Cinco de Bio
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Isotope
Same number of protons but different number of neutrons
Carbohydrates
CHO
Proteins
CHON
Lipids
CHOP
Nucleic Acids
CHONP
Ionic bond
Formed between two atoms when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Covalent bond
Formed when electrons are shared between atoms
Nonpolar covalent
Covalent bond with equally shared electrons
Polar covalent
Covalent bond with unequally shared electrons
Basic/alkaline
High pH; release hydroxide ions (OH-)
Acidic
Low pH; release hydrogen ions (H+)
Note: pH scale is logarithmic (pH of 3 is 10 times more acidic than pH of 4)
Note: pH scale is logarithmic (pH of 3 is 10 times more acidic than pH of 4)
Dehydration synthesis
Formation of polymers; a water molecule is lost
Hydrolysis
Polymers are broken down into monomers; water is added to break the bond between the monomers
Starch
Polysaccharide that stores sugar in plants
Glycogen
Polysaccharide that stores sugar in animals
Cellulose
Polysaccharide that’s a part of cell walls in plants
Amino acids
Organic molecules that serve as the building blocks of proteins
Note: amino acids differ only in the R-group (aka side chain)
Note: amino acids differ only in the R-group (aka side chain)
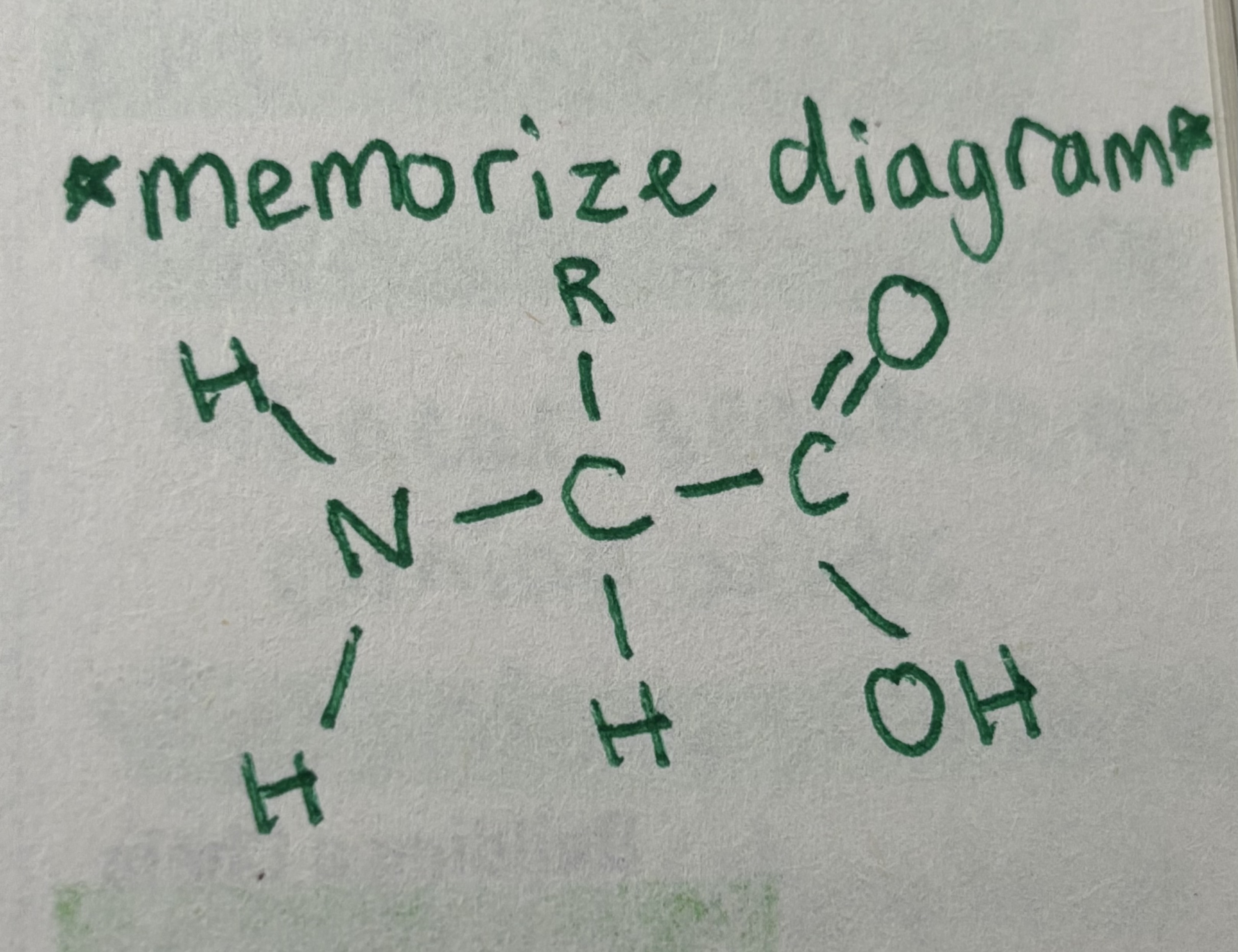
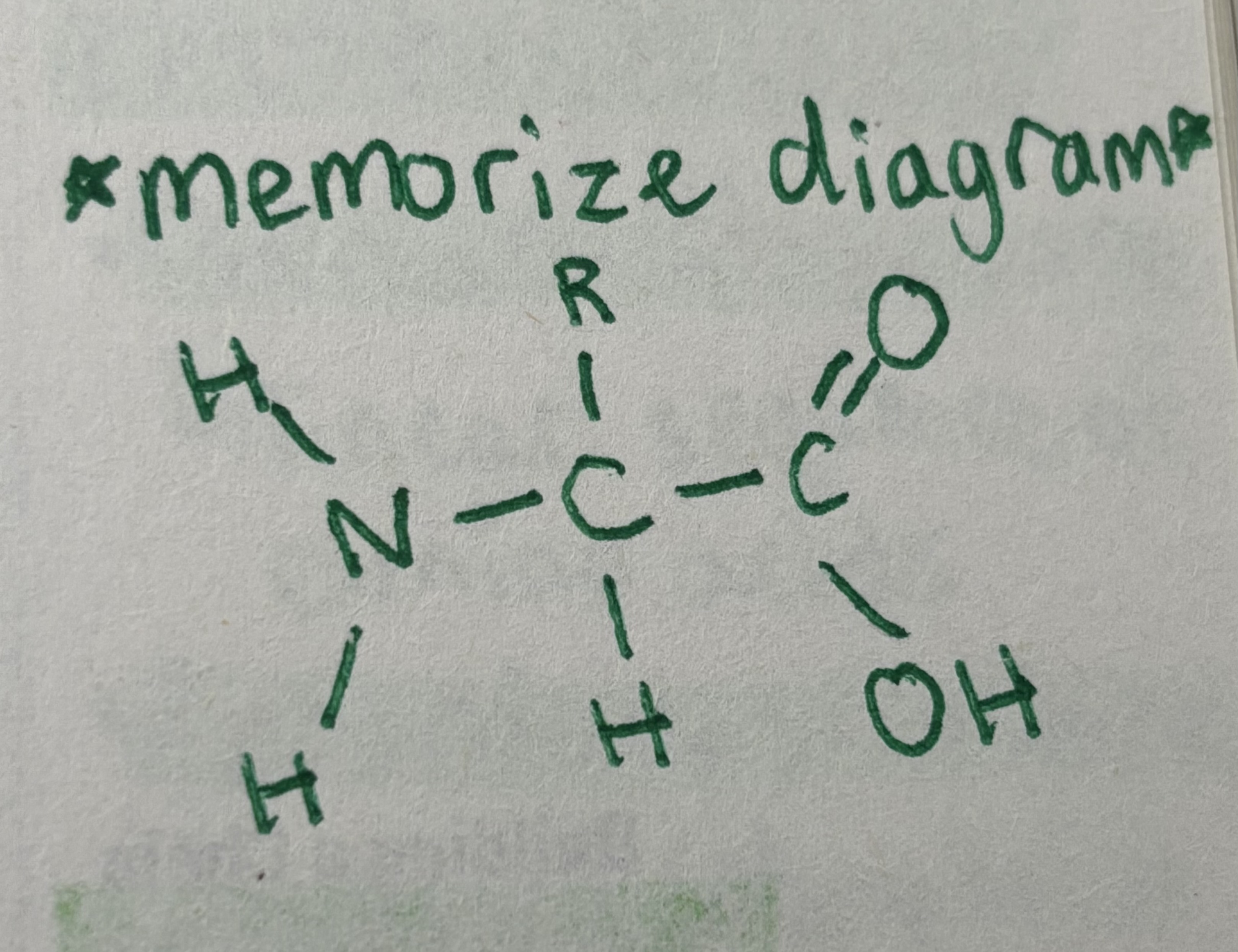
Hydrophobic
Non-polar and uncharged
Hydrophilic
Polar and charged
Dipeptide
Two joined amino acids
Peptide bond
Bond between two amino acids
Protein folding primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids
Protein folding secondary structure
Coiled (alpha helix) or zigzagged (beta-pleated sheet) version of the primary structure
Protein folding tertiary structure
Amino acids that were initially far away from each other are now able to interact with each other; minimizes free energy and locks the molecule in a stable 3D shape
Protein folding quaternary structure
Several different polypeptide chains interact with each other
Chaperone proteins (chaperonins)
Help protein folding
Saturated fatty acid
Straight and stackable
Unsaturated fatty acid
Bendy and not stackable
Cholesterol
Lipid that increases membrane fluidity (except at very high temperatures when it helps to hold things together instead)
Prokaryote
Cytoplasm, free DNA in the nucleoid, cell wall, plasma membrane, small ribosomes, flagella, capsule
Eukaryote
Plasma membrane, nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, mitochondria, lysosomes, centrioles, vacuoles, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cilia and flagella
Plasma membrane
Outer envelope; phospholipid bilayer
Nucleus
Largest organelle, home of DNA
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
Endoplasmic reticulum
Provides mechanical support while aiding in intracellular transport (rough er compartmentalizes the cell, smooth er makes lipids, hormones, and steroids and breaks down toxic chemicals
Golgi complex
Modifies, processes, and sorts products from rough er protein synthesis; package in vesicles and send to plasma membrane
Mitochondria
Convert energy from organic molecules into useful energy for the cell (ATP)
Lysosomes
Carry digestive enzymes to break down old, worn out organelles, debris, or large ingested particles
Centrioles
Produce microtubules for cell division
Vacuoles
Fluid-filled sacs that store water, food, waste, salts, or pigments
Peroxisomes
Detoxify various substances, producing H2O2 as a byproduct
Cytoskeleton
Holds a cell together and enables it to keep its shape
Cilia and flagella
Propel cells
Facilitated transport
Proteins act as tunnels through plasma membrane
Simple diffusion
The molecule that is diffusing is hydrophobic; non polar molecule drifts through the cell membrane without trouble
Facilitated diffusion
Requires help on channel-type protein
Osmosis
Diffusion of water
Active transport
Movement against the natural flow; ex. sodium potassium pump
Endocytosis
Cell membrane engulfs the substance
Bulk flow
One-way movement of fluids brought about by pressure
Dialysis
Diffusion of solutes across a selectively permeable membrane
Exocytosis
Transport of large particles out of the cell
Bioenergetics
Study of how cells release energy
First law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed; the sum of the energy in the universe is constant
Second law of thermodynamics
Energy transfer leads to less organization; the universe tends toward disorder (entropy)
Note: in order to power cellular processes, energy input must exceed energy loss
Note: in order to power cellular processes, energy input must exceed energy loss
Exergonic reactions
Products have less energy than the reactants; energy is released
Endergonic reactions
Require an input of energy
Activation energy
Energy needed to reach transition state
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up reactions
Enzyme specificity
Each enzyme catalyzes only one kind of reaction
Substrate
Targeted molecules in enzyme reactions
Active site
Location of enzyme-substrate reaction
Induced fit
Enzyme has to change its shape slightly to accommodate the shape of the substrates
Cofactors
Help enzymes catalyze reactions
Temperature and enzymes
Too hot means denatured, too cold means not moving
Saturation point
Concentration where all of the enzyme in a reaction is bound by substrate
Allosteric site
Enzymes can be turned on or off by things that bind to them at these sites or active sites
Competitive inhibitor
Blocks the intended substrate from getting into the active site (same shape)
Allosteric inhibitor
Inhibitor binds to the allosteric site
Noncompetitive inhibition
Distorts the enzyme shape so it can’t function
Adenosine triphosphate equation
ATP —> ADP + Pi [loose phosphate] + energy
Cellular respiration
Process of breaking down sugar and making ATP
Photosynthesis
Process by which light is converted to energy; 6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Note: prokaryotic photosynthesis likely contributed to the production of oxygen in the atmosphere
Note: prokaryotic photosynthesis likely contributed to the production of oxygen in the atmosphere
Light dependent reactions
Photons (energy units) of sunlight activate chlorophyll and excite electrons; these electrons are passed down a series of electron carriers, ultimately producing ATP and NADPH
Light independent reactions
Products of light dependent reaction (ATP and NADH) combine with CO2 to make carbohydrates; along the way, water is split and oxygen gets released
Phosphorylation
Light energy is used to make ATP
Absorption spectrum
Shows how well a certain pigment absorbs electromagnetic radiation
Emission spectrum
Gives information on which wavelengths are emitted by a pigment
Chlorophyll a
Absorbs mostly violet to blue light plus red
Chlorophyll b
Absorbs violet to green light
Cartenoids
Absorb mostly violet to green-yellow light
Photolysis
To replenish the electrons in the thylakoid, water is split into oxygen, hydrogen ions, and electrons
Note: as the energized electrons from photosystem II travel down the electron transport chain, they pump hydrogen ions into the thylakoid lumen; a protein gradient is established; as the hydrogen ions move back into the strong through ATP synthase, ATP is produced; after the electrons leave photosystem II, they go to photosystem I, where they are passed through a second electron transport chain until they reach the final electron acceptor NADP+ to make NADPH
Note: as the energized electrons from photosystem II travel down the electron transport chain, they pump hydrogen ions into the thylakoid lumen; a protein gradient is established; as the hydrogen ions move back into the strong through ATP synthase, ATP is produced; after the electrons leave photosystem II, they go to photosystem I, where they are passed through a second electron transport chain until they reach the final electron acceptor NADP+ to make NADPH
Thylakoid membranes
Location of light reactions of photosynthesis
Carbon fixation
CO2 from the air is converted into carbohydrates; occurs in the stroma of the leaf
Calvin cycle
Dark reactions of photosynthesis (light-independent)
Input of light-dependent reactions
Photons and H2O
Output of light-dependent reactions
NADPH, ATP, and O2
Input of light-independent reactions/calvin cycle
3CO2, 9 ATP, and 6NADPH
Output of light independent reactions/calvin cycle
Sugar
Photorespiration
Wasteful process that uses ATP and O2, produced more CO2, and doesn’t produce any sugars; occurs when less CO2 is available and O2 accumulates
Cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Aerobic respiration
Production of ATP in the presence of oxygen
Anaerobic respiration
Production of ATP in the absence of oxygen
Aerobic respiration steps
Glycolysis
Formation of acetyl-CoA
Krebs cycle (aka citric acid cycle)
Oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport chain and chemiosmosis)
Note: in the first three stages, glucose is broken down and energy molecules are made; in the fourth stage, energy is unloaded and used to make ATP