteritis
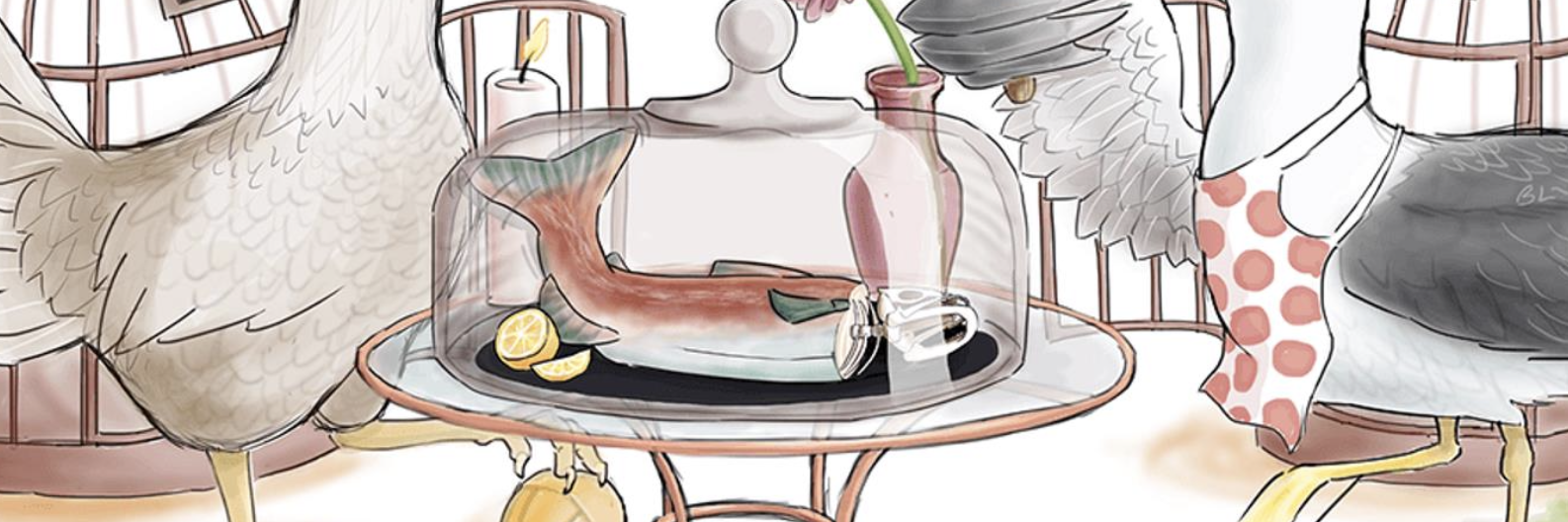
Hint: Red Hue
Red Color — Gram Negative
(Non-lactose Fermenter, White on MacConkey’s Agar)
Tail Flopping around — Motile

Black Plate — H2S Positive
(All motile enteric colonies stain black on hektoen agar)

Lemon — Acid Labile
(need high does to cause an infection. Patients w/ proton pump inhibitor are more susceptible to infection)
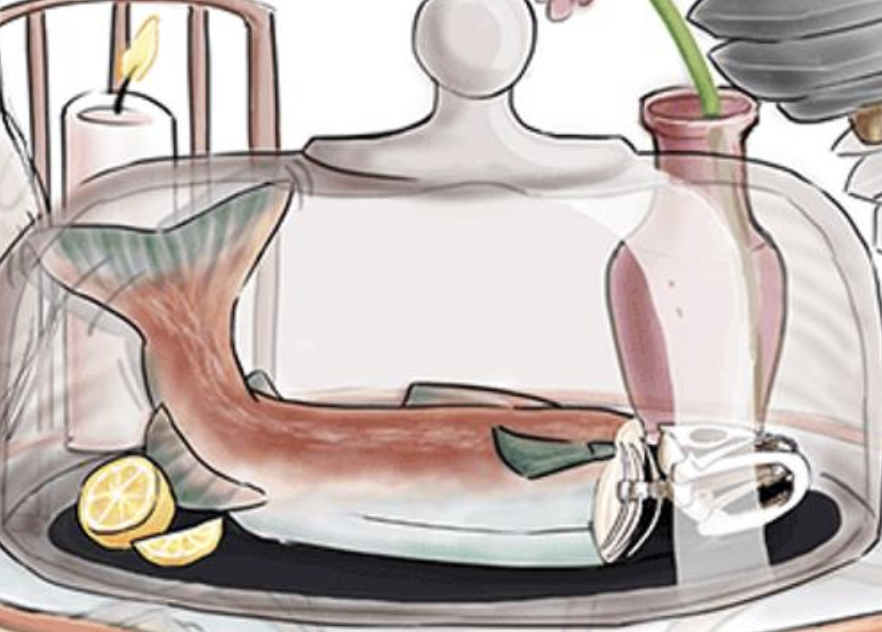

Glass Dome — Capsule
(Positive for citrate utilization turns indicator blue due to alkaline pH)
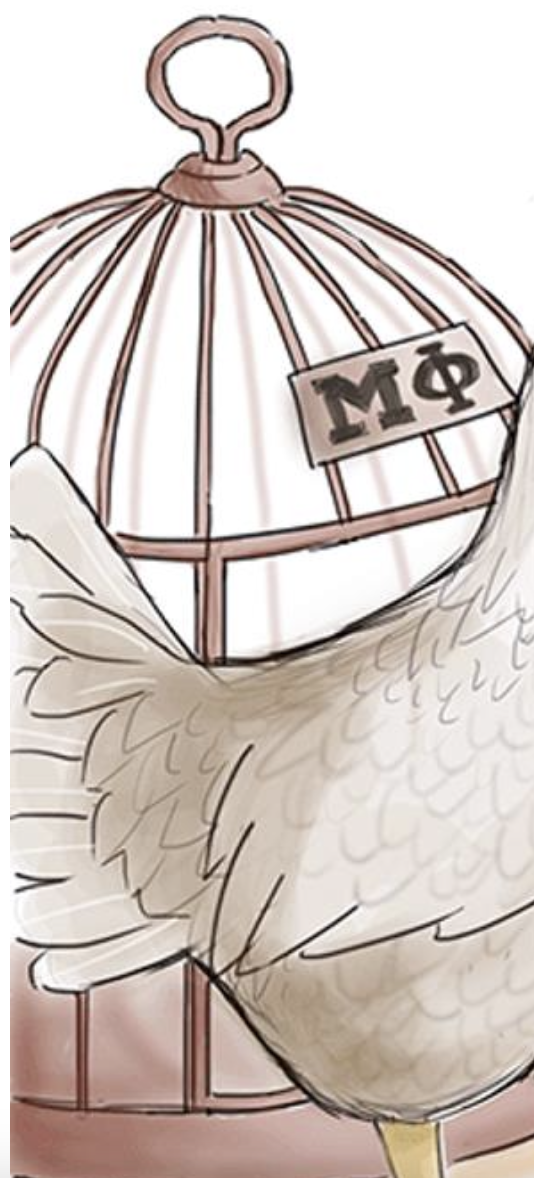

Bird Cages w/ MΦ — Facultative Intracellular
(Invades through colon through the macrophages to get into the colon)
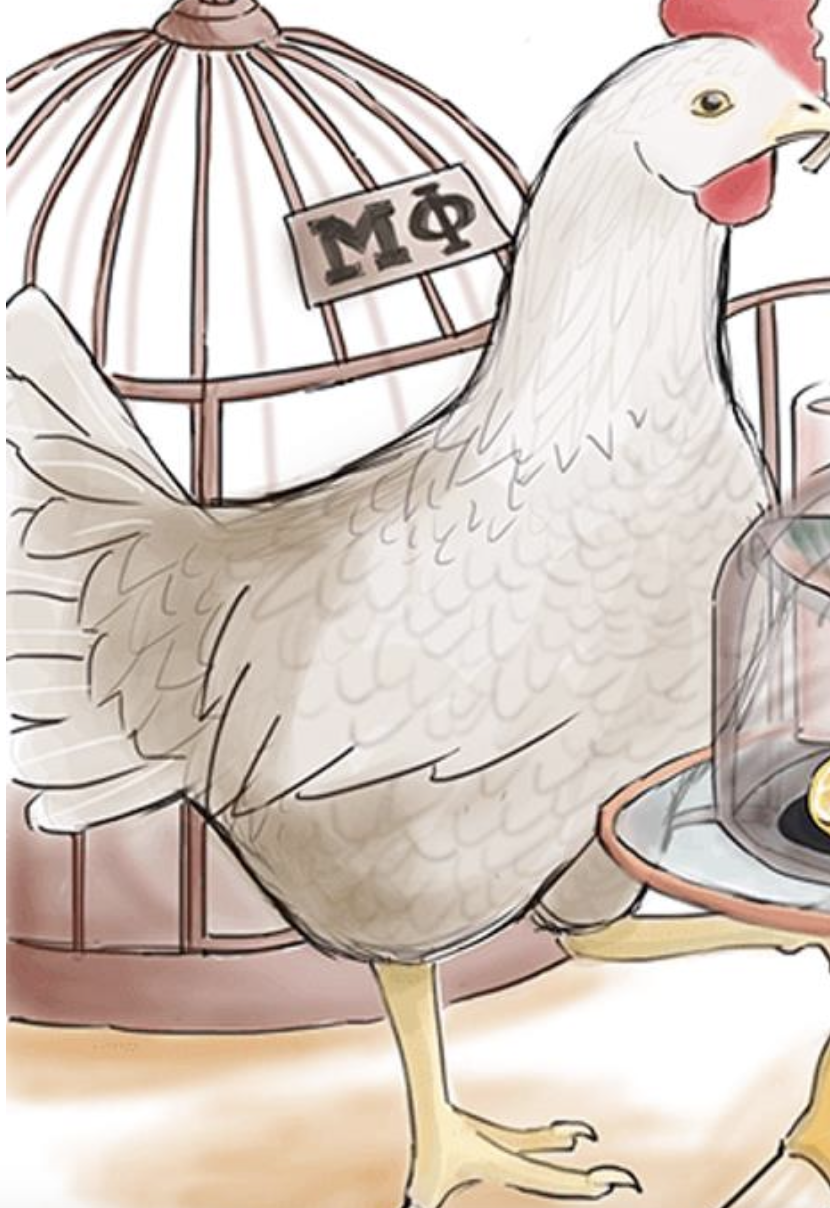

Hint: Which one is represented by the chicken
Chicken — Salmonella Enteritis

Chicken — Salmonella Enteritis most commonly acquired from Poultry, Eggs, Swine.
24 - 72h incubation period
(Food-borne outbreak)

Candle — Salmonella Enteritis causes inflammatory diarrhea, and Gastroenteritis
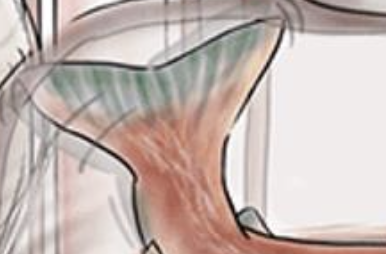
Turkey Baster — Salmonella Enteritis contains Type 3 secretion system; detects eukaryotic cells that will increase infectivity
What is the clinical progression of S. Enteritis?
Ingestion of S. Enteritis → Absorbed into epithelial cells of small intestine → Baceria penetrate cells and migrate to lamina propria of ileocecal region → multiply in lymphatic follicle → hypertrophy and hyperplasia → inflammatory response → prostaglandin release → cAMP stimulated → loose stool / diarrhea
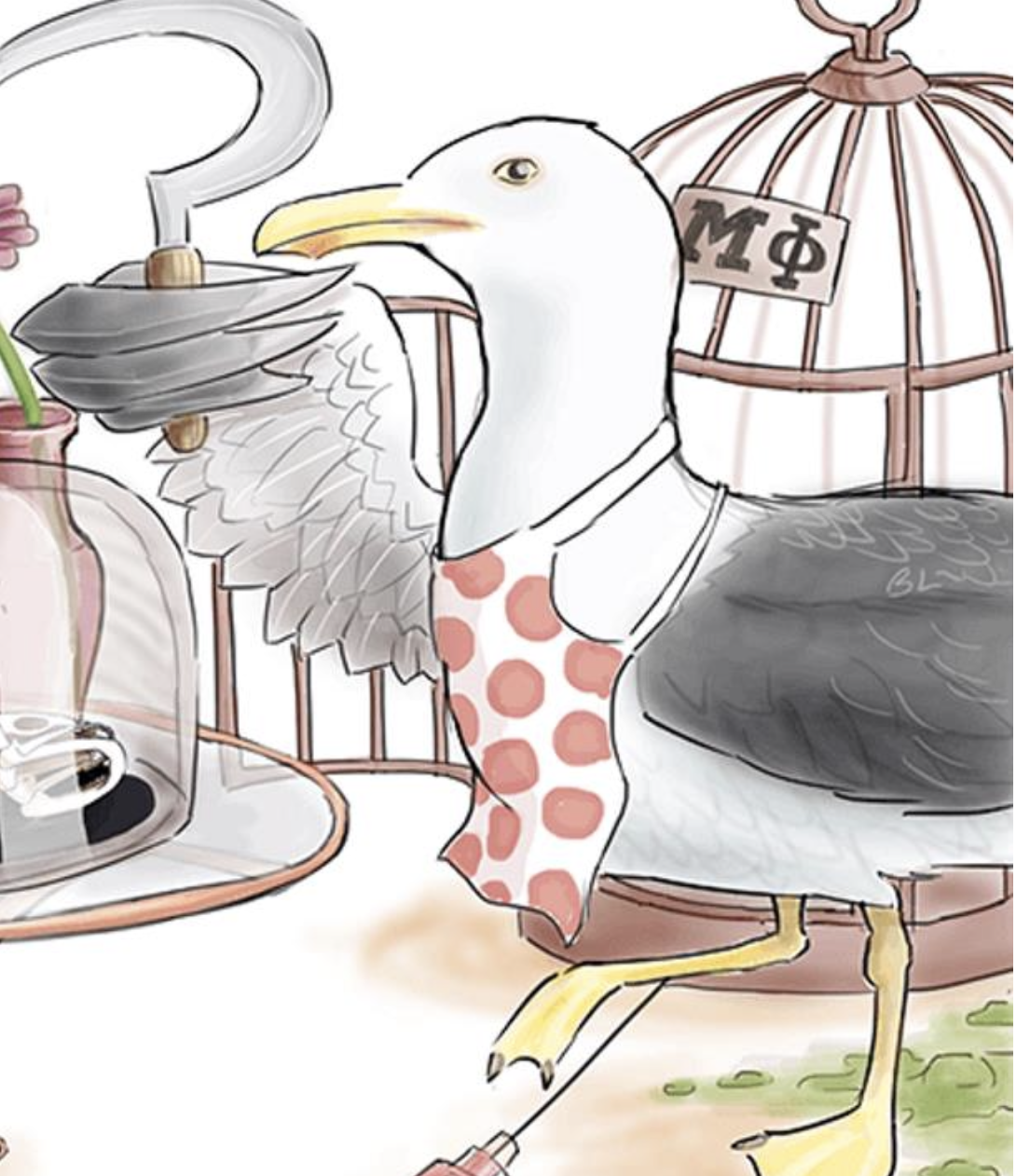

Seagull — Salmonella Typhi
SeaGULL = GALL bladder reservoir of carriers
What do we knw about S. Typhi
Strictly a human host
Causes Typhoid Fever
S. Paratyphi A,B,C cause Enteric Fever
Fecal-Oral Transmission
10-14 day incubation
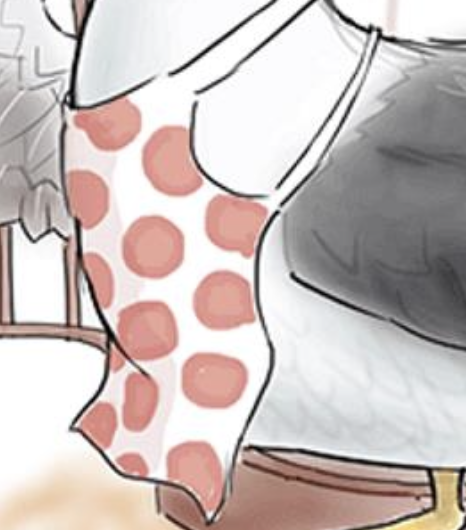
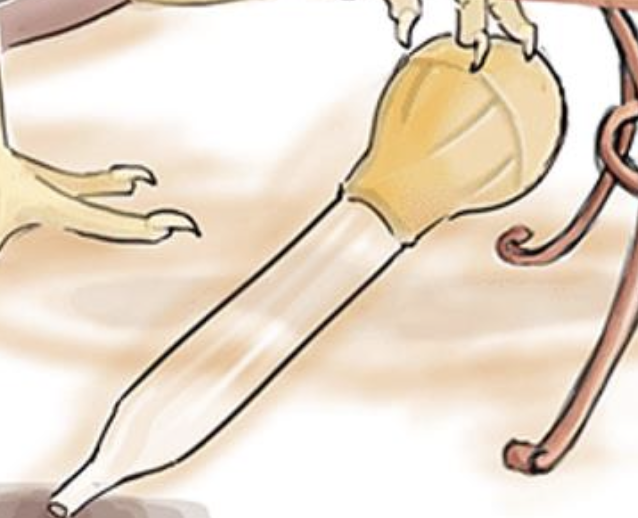
Chef Apron — think “Typhoid Mary”
(She knew she has Typhoid and continued cooking consciously infecting people; charged with second degree murder)

Hint: Spots
Red spots on apron — 25% of Enteric Fever patients get red spots on their stomach due to infection

Fish Bones — Salmonella Typhi is #1 cause of osteomyelitis in adults with sickle cell
Sickle — Sickle Cell Disease
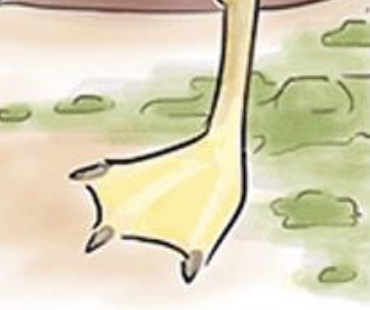
Bird Shit — S. Typhi can cause "pea soup" diarrhea
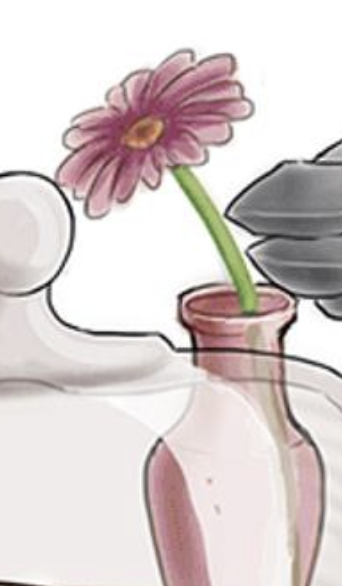
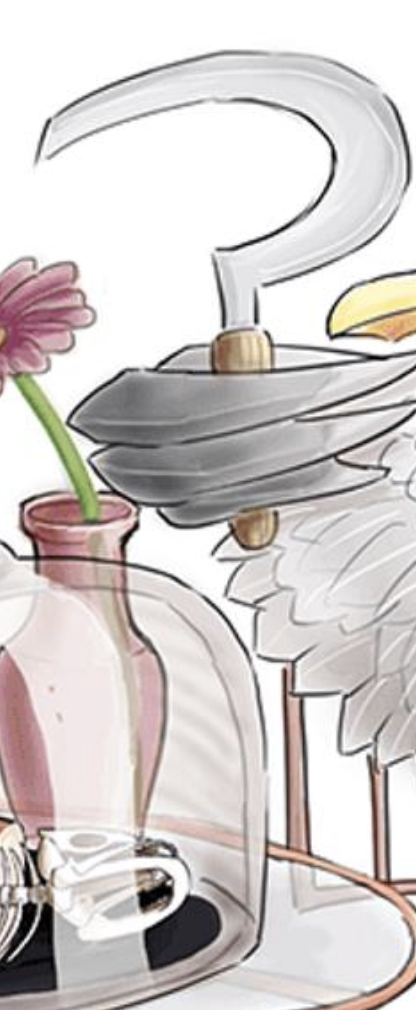
Flower on table — S. Typhi is treated with fluoroquinolone, or a cephalosporin (ceftriaxone)
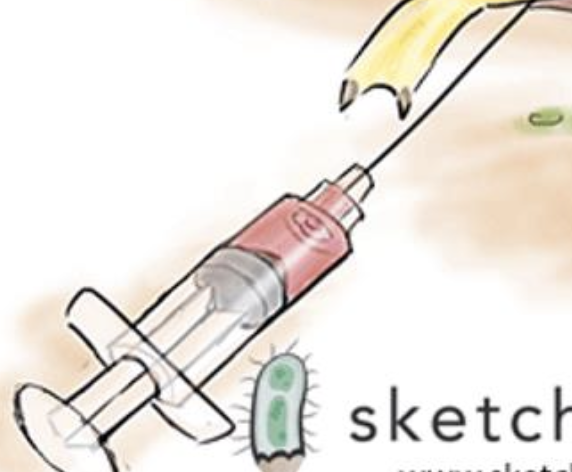
Syringe — S. Typhi has a Live, Attenuated
Vaccine
What is the clinical progression of Enteric Fever (Typhoid Fever)?
S. Typhi is ingested → Passes through ileocecal epithelial cells → Intraluminal multiplication → Macrophages engulf it (but its still viable) → Intracellular multiplication in Liver, Spleen, Bone Marrow → Necrosis, Hemorrhage, Perforation of Intestinal wall → re-enters bowels → gastrointestinal symptoms