Photons and the Photoelectric Effect
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
what is a photon?
a discrete packet of energy
photons are what electromagnetic radiation is made up of when it interacts with matter
what is the equation for the energy of a photon?
E=hf
where E= energy of the photon, f=frequency of the emr, h=the Planck constant, 6.63×10-34
what is the energy of a photon in terms of its wavelength
E=hc/wavelength
what is an electronvolt?
the energy transferred to or from an electron when it moves through a potential difference of 1V (it is 1.6×10-19J)
what is the photoelectric effect?
when high energy electromagnetic radiation (which is made up of photons) is incident on a metal, electrons are emitted from the surface of the metal
what is a photoelectron?
an electron which has been emitted from the surface of a metal during the photoelectric effect
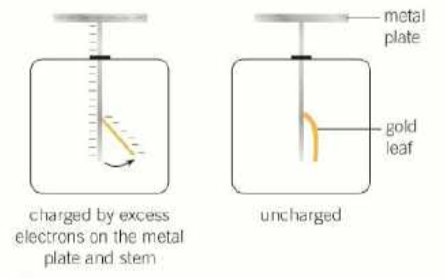
what is the gold-leaf electroscope practical?
in the beginning, the top plate is touched with a negative electrode, charging it with excess electrons
the negative charge from the plate spreads to the stem and the gold leaf
the stem and gold leaf both become negatively charged and drift away from each other
when zinc is placed on the electroscope and uv radiation is shone onto the zinc, the radiation causes photoelectrons to be emitted from the zinc
as the electroscope loses its negative charge, the gold leaf stops repelling the stem and drifts back towards it
what are the observations from the photoelectric effect?
photoelectrons are only emitted if incident radiation is above the threshold frequency
if incident radiation is above the threshold frequency, emission of photoelectrons is instantaneous
if incident radiation>threshold frequency, increasing intensity does not increase the kinetic energy; it just increases the number of electrons
to increase kinetic energy, increase frequency of incident radiation
what is the work function?
the minimum energy required to free an electron from the surface of a metal
each photon transfers its exact energy to one surface electron in a one-to-one interaction
how does increasing intensity increase the number of photoelectrons?
more intensity means more photons per second
as each photon interacts one-on-one with a surface electron, more photons per second means more photoelectrons emitted per second
rate of emission of photoelectrons is also directly proportional to intensity
how does increasing frequency increase kinetic energy of photoelectrons?
when frequency increases, energy of photon increases (E=hf)
when energy of photon increases, it is transferred to the electron, so the electron has more kinetic energy left after being emitted from the surface