BIO1108 FINAL
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:20 PM on 1/8/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
1
New cards
Innate immunity
present BEFORE any exposure to pathogens, nonspecific
2
New cards
What are the barrier defenses of innate immunity
Mucus skin (acidic), exoskeletons in incests
3
New cards
What are the internal defenses of innate immunity
Macrophages (white blood cells that eat foreign organisms in response to histamine),
Natural Killer Cells or NK (kills abnormal cells)
Antimicrobial peptides (produced by incests)
Natural Killer Cells or NK (kills abnormal cells)
Antimicrobial peptides (produced by incests)
4
New cards
Acquired immunity
A specific response to pathogens, unique to vertebrates
5
New cards
What are the defenses of acquired immunity
1. B-cell lymphocytes (white blood cells made in bones that can produce antibodies)
2. T-cell lymphocytes (mature in thymus gland and works with MHC proteins)
3. MHC proteins (highly variable and bind to antigens inside the cell)
2. T-cell lymphocytes (mature in thymus gland and works with MHC proteins)
3. MHC proteins (highly variable and bind to antigens inside the cell)
6
New cards
Fission/budding
type of asexual reproduction, animal splits into two new ones or new individuals grow out of parents body
7
New cards
Fragmentation
type of asexual reproduction, broken off pieces can grow into new organisms
examples: starfish, sponges, cnidarians, some segmented worms, sea squirts
examples: starfish, sponges, cnidarians, some segmented worms, sea squirts
8
New cards
Parthenogenesis
type of asexual reproduction, egg develops without being fertilized. can be haploid or diploid
examples: many fews, aphids, a few fish, frogs, lizards (Komodo dragons and hammerhead sharks)
examples: many fews, aphids, a few fish, frogs, lizards (Komodo dragons and hammerhead sharks)
9
New cards
Where does fertilization occur
In the oviduct (fallopian tubes)
10
New cards
What stage of development does the embyro implant into the uterine lining
At the blastocyst (lopsided blastula=hollow ball of cells) stage (???????)
11
New cards
What major organ or system does the ectoderm form?
Nerves and external tissue, in chordates a neural fold forms in the dorsal ectoderm of the embryo
12
New cards
What major organ or system does the endoderm form
interior lining of gut and respiratory system + organs that directly pour into gut but don’t have muscle-e.g.g. pancreas, liver, etc
13
New cards
What major organ or system does the mesoderm form
middle tissues like blood, muscle, cartilage, bone, and organs with those tissue
14
New cards
How is the neural fold formed in the embryo?
As the grove deepens, the ectoderm pinches together above, forming the neural tube
15
New cards
What genes are involved in patterning during embryonic development?
Hox/homeobox genes program complex patterning and segmentation (head, body, tail, limbs, etc)
16
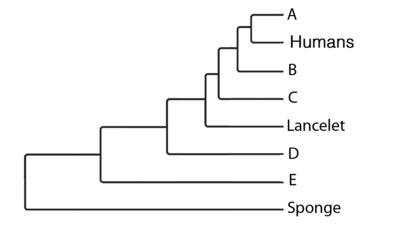
New cards
What is the difference in the complexity of hox genes when comparing chordates and vertebrates?
Chordates have few hex copies
Vertebrates/humans (also chordata) have more copies differentially expressed in different tissues during development.
- vertebrates go through multiple whole genome duplications-polyploidy events that give us 4 times the number of hox genes
Vertebrates/humans (also chordata) have more copies differentially expressed in different tissues during development.
- vertebrates go through multiple whole genome duplications-polyploidy events that give us 4 times the number of hox genes
17
New cards
Know how nerve cells propagate a signal and how a signal is transmitted from one nerve cell to the next
??????
18
New cards
Organismal Ecology
subfield of ecology, studies how an organism's structure, physiology, and behavior meet the challenges posed by the environment
19
New cards
Population ecology
subfield of ecology, focuses n the factors that affect how many individuals of a particular species live in an area and distribution of alleles in those populations
20
New cards
Community ecology
subfield of ecology, deals with interations between species in a community
21
New cards
Ecosystem ecology
subfield of ecology, emphasizes energy flow and chemical cycling among the various biotic and abiotic components
22
New cards
landscape ecology
subfield of ecology, deals with arrays of ecosystems, how they are arranged in geographic regions, and how they exchange energy, organisms, etc.
23
New cards
Global ecology
subfield of ecology, studies the functioning and distribution of organisms across the biosphere (the sum of all the planet's ecosystems)
24
New cards
What are the major causes of the variation in temperature, wind, and precipitation across the planet?
1. Angle of sunlight: affected by latitude, seasons, and local topography. Sunlight has to pass through more atmosphere near the poles, fewer photons per land area.
2. Global wind patterns: rooted in points at the equator moving much faster than points near the poles during the earth's revolution
- a residual effect of displaced air is wind, can be strong at the poles and the equator
- ascending moist air causes lots of rainfall near equator
- descending dry air at 30 degrees latitude leads to deserts
3. Mountains: has significant effect on the amount of sunlight that reaches an area, local temperature and rainfall patterns
- uplifted air cooling and dropping all moisture on the
windward side of mountains. This leaves only dry air once it
descends on the leeward side of the mountain range, which
LEADS TO RAIN SHADOW
2. Global wind patterns: rooted in points at the equator moving much faster than points near the poles during the earth's revolution
- a residual effect of displaced air is wind, can be strong at the poles and the equator
- ascending moist air causes lots of rainfall near equator
- descending dry air at 30 degrees latitude leads to deserts
3. Mountains: has significant effect on the amount of sunlight that reaches an area, local temperature and rainfall patterns
- uplifted air cooling and dropping all moisture on the
windward side of mountains. This leaves only dry air once it
descends on the leeward side of the mountain range, which
LEADS TO RAIN SHADOW
25
New cards
Climate
determines the distribution and structure of terrestrial biomes and has a great impact on the distribution of organisms.
- sometimes processes such as grazing or fire frequency
help differentiate biomes
- sometimes processes such as grazing or fire frequency
help differentiate biomes
26
New cards
Tropical forest
-Areas of relatively constant temperature and usually lots of rain
-Highest species diversity of any biome, especially with elevational gradients
-Highest species diversity of any biome, especially with elevational gradients
27
New cards
Desert
-low precipitation prevents the growth of trees, usually lots of open space between plants
-Cacti are only in North and South America, but cactus-like plants exist in the deserts of Africa, Australia, & Asia due to similar selective pressures.
-Cacti are only in North and South America, but cactus-like plants exist in the deserts of Africa, Australia, & Asia due to similar selective pressures.
28
New cards
Savanna
- grass-dominated ground habitat with evenly spaced, scattered trees
-Africa: lots of vegetation of grazing animals
-Southeastern US (including most of Southern GA): was formerly highly flammable Longleaf Pine/Wiregrass savanna
*Now only a few fragments in the area burn frequently such
as military bombing ranges (Ft. Benning and Stewart)
-Africa: lots of vegetation of grazing animals
-Southeastern US (including most of Southern GA): was formerly highly flammable Longleaf Pine/Wiregrass savanna
*Now only a few fragments in the area burn frequently such
as military bombing ranges (Ft. Benning and Stewart)
29
New cards
Chaparral
-shrubland prone to frequent fire in "Mediterranean" climates with very seasonal rainfall (usually cool)
-this is followed by periods of warm drought; fog from ocean assists in the survival of shrubs
-includes: Coastal California, South Africa, etc.
-this is followed by periods of warm drought; fog from ocean assists in the survival of shrubs
-includes: Coastal California, South Africa, etc.
30
New cards
Temperate Grassland
-frequent burns or grazing usually prevents tree establishment
-grass gets taller as rain increases
-Underlying rich soil makes it ideal to grow vast areas of grass crops (corn, wheat, barley, rye, etc.)
*This makes it one of the most degraded biomes
-Includes: US prairies, further west of Rocky Mt. rain shadow
-grass gets taller as rain increases
-Underlying rich soil makes it ideal to grow vast areas of grass crops (corn, wheat, barley, rye, etc.)
*This makes it one of the most degraded biomes
-Includes: US prairies, further west of Rocky Mt. rain shadow
31
New cards
Temperate Broadleaf Forest
-More widley distributed in Northern Hemisphere than Southern Hemisphere
-Many plant genera only found in China and East US
*Others found only in East US, Europe, and China
-Many plant genera only found in China and East US
*Others found only in East US, Europe, and China
32
New cards
Northern Coniferous Forest
-Only in Northern Hemisphere
-Conifer leaves (needles) don't dry out in cold, dry air
-Extends southward at higher elevations in the mountains of West North America
*Occurs at a few spots as far south as North Carolina in the
east
-Conifer leaves (needles) don't dry out in cold, dry air
-Extends southward at higher elevations in the mountains of West North America
*Occurs at a few spots as far south as North Carolina in the
east
33
New cards
Tundra
-Permafrost
-Layer of soil a few inches down that remains frozen all year
*Prevents the establishment of trees
-Cold, high winds
-short growing season limits plant height
-No land in southern hemisphere at proper latitude for Tundra
-Layer of soil a few inches down that remains frozen all year
*Prevents the establishment of trees
-Cold, high winds
-short growing season limits plant height
-No land in southern hemisphere at proper latitude for Tundra
34
New cards
High mountains
-habitats similar to tundra above the treeline
-Alpine Tundra
-Alpine Tundra
35
New cards
Photic zone
type of aquatic biome zonation, sufficient light for photosynthesis
36
New cards
Aphotic zone
type of aquatic biome zonation, little light penetrates
37
New cards
Benthic zone
type of aquatic biome zonation, the body of any body of water on the substrate
38
New cards
Pelagic zone
type of aquatic biome zonation, open water
39
New cards
Abyssal zone
type of aquatic biome zonation, oceanic benthic zone below 2000m
40
New cards
Oligotrophic lakes
-low nutrient levels
-low vegetation
-high oxygen
-clear water
-low vegetation
-high oxygen
-clear water
41
New cards
Eutrophic lakes
-high nutrient levels
-lots of vegetation
-high levels of decaying organic matter because of depleted oxygen, murky water
-lots of vegetation
-high levels of decaying organic matter because of depleted oxygen, murky water
42
New cards
What are the types of aquatic biomes?
1. Wetlands
2. Streams and Rivers
3. Estuaries
4. Intertidal Zones
5. Oceanic Pelagic Zone
2. Streams and Rivers
3. Estuaries
4. Intertidal Zones
5. Oceanic Pelagic Zone
43
New cards
Lakes
permanent bodies of standing water
44
New cards
Wetlands
-areas with saturated soil for significant portions of the year
*many also dry out for extended periods
-frequent on margins of lakes and ponds may be tree, shrub, or herbaceous plant dominated
*many also dry out for extended periods
-frequent on margins of lakes and ponds may be tree, shrub, or herbaceous plant dominated
45
New cards
Streams and Rivers
-flowing water, oxygen level depends on turbidity (mixing with air) caused by flow rate
-temperature and light are highly variable
-Move nutrients and aquatic organisms from biome to biome
-temperature and light are highly variable
-Move nutrients and aquatic organisms from biome to biome
46
New cards
Estuaries
-where rivers meet larger bodies of water with significantly different chemistry and organisms
-usually refers to freshwater rivers meeting saltwater sea/oceans
*can also occur where rivers flow into large lakes with unique chemistry
-usually refers to freshwater rivers meeting saltwater sea/oceans
*can also occur where rivers flow into large lakes with unique chemistry
47
New cards
Intertidal Zones
-places where tidal action creates unique ecosystems with organisms that can deal with inundation and desiccation twice daily for many areas
*further from the shoreline inundation many occur only
during extreme tide events
-can be rocky or sandy and extent of intertidal zones varies widely throughout the year
*biggest difference between high and low tide is usually
during the full moon
-Tidal action also travels very far upstream in larger rivers
*further from the shoreline inundation many occur only
during extreme tide events
-can be rocky or sandy and extent of intertidal zones varies widely throughout the year
*biggest difference between high and low tide is usually
during the full moon
-Tidal action also travels very far upstream in larger rivers
48
New cards
Oceanic Pelagic Zone
-open ocean
-typically low nutrient levels and low density of organisms
*except in areas of nutrient upwelling
-sometimes organisms concentrate around areas of food, but mostly widely spaced
-Despite low average density of organisms, vast area (70% of earth) means THIS BIOME CONTAINS A LARGE PORTION OF THE EARTH'S BIOMASS
-typically low nutrient levels and low density of organisms
*except in areas of nutrient upwelling
-sometimes organisms concentrate around areas of food, but mostly widely spaced
-Despite low average density of organisms, vast area (70% of earth) means THIS BIOME CONTAINS A LARGE PORTION OF THE EARTH'S BIOMASS
49
New cards
population
a group of individuals of a single species living in the same general area- highly variable in definition depending on the study
50
New cards
density
-the number of individuals per unit area or volume;
-the result of the interplay between processes that add individuals to a population and those that
remove individuals from it: Birth, Death, Immigration, Emigration
-the result of the interplay between processes that add individuals to a population and those that
remove individuals from it: Birth, Death, Immigration, Emigration
51
New cards
dispersion
the pattern of spacing among individuals within the boundaries of the population
52
New cards
Clumped dispersion
individuals aggregate in patches - may be influenced by resource availability and behavior (social organisms)
53
New cards
uniform dispersion
individuals are evenly distributed; very rare, but influenced by social interactions such as territoriality (e.g. nesting
penguins)
penguins)
54
New cards
random dispersion
the position of each individual is independent of other individuals
55
New cards
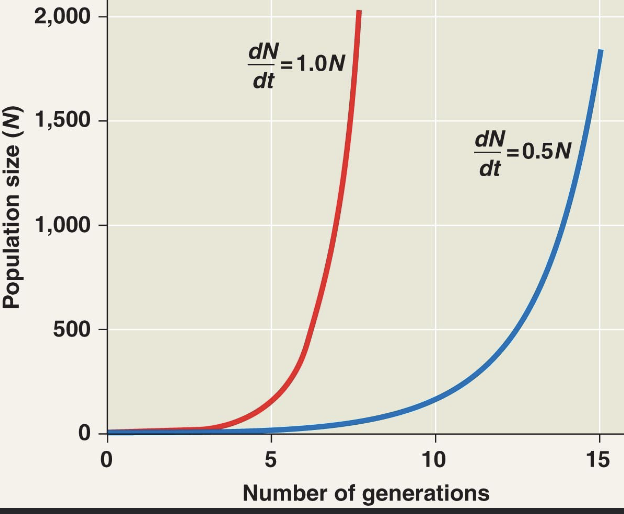
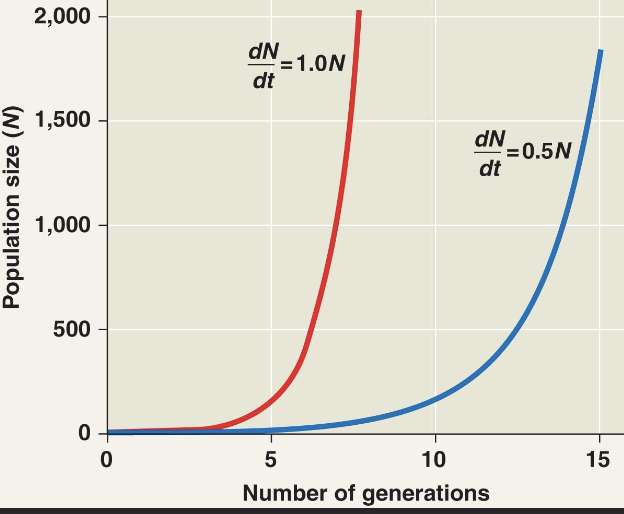
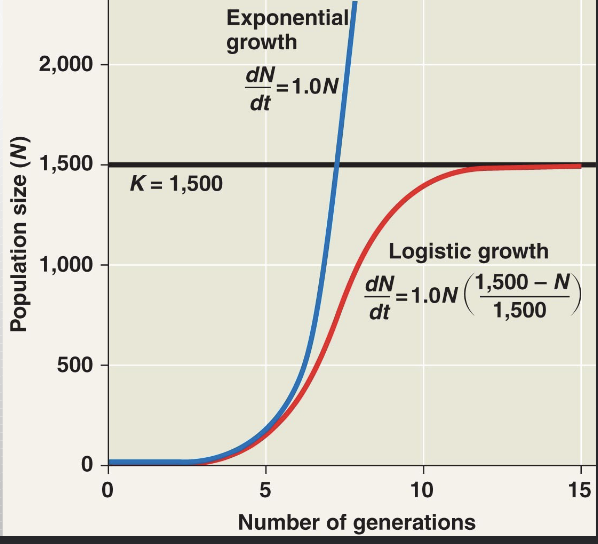
exponential population growth
population increase under idealized conditions
- cannot be sustained for long in most populations
-under these conditions, the rate of reproduction is at its maximum
*called the intrinsic rate of increase (r-max)
-this graph is usually a j-shaped curve
- the equation is dN/dt=r-maxN
*N=population size
* the result is the change in population over time
- cannot be sustained for long in most populations
-under these conditions, the rate of reproduction is at its maximum
*called the intrinsic rate of increase (r-max)
-this graph is usually a j-shaped curve
- the equation is dN/dt=r-maxN
*N=population size
* the result is the change in population over time
56
New cards
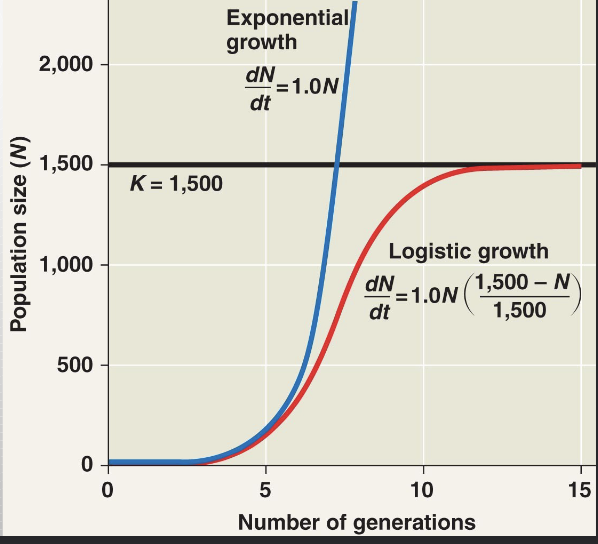
Logistic Population Growth
A more realistic population model limits growth by incorporating a carrying capacity
- carrying capacity (K) is the maximum population size the environment can support
-the equation is dN/dt=r-maxN (K-N)/K
* (=exponential growth x % of carrying capacity remaining)
- carrying capacity (K) is the maximum population size the environment can support
-the equation is dN/dt=r-maxN (K-N)/K
* (=exponential growth x % of carrying capacity remaining)
57
New cards
The human population
- increased slowly until 1650, then became exponential due to technological advancements
-the population grows by 1.5 million every week
- an equivalent of the US population is added every 4 years
-the population grows by 1.5 million every week
- an equivalent of the US population is added every 4 years
58
New cards
biological community
assemblage of populations of various species living close enough for potential interaction
59
New cards
interspecific interations
-what populations are linked to
- affects survival and reproduction (biological fitness) of species engaged in the interaction
- affects survival and reproduction (biological fitness) of species engaged in the interaction
60
New cards
Competition (-/-)
* + increases survival and reproduction, - decreases survival and reproduction
Predation = +/- (being eaten is bad for survival and reproduction!)
Herbivory = +/- (basically predation on something photosynthetic)
Parasitism = +/- (being slowly eaten by small, multicellular organisms)
Disease = +/- (being slowly eaten by small, unicellular organisms)
Mutualism = +/+ (benefits both; corals, lichens, mycorrhizal interactions, etc.)
Commensalism = +/0 (rare for an interaction to have absolutely no effect)
Predation = +/- (being eaten is bad for survival and reproduction!)
Herbivory = +/- (basically predation on something photosynthetic)
Parasitism = +/- (being slowly eaten by small, multicellular organisms)
Disease = +/- (being slowly eaten by small, unicellular organisms)
Mutualism = +/+ (benefits both; corals, lichens, mycorrhizal interactions, etc.)
Commensalism = +/0 (rare for an interaction to have absolutely no effect)
61
New cards
Interspecific competition
when species compete for a particular resource that is in short supply
62
New cards
Competitive exclusion
- what strong competition leads to
- the local elimination of one of the two competing species
- the local elimination of one of the two competing species
63
New cards
Ecological niche
the total of an organism’s use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment
64
New cards
niches
Ecologically similar species can coexist in a community if there are one or more significant difference in these
65
New cards
Cryptic coloration
camouflage, makes predators or prey difficult to see
66
New cards
Aposematic coloration
warning coloration for predators to stay away
67
New cards
Mimicry
one prey species may gain significant protection by mimicking the appearance of another
68
New cards
Batesian mimicry
a palatable or harmless species mimics an unpalatable or
harmful model
harmful model
69
New cards
Müllerian mimicry
two or more unpalatable species resemble each other, giving added protection to both
70
New cards
Three levels of biodiversity
-Genetic diversity
–Species diversity
–Ecosystem diversity (think of driving across Iowa vs. driving across California)
–Species diversity
–Ecosystem diversity (think of driving across Iowa vs. driving across California)
71
New cards
Extinction vortex
-occurs in a small population that is prone to positive feedback loops
KEY FACTORS DRIVING THE VORTEX:
1. loss of genetic variation necessary to enable evolutionary responses to environmental changes
2.excessive homozygosity of deleterious mutations
-(inbreeding depression)
KEY FACTORS DRIVING THE VORTEX:
1. loss of genetic variation necessary to enable evolutionary responses to environmental changes
2.excessive homozygosity of deleterious mutations
-(inbreeding depression)
72
New cards
Dominant species
most abundant or most biomass
73
New cards
invasive species
not naturally occurring, alters the species diversity of a community
74
New cards
Keystone species
not numerically dominant, but greatly affects the rest of the community
75
New cards
foundation species
change habitat and allow for a new community to develop
76
New cards
Invasive species
- a threat to biodiversity
-humans have moved species to new geographic regions
-introduced species that usually disrupt their new habitat/community
-islands are often vulnerable to the introduction of predators
-humans have moved species to new geographic regions
-introduced species that usually disrupt their new habitat/community
-islands are often vulnerable to the introduction of predators
77
New cards
Overexploitation
-a threat to biodiversity
-human harvesting of wild organisms at rates exceeding the populations' ability to rebound
-example: passenger piegon
-human harvesting of wild organisms at rates exceeding the populations' ability to rebound
-example: passenger piegon
78
New cards
Habitat loss and Fragmentation
-a threat to biodiversity
-human alteration of habitat is the single greatest threat to biodiversity
-Habitat destruction has brought about commercial, agricultural, recreational, and climate change
-natural landscapes are broken up, fragmenting habitat into small patches
-human alteration of habitat is the single greatest threat to biodiversity
-Habitat destruction has brought about commercial, agricultural, recreational, and climate change
-natural landscapes are broken up, fragmenting habitat into small patches
79
New cards
ecosystem
all organisms living in a biological community plus all the abiotic factors with which they interact
- involves two processes energy flow and chemical cycling
- involves two processes energy flow and chemical cycling
80
New cards
Energy flow
-Energy flows THROUGH ecosystem entering as light and exiting as heat,
-while matter cycles within them
-while matter cycles within them
81
New cards
Trophic efficiency
- percentage of production transferred from one trophic level to the next
- about 90% of energy is lost with each transfer in a food chain
-as a result, there is a sharp DECREASE in biomass at successively higher trophic levels
*it takes almost 10x as much land to generate
enough primary production to sustain a
CARNIVORE than it does to sustain a HERBIVORE
- about 90% of energy is lost with each transfer in a food chain
-as a result, there is a sharp DECREASE in biomass at successively higher trophic levels
*it takes almost 10x as much land to generate
enough primary production to sustain a
CARNIVORE than it does to sustain a HERBIVORE
82
New cards
Nutrient cycling
nutrient cycles that move matter through an ecosystem involve both biotic and abiotic components and are often called BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES
83
New cards
Global cycling nutrients
carbon, oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen
84
New cards
Local cycling nutrients
phosphorous, potassium, and calcium
85
New cards
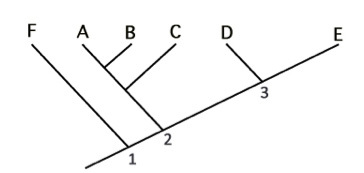
A grouping of species A, B, D, and E based on a trait that was present in the ancestor at node 2 would be considered:
Paraphyletic
86
New cards
If a locus in the genome has two alleles, and the frequency of one allele is 0.4 (40%), what is the frequency of heterozygotes in the population if the locus is in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
48
87
New cards
Which nutritional modes are found in eukaryotes? (circle all that apply)
Photoautotroph and Chemoheterotroph
88
New cards
Which of the following supergroups contains multicellular organisms?
SAR Clade
Archaeplastida
Unikonta
Only Archaeplastida and Unikonta
Archaeplastida
Unikonta
Only Archaeplastida and Unikonta
89
New cards
Which of the following is NOT an example or component of innate immunity?
MHC protiens
90
New cards
Nerves cannot partially fire.
true
91
New cards
What is the closest-related animal to us that is capable of reproduction through fragmentation?
Sea Squirt
92
New cards
Two flowers live in the same forest but bloom at different times of day. Their reproductive barrier is:
Temporal Isolation
93
New cards
Coal primarily comes from members of which modern plant lineage?
Gymnosperms
94
New cards
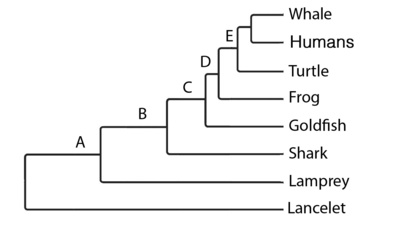
Which of these characteristics evolved at node E?
Skull
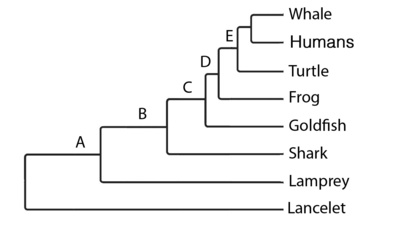
95
New cards
What ion rushes into the axon during an action potential ?
Chlorine
96
New cards
At what embryonic stage does implantation occur in placental mammals?
Blastula
97
New cards
The brain forms from what embryonic tissue layer?
Ectoderm
98
New cards
Ancient duplications in Hox genes directly lead to the increase in complexity seen in vertebrates relative to lancelets.
true
99
New cards
Match the following characteristics to the supergroup that best matches:
Contains humans - Unikonta
Contains plants - Archaeplastida
Contains Euglena - Excavata
Contains Malaria - SAR Clade
Contains plants - Archaeplastida
Contains Euglena - Excavata
Contains Malaria - SAR Clade
100
New cards
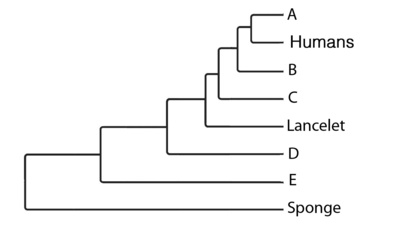
Match the letters to the organism that belongs in that place on the phylogenetic tree
A - Turtle
B - Frog
C - Shark
D - Earthworm
E - Coral
B - Frog
C - Shark
D - Earthworm
E - Coral