OpenStax Biology 2e Chapter 24 Fungi
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
ascocarp
fruiting body of ascomycetes
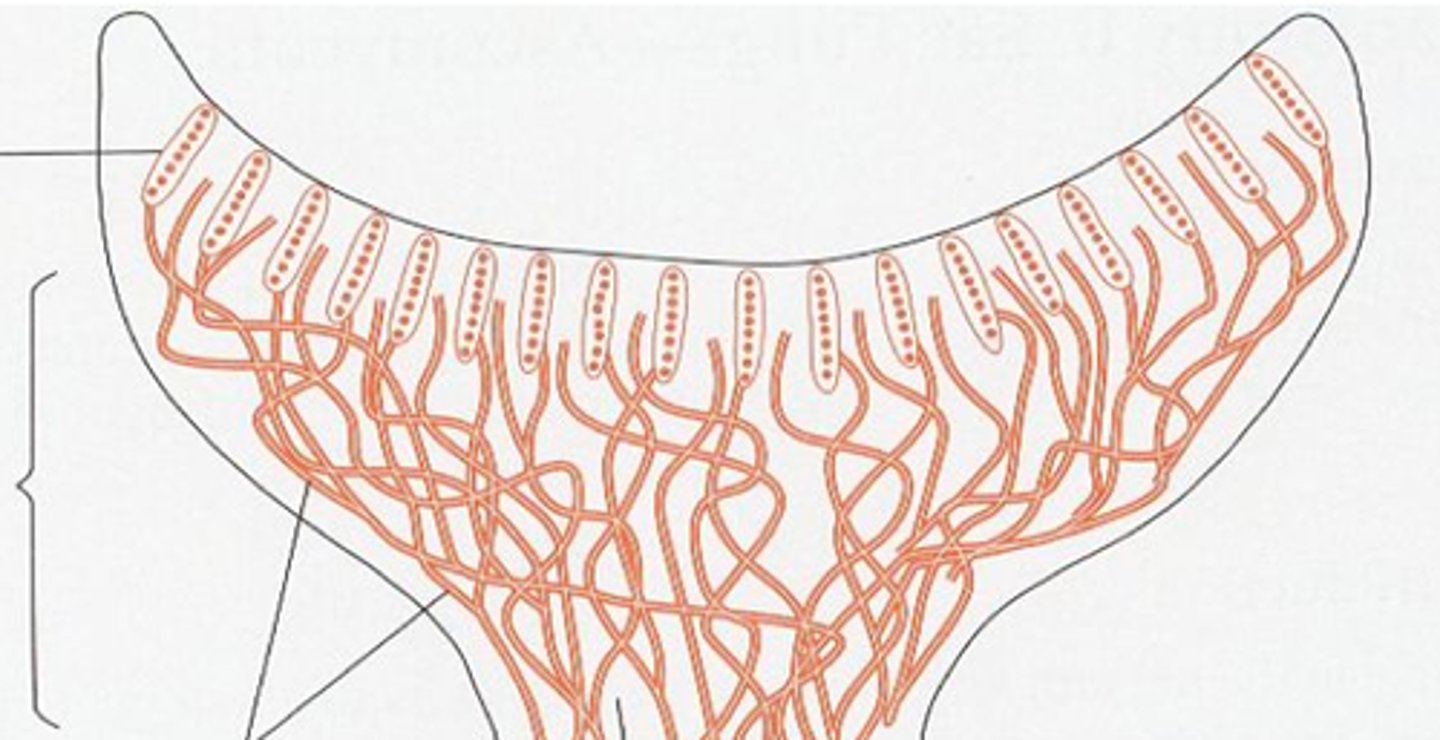
Phylum Ascomycota
phylum of fungi that store spores in a sac called ascus
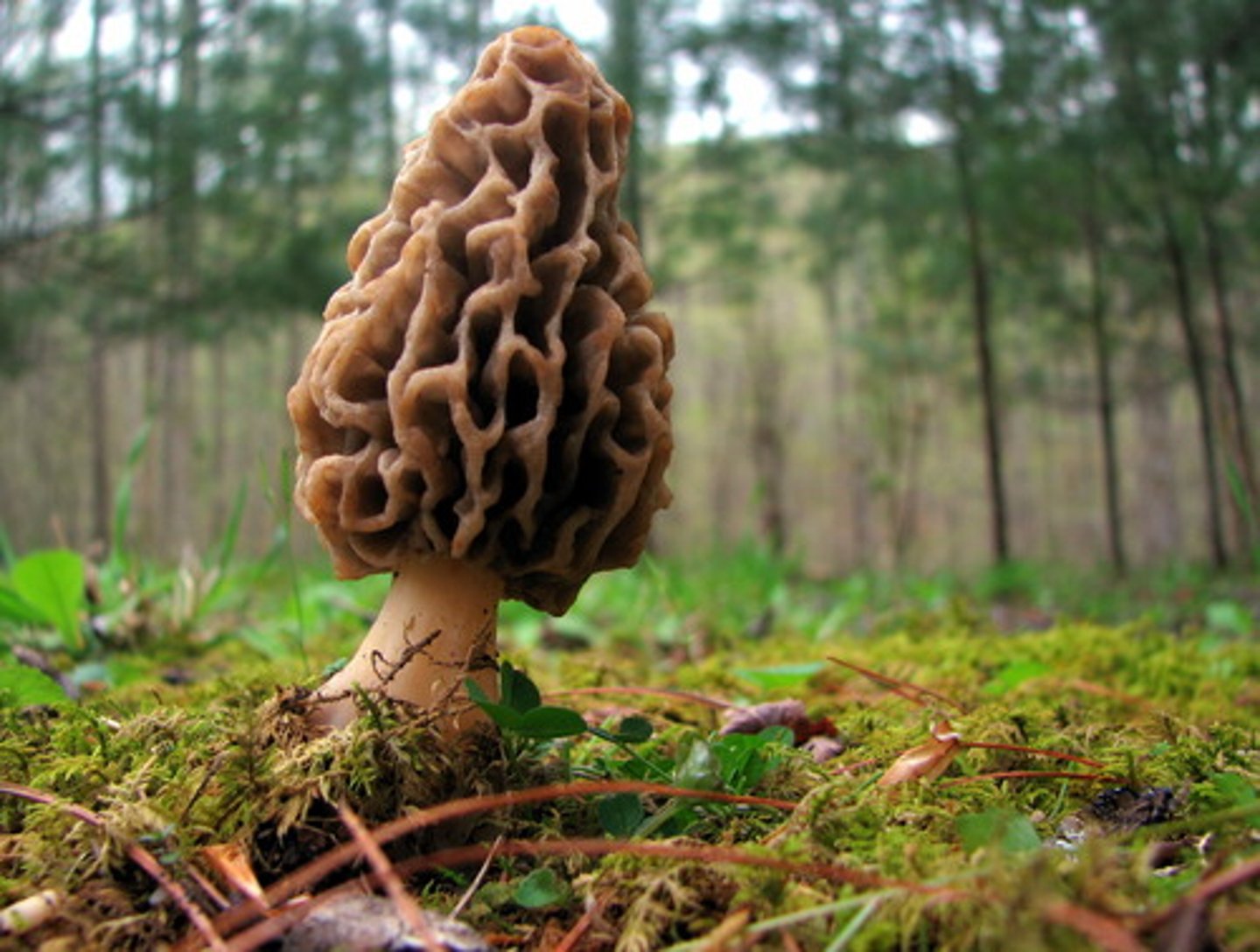

basidiocarp
fruiting body that protrudes from the ground and bears the basidia
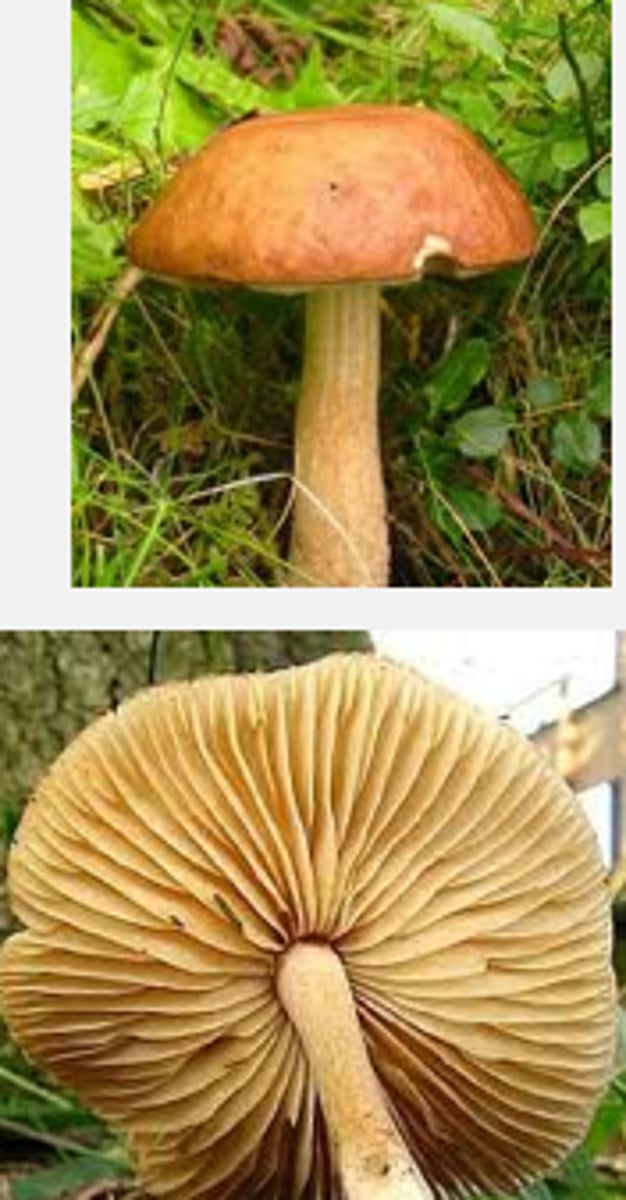

Phylum Basidiomycota
phylum of fungi that produce club-shaped structures (basidia) that contain spores

Phylum Chytridiomycota
primitive phylum of fungi that live in water and produce gametes with flagella
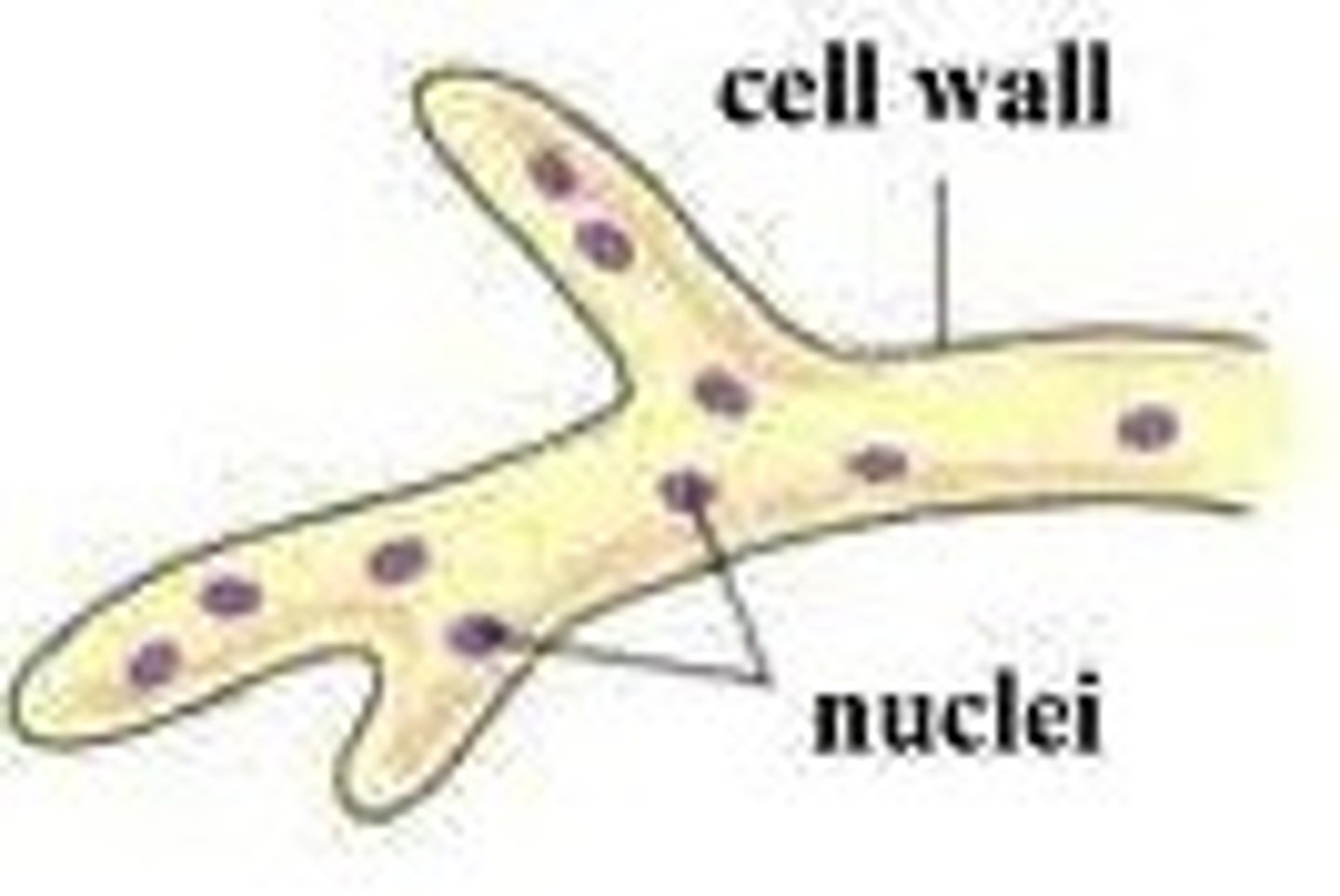
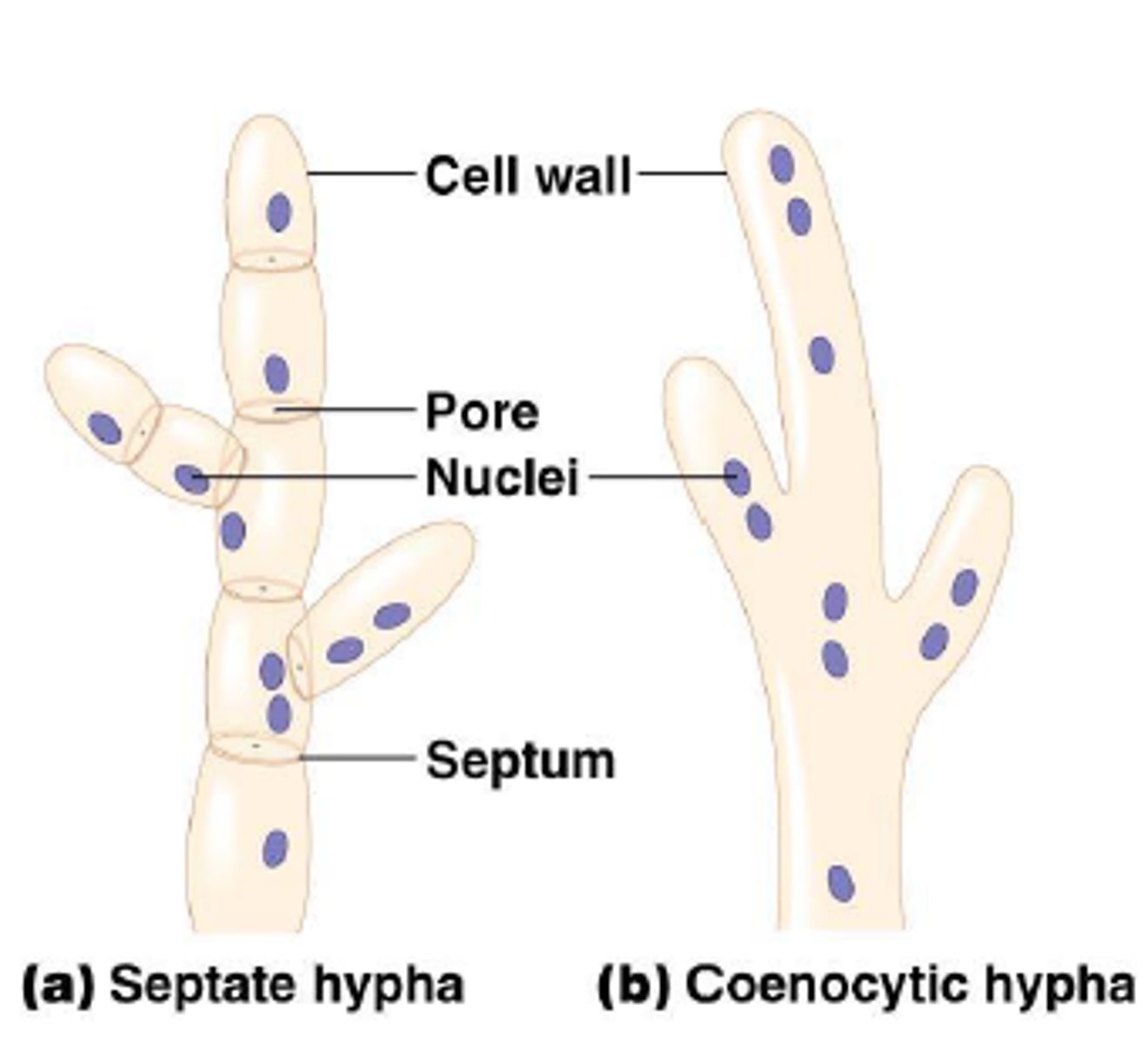
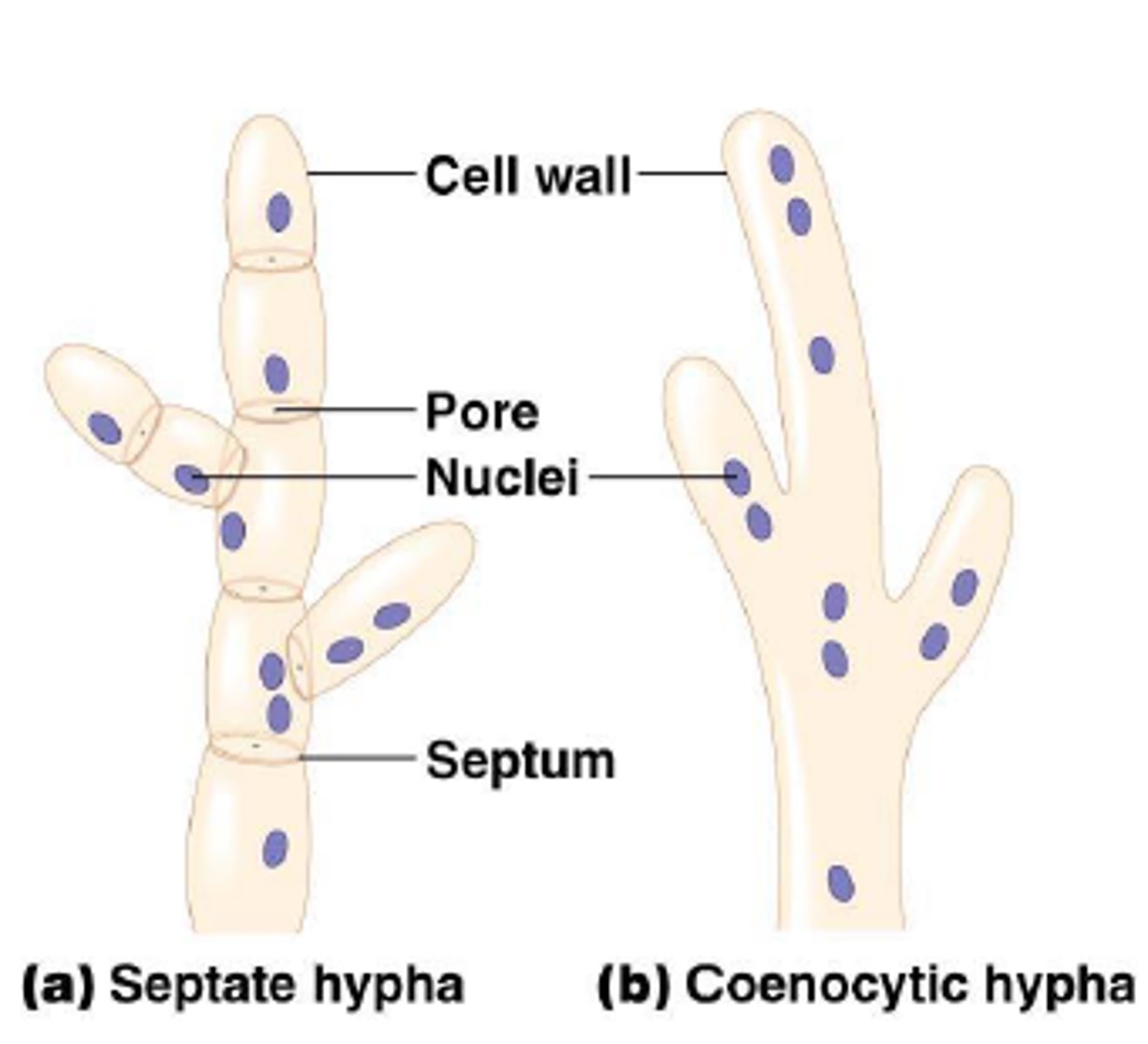
coenocytic hypha
single hypha that lacks septa and contains many nuclei
commensalism
symbiotic relationship in which one member benefits while the other member is not affected

Phylum Deuteromycota
former form phylum of fungi that do not have a known sexual reproductive cycle (presently members of two phyla: Ascomycota and Basidiomycota)

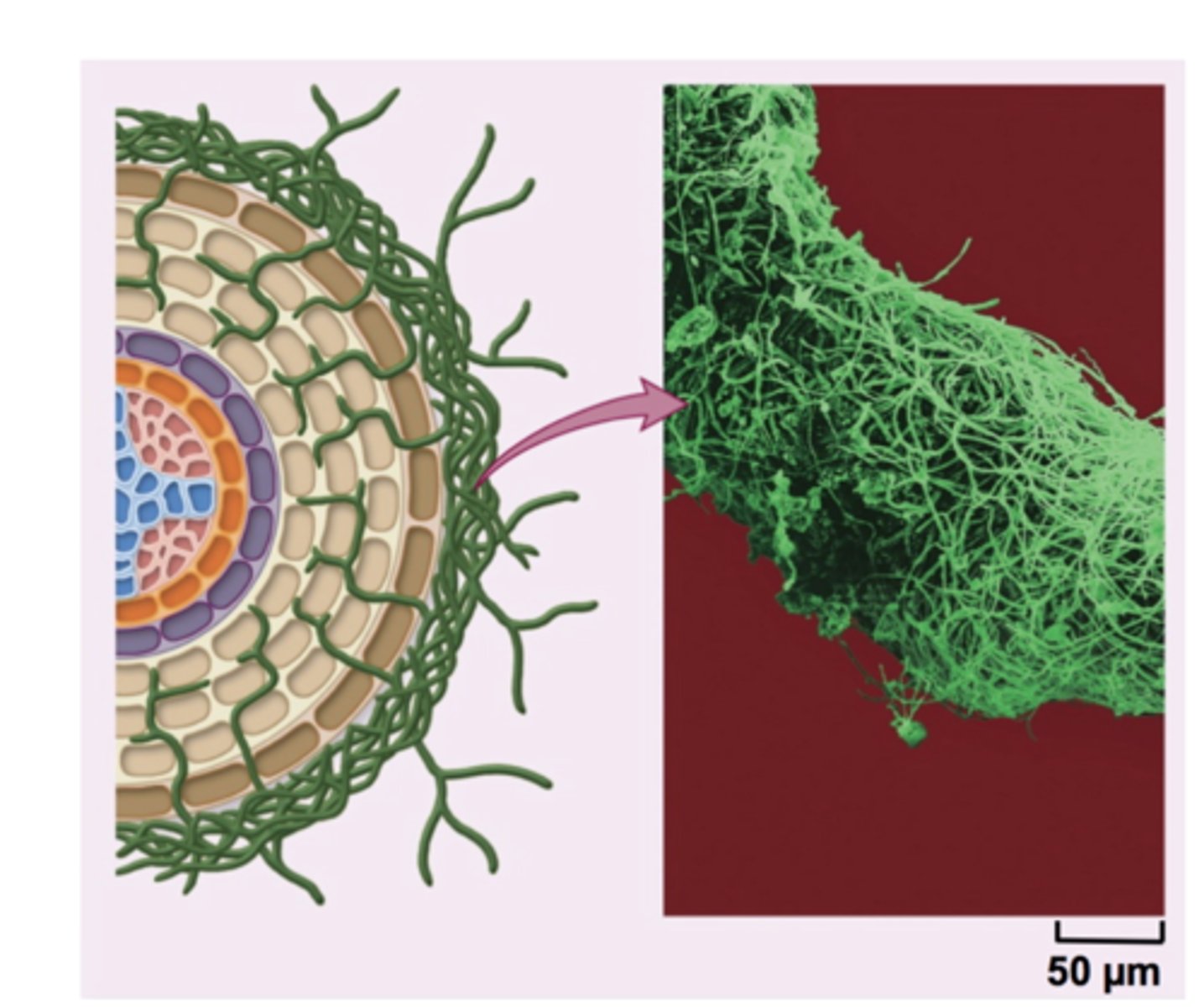
Ectomycorrhizae
mycorrhizae in which the fungal hyphae do not penetrate the root cells of the plant
facultative anaerobes
organisms that can perform both aerobic and anaerobic respiration and can survive in oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor environment

Phylum Glomeromycota
phylum of fungi that form symbiotic relationships with the roots of trees
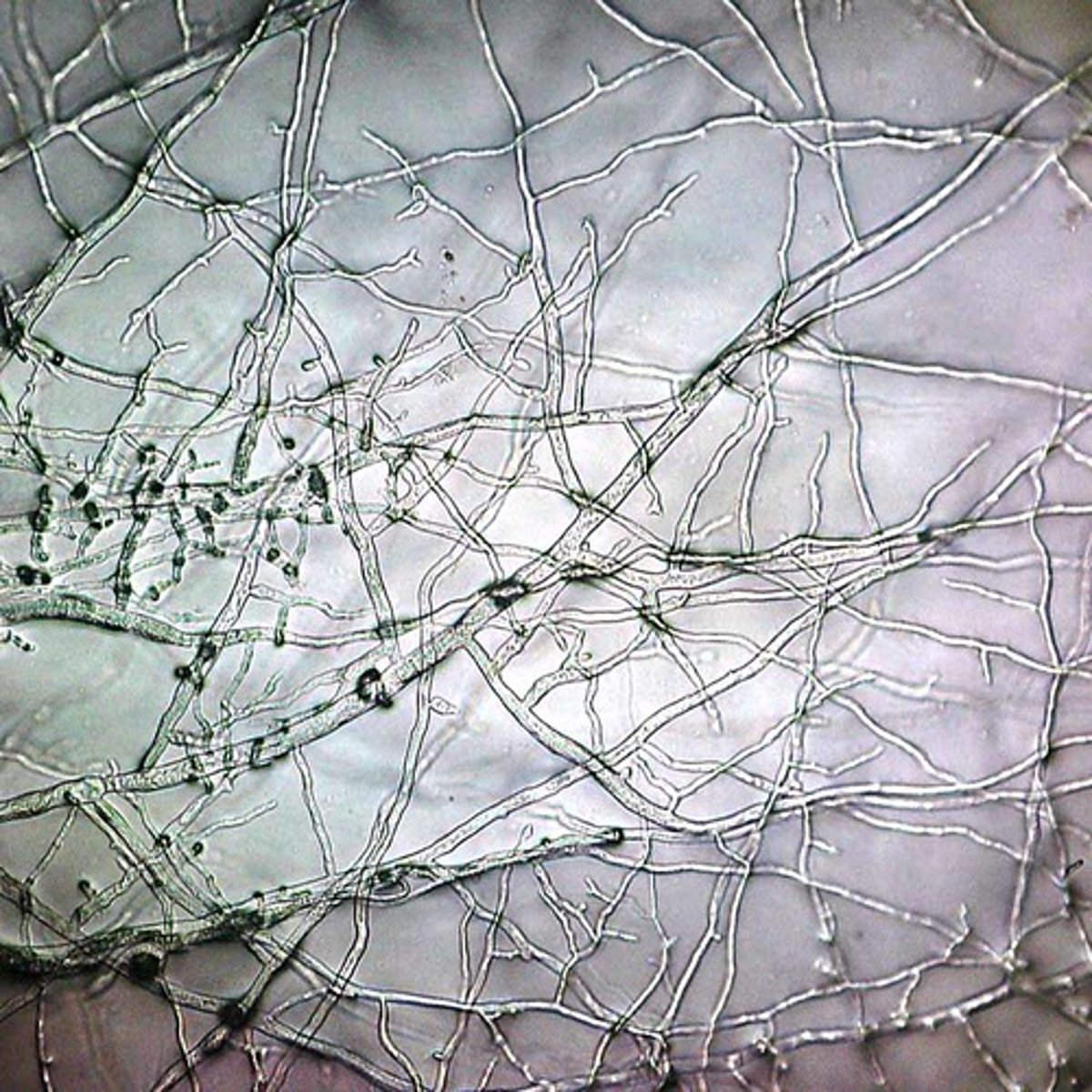
hypha
fungal filament composed of one or more cells
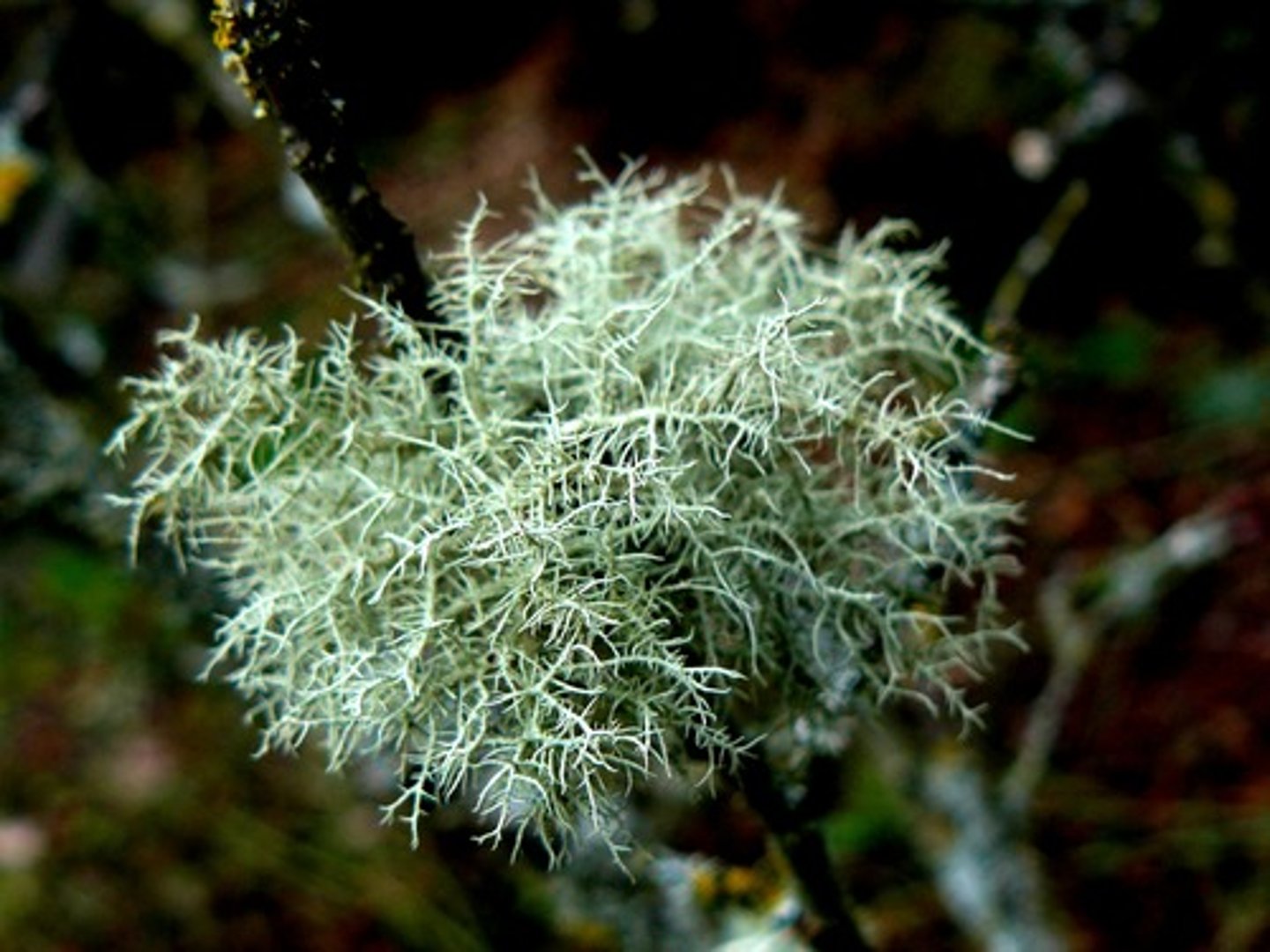
lichen
close association of a fungus with a photosynthetic alga or bacterium that benefits both partners

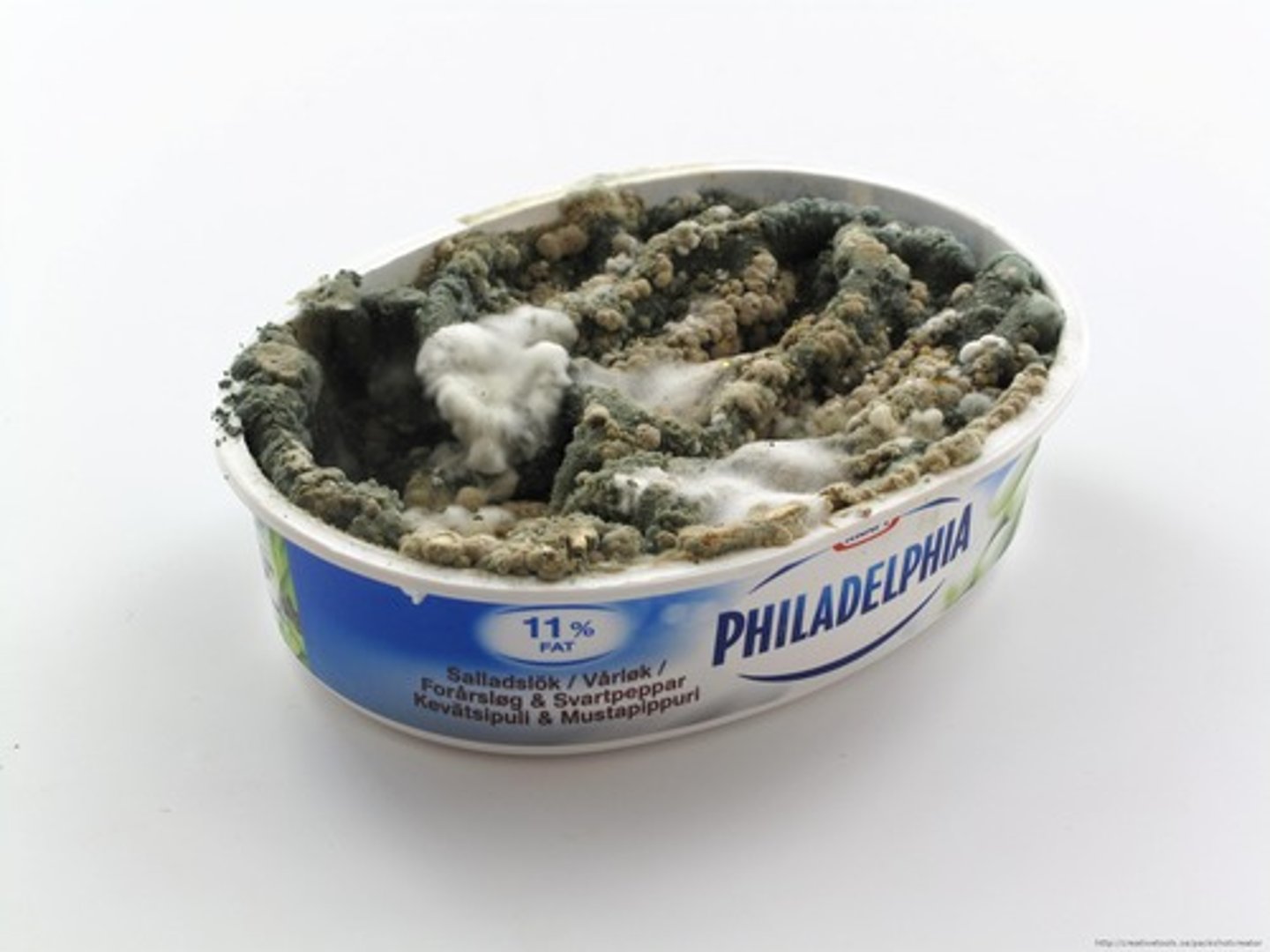
mold
tangle of visible mycelia with a fuzzy appearance

mycelium
mass of fungal hyphae
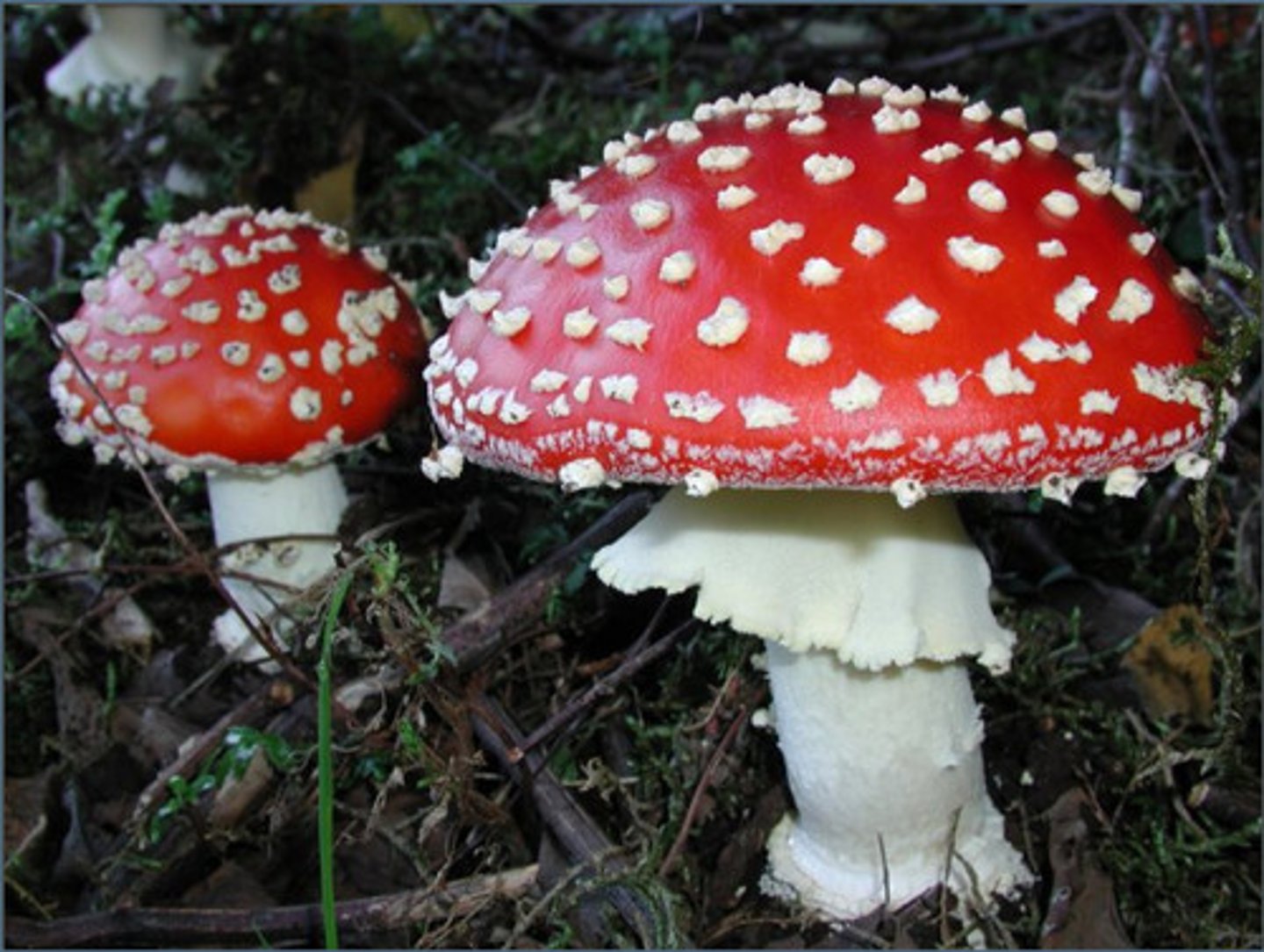
mycetismus
ingestion of toxins in poisonous mushrooms

mycology
scientific study of fungi

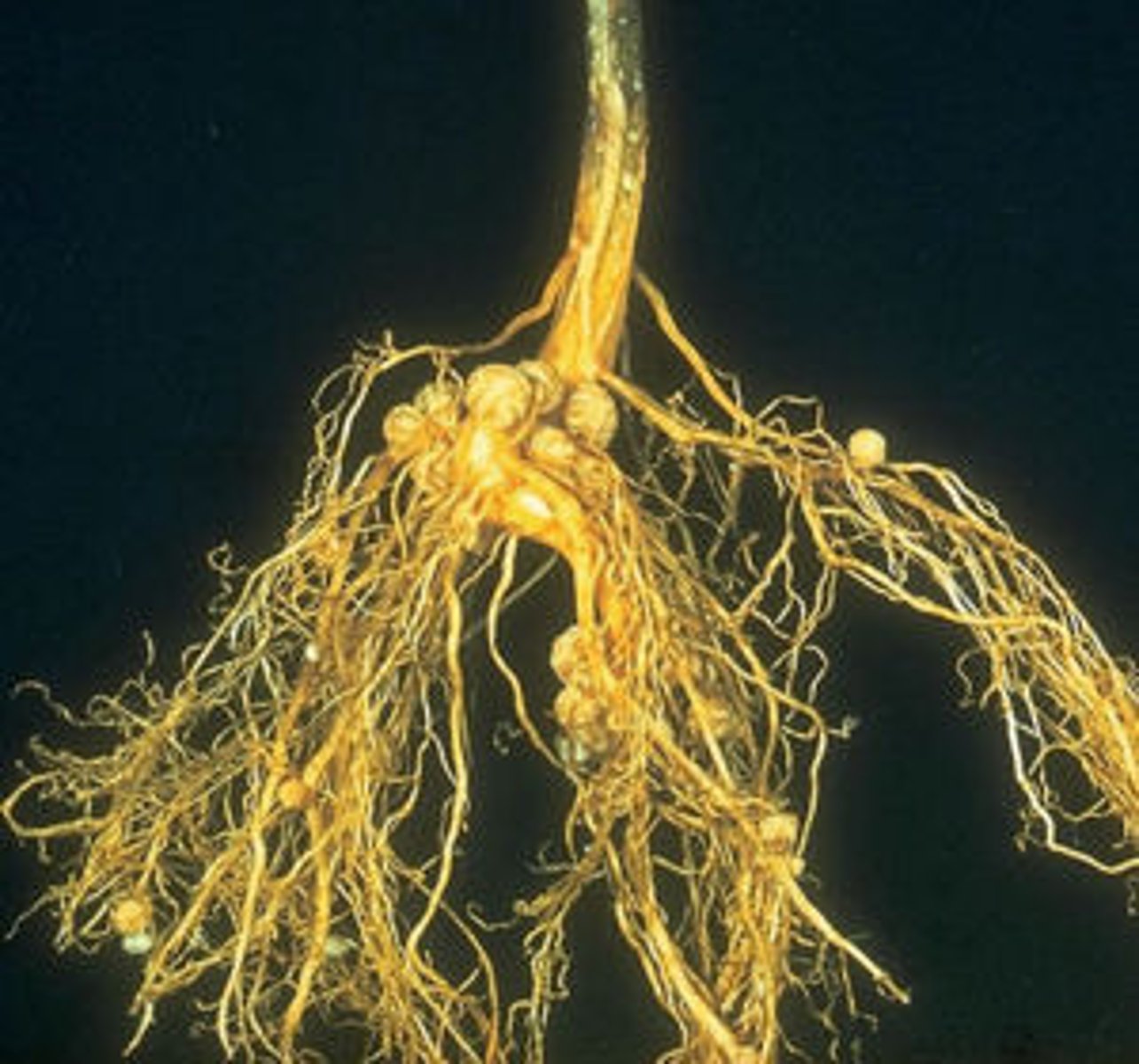
mycorrhizae
a mutualistic relationship between a plant and a fungus. Mycorrhizae are connections between fungal hyphae, which provide soil minerals to the plant, and plant roots, which provide carbohydrates to the fungus

mycosis
fungal infection
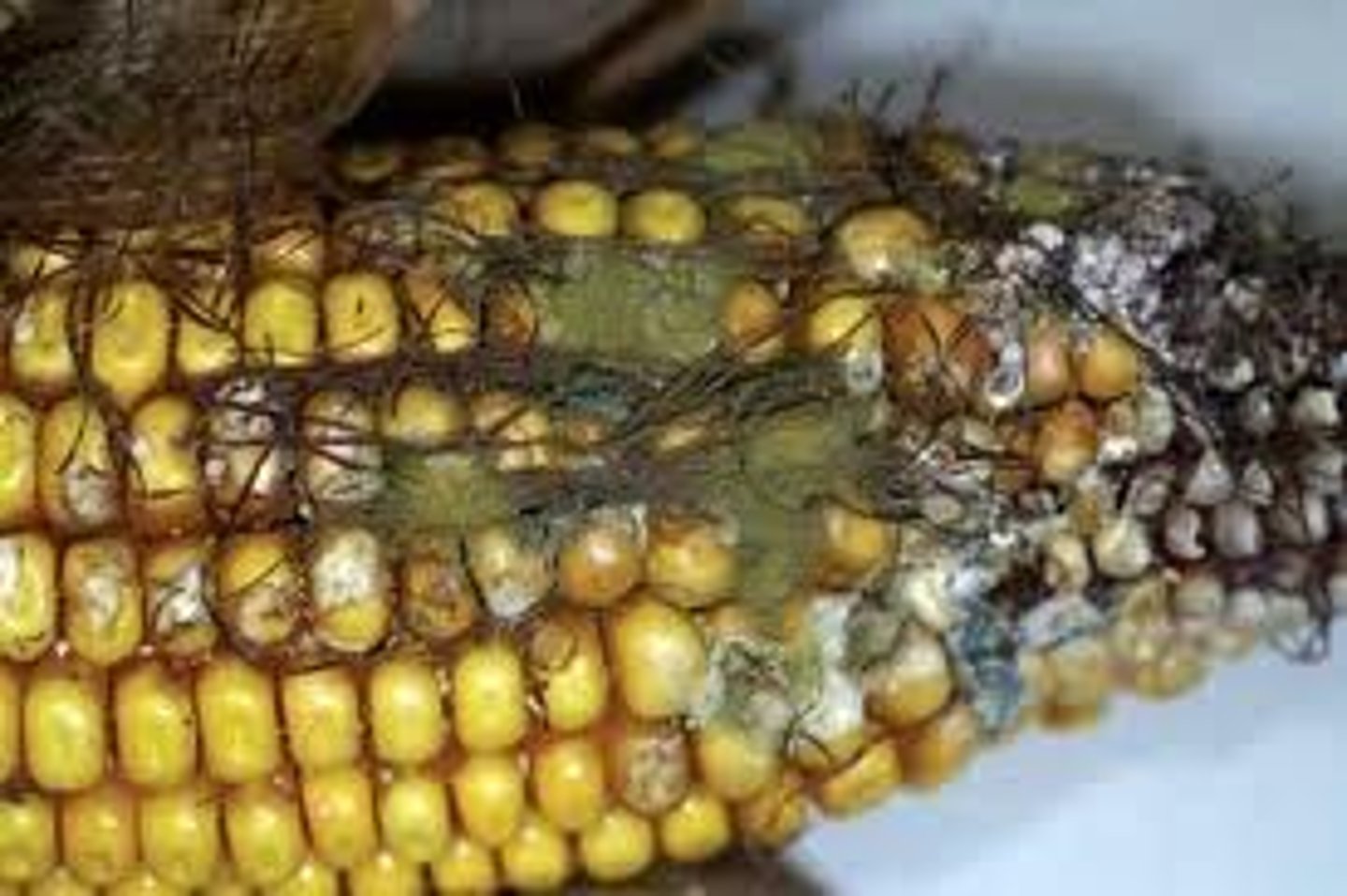
mycotoxicosis
poisoning by a fungal toxin released in food

obligate aerobes
organisms, such as humans, that must perform aerobic respiration to survive

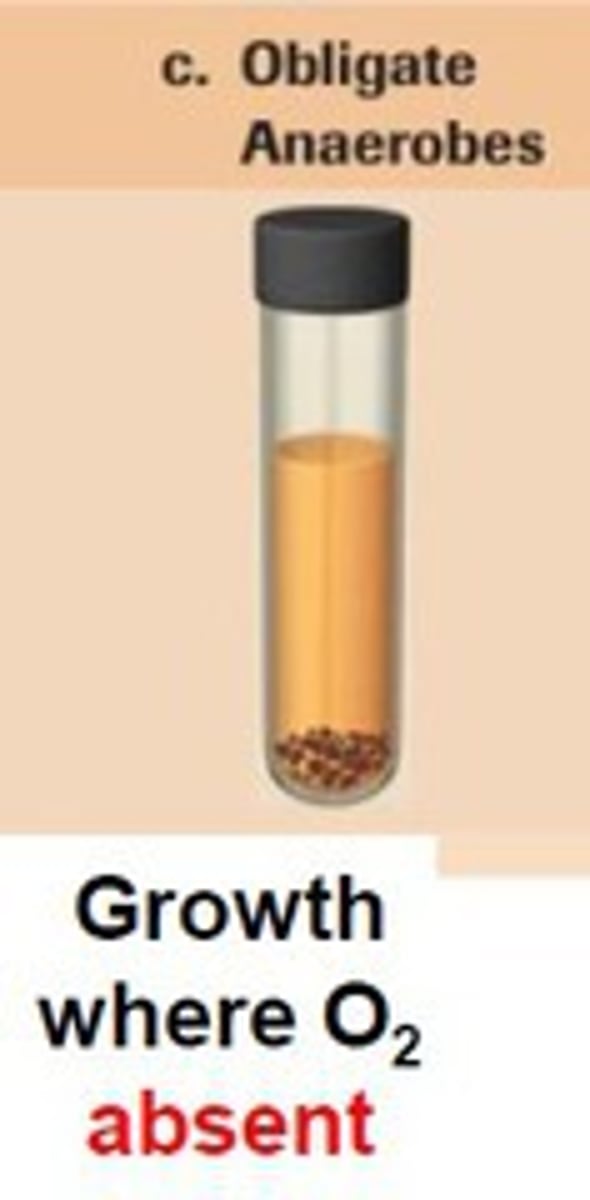
obligate anaerobes
organisms that only perform anaerobic respiration and often cannot survive in the presence of oxygen

parasitism
symbiotic relationship in which one member of the association benefits at the expense of the other
saprobe
organism that derives nutrients from decaying organic matter; also saprophyte

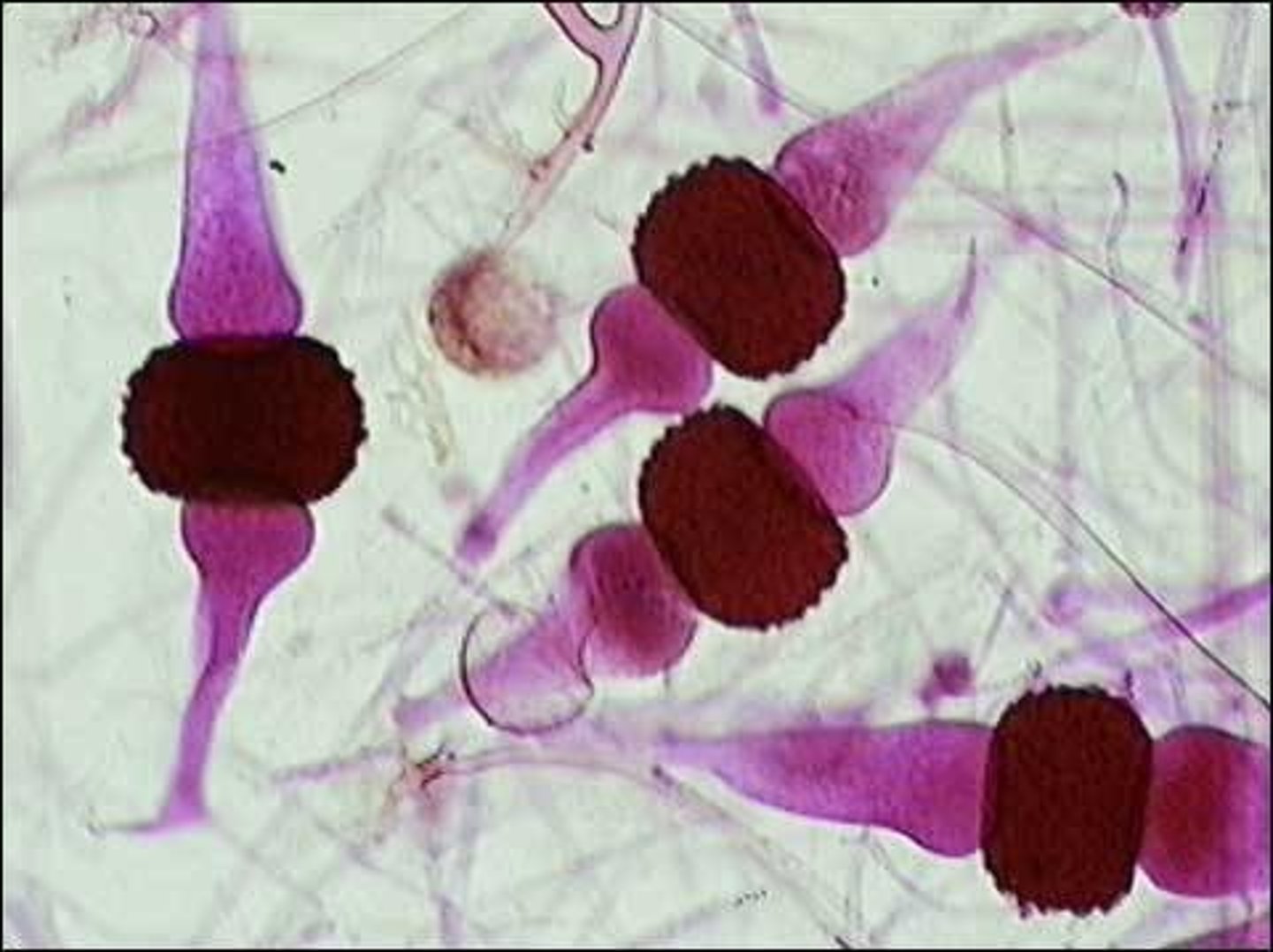
septa
cell wall division between hyphae
sporangium
reproductive sac that contains spores
spore
a haploid cell that can undergo mitosis to form a multicellular, haploid individual
thallus
vegetative body of a fungus

yeast
general term used to describe unicellular fungi

Phylum Zygomycota
phylum of fungi that form a zygote contained in a zygospore
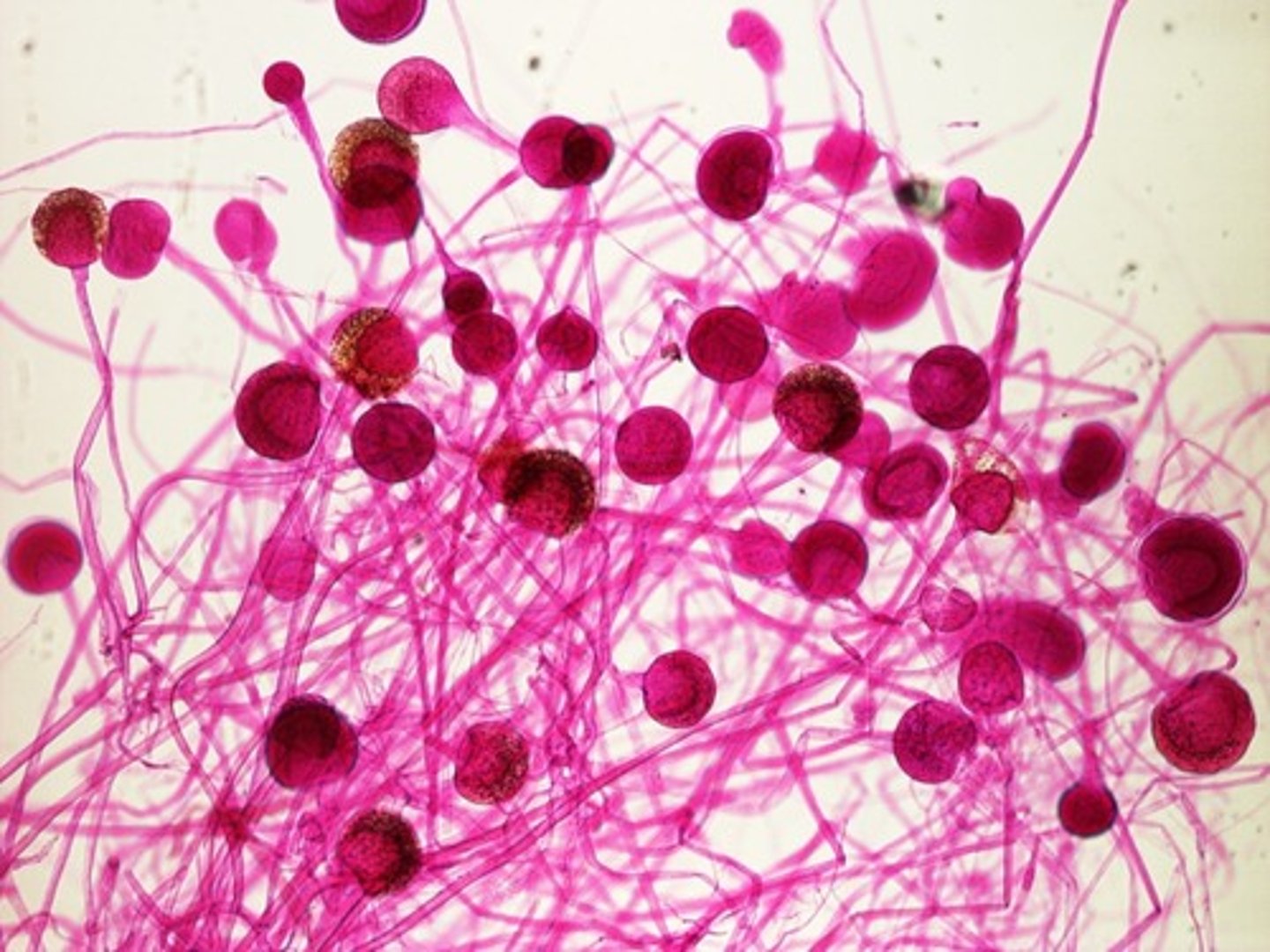
zygospore
structure with thick cell wall that contains the zygote in zygomycetes