Oxygen Dissociation Curve
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
direction of Deoxyhemoglobin + O2 ↔ Oxyhemoglobin depends on
partial pressure of oxygen (PO₂) in blood & affinity between hemoglobin (Hb) & O₂
Compounds that yield positively charged hydrogen ions in solution
acids
Compounds that yield (-) charged hydroxyl ions in solution
bases
Pulmonary ventilation helps remove H⁺ from the blood through which reaction?
bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) reaction
Increased ventilation results in CO2 exhalation which has what affect on PCO2?
↓ PCO2 & H+ concentration (pH increase) → more basic
↓ ventilation results in buildup of CO2 which has what affect on PCO2 & H+?
↑ PCO2 & H+ concentration (pH ↓), more acidic
Changes in pH affect the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve. When blood pH ↓ (more acidic), strength of bonds between oxygen & hemoglobin weakens, leading to ↑ oxygen unloading to the tissues. What is this phenomenon called?
bohr effect
Myoglobin (Mb) – protein in skeletal & cardiac muscle shuttles
O2 from the cell membrane to the mitochondria
Mb has a higher affinity for
O2 than hemoglobin
what is the Ratio of ventilation rate to oxygen consumption (# of L of air breathed for every 100 mL of oxygen consumed)
ventilatory equivalent
What is the exercise intensity or relative intensity at which blood lactate begins an abrupt ↑ above the baseline concentration?
Lactate threshold (LT)
The steady increase in blood lactate accumulation that follows the lactate threshold (LT) is known as the
onset of blood lactate accumulation (OBLA)
What is the ratio of oxygen consumption to CO2 expiration?
>1.0 indicates glucose utilization
1.0 corresponds to maximal exercise. Greater CO2 production during glycolysis & anaerobic glycolysis
0.7 indicates primarily fat oxidation
respiratory exchange ratio (RER)
once lactate threshold is reached what fuel source did we switch to?
anaerobic
As exercise intensity ↑, a-vO2 difference ↑ This causes a
↓ in venous blood PO2 & an ↑ in venous blood PCO2 (more CO2 less O2)
the ability to inhale oxygen, or amount of ambient oxygen is not a limiting factor in
VO2 max (only adaptations in CO, ability to pull oxygen)
respiratory control center is in medulla oblongata, gets input from chemoreceptors which are sensitive to
PO2, PCO2, H+, and K+ concentrations in blood
Chemoreceptors located in medulla oblongata (central chemoreceptor), gets feedback from PCO2, & responds by sending signals to ↑ alveolar ventilation, therefore
elimination of CO2
Carotid body (peripheral chemoreceptor) measures ↑ in PCO2, & ↓ in PH/PO2. It responds by sending signals to
increase ventilation
Aortic body (peripheral chemoreceptor) detects increase in PCO2 & decreases in pH, so it responds by sending signals to
increase breathing (exhalation)
Muscle mechanoreceptors detect muscle contractile activity increases & respond by sending neural signals to the respiratory control center to
increase breathing in direct proportion to exercise intensity
Muscle chemoreceptors (also called muscle metaboreceptors) detect decrease in pH & increase in K+ & responds by
signaling to the respiratory control center to increase breathing
lung stretch receptors detect stretch of bronchi and respond by
limiting depth of inspiration
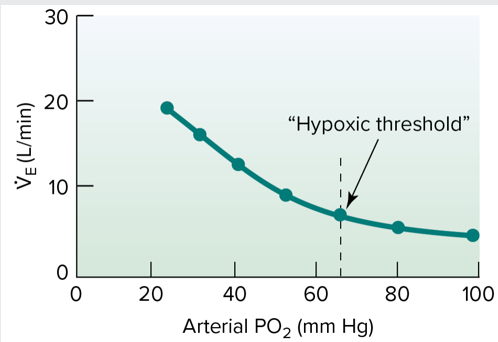
VE rises rapidly at the lower end of the curve as oxygen saturation drops, reaching the
hypoxic threshold
Submaximal exercise primary drive: Higher brain centers (central command), this is fine tuned by
Humoral chemoreceptors, Neural feedback from muscle
Heavy exercise shows a linear rise in VE occurs due to: ↑ blood H+ (from lactic acid) stimulates carotid bodies. leads to increases in
K+, body temp, & blood. catecholamines may also stimulate breathing