AP Psych - Personality
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
personality
an individual’s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting
2
New cards
free association
* **psychoanalysis**
* method of exploring the unconscious where an individual relaxes and said whatever comes to mind
* method of exploring the unconscious where an individual relaxes and said whatever comes to mind
3
New cards
psychoanalysis
* **Freud’s** theory of personality
* attributes emotions to __unconscious__ thoughts
* attributes emotions to __unconscious__ thoughts
4
New cards
unconscious
* according to Freud, the ______ is a reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings and memories
* according to contemporary psychologists, information processing we are unaware of
* according to contemporary psychologists, information processing we are unaware of
5
New cards
id
* reservoir of unconscious energy that strives to satisfy sexual and aggressive drives
* operates of the **pleasure principle**, demanding immediate gratification
* operates of the **pleasure principle**, demanding immediate gratification
6
New cards
ego
* largely conscious, “executive” part of personality that mediates the demands of the **id, superego**, and reality
* operates on the **reality principle**, satisfying the **id’s** desires that will bring pleasure rather than pain
* operates on the **reality principle**, satisfying the **id’s** desires that will bring pleasure rather than pain
7
New cards
superego
* part of personality that represents internalized ideas
* provides standards for judgement and future aspirations
* provides standards for judgement and future aspirations
8
New cards
pleasure principle
driving force of **id** that seeks immediate gratification
9
New cards
reality principle
the opposing force to the instinctual urges of the **pleasure principle**
10
New cards
psychosexual stages
* childhood stages of development (oral, anal, phallic, latent, genital) proposed by **Freud**
* during these, the **id’s** pleasure-seeking focuses on distinct erogenous zones
* during these, the **id’s** pleasure-seeking focuses on distinct erogenous zones
11
New cards
oral stage
* one of **Freud’s** psychosexual stages; 0-18 months
* pleasure centered on the mouth (sucking, biting, chewing)
* pleasure centered on the mouth (sucking, biting, chewing)
12
New cards
anal stage
* one of **Freud’s** psychosexual stages; 18-36 months
* pleasure focused on bowel and bladder, coping w/ demands for control
* pleasure focused on bowel and bladder, coping w/ demands for control
13
New cards
phallic stage
* one of **Freud’s** psychosexual stages; 3-6 years
* pleasure zone is the genitals, coping w/ incestuous sexual feelings
* pleasure zone is the genitals, coping w/ incestuous sexual feelings
14
New cards
latent stage
* one of **Freud’s** psychosexual stages; 6 to puberty
* dormant sexual feelings
* dormant sexual feelings
15
New cards
genital stage
* one of **Freud’s** psychosexual stages; puberty on
* maturation of sexual interests
* maturation of sexual interests
16
New cards
Oedipus complex
**Freud’s** idea that a boy has sexual desires toward his mother and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival father
17
New cards
Electra Complex
* opposite of **Oedipus complex**
* **Carl Jung’s** idea that a girl has sexual desires toward her father and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival mother
* **Carl Jung’s** idea that a girl has sexual desires toward her father and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival mother
18
New cards
identification
according to **Freud**, the process by which children incorporate their parents’ values into their developing **superegos**
19
New cards
fixation
according to **Freud**, the lingering focus on unresolved pleasure seeking from an earlier **psychosexual stage**
20
New cards
defense mechanisms
in **psychoanalytic theory**, the **ego’s** protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality
21
New cards
repression
* defense mechanism where an individual banishes anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories from consciousness
* ex. *a victim of a car accident doesn’t remember anything about the accident*
* ex. *a victim of a car accident doesn’t remember anything about the accident*
22
New cards
regression
* defense mechanism where an individual dealing with anxiety retreats to a more infantile stage
* ex. *following the anxious first day of school, a child may revert to comfort of thumb-sucking*
* ex. *following the anxious first day of school, a child may revert to comfort of thumb-sucking*
23
New cards
reaction formation
* defense mechanism where the **ego** unconsciously switches unacceptable impulses into their opposites
* ex. *“I love them” becomes “I hate them”*
* ex. *“I love them” becomes “I hate them”*
24
New cards
projection
* defense mechanism where people disguise their own impulses by attributing them to others
* ex. *“they’re such a gossip” when in reality, the person speaking is insecure about their gossiping habits*
* ex. *“they’re such a gossip” when in reality, the person speaking is insecure about their gossiping habits*
25
New cards
rationalization
* defense mechanism that offers self-justifying explanations in place of the real, more threatening reasons for one’s actions
* ex. *an alcoholic says they drink with their friends ”just to be sociable”*
* ex. *an alcoholic says they drink with their friends ”just to be sociable”*
26
New cards
displacement
* defense mechanism that shifts sexual or aggressive impulses toward a more acceptable outlet
* ex. *someone is angry and wants to hit someone, but they redirect that energy towards punching a wall*
* ex. *someone is angry and wants to hit someone, but they redirect that energy towards punching a wall*
27
New cards
denial
* defense mechanism where people refuse to believe or percieve painful realities
* ex. *someone ignores evidence of their partner’s affair*
* ex. *someone ignores evidence of their partner’s affair*
28
New cards
collective uncounsciousness
**Carl Jung’s** concept of a shared, inherited reservoir of memory that is derived from our universal experiences
29
New cards
projective test
a personality test, like the **Rorschach** or **TAT** that provides ambiguous stimuli designed to trigger projection of one’s internal dynamics
30
New cards
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
a personality test where people view ambiguous pictures and make up a story
31
New cards
Rorschach inkblot test
well known projective test that attempts to identify people’s inner feelings by analyzing their interpretation of inkblots
32
New cards
terror-management theory
* theory of death-related anxiety
* explores people’s emotional and behavioral responses to reminders of death
* explores people’s emotional and behavioral responses to reminders of death
33
New cards
self-actualization
**Maslow’s** theory of the motivation to fufill one’s potential after basic physical and psychological needs are met
34
New cards
unconditional positive regard
**Carl Rogers’** idea of an attitude of total acceptance toward another
35
New cards
self-concept
all of our thoughts and feelings about ourselves
36
New cards
trait
a characteristic pattern of behavior
37
New cards
personality inventory
a questionnaire used to assess selected personality traits
38
New cards
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
the most widely researched and clinically used personality test
39
New cards
empirically derived test
a test (such as the MMPI) developed by testing a pool of items and then selecting those that differentiate between groups
40
New cards
social-cognitive perspective
views behavior as influenced by the interaction between people’s traits (including thinking) and their social context
41
New cards
reciprocal determinism
the interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and enviroment
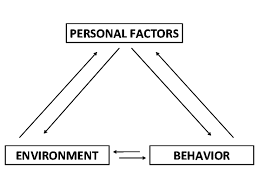
42
New cards
personal control
the extent to which people perceive control over their environment
43
New cards
external locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond personal control determine one’s fate
44
New cards
internal locus of control
the perception that you control your own fate
45
New cards
learned helplessness
the hopelessness and resignation an individul learns when unable to avoid repeated averse effects
46
New cards
positive psychology
the scientific study of optimal human functioning; aims to promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive
47
New cards
self
the center of personality, the organizer of our thoughts, feelings, and actions
48
New cards
spotlight effect
overestimating others’ observation and evaluation of our appearance, performance, and blunders (as if we pretend a spotlight shines on us)
49
New cards
self-esteem
one’s feelings of high or low self worth
50
New cards
self-serving bias
a readiness to perceive oneself favorably
51
New cards
Alfred Adler
* Neo-Freudian
* Importance of child social (not sexual) tension
* Inferiority complex
* Birth order psychology
* Importance of child social (not sexual) tension
* Inferiority complex
* Birth order psychology
52
New cards
Karen Horney
* Neo-Freudian
* Sought to balance **Freud's** masculine biases
* “Womb envy”
* Sought to balance **Freud's** masculine biases
* “Womb envy”
53
New cards
Carl Jung
* Neo-Freudian
* **Collective unconscious**
* Archetypes (self, persona, shadow, anima, ect.)
* **Collective unconscious**
* Archetypes (self, persona, shadow, anima, ect.)
54
New cards
Sigmund Freud
Psychoanalyst
* Unconscious
* **Id, ego, superego**
* **Free association**
* Unconscious
* **Id, ego, superego**
* **Free association**
55
New cards
Abraham Maslow
* Humanistic psychologist
* **Self-actualization**
* **Hierarchy of needs**
* **Self-actualization**
* **Hierarchy of needs**
56
New cards
Carl Rogers
* Humanistic psychologist
* Focused on growth and fulfillment
* Unconditional positive regard
* Focused on growth and fulfillment
* Unconditional positive regard
57
New cards
Julian Rotter
* Psychologist
* Social learning theory
* **Locus of control**
* Social learning theory
* **Locus of control**
58
New cards
Albert Bandura
Viewed behavior as influenced by the interaction between persons and their social context
59
New cards
Hans and Sybil Eysenck
Used two primary personality factors (neuroticism and extraversion) as axes for describing personality variation
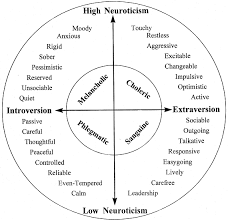
60
New cards
Gordon Allport
* Psychologist
* **Trait theory**
* **Trait theory**
61
New cards
Paul Costa and Robert McCrae
* The big five traits
* OCEAN (Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism)
* OCEAN (Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism)
62
New cards
Raymond Cattell
* Psychologist
* 16 personality factors
* Fluid and crystalized intelligence
* 16 personality factors
* Fluid and crystalized intelligence
63
New cards
Martin Seligman
* Psychologist
* Positive psychology
* **Learned helplessness**
* Positive psychology
* **Learned helplessness**